Anatomy Notes
Anatomy Notes
Uploaded by
Claire BuliyatCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy Notes
Anatomy Notes
Uploaded by
Claire BuliyatCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy Notes
Anatomy Notes
Uploaded by
Claire BuliyatCopyright:
Available Formats
ANATOMY: 02/23/2012 DR.
ABIOG [ANKLE AND FOOT: KINESIOLOGY AND RELATED STRUCTURE] *Tarsal (7) Talus Calcaneus Navicular Cuboid Cuneiforms (medial, intermediate,lateral) *Metatarsals (5) *Phalanges (14) Retinaculum (20) a. Extensor Retinacula hold extensor tendons in place prevents bowstringing -Superior (transverse crural) -Inferior (cruciate crural) joins the superior Superficial Deep b. Flexor retinaculum (laciniate ligament) -holds the flexor tendons in place -converts bony grooves into 4 osseofibrous canals for the following: (medial to lateral) -Tendon of tibialis posterior -Tendon of the FDL -Posterior tibial artery and vein -Tibial Nerve -Tendon of the FHL **Dance Anatomy and Kinesiology BONES OF THE LOWER LEG a) Fibula -Transfers minority of wt bearing load through the leg Distal end is the lateral malleolus of the ankle b) Tibia -distal end is the medial malleolus of the ankle Transfers majority of the wt bearing load through the leg **Torsion Angle 20 - 300 external rotation
ANKLE AND FOOT **Primary function is to provide shock absorption and to impart thrust to the body during walking or ambulation. *AMBULATION-umbrella term for transfer movements from one place to another ex. Walking -pliability to absorb force of body wt. -rigidity to provide propulsive thrust *functions through an interaction of interrelated joints MOTIONS AT THE ANKLE AND FOOT -motions about the foot and ankle are considered triplanar but move on an oblique axis -pronation -eversion/abduction/dorsiflexion -supination -inversion/adduction/plantar flexion (actually happens in an oblique axis) ANKLE JOINT -talotibial (talocrural, ankle mortise) -bones(3) -medial, lateral and talus -type of joint -ginglymus (hinge) -movements -dorsiflexion/plantar flexion SUBTALAR JOINT -talocalcaneal -bones -talus and calcaneus -type of joint -arthrodial -movements -inversion elevation of the medial border -roll inward -eversion roll outward TRANSVERSE TARSAL JOINT -talonavicular of the TCN joint and calacaneocuboid (together they are called Choparts, midtarsal, TTJ) -bones -talus, navicular and partly calcaneus -calcaneus and cuboid -type of diarthrodial joint -arthrodial 1
-movements -inversion/eversion -partly adduction/abduction **Lateral malleolus (reach the level of the talus) is longer than the medial malleolus (reach the 1/3 part of the talus) **Tarsometatarsal joint aka the Lisfranc joint **Interphalangeal Joint only 1 at the hallux/big toe SUPINATION VS PRONATION Supination -inversion -plantarflexion -adduction Pronation -eversion -dorsiflexion -abduction SUMMARY OF ANKLE/FOOT MOVEMENTS Plantarflexors -gastrocnemius -soleus -tibialis posterior -FHL -FDL -peroneus longus -peroneus brevis -plantaris Dorsiflexors -tibialis anterior -EDL -EHL -peroneus tertius Invertors -tibialis anterior - tibialis posterior -FHL -FDL -EHL (included bec. of its axis of motion) Evertors -peroneus longus -peroneus brevis -peroneus tertius -EDL 2 *Ankle joint (must know) Ligaments -medial collateral lig (deltoid) -lateral collateral lig Deltoid 4 ligaments -tibiotalar ant. And post. -tibionavicular in between -tibiocalcaneal Lateral Collateral Ligament 3 Ligaments Ligaments (most frequently sprained) -ant. Talobifular 1st to be fractured -post. Talobifular 3rd; thickest -calcaneofibular 2nd **High ankle sprain ant. Inf. Tibiofibular lig affectation Bowstrings Ligaments -plantar calcaneonavicular (spring lig) -plantar calcaneocubiod (short plantar lig) -long plantar ligament **tibialis posterior maintains medial arch (dynamic stability) **tibialis anterior static stability
You might also like
- Watkins Manual of Foot and Ankle Medicine and Surgery 2016Document931 pagesWatkins Manual of Foot and Ankle Medicine and Surgery 2016Karolina100% (8)
- Table of Lower Limb Muscles RWDocument9 pagesTable of Lower Limb Muscles RWVirronChahal100% (2)
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus FinalDocument28 pagesCongenital Talipes Equinovarus FinalLakshmi Narayan R100% (2)
- Polio - Ankle and FootDocument9 pagesPolio - Ankle and FootDoc DelowerNo ratings yet
- Table of Lower Limb MusclesDocument7 pagesTable of Lower Limb MuscleskavindukarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy Summary ANKLE FOOTDocument32 pagesManual Therapy Summary ANKLE FOOTnataleebella100% (2)
- Ilizarov Technique For Complex Foot and Ankle Deformities Oxidative Stress Amp DiseaseDocument476 pagesIlizarov Technique For Complex Foot and Ankle Deformities Oxidative Stress Amp DiseaseSathyadharan Paneer100% (4)
- Anklefootbiomechanics-180308063536 (1) - CompressedDocument98 pagesAnklefootbiomechanics-180308063536 (1) - CompressedMichael SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The FootDocument26 pagesAnatomy of The FootKumar BalramNo ratings yet
- Ankle Joint - Physical ExaminationDocument5 pagesAnkle Joint - Physical ExaminationAdi ShabatNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Bones and JointsDocument43 pagesFoot and Ankle Bones and Jointshannah murphyNo ratings yet
- Anatomia y Biomecanica Pie TobilloDocument21 pagesAnatomia y Biomecanica Pie TobilloJoel OntiverosNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The Ankle and Foot. JohanesDocument58 pagesPhysical Examination of The Ankle and Foot. JohanesSaaldy ReivanNo ratings yet
- Ankle & Foot MechanicsDocument47 pagesAnkle & Foot MechanicsAhmed El goharyNo ratings yet
- Tut BManklefutcisDocument71 pagesTut BManklefutcisosteoferdianNo ratings yet
- Ankle JointDocument84 pagesAnkle JointPoojitha reddy MunnangiNo ratings yet
- Repercussions of Non-Compliance With A Ballet Dancer Hypermobile Ankle - A Case StudyDocument14 pagesRepercussions of Non-Compliance With A Ballet Dancer Hypermobile Ankle - A Case Studychajepark6296No ratings yet
- Kinesiology Ankle and Foot WULDocument46 pagesKinesiology Ankle and Foot WULwulandari pramanaNo ratings yet
- Magsombol, Hazel Anne A. OT2-1 Ankle and Feet BiomechanicsDocument4 pagesMagsombol, Hazel Anne A. OT2-1 Ankle and Feet Biomechanicshazell_aseronNo ratings yet
- Practical Problem Solving Questions Foot and AnkleDocument2 pagesPractical Problem Solving Questions Foot and Anklesirish413No ratings yet
- L12Document45 pagesL12Ahmed El goharyNo ratings yet
- EXSC 322 - Ankle & Foot Part 1Document52 pagesEXSC 322 - Ankle & Foot Part 1ChelseyNo ratings yet
- Lower LimbDocument24 pagesLower LimbKhadija AbouslimaNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle JointDocument15 pagesFoot and Ankle JointnovitaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Skeletal System Lower Limb (Structure Function)Document23 pagesLecture 12 Skeletal System Lower Limb (Structure Function)hafiz patahNo ratings yet
- Ankle JointDocument39 pagesAnkle Jointheena solankiNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Knee COMPLEX: Dr. Sumit Raghav (PT)Document52 pagesBiomechanics of Knee COMPLEX: Dr. Sumit Raghav (PT)Kavya MittalNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy and Biomechanics - Ankle andDocument7 pagesFunctional Anatomy and Biomechanics - Ankle andlinaos41No ratings yet
- Anatomi Ankle 1Document114 pagesAnatomi Ankle 1Zera DirgantaraNo ratings yet
- Ankle Anatomy and Blood Supply of TalusDocument66 pagesAnkle Anatomy and Blood Supply of TalusShashank29 LakkalaNo ratings yet
- Presentor-Dr. Momin Mohammad Farhan Moderator-Dr. M. A. Q. AnsariDocument48 pagesPresentor-Dr. Momin Mohammad Farhan Moderator-Dr. M. A. Q. Ansarimohammad farhanNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Foot ComplexDocument94 pagesAnkle and Foot ComplexMichelle Peters100% (1)
- ANKLE JOINT &joints of FootDocument35 pagesANKLE JOINT &joints of Foothhaanniiss3870No ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Ankle and FootDocument40 pagesBiomechanics of Ankle and FootNujella BalajiNo ratings yet
- Arthrology of The FootDocument55 pagesArthrology of The Footolle3870No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 11 NotesAzwar Arsyad S SiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 The Ankle Joint 2023Document69 pagesLecture 10 The Ankle Joint 2023carolyeung09No ratings yet
- Anatomy Foot and AnkleDocument33 pagesAnatomy Foot and Ankledewiswahyu100% (1)
- Lec 18 THE ANKLE JOINTDocument12 pagesLec 18 THE ANKLE JOINTMaheen IrfanNo ratings yet
- Foot Ankle AnatomyDocument26 pagesFoot Ankle AnatomyBrad HunkinsNo ratings yet
- Ankle ComplexDocument95 pagesAnkle ComplexMangala Prema MohanarangamNo ratings yet
- ARCHDocument63 pagesARCHDebashish Chanda100% (1)
- Foot and AnkleDocument58 pagesFoot and Anklekyliever100% (1)
- Gen Ana Assignment 1 2Document2 pagesGen Ana Assignment 1 2Jei SanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper Limb: 1) ClavicleDocument4 pagesAnatomy - Upper Limb: 1) ClavicleJasmine TeoNo ratings yet
- Gen Ana Assignment 1 2Document2 pagesGen Ana Assignment 1 2Jei SanNo ratings yet
- (9F) Ankle - Bones, Joints, Tendons and LigamentsDocument4 pages(9F) Ankle - Bones, Joints, Tendons and LigamentsJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of FeetDocument22 pagesAnatomy of FeetsherysheryyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lower Limb: by Dr. G. TowoDocument146 pagesAnatomy of The Lower Limb: by Dr. G. TowoVuluwa GeorgeNo ratings yet
- The Talonavicular and Subtalar Joints The Calcaneopedal Unit ConceptDocument11 pagesThe Talonavicular and Subtalar Joints The Calcaneopedal Unit ConceptAnonymous kdBDppigENo ratings yet
- Ankle BiomechanicsDocument23 pagesAnkle Biomechanicsnahymhmd32No ratings yet
- Appendicular SkeletonDocument23 pagesAppendicular SkeletonFachriza Effendi100% (1)
- Knee MechanicsDocument107 pagesKnee MechanicsAhmed El goharyNo ratings yet
- Bones: Kinesiology: Chap 11: Ankle & FootDocument5 pagesBones: Kinesiology: Chap 11: Ankle & FootEdsel JavellanaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ankle JointDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Ankle JointOtim JacNo ratings yet
- LecturesDocument25 pagesLecturesAmr Mohamed GalalNo ratings yet
- FootDocument9 pagesFootToday NewsNo ratings yet
- Shoulder JointDocument32 pagesShoulder JointRafli Antariksa100% (1)
- Lower Limb Muscles: Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Main ActionsDocument6 pagesLower Limb Muscles: Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Main ActionsJade Phoebe AjeroNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Ankle and FootDocument15 pagesBiomechanics of Ankle and FootJaime Aguilera100% (1)
- AnkleDocument6 pagesAnkleyaraa6805No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ankle and FootDocument13 pagesAnatomy of The Ankle and FootRichard MillerNo ratings yet
- 0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSDocument24 pages0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSArijeet77No ratings yet
- Improving Ankle and Knee Joint Stability: Proprioceptive Balancefit Discs DrillsFrom EverandImproving Ankle and Knee Joint Stability: Proprioceptive Balancefit Discs DrillsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - The Lower Limb: Snell 9 EdDocument138 pagesChapter 10 - The Lower Limb: Snell 9 EdFerjie Angelica DalandaoNo ratings yet
- Help CfponsetiDocument32 pagesHelp CfponsetiShAi_MyStERiOuSNo ratings yet
- KINESIOLOGY - Carmina Cortez, MD - September 27, 2017Document9 pagesKINESIOLOGY - Carmina Cortez, MD - September 27, 2017Johann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Cavovarus Foot JOT 2018Document5 pagesCavovarus Foot JOT 2018Noel Yongshen LeeNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Single Best Answers: Midfoot and ForefootDocument25 pagesFoot and Ankle Single Best Answers: Midfoot and ForefootDahir HusseinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lower Limb: by Dr. G. TowoDocument146 pagesAnatomy of The Lower Limb: by Dr. G. TowoVuluwa GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle ANATOMY PDFDocument80 pagesFoot and Ankle ANATOMY PDFMark JayNo ratings yet
- Postcranial Skeletal Morphology in Living and Fossil African SuidaeDocument9 pagesPostcranial Skeletal Morphology in Living and Fossil African SuidaeMaría EscobarNo ratings yet
- Ankle Foot BiomechanicsDocument38 pagesAnkle Foot BiomechanicsAnish BishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Extremitas InferiorDocument28 pagesExtremitas InferiorIshry Ahsani aulia askarNo ratings yet
- Ankle N Foot 3Document63 pagesAnkle N Foot 3YusraNo ratings yet
- MR Requirements Musculoskeletal MRIDocument56 pagesMR Requirements Musculoskeletal MRIDifa ZafiraNo ratings yet
- Surgical Treatment of ClubfootDocument49 pagesSurgical Treatment of Clubfootvishwas dabasNo ratings yet
- Full Download Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics 4-Volume Set 14th Edition Frederick M. Azar PDFDocument64 pagesFull Download Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics 4-Volume Set 14th Edition Frederick M. Azar PDFachabamanna100% (2)
- Musculoskeletal: Unit 553 September 2018Document34 pagesMusculoskeletal: Unit 553 September 2018dragon66No ratings yet
- FRCR 2a MSK Chest NotesDocument34 pagesFRCR 2a MSK Chest Noteskencheung888100% (4)
- Full Download Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics, 4-Volume Set-Elsevier (2020) Frederick M. Azar PDFDocument64 pagesFull Download Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics, 4-Volume Set-Elsevier (2020) Frederick M. Azar PDFhesniarijs100% (1)
- Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Review: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesRadiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Review: ObjectiveEGNo ratings yet
- Accessory Navicular BoneDocument29 pagesAccessory Navicular BonePhysiotherapist AliNo ratings yet
- MRI of The Foot: Muhammad Ali, MB BS Tim S. Chen, MD John V. Crues, III, MDDocument10 pagesMRI of The Foot: Muhammad Ali, MB BS Tim S. Chen, MD John V. Crues, III, MDOralBoards100% (1)
- Basic Orthopedic HardwareDocument17 pagesBasic Orthopedic HardwareDanica SayasNo ratings yet
- Calcaneal FractureDocument34 pagesCalcaneal Fracturemmm.orthoNo ratings yet
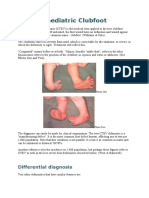
- Paediatric Clubfoot: Differential DiagnosisDocument10 pagesPaediatric Clubfoot: Differential DiagnosisVishwas MohanNo ratings yet
- Immediate download Tachdjian s Pediatric Orthopaedics 5th Edition John Anthony Herring (Ed.) ebooks 2024Document64 pagesImmediate download Tachdjian s Pediatric Orthopaedics 5th Edition John Anthony Herring (Ed.) ebooks 2024sizerigoorah100% (2)