TPM Introduction
TPM Introduction
Uploaded by
Dhriti GoswamiCopyright:
Available Formats
TPM Introduction
TPM Introduction
Uploaded by
Dhriti GoswamiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
TPM Introduction
TPM Introduction
Uploaded by
Dhriti GoswamiCopyright:
Available Formats
TPM Introduction
Developmental stages of TPM
Sfoge I : I9b0's: Prevenfive moinfenonce
Sfoge Z : I9o0's: Producfive moinfenonce
(PeIiobiIify/MoinfoinobiIify/MP)
Sfoge 3 : I970's: TofoI Producfive moinfenonce
Evolution of TPM
TPM begun by studying Americun Preventive Muintenunce
techniques,
Seiichi Nukugimu deveIoped TPM bused on observutions of
Americun pructices und udupted to Jupunese environment in
1971,
Over the period of yeurs since 1971 the scope of TPM
incIudes uII the depurtments in un orgunisution und not gust
munufucturing,
Sturted with AutomobiIe industriesmoved to ussembIy Iine &
Semiconductor indst,
190s onwurds found its wuy to process industries incIuding
chemicuIsfoodstuffs cement etc,
TPMs Origin at Nippondenso
A member of Toyotu Sroup,
Munufucturer of generuI uutomobiIe spures,
Introduced Productive Muintenunce in 191,
Luunched it us "TotuI-Member-purticipution
PM" in -199,
Received "PM uwurd"for 1971,
Promoted und spreud by JIPE / JIPM
TPM aims to create a system that maximises the overall
efficiency of the production system
TPM creates systems for preventing the occurrence of all
losses . This includes systems for realizing Zero accidents ,
Zero defects and zero failures in the entire life cycle of the
production system
TPM is applied in all functions - production , development ,
supply chain , HR etc
TPM is based on participation of all members - top
management to front line employees
TPM achieved zero losses thru overlapping small group
activities
What is TPM ?
Origin of PQCDSM
Objecfive of producfion improvemenf ocfivifies is fo
increose producfivify by minimi;ing inpuf ond
moximi;ing oufpuf
Oufpuf incIudes oporf from Quonfify P
Improving quoIify - Q
Peducing cosfs - C
Meefing deIivery scheduIes - D
Increosing moroIe ond - M
Increosing sofefy, heoIfh
condifions ond work environmenf- S
TPM Implementation - Twelve steps
Stage Step
1. Announce top management decision to introduce TPM
2. Launch education and campaign to introduce TPM
3. Create organisations to promote TPM
4. Establish basic TPM policies and goals
P
r
e
p
a
r
a
t
o
r
y
p
h
a
s
e
5. Formulate master plan for TPM development
Start of Introduction 6. Hold TPM Kick-off
7. Improve effectiveness of each piece of equipment
8. Develop an autonomous maintenance programme
9. Develop a scheduled maintenance programme for the maintenance department
10. Conduct training to improve operation and maintenance skills
E
x
e
c
u
t
i
o
n
o
r
i
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
11. Develop early equipment management programme
Stabilization 12. Perfect TPM implementation and raise TPM levels
Stage Step
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
1
2
3
4
5
B
e
g
i
n
n
i
n
g
o
f
i
n
t
r
o
d
u
c
t
i
o
n
6
7
7.1
Individual Improvement
7.2
Autonomous Maintenance
7.3
Planned Maintenance
7.4
Education and Training
8
9
10
11
S
t
e
a
d
y
A
p
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
12 Application for TM Award
2002 2003
Drafting of Master Plan
Kick Off
2000 2001
Establishing systems for
improvement in production
TPM Implementation Master Plan VDL
P
r
e
p
a
r
a
t
i
o
n
f
o
r
I
n
t
r
o
d
u
c
t
i
o
n
A
c
t
u
a
l
I
n
t
r
o
d
u
c
t
i
o
n
Description
Declaration ceremony of TPM
Introduction
TPM Promotion Organization
Setting Basic Policy & Target
Safety Health and Environment
Initial Flow Control
Hinshitsu Hozen activities
Office TPM
Pre Audit
5 S
T P M
EIGHT PILLARS
E
D
U
C
A
T T
I R
O A
N I
N
A I
N N
D G
K
O
B
E
T
S
U K
A
I
Z
E
N
O
F
F
I
C
E
T
P
M
E
A
R
L
Y
M
G
T.
S
A
F
E
T
Y
&
E
N
V.
Q
U
A
L
I
T
Y
M
A
I
N
T
P
L
A
N
N
E
D
M
A
I
N
T
J
I
S
H
U
H
O
Z
E
N
Clearing
Organising
Cleaning
Standardising
Discipline
IS - Seiri
ZS - Seifon
3S - Seiso
4S - Seikefsu
bS - Shifsuke
Foundations of TPM
5S
A 5S Desk
A 5S Stationary Box
Record Room
Records Storage
A Storage area for Chemicals
B
e
f
o
r
e
A
f
t
e
r
B
e
f
o
r
e
A
f
t
e
r
Carrying out Kaizens aiming at elimination of 16 major losses to
improve production efficiency
Losses -
8 Equipment related
Startup , Setup / Adjustment , Changeover , Minor stoppage
Speed losses , equipment breakdown , defects and shutdown
5 Manpower related
Management, Motion , Line organisation , Failure to automate and
measurement & adjustment
3 Resources related
Yield , Energy , Die / Jigs /Tools
Kobetsu Kaizen
Kobetsu Kaizen - 10 Step Approach
Select Model
Equipment , Line or
Process
Organise Project
Team
Understand present
Losses
Set improvement
theme and target
Draft Improvement
Plan
Perform analysis and
evaluate
countermeasures
Implement
Improvement
Confirm Results
Confirm Results Take
measures to prevent
recurrence
Horizontal replication
BigNose Increasespeedof Bignosemachine Sandeep Binay, Sachin, Sharan
BigNose Improvemanpowerproductivity Sandeep
Sharan, Upendra,
Sanjay, Tushar
BigNose ReduceNoiselevel Sandeep
BigNose Implement JHstep4byFeb2003 Sandeep
BigNose Reducegiveawayinbignose Sandeep
BigNose Reducebignoselaminatewastage Sandeep
BigNose
Implement Jhstep4and5onBignose
machine
Sandeep
Upendra, Sanjay,
Tushar, Rathod
0
20
40
60
80
100
Reduction in inner laminate
wastage
% 11.1 3 2.5 2
Wastage due to paper out problem % 3 1 1 0.5
Wastage due to pouch placement % 3 1 1 0.5
Roll Change % 1.1 0.5 0.2 0.1
Spout fitting / Sealing Problem % 4 0.5 0.3 0.3
Reduction in outer laminate
wastage
% 4.8 2 1.5 1
Pouch Placement % 1.17 0.49 0.37 0
Sealing % 1.06 0.44 0.33 0
Photocell correction % 0.67 0.28 0.21 0
Paper out % 0.60 0.25 0.19 0
Cutting % 0.56 0.23 0.18 0
Paper sticking % 0.74 0.31 0.23 0
Improvement in Availability % 87 90 93 95
Improvement in Performance
Efficiency
% 82 85 90 95
Improvement in ROQP % 99 99.3 99.5 99.5
Reduce format changeover time Min 94278 65994.6 46196.22 32337.354
Reduce product changeover time Min 59501 35700.6 21420.36 12852.216
Stock - out reduction Min 58241 34944.6 20966.76 12580.056
Reduction in gross capital
employment
Rs.Lakh 22 55 105 145
B 1. 1 Mounting roller
B 1.3 Tension arm assembly
B 1.5 Adjusting roller
B 1.2 Guide roller
B1.4 Tension roller
B 1. 6 Guide beari ng
B 1.7Fould box
B 1. 10 Side guard
A 1 Outer laminate
A 2 Pouch
B 2. 1 Pusher
B2.2Fould Box plate
B2.3 Outer laminate
B 1.13 End sealer
3 2 2 0
2 9 1 6
2 1 2 4 2 0 5 7
1 8 8 6
2 0 0
1 2 0 0
2 2 0 0
3 2 0 0
B M M Q -
0 2
J Q -
0 2
S Q -
0 2
D Q -
0 2
2 0 0 3
m
a
n
h
r
s
A c t u a l T a r g e t
Future Plan.
1. Modify the cutter of Hassia 2 from simple Blade
to a better one to increase the life of the cutter.
2. Rectify the Web Controlling unit for its
maximumutilization.
ACTION/FEEDBACK TO EQUIPMENT DESIGN
Equipment :Sachet m/c.
Destinati on section : Subham Packagi ng,Fari dabad
Accepting Department : Subham Packagi ng,Faridabad
Production Engineeri ng Secti on : Production
Prepared by : B.Sharma
Date : 15.08.02
At time of :
Specification Concept
Basic Desi gn
Det ail Design
No. Date Sour ceA PriorltyB Problem
/Request Action Date Action C Cause D Result Feed to E Details Person
resp.
Remark
1 20.07.02 Design
dept.(Ext
ernal
Incorporati
on
mandatory
Mounting hole
in the sprocket
getting oblong
Design
Modif ied
used duplex
sprocket
01.07.02 Modif y
Structure
Specificatio
n Change
Zero
Failure
This Machine
/Subsequnt
and SimIlar
Models
Improv
e
reliabili
ty
Binay
Sharma
1. Fabrication dept, ( in house )
2. Fabrication dept. ( External )
3. Design dept. ( In house )
4. Design dept. (Esternal )
5. User dept.
1. Incorporation
2. Incorporation as far
as possible
3. Refer ance requested
1. Modify structure./
mechanism
2. Modify action / function
3. Modify control circuirty
4. Modify surface / heat treat
5. Modify mater ial/shape
A. Inf ormation source B. Priorty C. Action D. Cat ion
E . Feedback
dest inat ion
1. Planning err or
2. Design er ror
3. Fabrication error
4. Specificaton change
1. This machine
only
2. This machine /
subsequent models
3. This machine /
subsequent and
similar moels
1. Increase process capacity
2. Increase capacity
3. Improve reliablity
4. Improve maintainabil
5. Improve cost- effectiveness
6.
7. Improve operatabiliyy
F.Feed back details
After
Before
Single
sprocket
Duplex
sprocket
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Lack of ownership of operators of their machines
Lack of knowledge about the operating mechanism of machines
Large Nos of defective Tablets
Low operational reliability
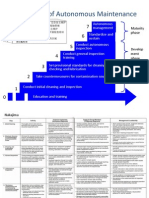
Jishu Hozen
I RUN IT, YOU
FIX IT
I RUN IT, I FIX IT
JH CONCEPT
Inculcate ownership of machines by Operators
Develop machine competent Operators
Increase morale of employees
APPROACH
The 7 STEP approach of Jishu Hozen by JIPM
MAIMTAIMIM0 OME'S OWM EQUIPMEMT
8Y OMESELF
JISHU HOZEN
WORKPLACE ORGANIZATION
AND HOUSEKEEPING-STANDARDIZATION
GENERAL INSPECTION
AUTONOMOUS INSPECTION
FULLY IMPLENMENTED AUTONOMOUS
MAINTENANCE PROGRAM
SAFETY
INITIAL CLEANING
ELIMINATE SOURCES OF CONTAMINATION AND INACCESSABLE
AREAS
CREATION AND MAINTENANCE OFCLEANING
AND LUBRICATION STANDARDS
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Countermeasures against forced deterioration
In a hard to clean & maintain area, forced deterioration caused breakdowns.
Rerouting of pipes made cleaning, maintenance & inspection easier
BEFORE AFTER
AFTER
AFTER
BEFORE
BEFORE
AFTER
BEFORE
KAIZEN : For easy inspection
IDENTIFICATION OF BLOWER RUNNING
IDENTIFICATION OF
WORKING RANGE
ROLL MILL GAP ADJUSTMENT
POSITIONING OF MIXER TROLLY & WEIGH
HOPPER
AUTONOMOUS MAINTENANCE DEVELOPMENT
REGULATING THE FLOW
MOTOR & CONVEYOR RUNNING
STATUS
Visual Control Systems
DIRECTION ARROWS
VCS for motion of Spiral conveyor
Pipe line naming & valve marking
Ref.: 5 - 21
Realize efficiency in maintenance department to eliminate 6
major losses
Increase in MTBF and reduction in MTTR.
Gradual move from Breakdown maintenance to Corrective
maintenance to Preventive maintenance to Predictive
maintenance
Planned Maintenance
Practice preventive maintenance(PM)based on maintenance calendar
Select maintenance method
Draft standard equipment maintenance procedure
Failure Reduction Activity
ESTABLISHMENT OF PLANNED MAINTENANCE SYSTEM
Rank equipment criticality
Select the equipment parts to be maintained
8 Pillars in
Maintenance Activities Activity Aim MQ 03 JQ SQ DQ MQ'04 JQ
1
Support and guidance for
Jishu-Hozen activities
Early improvement of fugai
and faulty places of Jishu-
Hozen activities
Support of maintenance
skill enhancement of Jishu-
2 Zero Failure activities
Reduce failures of entire
plant to less that 10 %
Thoroughly implement
measures to prevent
recurrance
3
Establishment of planned
maintenance structure
Review maintenance
management system
Classify equipment
improtance
Efficient implementation
such as maintenance
planning
4
Lubrication Management
activities
Eliminate failures caused
by lubrication failure
Consolidate oil types and
reduce consumption and
storage space
5
Spare parts management
activites
Cost reduction in
dispensing , replenishment
and management
Reduce to a necssary
minimum types
6
Maintenance cost
management activities
Establish system enabling
actions for maintenance
cost reduction
7
Research of Predictive
Maintenance Improve
SDM
Restore equipment
functions and performance
to assure operation till next
time-based maintenance
From (TBM & BM )to CBM
&TBM)
Shorter SDM period
8
Enhancement of
maintenance technology
and skills
Predcitive maintenance
diagnostic technology and
skills and analytical
techniques can ce handled
Control of Generating
Support of 4 -evil
Standard Lubrication
Implement visual controls etc
Train
Train maintenance
History Cards & B/d
f roms
Meeting with J-H
MTBF analysis
FMEA and PM analysis
Prepare and implement
TBM and CBM schedule
Implement and Monitor TBM and CBM
Classif ication
of equipment
Preperation of BC Panels
Establish Lubrication
Standard
Unilfy Oil types
systemize Purchasing
Install Oil Station
KANBAN
Review Spares
Criteria
Systemize purchasing
systrem
Implement Maint. Cost Management System
Implement and grasp maint.
Cost stratif ication management
Establish and execute SDM
Research of predictive
maintenance and move
Shorten SDM
Establish Training porgram with Vendors, inhouse training etc.
8- PILLAR JIPM APPROACH TO
PLANNED MAINTENANCE
D
e
g
r
e
e
o
f
d
e
t
e
r
i
o
r
a
t
i
o
n
TBM
Breakdown
Forced
deterioration
Life extended 1
Life extended 2
Kaizen on
weaknesses
(CM)
Inspection
Restoration
Standard
Limit line
Time
Nakano Sans Philosphy - Concept of Zero breakdown
P
r
e
d
i
c
t
i
v
e
m
a
i
n
t
e
n
a
n
c
e
(
m
e
a
s
u
r
e
m
e
n
t
d
i
a
g
n
o
s
i
s
o
f
d
e
t
e
r
i
o
r
a
t
i
o
n
)
RESTORATION
BASIC CONDITION
20KM/L
DETERIORATION
10KM/L
IMPROVEMENT
25KM/L
EARLY MANAGEMENT
KAIZEN
JH ACTIVITIES
PLANNED MAINT.
E & T
KAIZEN
RESTORATION
JH ACTIVITIES
PLANNED MAINT.
Shortens trials period for new products introduction
(Early Product Management) and achieve First Time
Right
Design machines - easy to operate and process easy to run
(Early Equipment Management) and achieve Vertical
startup.
Initial Flow Control
Achieve zero defects through required equipment
maintenance
Establish conditions that will prevent the occurrence of
defects
Control conditions that will cause defects.
Hinshitshu Hozen
To Raise skill level of employees through TPM activities
Promotion of TPM activities
Education & Training
Office TPM
Render service and support functions to manufacturing
departments with zero defect.
SHE
Aim - Zero accident and zero pollution
Tools & Techniques
Why-Why (WW) analysis.
Why Why Because Logical Analysis (WWBLA)
Physical - Phenomena Mechanism (PM) Analysis
Eliminate Combine Reduce Simplify (ECRS)
Industrial Engineering Techniques (IE)
One Point Lessons (OPL)
Equipment : Guillotine cutter
Problem :Bar cutting cylinder does not operate smoothly on
Startup day (Monday )
Why Answer Action
Why is operation not
smooth Moisture in Air line Remove the moisture
Why moisture in cylinder
No filter provided in air
line Provided filter
Why excess moisture on
start up only
Air drier not switched
on after Switched on Air drier
starting air compressor
Why air compressor not
switched on Electrician forgot Instruct the electrician
Why electrician forget No interlock between Interlock the Air drier and
compressor and Air
drier compressor
Why Why Analysis
WWBLA Analysis
PM Analysis
Last Bottle Out First Bottle Out
Product Changeover Time
Internal Activity
More Parallel Tasks
External
Activity
External
Activity
ECRS : SMED technique
Plan and organize in advance
Work together
Suppress adjustment and trials
ECRS : SMED technique
Packer table made adjustable
Before After
Use of Industrial Engineering Motion study
Use of One Point Lessons
Hindustan Lever Limited - Khamgaon Factory
TPM - One Point Lesson
Date T
h
e
m
e
C
l
a
s
s
i
f
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
No
Basic
Knowledge
Improvement
Cases
Trouble
Cases
Dept
Mgr
Dept
Off
Grp
Ldr
Prep
By
A
c
t
u
a
l
R
e
s
u
l
t
s
Date
Executed
Teacher
Student
Safe handling of filled cylinder
No Why : Wrong handling can cause body leak & thus safety risk
Know: Dont Roll Gas Cylinders
M. Anand Bhaskar
21.2.02
TPM in Sales
How will TPM help generate value in Sales?
Field Depot
Br.Office
Sales (Vs Target)
Value = -------------------------
Cost and Time
8econdary
sa|es
exce||ence
8econdary
sa|es
exce||ence
est |n
c|ass
serv|ce
est |n
c|ass
serv|ce
TPH at R8
TPH at the ranch
TPH at the depot
TPM IN SALES
Value creation across the
sales value chain
Process efficiency
Manpower productivity
Visibility
Customer Service
Delivery efficiency
Stock availability
Market coverage
Stock availability
Outlet leadership
Service
Leadership
RS Retail Branch Depot
Growth Vision
Sales
J
|
8
h
U
h
0
Z
E
N
S
U
P
P
L
Y
C
H
A
I
N
M
A
N
A
G
E
M
E
N
T
I
N
I
T
I
A
L
F
L
O
W
C
O
N
T
R
O
L
E
D
U
C
A
T
I
O
N
&
T
R
A
I
N
I
N
G
S
H
E
K
O
B
E
T
S
U
K
A
I
Z
E
N
Policy Deployment
5 - S
TPM
Policy Deployment Approach - Sales
Business
Expectations
Benchmarking
a
SHE Issues Loss / Cost
Matrix
Key Branch targets (PQCDSM) - 3 yrs
Six Pillar Targets
KK JH E & T
SCM
IFC
SHE
Task Force Circle Targets
REVIEW
MECHANISM
Major
Themes
Minor
Themes
4 Loss Category & description of Losses
Financial Losses
Overheads
Sales tax Surprise Liability
Bouncing
Support Expenditure
Logistics
Stock related
Case fill and line fill
RS Stock availability index
Delivery loss
Service Losses
Manpower Loss
Manpower availability loss
Down time loss
Sales Losses
Coverage loss
Visibility and Merchandising loss
Line / Value per line losss
3 3
2
6
Branch Depot Field KK AM SCM E & T IFC SHE P Q C D S M
1.1 Coverage % RSM ASM
1.2 Visiblity and Merchandising ASM
1.3 Line / Value per Line Rs RSM ASM
2.1 Case Fill Line Fill % RSM LM ASM
2.2 RS SAI % LM ASM
2.3 Delivery % LM ASM
3.1 Manpower Availability Hrs/Day HRM ASM
3.2 Downtime Hrs/Day RSM/HRM ASM
4.1 Overheads Rs RCM ASM
4.2 Sales Tax Surprise Liability Rs RCM ASM
4.3 Bouncing Rs RCM ASM
4.4 Support Expenditure Rs RCM ASM
4.5 Logistic Rs RCM LM ASM
4.6 Stock Related Rs RCM LM ASM
Major Minor
Loss Category linkage to functions & pillars
Sr.No
Major
losses
Sub Losses Unit
Functional Owner Pillar Owner Target Linkage
4
3
2
1
Sales
Losses
Service
Losses
Manpower
Losses
Financial
Losses
TPM - Journey from Excellance to World Class
WorldClass
Thanks
TPM CULTURE
Score
I KNOWLEDGE 1 to 5
1. How many TPM instructors/Trainers on advance tools have we developed?
2. How much % of our employees have gone through Step-4 training?
3 How much % of our employees individual training needs identified/monitored?
4 Have we developed/implemented test procedures for general/specific job skills?
5 How many worker teachers have been developed so far?
6 How much % of employees have upgraded their skills from 2 to 3 (or) 3 to 4 levels during
the last 2 years?
7 Do we have a system of review of plans(from TINS) bridging the gaps in skills?
II PARTICIPATION / INVOLVEMENT
1 How many circles do carry out regular AM activity at their workplace?
2 How much % of employees write suggestions/OPLs/Kaizens?
3 Are we implementing Kaizens/making efforts to improve participants?
4 How many circles do meet weekly? Are we following up/facilitating training at these
meetings?
5 Are we encouraging excellent visual control/management initiative, model creation, TTC
activities in the last 6 months?
6 Do we have clarity in PQCDSM targets for circles cascaded down and a regular review
system in place?
III REWARD/RECOGNITION
1 Do we have regular 5S audit and reward mechanism in place?
2 Are we having regular Kaizen/OPL/MP sheets rewarding ceremony?(atleast once in a
Quarter)
3 Do we have clear link of promotion/merit rewarding (annual) based on performance?
4 How much % of employees have presented activity boards to VIPs/Sr.Managers?
6 Do we have newsletters/displays highlighting individual/group performances?
TPM CULTURE
Score
IV. PROCESS / RESULTS 1 to 5
1 Is the PQCDSM targets set by the factory aligned to business needs/world class
benchmarks?
2 Do we have stretched targets/significant improvement plans like (a) Achieve 90%- OEE
(b) double the speed ( c) in house machine development(LCA) (d) 20-30% cost reduction
(e) Zero incident injuries & so on?
3 Do we have a system of capturing feedback from visitors & actions on these?
4 How are processes linkage to the results during last few years?
5 How do you rate the achievement of results in your units? What is the level of
morale/motivation of the employees?
6 Are our activities oriented always towards loss/cost improvement?
7 How many Kaizens repacated from other lines/factories?
V TOP MANAGEMENT COMMITMENT
1 Do the Senior Management review ask questions on TPM/progress & facilitate?
2 Do the TPM steering committee meet every month to review pillar/circulate activities
results/processes?
3 How many Managers/Officers do take part in regular AM activities(daily/weekly) with the
circles?
4 Do we have required resources/organisation/training inputs in place?
5 Do we have regular AM step audits (by circle leader/TPM Secretariat & the by the FMs)
for the circles?
6 Are there regular events like zero breakdown week/OPL week so on & so forth?
7 Do the managers point out /address abnormality while on shopfloor?
* Score Criterion : Not Good-1; Average-2; Satisfactory-3;Good-4; Very Good-5
Classification TQC TPM
Pupose
Objects of management
Means of attaining goals
Development of personnel
Small-group activities Voluntary circle activities
Targets PPM order quality
Unification of formal organization-based
activities and small group activities
Thorough elimination of losses and
waste ( Inclination toward zero)
Systematization of control
(Systematization, standardization)-
Software oriented-
Realization of the ideal conditions of
the workshop and actual goods -
Hardware oriented -
Centered on control technolody (QC
method)
Centered on inherent technology
(Equipment technology, maintenance
skills)
Structural improvement of enterprises
(Improvement of business
achievements, creation of a pleasant
work environment)
Structural improvement of enterprises
(Improvement of business
achievements, creation of a pleasant
work environment)
Quality(Emphasis on output and
results)
Equipment ( Emphasis on input and
causes)
Comparison of Characteristics of TQC & TPM
PM - Maintenance
Classification Activity
Operation Maintenance
Correct operation
Setup and Adjustement
Cleaning , adress latent defects
Lubrication
Retightening
Routine inspection
Minor repair
Periodic inspection
Periodic examination
Time based overhaul
Trend control
LLF
Unscheduled overhaul
Early detection of failure and quick repair
Sporadic repair
Enhancement of material strength
Reducton of load
Enhancement of accuracy
Development of condition monitoring
Improvement of inspection work
Improvement of maintenance work
Enhancement of maintenance quality
Responsibilty
Normal operation
Routine
maintenance
Corrective
maintenance
(reliability)
Corrective
maintenance
(maintenability)
Periodic
maintenance
Predective
maintenance
Breakdown
maintenance
AM AND PM MAINTENANCE ACTIVITIES CLEARLY
DEFINED
Date of Commisn:
Date Problem Details Probable Causes
Materials
Consumed
Qnty.
Man hrs.
worked
Material
Cost
Manpower
cost
Remarks
Details :-
Model No:
NAME OF EQUIPMENT :- Area:
Sr.no
Supplier:
Date of
manufacturing:
Plant :
Make:
Asset No.:
VDL -EQUIPMENT HISTORY CARD
A B C
CBM L L F Remark Sr.No. Equipment List
Rating
TBM
Ranking of Equipment and Maintenance systems
Sr.No. Equipment
W1 W2 W3 W4 W1 W2 W3 W4 W1 W2 W3 W4 W1 W2 W3 W4 W1 W2 W3 W4 W1 W2 W3 W4 W1 W2 W3 W4 W1 W2 W3 W4 W1 W2 W3 W4 W1 W2 W3 W4
1 Super Chilling No 1 M S M M M M M M S M M M
2 Super Chilling No 2 M S M M M M M M S M M M
3 Cold Well Pump 1 M M M M M M M M M M
4 Cold Well Pump 2 M M M M M M M M M M
5 Hot Well Pump No 1 M M M M M M M M M M
6 Hot Well Pump No 2 M M M M M M M M M M
7 Water Chilling Plant 1 M S M M M M M M M S M M
8 Water Chilling Plant 2 M S M M M M M M M S M M
PRLVLN1IVL CHLCKING SCHLDULL
CHILLING PLANT (TSP)
SEP OCT MAY JUNE JULY AUG JAN FEB MAR APRIL
MAINTANANCE SCHEDULE (TSP Crutcher)
SR.
NO. EQUIPMENT NAME.
EQUIPMENT
NO. RESPONSIBILITY REASON
WORK
INSTRUCTION FRQUANCE JAN FEB MAR APRI MAY
101 HOT WELL PUMP- A 232069 S.V.SALVI VDL/TSP/M101 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
102 HOT WELL PUMP- B 232070 S.V.SALVI VDL/TSP/M102 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
103 OPEN CRUTCHER PUMP-A 236343 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M103 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
104 OPEN CRUTCHER PUMP-B 236344 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M104 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
105 MAZZONI PLODDER 209008 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M105 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
106 RECUBRATOR- A 206005 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M106 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
107 RECUBRATOR- B 206004 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M107 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
108 MAZZONI BLOWER 240091 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M108 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
109 Service dry Vaccum pump-A 227013 S.V.SALVI VDL/TSP/M109 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
110 Service dry Vaccum pump-B 227014 S.V.SALVI VDL/TSP/M110 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
111 Water eing. Vaccum pump 227935 S.V.SALVI VDL/TSP/M111 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
112 Colling tower pump- A S.V.SALVI VDL/TSP/M112 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
113 Colling tower pump- B S.V.SALVI VDL/TSP/M113 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
114 CLOSED CRUTCHER PUMP-A M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M114 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
115 CLOSED CRUTCHER PUMP-B M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M115 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
116 CR-4 CERCULATION PUMP S.B.PAWAR VDL/TSP/M116 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
117 SCRAP BOILING TRANSFER PUMP M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M117 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
118 OPEN CRUTCHER- A M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M118 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
119 OPEN CRUTCHER- B M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M119 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
120 CLOSED CRUTCHER- A M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M120 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
121 CLOSED CRUTCHER- B M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M121 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
122 CLOSED CRUTCHER- C M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M122 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
123 FEED PUMP M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M123 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
124 HEAT EXCHANGER- A 249001 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M124 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
125 HEAT EXCHANGER- B 249002 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M125 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
126 BAROMATRIC CONDENSER-A250018 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M126 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
127 BAROMATRIC CONDENSER-B250017 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M127 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
128 FEED TANK 237075 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M128 YEARLY 10
129 COUSTIC STORAGE TANK-A 237085 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M129 YEARLY 10
130 COUSTIC STORAGE TANK-B 237084 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M130 YEARLY 10
131 COUSTIC STORAGE TANK(48%) 237083 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M131 YEARLY 10
132 CR-10 HOT WATER TANK 237082 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M132 YEARLY 10
133 CODEX TANK 237081 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M133 YEARLY 10
134 DFA BLEND CR-13 A 237079 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M134 YEARLY 10
135 DFA BLEND CR-13 B 237080 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M135 YEARLY 10
136 SCRAP PER GEAR BOX M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M136 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
137 COUSTIC BLENDING TANK 250033 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M137 YEARLY 10
138 SALT MELTING TANK 250032 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M138 YEARLY 10
139 SCRAP BOILING TANK-A 237073 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M139 YEARLY 10
140 SCRAP BOILING TANK-B 237074 M.L.BHOSLE VDL/TSP/M140 YEARLY 10
141 HEAT EXCHANGER CIRCULATION PUMP S.B.PAWAR VDL/TSP/M141 WEEKLY 3,10,17&24 7,14,21&28 7,14,21&28 4,11,18&25 2,9,16&23
Location:
Done By:
Sr.No. Frequency of check
1 Y
2 Y
3 M
4 M
5 M
6 Y
7 Y
8 M
9 M
10 Y
11 Y
12 M
13 M
14 M
Sign of Officer
MOTOR UNLOAD
CURRENT
MOTOR ON LOAD
CURRENT
MOTOR FOUNDATION
CABLE GLAND
MOTOR EARTHING
COOLING FAN
No. of Hrs
PH TO PH
DE
BEARING CONDITION
Spares consumed :
IR VALUE
WDG. RESISTANCE
PH TO E
MOTOR TERMINALS
TERMINAL CONNECTOR
NDE
FAN COVER
END COVERS
DE
NDE
BEARING LUBRICATION
Date:
Description Remarks
CHECKLIST FOR MOTOR
Equipment No.
VDL/DFA/WI - 02 REV 00 HIGH PRESSURE PUMP MAINT.
Purpose Precautions to be taken while doing maint. job on H.P. pump
Scope - This procedure is applicable for h.p. pumps.
Frequency As on when required.
Responsibility Engineering officer and fitter
Detail of operation -
1 Shut the pump
2. Shut suction and discharge valve of pump
3. Drain line at suction and discharge through drain point.
4. Shut low pressure feeding pump.
5. Isolate pump electrically and remove fuses . Before starting pump
maint. ,ensure pump is not getting start.
6. Ensure discharge valve is not pass .
7. Inform operator about your job.
8. Take instuction from officer what job is to be done.
9. Wear required PPE before opening of pump.
10.Use proper tools for maint.
Prepa red by Revised by Aut ho rised by
Sr. No. Break Down Date Start Time End Time TTR T.B.F. Remark
Equipment Name:
Equipment Name Type
RPM
RPM
RPM
RPM
RPM
1 2 3 4 5 6
Inspection
Period
Measuring
location
Date
5 6 1 2 3 4
Bearing No
Initial value Reading
Measuring
Location
Horizontal
Vertical
Spike Energy Remarks
Area Schematic Dig
VDL - IRD Reading Sheet
Plant
Bearing No
Bearing No
Bearing No
Bearing No
1 2 3 4 5
6.1.2 APPROACH
OBJECTIVES, TARGETS
& MASTER PLAN
PM ACTIVITIES TO
IMPROVE MACHINE
AVAILABILITY
MAINTENANCE
COST REDUCTION
ASSISTANCE TO JH
ACTIVITIES
CORRECTIVE
MAINTENANCE
ACTIVITIES FOR ZERO
BREAKDOWN
PM PILLAR
ACTIVITIES
You might also like
- HUNTINGTON NATIONAL BANK StatementDocument7 pagesHUNTINGTON NATIONAL BANK StatementEmannuel Ontario74% (35)
- Tax Invoice: Delivery ToDocument1 pageTax Invoice: Delivery ToManoj MalikNo ratings yet
- CII JH Step 4Document4 pagesCII JH Step 4Kumar Swami50% (2)
- Keikaku Hozen Master PlanDocument9 pagesKeikaku Hozen Master PlanHarshad_SNo ratings yet
- Daily Management (JSQC) - EnglishDocument19 pagesDaily Management (JSQC) - EnglishSukhdev BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Maintenance Step 1-7Document18 pagesAutonomous Maintenance Step 1-7riade8886% (7)
- Planned Maintenance Step 2 Audit SheetDocument4 pagesPlanned Maintenance Step 2 Audit SheetDũng Tây NinhNo ratings yet
- RESEARCHPAPERDocument16 pagesRESEARCHPAPERUlquiorra Garcia47% (19)
- Manual 1 - Jishu-Hozen PDFDocument14 pagesManual 1 - Jishu-Hozen PDFvignesh88in2332No ratings yet
- TPM Conference - JIPM - NakanoDocument38 pagesTPM Conference - JIPM - Nakano1977jul50% (2)
- Autonomous Maintenance Step 3 Audit SheetDocument6 pagesAutonomous Maintenance Step 3 Audit SheetDũng Tây NinhNo ratings yet
- TPM Basics and Am Step 1 To 5Document90 pagesTPM Basics and Am Step 1 To 5Gaurav Mittal100% (5)
- Autonomous MaintenanceDocument9 pagesAutonomous MaintenanceElisha Maris LopezNo ratings yet
- Event TPM JipmDocument29 pagesEvent TPM JipmImamRN100% (3)
- Ishu Ozen: Autonomous MaintenanceDocument16 pagesIshu Ozen: Autonomous MaintenanceVictor ArokiyamNo ratings yet
- TPM LiteratureDocument99 pagesTPM LiteratureRajesh Kulkarni75% (4)
- TPM Mean Autonomous MaintenanceDocument27 pagesTPM Mean Autonomous Maintenancesydeng100% (1)
- TPM Presentation 12 Steps 1 121Document46 pagesTPM Presentation 12 Steps 1 121Jyoti_Malik_874494% (17)
- Step 0 and 1 Management Part 1Document14 pagesStep 0 and 1 Management Part 1murilocabriniNo ratings yet
- Jishu Hozen: Presentation By: V.P.SINGHDocument41 pagesJishu Hozen: Presentation By: V.P.SINGHAbhishek Xc57% (7)
- VSM PDFDocument52 pagesVSM PDFChip ChopNo ratings yet
- Training JH PillarDocument41 pagesTraining JH PillarSelvamNo ratings yet
- The World Class Manufacturing Programme at ChryslerDocument4 pagesThe World Class Manufacturing Programme at ChryslerNarasimharaghavanPuliyurKrishnaswamyNo ratings yet
- TPM ChecklistDocument14 pagesTPM Checklistmuneerpp100% (2)
- Jishu Hozen (Autonomous Maintenance)Document118 pagesJishu Hozen (Autonomous Maintenance)Harshit Modhia100% (2)
- Study of JH Implementation ReadyDocument27 pagesStudy of JH Implementation ReadyNaveen Jangid100% (1)
- Autonomous Operator Training Step 0 PDFDocument17 pagesAutonomous Operator Training Step 0 PDFjesusmemNo ratings yet
- P-M Analysis An Advanced Step in TPM Implementation - Shirose Kimura Kaneda - 2012Document196 pagesP-M Analysis An Advanced Step in TPM Implementation - Shirose Kimura Kaneda - 2012renzoppalominoNo ratings yet
- TPM BookletDocument26 pagesTPM Bookletamishraioc100% (5)
- TPM Jipm Seiichi Nakajima 2007 KlmanagementDocument40 pagesTPM Jipm Seiichi Nakajima 2007 KlmanagementDipankar Mukherjee100% (1)
- 06 - PMDocument113 pages06 - PMMohaiminNo ratings yet
- Kaizen BookletDocument71 pagesKaizen Bookletudayraj_vNo ratings yet
- TPMDocument42 pagesTPMShalini YadavNo ratings yet
- TPM Award OutlineDocument33 pagesTPM Award OutlineSunil Rathee100% (2)
- Total Productive Maintenance Section 8: Uptime Strategies For Excellence in Maintenance ManagementDocument38 pagesTotal Productive Maintenance Section 8: Uptime Strategies For Excellence in Maintenance ManagementWadiin23No ratings yet
- TPM TrainingDocument33 pagesTPM TrainingFERCHIU CRISTIANNo ratings yet
- TPM TrainingDocument57 pagesTPM Trainingnaga67% (3)
- TPM Assessment CriteriaDocument6 pagesTPM Assessment CriteriaSerdar OzkulaNo ratings yet
- HERCA - Tool - MasterDocument1 pageHERCA - Tool - MasterbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- WCM Tofas 2012 EngDocument11 pagesWCM Tofas 2012 Engjames007bondsgNo ratings yet
- World Class Manufacturing - 1Document46 pagesWorld Class Manufacturing - 1Prakash VermaNo ratings yet
- TPMDocument41 pagesTPMArun Narayanan100% (1)
- GEN-NA-STD-Approved TPM Pillars, Imp Team Routes Manuf-01.10.13.041-May2013Document76 pagesGEN-NA-STD-Approved TPM Pillars, Imp Team Routes Manuf-01.10.13.041-May2013Yen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Processing Point AnalysisDocument35 pagesProcessing Point AnalysisSophanNo ratings yet
- Stage Step (Nakajima's 12 Steps) : Decision To Introduce TPMDocument16 pagesStage Step (Nakajima's 12 Steps) : Decision To Introduce TPMKarisma Lumban GaolNo ratings yet
- 12 Steps TPM Implementation and Consultation Plan of ActivitiesDocument15 pages12 Steps TPM Implementation and Consultation Plan of ActivitiesMark Zenen Panganiban100% (1)
- Apply The E.C.R.S. Technique and Identify Improvement Actions: Mechanise Some MovementsDocument13 pagesApply The E.C.R.S. Technique and Identify Improvement Actions: Mechanise Some MovementsRahul RawatNo ratings yet
- BPS by SH ShettyDocument9 pagesBPS by SH ShettyNikhil SkariahNo ratings yet
- TPMDocument27 pagesTPMkathir100% (4)
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness Simplified: Analyzing OEE to find the Improvement OpportunitiesFrom EverandOverall Equipment Effectiveness Simplified: Analyzing OEE to find the Improvement OpportunitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SMED single minute exchange of die Complete Self-Assessment GuideFrom EverandSMED single minute exchange of die Complete Self-Assessment GuideNo ratings yet
- A Case Study and Presentation of TATA NANODocument11 pagesA Case Study and Presentation of TATA NANOK Y RajuNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Just in TimeDocument70 pagesProject Report On Just in TimeKrishna Sharma100% (1)
- 5S Kit - Formats 5'S - RevDocument14 pages5S Kit - Formats 5'S - RevOffice Mail Hyundai SiteNo ratings yet
- Gurunanak Commodities, Bhadra: Date Material Buy Sell Margin SL NO. Deposi T Margi N Rate Nett Margin Broke RageDocument10 pagesGurunanak Commodities, Bhadra: Date Material Buy Sell Margin SL NO. Deposi T Margi N Rate Nett Margin Broke RageHimanshu JoshiNo ratings yet
- ASNG Consultancy Services - Company ProfileDocument4 pagesASNG Consultancy Services - Company ProfilesatyagoltiNo ratings yet
- A Note On Comdisco - S Lease AccountingDocument25 pagesA Note On Comdisco - S Lease AccountingHussain HaidryNo ratings yet
- All Icm Address 2023Document4 pagesAll Icm Address 2023KUMAR TNo ratings yet
- Thursday, September 20, 2012: Davanagere To Bangalore VRL TravelsDocument1 pageThursday, September 20, 2012: Davanagere To Bangalore VRL TravelsAnonymous mcHqIfbnV1No ratings yet
- Bajaj XCDDocument4 pagesBajaj XCDshruti.shindeNo ratings yet
- Liquor Case StudyDocument4 pagesLiquor Case StudyEdwardNo ratings yet
- Cosh Topic PDFDocument79 pagesCosh Topic PDFJoseph Ryan ManandegNo ratings yet
- Accenture TranslateDocument4 pagesAccenture TranslateDewi SeskowantiNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument9 pagesStrategic ManagementRuishabh RunwalNo ratings yet
- SAP XI 3.0-CPACacheDocument8 pagesSAP XI 3.0-CPACacheumesh.soniNo ratings yet
- KamiasDocument20 pagesKamiasGliezel Ann PajarillaNo ratings yet
- Nota Keusahawanan Week 1 (Introduction)Document20 pagesNota Keusahawanan Week 1 (Introduction)Mazliah Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Accounting Training in NepalDocument2 pagesAccounting Training in NepalDhurba Bahadur Bk0% (1)
- Capstone Unit 2 Assignment - Strategic LeadershipDocument7 pagesCapstone Unit 2 Assignment - Strategic LeadershipGinger RosseterNo ratings yet
- Pharmexcil Pharmaceutical Export Promotion Council (Set Up by Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Govt., of India)Document6 pagesPharmexcil Pharmaceutical Export Promotion Council (Set Up by Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Govt., of India)Neha ThakkarNo ratings yet
- OLFM Training3Document57 pagesOLFM Training3Srinibas Mohanty0% (1)
- Sudbury: Greater Downtown Vision, Plan and Action StrategyDocument28 pagesSudbury: Greater Downtown Vision, Plan and Action StrategyGreen SudburyNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument4 pagesResumeRachel NicoleNo ratings yet
- Skechers v. IPITDocument1 pageSkechers v. IPITSarah Tarala MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Theory of Constraints (TOC) & Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)Document16 pagesIntroduction To The Theory of Constraints (TOC) & Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)AnnaNo ratings yet
- 27 Aug 2014 Circular NoDocument3 pages27 Aug 2014 Circular NockzeoNo ratings yet
- R12.2 Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning Fundamentals Ed 2Document5 pagesR12.2 Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning Fundamentals Ed 2Anonymous t2VF6DNo ratings yet
- Invoice:SLA193355527108, Purchased On:2023-11-09Document3 pagesInvoice:SLA193355527108, Purchased On:2023-11-09shyamborntowin95No ratings yet