0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsATOMS
Uploaded by
schoolwork7002Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsATOMS
Uploaded by
schoolwork7002Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 2
Atoms~~
Discovery of Atom: Failure:
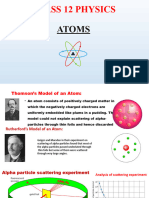
Thomson’s model: Atom is neutral. Couldn’t explain the stability of
Atoms are like positively charged sphere hydrogen.
with electrons spread into it like Couldn’t explain the spectral lines of
watermelon’s seed. Hydrogen.
Drawbacks: Closest Distance of approach:
1. Alpha-scattering couldn’t be The distance of the charged particle from
explained. the center of the target nucleus, at which
2. Atomic spectral lines couldn’t be the whole Kinetic Energy of the charged
explained. particle gets converted into potential
energy (or balanced by the coloumbic force
RUTHERFORD MODEL:
of repulsion).
(Alpha particle scattering experiment.)
k i+ v i=k f + v f
Alpha-particle means He 2+
1 1 k (ze)(2 e)
Took gold foil because it’s most m v 20 +0= m(0)+
2 2 d
ductile. Easy to make sheet. As
screen he took ZnS which produces 1 2 2 k ze
2
spark when He is touched. ¿ m v 0=
2 d
¿
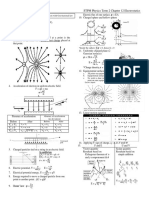
Observations:
2
4 k ze
Most of the alpha particles, pass d= 2
undeviated. mv 0
0.15% deflected more than 1 degree.
1 in 8000 deviated more than 90
degrees. Bohr’s Postulates:
Conclusion: The e- revolve around the nucleus in
fixed orbits, but they do not radiate
Most of the space is empty light while revolving.
because many particles are Only those orbits exist for which
undeviated. angular momentum is quantized. ( L
There must be strong positive = mvr {angular mome.})
charge at center. nh
Size of nucleus = 10-15 m L=mvr=
2π
Size of atom = 10-10 m The electrons emit light or energy
There must be e- s in the atom to when they move from higher orbit to
keep it neutral. They revolve lower orbit.
around in circular orbits around
the nucleus. The centripetal force
is provided by the electrostatic
attraction between the nucleus
The Relation of nth Orbit:
Time Period: Time taken by e- to revolve
Let’s assume an e is revolving in n orbit
- th
one complete round around a nucleus.
of radius ‘rn’ with velocity ‘vn’. By using
angular momentum theory 2 π rn
Time period =
Vn Vn
nh
m v n r n=
2π rn 2 π r o n3
T= V o Z2
nh
v n=
2 πmr n
Ze 3
n
T = To 2 [ To = 1.51 * 10-16
F e ∧¿ F c Z
k ( ze ) e m v 2n s]
∧¿
r 2n rn
1 Z e2
( )
2
nh
∧¿ m Z
2
4 π ε0 rn πm r n Frequency, f = fo 3 [ fo = 6.62 *
2 2 2 n
1 Ze mn h
= 2 2 2 1015 s-1 ]
4 π ε 0 λn 4 π m r n
2 2
ε0 n h
rn = 2
Z e πm
2
ε 0 h n2
rn = 2
e πm Z
2
n
r n =r 0
Z
[ ro = 0.53A = 0.53 * 10-
10
m]
nh
v n=
2 πmr n
2
e Z
v n=
2 ε 0 hn
2
e Z
v n=
2 ε 0 hn
Z
v n=V o
n
[ Vo = 2.2 * 10 6
m/s ]
You might also like
- BS EN 12596 - Dynamic Viscosity by Vacuum CapillaryNo ratings yetBS EN 12596 - Dynamic Viscosity by Vacuum Capillary22 pages
- Atomic-structure-Theory & Solved Examples Module-6No ratings yetAtomic-structure-Theory & Solved Examples Module-617 pages
- Atomic Physics Sommerfel BohrInitiaklQuantumMechanicsNo ratings yetAtomic Physics Sommerfel BohrInitiaklQuantumMechanics44 pages
- Materials Molecules Atoms Atoms Protons + Neutrons + Electrons Protons and Neutrons Are Made of QuarksNo ratings yetMaterials Molecules Atoms Atoms Protons + Neutrons + Electrons Protons and Neutrons Are Made of Quarks33 pages
- 27 Dec Modern Physics Atoms #BounceBack SprintNo ratings yet27 Dec Modern Physics Atoms #BounceBack Sprint111 pages
- Chap 12P Atoms_47875231_2025_01_04_20_07No ratings yetChap 12P Atoms_47875231_2025_01_04_20_0753 pages
- 12. Atoms: Rutherford's α-particle scattering experiment - When α-particlesNo ratings yet12. Atoms: Rutherford's α-particle scattering experiment - When α-particles6 pages
- EE2111E6-7E44-4FE4-BCF4-7443B100589D-exportNo ratings yetEE2111E6-7E44-4FE4-BCF4-7443B100589D-export20 pages
- Rutherford's Model, Bohr's Model and It's 3 PostulatesNo ratings yetRutherford's Model, Bohr's Model and It's 3 Postulates15 pages
- Atomic and Nuclear Physics: Thomson's Atomic ModelNo ratings yetAtomic and Nuclear Physics: Thomson's Atomic Model23 pages
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Resource 20240525092946 Ix Holiday HomeworkNo ratings yetResource 20240525092946 Ix Holiday Homework3 pages
- NANO 2172 Final Exam- 219xxx 2023 [1]-RT-kkmsNo ratings yetNANO 2172 Final Exam- 219xxx 2023 [1]-RT-kkms6 pages
- Current, Resistance and Electromotive ForceNo ratings yetCurrent, Resistance and Electromotive Force20 pages
- School of Electronic and Communications EngineeringNo ratings yetSchool of Electronic and Communications Engineering18 pages
- Pair By: Mechanics 2 Hour) Test 2 Answer QuestionsNo ratings yetPair By: Mechanics 2 Hour) Test 2 Answer Questions6 pages
- ECEN 460 Power System Operation and Control: Lecture 20: Transient StabilityNo ratings yetECEN 460 Power System Operation and Control: Lecture 20: Transient Stability25 pages
- Assignment 5 Chapter - Quantum Mechanics (Applications of Schrodinger's Equation)No ratings yetAssignment 5 Chapter - Quantum Mechanics (Applications of Schrodinger's Equation)6 pages
- H. R. Vallentine (Auth.) - Applied Hydrodynamics-Springer US (1967) PDFNo ratings yetH. R. Vallentine (Auth.) - Applied Hydrodynamics-Springer US (1967) PDF305 pages
- Chapter 2 - Newton's First Law of Motion - InertiaNo ratings yetChapter 2 - Newton's First Law of Motion - Inertia45 pages