Carbonyl Compounds
Carbonyl Compounds
Uploaded by
Palash DebnathCopyright:
Available Formats
Carbonyl Compounds
Carbonyl Compounds
Uploaded by
Palash DebnathCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Carbonyl Compounds
Carbonyl Compounds
Uploaded by
Palash DebnathCopyright:
Available Formats
Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic acids
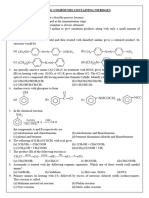
1. Which of the following can be (a) I (b) II
used for the synthesis of 3- (c) III (d) I–V
methyl-1-butanol? 6. The oxidation of 2-hexanol with
(a) n-C3H7MgBr + CH3CHO H2CrO4 gives
(b) (CH3)2CHCH2MgBr + CH2O (a) CH3COOH
(c) C2H5MgBr + CH3COCH3 (b) CH3CH2CH2COOH
(d) (CH3)3CMgBr + CH2O (c) CH3(CH2)3COCH3
2. Among the following, which will (d) CH3(CH2)4COOH
react most rapidly with HBr? 7. The order of reactivity towards
(a) C6H5CH2CH2CH2OH Nucleophilic addition in CH2O (I),
(b) C6H5CH(OH)CH2CH3 CH3CHO (II) and CH3COCH3 (III) is
(c) C6H5CH2CH(OH)CH3 (a) I > II > III (b) III > II > I
(d) (CH3)3CCH2OH (c) II > I > III (d) III > I > II
3. The conversion 8. The trans-hydroxylation of cyclo
hexene can be done by
(a) dilute KMnO4
(b) using OsO4
(c) converting cyclo hexene into an
epoxide and then opening the
epoxide ring
(d) none of these
Can be effected by using the 9. The reaction
reagent
(a) H2O, H2SO4 (b) O2
(c) C6H5CO3H (d) CrO3, H2SO4
4. The major product obtained in the
reaction is known as
(a) Aldol condensation
(b) Cannizzaro reaction
(c) Internal Cannizzaro reaction
is (d) Benzilic acid rearrangement
(a) (CH3)3C-CH2COCH3 10. Reaction of formaldehyde and
(b) (CH3)2C=CHC(OH)-(CH3)2 ammonia gives
(c) (CH3)2CH-CH(CH3)COCH3 (a) Hexamethylene tetramine
(d) (CH3)2C=CH-CH(OH)(CH3) (b) Bakelite
5. Which of the following hydrogen (c) Urea
will be the most acidic? (d) Triethylene tetramine
11. Which of the following does not
undergo benzoin condensation?
(a) Benzene carbaldehyde
(b) P-toluene carbaldehyde
(c) Phenylethanal
(d) 4-methoxy benzaldehyde
12. The common name of
hexamethylene tetramine is
(a) Nylon-6, 6
(b) Urotropine
Provided by – Palash Debnath
Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic acids
(c) Formaldehyde resin (a) I < II < III (b) III < II < I
(d) Acetamide (c) I < III < II (d) II < III < I
13. Which of the following is 21. An organic compound reduces
constituent of oil of winter green? Tollen’s reagent and Fehling’s
(a) Aspirin (b) Salol solution. It can be
(c) Methyl Salicylate (a) CH3CH2CHO (b) C6H5CHO
(d) None of these (c) CH3COCH2CH3 (d) (CH3)3CCOCH3
14. A mixture of benzaldehyde and 22. Acetyl bromide reacts with excess
formaldehyde on heating with of CH3MgI followed by treatment
aqueous NaOH solution gives: with a saturated solution of NH4Cl
(a) Benzyl alcohol & sodium formate gives
(b) Sodium benzoate & methyl (a) 2-methyl-2-propanol
alcohol (b) Acetamide
(c) Sodium benzoate & sodium (c) Acetone (d) Acetyl iodide
formate 23. Silver mirror test is given by
(d) Benzyl alcohol & methyl alcohol
which one of the following
15. Aldehydes and ketones form
compounds?
hydrocarbons by
(a) Acetaldehyde (b) Acetone
(a) Clemmensen reduction
(c) Formaldehyde
(b) Cannizzaro reaction
(d) Benzophenone
(c) Rosenmund reduction
24. In the reaction:
(d) Aldol Condensation
16. Which of the following respond
positively to the iodoform test? the product C is
(a) 2-Pentanone (b) 1-Pentanal (a) Acetaldehyde (b) Acetylene
(c) 3-Pentanone (d) Pentanol (c) Ethylene
17. Paraldehyde is a (d) Acetyl chloride
(a) dimer of formaldehyde 25. The best oxidising agent for
(b) trimer of acetaldehyde oxidation of CH3-CH=CH-CHO to
(c) hexamer of formaldehyde CH3- CH=CH-COOH is
(d) hexamer of acetaldehyde (a) Baeyer’s Reagent
18. The conversion of acetone into (b) Tollens’ Reagent
diacetone alcohol is carried out in (c) Schiff’s Reagent
the presence of (d) Acidified dichromate
(a) Dry HCl(g) (b) Conc. H2SO4 26. Hydrocarbons are formed when
(c) Ba(OH)2 (d) Heat aldehydes and ketones are
19. Meso tartaric acid and d-tartaric reacted with amalgamated Zn and
acid are conc. HCl. The reaction is called
(a) Diastereomers (a) Cannizaro reaction
(b) racemic mixtures (b) Clemmensen reaction
(c) enantiomers (c) Rosenmund reaction
(d) position isomers (d) Wolff-Kishner reaction
20. The boiling points of acetic 27. Which of the following carboxylic
anhydride (I), propionic acid is highly insoluble in water?
anhydride (II) and butyric (a) Propanoic acid
anhydride (III) follow the order (b) Butanoic acid
Provided by – Palash Debnath
Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic acids
(c) Pentanoic acid (R): The >C=O bond is present in
(d) Decanoic acid carbonyl compounds & carboxylic
28. Which of the following statement acid while C—O bond is in alcohols.
is correct regarding formic acid? 32. (A): Cannizzaro reaction converts
(a) It is a reducing agent HCHO into HCOO-Na+ and CH3OH.
(b) It is a weaker acid than acetic
(R): It is a proton-hydride transfer
acid
(c) It is an oxidising agent reaction.
(d) When its calcium salt is heated, it 33. (A): Protonation of the carbonyl
forms acetone group increases its electrophilic
29. Which of the following will not nature.
undergo HVZ reaction? (R): This is an example of
(a) Propanoic acid electrophilic addition on
(b) Ethanoic acid Nucleophilic oxygen.
(c) 2-methylpropanoic acid 34. (A): In aliphatic carboxylic acids,
(d) 2, 2-dimethylpropanoic acid
presence of strong electron-
Directions (Q. Nos. 30 – 34). This
withdrawing groups on hydrocarbon
section contains Assertion (A) and Reason
chain increases the acidity.
(R) type questions. Each question has 4 (R): Chloroacetic acid is stronger
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which than acetic acid.
only one is correct. 35. Formalin is used
(a) For the preservation of biological
(a) Both Assertion & Reason are specimens
correct, and reason is the correct (b) As a disinfectant
explanation of Assertion. (c) As a germicide
(d) All of the above
(b) Both Assertion & Reason are 36. DiBAL – H reacts with cyanide to
correct, but reason is not the form an intermediate known as
correct explanation of Assertion. (a) Amide (b) Aldehyde
(c) Assertion is correct but Reason is (c) Imine (d) Amine
37. Schiff’s reagent is
incorrect.
(a) Rosanilin hydrochloride solution
(d) Assertion is incorrect but Reason (b) Alkaline KMnO4 solution
is correct. (c) Sodium amalgam in HCl
(d) None of these
30. (A): Carbonyl compounds are more 38.
soluble in water than the
corresponding alkanes.
(R): H-bonding between carbonyl
oxygen and water renders carbonyl
compounds more water soluble than
hydrocarbon.
31. (A): The >C=O bond (0.122nm) is
shorter than the C—O bond
(0.141nm).
Provided by – Palash Debnath
You might also like
- Jack KruseDocument50 pagesJack KruseJosh88% (8)
- Lesson Plan For SpeakingDocument3 pagesLesson Plan For SpeakingAri Pacaro100% (1)
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 10+11+12 B-II)XXXNo ratings yet
- AldehydesDocument22 pagesAldehydesjksiddharth24No ratings yet
- C12 - ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (1) .9cfd4beDocument4 pagesC12 - ALDEHYDES KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (1) .9cfd4beakashkishore363No ratings yet
- Waghs Chemistry: Chapter-Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesWaghs Chemistry: Chapter-Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic AcidsRiddhesh100% (1)
- 12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument23 pages12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsBedosi Bidita PandaNo ratings yet
- namma_kalvi_12th_chemsitry_unit_12_study_material_english_medium_216129Document29 pagesnamma_kalvi_12th_chemsitry_unit_12_study_material_english_medium_216129codofficial61No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds SheetDocument6 pagesCarbonyl Compounds SheetRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDocument20 pages12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123No ratings yet
- Aldehydes & KetonesDocument23 pagesAldehydes & KetonesManthan JhaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid Unit 11 MCQDocument4 pagesAldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid Unit 11 MCQAbhinav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acidskavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Alkanes 24.12...........Document4 pagesAlkanes 24.12...........vengateshwaran kNo ratings yet
- C11 - ALCOHOLS PHENOLS & ETHERS (1) .9c6f83eDocument4 pagesC11 - ALCOHOLS PHENOLS & ETHERS (1) .9c6f83eakashkishore363No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-12-02 at 4.29.37 AMDocument7 pagesScreenshot 2024-12-02 at 4.29.37 AMkaurswarnjit102No ratings yet
- Organic Test 1Document4 pagesOrganic Test 1binodNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10Document3 pagesChapter-10rsyadav05082005No ratings yet
- CH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsDocument3 pagesCH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsPranav ShankarNo ratings yet
- (Xii) Alcohol, Phenol, EtherDocument10 pages(Xii) Alcohol, Phenol, EtherAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 04, 2024 (1)Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 04, 2024 (1)bohrajiah16No ratings yet
- MCQ - Alcohols, phenols and ethers (1)Document6 pagesMCQ - Alcohols, phenols and ethers (1)manasi.mysoreNo ratings yet
- 3 - Aldehydes and Ketones (Assignment) Booklet-2Document15 pages3 - Aldehydes and Ketones (Assignment) Booklet-2kraken monster100% (1)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Q 5Document3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Q 5jayjena007No ratings yet
- C10 - HALOALKANES & HALOARENES (1) .9bd6790Document4 pagesC10 - HALOALKANES & HALOARENES (1) .9bd6790akashkishore363No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones - 3Document6 pagesAldehydes and Ketones - 3iitlectureNo ratings yet
- Chem Class 12 WorksheetDocument8 pagesChem Class 12 WorksheetBHAVYA KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- XII CH#09 P.S#01 HareshDocument3 pagesXII CH#09 P.S#01 Hareshpapukhan67zkqNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument22 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsBhavesh K100% (1)
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument9 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersarshadumerkhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch9,10 Part IIDocument4 pagesChemistry Ch9,10 Part IIdania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument5 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloareneskavitha2511977No ratings yet
- CH# 11 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)Document4 pagesCH# 11 XII (Chem 12 Exam Task)Zeeshan Haider ChemistNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 11 MCQJay VermaNo ratings yet
- Bottom of Pyramid - Test # 15 - Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesBottom of Pyramid - Test # 15 - Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds Containing NitrogenDocument6 pagesOrganic Compounds Containing Nitrogenkavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ Assertion-3Document5 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ Assertion-3bullet4478No ratings yet
- 3B-HYDROCARBON Assignment - FinalDocument49 pages3B-HYDROCARBON Assignment - Finalkraken monsterNo ratings yet
- Diwali Assignment 12thDocument19 pagesDiwali Assignment 12thNishantPlayz YtNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument21 pagesQuestion Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsSahilNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-31-OctDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-31-Octolivia.benson9331No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: CHO H CH CH C CHDocument8 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: CHO H CH CH C CHUjjwal TomarNo ratings yet
- Attempt Any 40) : So HCL CL H CDocument4 pagesAttempt Any 40) : So HCL CL H CJatin ChouhanNo ratings yet
- diwali holiday homework for class 12th-2024Document10 pagesdiwali holiday homework for class 12th-2024leomessigoat873No ratings yet
- 03-CET-REV Chemistry - Solutions - M4 (1)Document14 pages03-CET-REV Chemistry - Solutions - M4 (1)shashaank2patilNo ratings yet
- CH 11. Aldehydes - Ketones Tatva (NM)Document48 pagesCH 11. Aldehydes - Ketones Tatva (NM)chandan mallikNo ratings yet
- All Boards Full Book McqsDocument9 pagesAll Boards Full Book Mcqsbebetterpls3No ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch7,8 Part IIDocument4 pagesChemistry Ch7,8 Part IIdania.siddiqui195No ratings yet
- Chem Book 2 TestDocument3 pagesChem Book 2 TestHishq DhimanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic AcidsDocument47 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acidssuryakala.ganapathyNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument10 pagesAldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic Acidgoodgirlz946No ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-15MCQsDocument4 pages12th Chemistry CH-15MCQsRana DugNo ratings yet
- 07 Addition and Condensation of Enols and Enolate Ions (1) .PDF - 1Document15 pages07 Addition and Condensation of Enols and Enolate Ions (1) .PDF - 1JeetNo ratings yet
- (Xii) Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument11 pages(Xii) Haloalkanes and HaloarenessitaramroyalNo ratings yet
- FNT XII 01 - JP © Mdcatian's Stetho Converted - Mdcat Aspire AvenueDocument3 pagesFNT XII 01 - JP © Mdcatian's Stetho Converted - Mdcat Aspire Avenuekhand.ahmadanimehboob7788No ratings yet
- Organic Part Full Length PaperDocument4 pagesOrganic Part Full Length PaperChemistry guideNo ratings yet
- 09 HydrocarbansDocument7 pages09 HydrocarbansarshadumerkhanNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon - Practice SheetDocument3 pagesHydrocarbon - Practice SheetAbhishek PathakNo ratings yet
- Alkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 3Document3 pagesAlkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 3Vishal_93100% (1)
- KCET 2024 Chemistry Paper With AnswerDocument9 pagesKCET 2024 Chemistry Paper With Answerthejasmath2005No ratings yet
- Topic: Organic Compounds Containing HalogensDocument5 pagesTopic: Organic Compounds Containing Halogensvictoria schoolNo ratings yet
- Notes Pharmacy Exam SaudiaDocument6 pagesNotes Pharmacy Exam SaudiaAli ButtNo ratings yet
- Class Notes - Agrarian Revolution #1Document6 pagesClass Notes - Agrarian Revolution #1desmaroclarke2No ratings yet
- Business Metrics Lesson: Terminology and Formulas: Metric Formula Commonly Used Alternate TermsDocument3 pagesBusiness Metrics Lesson: Terminology and Formulas: Metric Formula Commonly Used Alternate Termsyogesh patilNo ratings yet
- What Is EcotourismDocument2 pagesWhat Is EcotourismFitri AzzahraNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Extracurricular Activities On Student'S Academic PerformanceDocument33 pagesThe Impact of Extracurricular Activities On Student'S Academic PerformanceIshika PrasadNo ratings yet
- Political InstitutionsDocument50 pagesPolitical InstitutionsCBSE UGC NET EXAMNo ratings yet
- User Manual GMT 050 Felling Grapple Serial Number: 053 Up To and Including 254Document38 pagesUser Manual GMT 050 Felling Grapple Serial Number: 053 Up To and Including 254Jorge Reyes AguilarNo ratings yet
- Haircoloring and Bleaching Schemes of WorkDocument8 pagesHaircoloring and Bleaching Schemes of WorkBarrack koderaNo ratings yet
- Resolution of Bangladesh-India Maritime Boundary: Dalam Model Penyelesaian Sengketa Terhadap Laut Cina SelatanDocument150 pagesResolution of Bangladesh-India Maritime Boundary: Dalam Model Penyelesaian Sengketa Terhadap Laut Cina SelatanBina SabrinaNo ratings yet
- IR Music Transmitter and ReceiverDocument17 pagesIR Music Transmitter and ReceiverNeeharika Chekuri100% (2)
- Demand ScheduleDocument9 pagesDemand ScheduleCarl John Sedimo100% (1)
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)Document12 pagesObsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)Kfrey722No ratings yet
- Theory of Automata Handouts 1Document4 pagesTheory of Automata Handouts 1Gaming Addict BrosNo ratings yet
- ARMLab LaTeX Beamer TemplateDocument10 pagesARMLab LaTeX Beamer TemplateDiómedes Miguel Perez HuamaniNo ratings yet
- Lenguaje No Sexista. Una Apuesta Por La Visibilización de Las Mujeres PDFDocument11 pagesLenguaje No Sexista. Una Apuesta Por La Visibilización de Las Mujeres PDFLucila GiorginiNo ratings yet
- Lambino Vs COMELECDocument3 pagesLambino Vs COMELECKariz EscañoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Must KnowDocument5 pagesMicrobiology Must Knownathanmrrk pacayNo ratings yet
- The Typology of Parts of Speech Systems - The Markedness of Adjectives (PDFDrive) PDFDocument233 pagesThe Typology of Parts of Speech Systems - The Markedness of Adjectives (PDFDrive) PDFRoman Tilahun100% (1)
- Ancient HistoryDocument156 pagesAncient HistoryNiran ChueachitNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Music Periodical 1st Quarter 2018Document3 pagesGrade 8 Music Periodical 1st Quarter 2018Kareen Pantilano100% (2)
- Multiple Choice QuizDocument2 pagesMultiple Choice QuizchatnarenNo ratings yet
- AVE MOD 002 INS - I03 Boeing737 - InstallationInstructionsDocument26 pagesAVE MOD 002 INS - I03 Boeing737 - InstallationInstructionsdianavg.9319No ratings yet
- Glossary of Immunology Terms: Study Online atDocument12 pagesGlossary of Immunology Terms: Study Online atKurdii LaraNo ratings yet
- MA SIN Consent FormDocument1 pageMA SIN Consent FormAnonymous 1OlQQ3cWNo ratings yet
- MCQ's On Financial ManagementDocument22 pagesMCQ's On Financial ManagementsvparoNo ratings yet
- Happiness: Towards A Holistic Approach To Development. Note by The Secretary-GeneralDocument16 pagesHappiness: Towards A Holistic Approach To Development. Note by The Secretary-Generalbsergiu2No ratings yet
- Data ObatDocument93 pagesData Obatmemyu mahmudahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.6Document13 pagesChapter 1.6Praneshvar PraneshvarNo ratings yet