0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 viewsAPHG Chapter 2 Review Powerpoint
1) The document provides an overview of key concepts related to population including population density, distribution, growth, and policies. It defines terms like crude birth rate, death rate, life expectancy, and more.
2) Population distribution is discussed for regions like East Asia, South Asia, Europe, and North America. Most of the world's population increases have occurred since 1900, growing from 1.6 billion to 6.1 billion by 2000.
3) Government policies aim to influence population growth through expansive, restrictive, and eugenic approaches. Thomas Malthus warned of exponential population growth outpacing linear food production.
Uploaded by
Derrick ChungCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 viewsAPHG Chapter 2 Review Powerpoint
1) The document provides an overview of key concepts related to population including population density, distribution, growth, and policies. It defines terms like crude birth rate, death rate, life expectancy, and more.
2) Population distribution is discussed for regions like East Asia, South Asia, Europe, and North America. Most of the world's population increases have occurred since 1900, growing from 1.6 billion to 6.1 billion by 2000.
3) Government policies aim to influence population growth through expansive, restrictive, and eugenic approaches. Thomas Malthus warned of exponential population growth outpacing linear food production.
Uploaded by
Derrick ChungCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 26
Population REVIEW: CHAPTER 2
By: Derri ck &
Zach
Ari thmetic population densi ty i s
a) the number of people per gi ven uni t of l and
b) the number of people per uni t of arabl e l and
c) the number of people i n a gi ven population that has basi c
math ski l ls
d) the number of people i n urban ci ti es
QUIZ!
Of the fol l owing countri es, the l owest crude bi rth rate i s found
i n
a) Japan
b) Australia
c) Russi a
d) Si ngapore
QUIZ!
The fi rst stage of the demographic transi tion model has
a) hi gh CBR and hi gh CDR
b) hi gh CBR and l ow CDR
c) l ow CBR and hi gh CDR
d) l ow CBR and l ow CDR
QUIZ!
Chi l d mortal ity rate i s the number of chi l dren that di e between
the .
a) 1
st
and 3
rd
years of thei r l i ves
b) 1
st
and 5
th
years of thei r l i ves
c) 1
st
and 10
th
years of thei r l i ves
d) 1
st
and 15
th
years of thei r l i ves
QUIZ!
Eugenic popul ation pol i cies i s when the government
a) encourages l arger fami lies by gi ving i ncenti ve to i ncrease
rate of natural i ncrease
b) puts ef fort to reduce rate of natural i ncrease
c) favors one raci al or cul tural sector of a population
d) favors the urban sector of a population
QUIZ!
Population densi ty: A measurement of the number of people
per gi ven uni t of l and
Population density assumes an even distribution of the population
over land
Ari thmetic population densi ty: popul ati on densi ty
No country has an evenly distributed population and the population
density will not always reflect population density accurately
Physiol ogical population densi ty: the number of peopl e per
uni t of arable l and
This form of measurement will not always give accurate population
densities as many countries do not have arable land
To calculate physiologic population density the total population is
divided the amount of arable land
POPULATION DENSITY
Population di stribution: description of l ocati ons on the Earth s
surface where populations l i ve
Often shown through dot maps
Hi stori cally, people l ocated themselves near agri cultural l ands
However, with globalization this pattern is changing
POPULATION DISTRIBUTION
East Asi a
China, Japan, and Korea
Chinas rivers, Yangtze and Yellow rivers, has a large population
along the path of the river
South Asi a
India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka
South Asian population is contained by the Himalayan mountains and
the Indus River Valley
Europe
Ireland, UK, Russia, Germany, Poland, Ukraine, Belgium, France, Italy
Much of the population live in mountainous areas and urban areas
North America
East coast is filled with megalopolises
Megalopolis: when several l arge ci ti es merge together as thei r
borders grow. the resulting super ci ty i s a megal opolis
WORLD POPULATION DISTRIBUTION
Census: a peri odic and of fi ci al count of a country s popul ati on
US census is taken every 10 years
Censuses are i mportant as i t hel ps governments l ayout pl ans
according to the popul ation data
Bei ng undercounted can cause mi srepresentation i n
congressional seats al l otted for each state
The Worl d Bank and Popul ation Reference Bureau gather data
and generate reports of populations around the worl d
CENSUSES
In 1798 Mal thus publ ished an essay cal l ed An essay on the
Principles of Population
He warned the worlds population was growing faster than food
production as population grew exponentially and food grew linearly
Thomas Mal thus argued that because of the natural human
urge to reproduce human popul ati on i ncreases geometri call y
However, food supply, at most, can only increase arithmetically
Today, food production i s grown exponentially wi th modern
agri cultural technol ogy
Neo- Malthusi ans don t agree wi th al l the poi nts wi th Mal thus
but they do bel ieve popul ation i s growing too fast
THOMAS MALTHUS
Between 1900- 2000 the worl d popul ation went from 1. 6
bi l li on to 6.1 bi l l ion people
Total ferti lity rates (TFR): The average number of chi l dren born
to a woman duri ng her chi l dbearing years
To keep a stable population an ideal TFR is 2.1
Agi ng i ndex: the number of peopl e aged 65 years and ol der
per 100 chi l dren aged 0 to 14 years i n a population
In developed countries there are more older than younger and vice
versa for developing countries
Women are del ayi ng or not havi ng chi l dren
Women are choosing to go to school and work and delaying
marriages
Many pl aces i n the worl d are decl ining i n TFR
POPULATION GROWTH
There was a ti me when l ow TFR was desi rable however thi s
created soci al security probl em
Many governments took countermeasures to increase TFR such as
financial incentives to have more children
Despi te l ow TFR the population i s sti l l growing due to
countri es wi th hi gh TFR such as Indi a and Bangl adesh
Doubl ing ti me: the ti me i t takes for a population to doubl e
Doubling times are getting shorter due to exponential population
growth
Population explosion: The rapi d growth of a human population
duri ng the past century
Zero population growth: when there i s no i ncrease i n
population growth
Predicted to happen in the next 50 years
POPULATION GROWTH
Natural i ncrease: the di f ference between the numbers of
bi rths and number of deaths
Crude bi rth rate (CBR): number of l i ve bi rths per 1000 peopl e
Crude death rate (CDR): number of deaths per 1000 peopl e
Demographic transi tion model : a model that shows the
transi tions of hi gh CBR and CDR to l ow CBR and l ow CDR
DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL
Stati onary population l evel s: the l evel at whi ch a nati onal
population ceases to grow
United Nations projected the world would stabilize at 10 billion in
200 years
Agencies reporting SPL have to revise predictions due to changes in
total fertility rate
Many countries that have reported SPL have had to change their
predictions as they have already been surpassed
STATIONARY POPULATION LEVELS
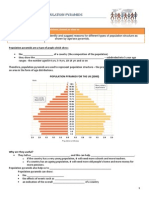
Population composition: structure of a population i n terms of
age, sex and other properti es such as marti al status and
education
Population pyramids: a vi sual representation of the age and
sex composi tion of a popul ation
In poorer countries with high CBR and high CDR the population
pyramid looks like a pyramid
In wealthier countries with low CDR and low CDR the shape looks like
a lopsided vase with the largest section being the middle
POPULATION PYRAMIDS
Infant mortal ity rate: a fi gure that describes the number of
babies that di e wi thin the 1
st
year of thei r l i ves i n a population
The highest rates of IMR is usually located in poorer regions such as
Africa and Asia
Globally, IMR has been declining, even in poverty -stricken regions
In wealthy countries, most IMR is due to premature births and
influences from the mother such as drugs
Chi l d mortal ity rate: a fi gure that describes the number of
chi l dren that di e between the 1
st
and 5
th
years of thei r l i ves i n
a popul ati on
Like IMR, CMR is high in Africa and Asia
Tropical and sub-tropical children usually die due to protein-deficient
called marasmus
MORTALITY RATES
Li fe expectancy: number of years, on average, someone may
expect to remain al i ve
Women general ly outl i ve men
Li fe expectancy has ri sen
2010 Russian males life expectancy was 63 now 2011 is 75
Li fe expectancy does not excl ude any deaths
Life expectancy in Africa is skewed as there is a large number of
children dying from AIDS
LIFE EXPECTANCY
Infectious di seases: di seases carri ed by a host
Malaria and AIDS in Africa is a rising problem
Chroni c/degenerative di seases: di seases that come from
l ongevity of l i fe
EX: Heart disease, cancer, stroke
Geneti c/inherited di seases: di seases that are i n the genetics
and are born wi th
EX: Down syndrome, turner syndrome, hemophilia
Endemic = smal l area Epi demic = l arge area
Pandemic = worl d- wide
DISEASES
Expansive population pol i cy: encourages l arger fami l ies and
rai se the rate of natural i ncrease
Prime Minister of Russia Vladimir Putin offers cash subsidies for 2
nd
or 3
rd
children in order to raise the total fertility rate
Eugenic popul ation pol i cy: favor one raci al or cul tural sector
of a population
Nazi Germany had a eugenic population policy of favoring physical
features
Restri ctive popul ation pol i cy: government pol i cies to reduce
the rate of natural i ncrease
Chinas one child policy is an example of restrictive population policy
by allowing only one child to be born. If the policy is not followed
there will be a fine
POPULATION POLICIES
Whi ch separates the south Asi an population from the rest of
Asi a?
a) the Ganges ri ver and the Hi mal ayan mountains
b) the Yangtze ri ver and the Hi malayan mountains
c) the Ti gris ri ver and Mount Everest
d) the Indus Ri ver Val ley and the Hi malayan mountains
QUIZ!
In North America, where i s most of the population l ocated?
a) west coast
b) sun bel t
c) east coast
d) al ong the US- Canadian border
QUIZ!
Infant mortal ity rates have been
a) decl ining everywhere except poverty - stricken regions
b) decl ining everywhere
c) i ncreasi ng due to a l arge popul ation
d) stable
QUIZ!
Epi demic i s endemic i s and pandemic i s
a) smal l area; l arge area; worl d- wide
b) i n a smal l ci ty; i n a country; worl d- wide
c) i n a l arge area; i n a smal l area; worl d- wide
d) worl d- wide; l arge area; smal l area
QUIZ!
Between the years 1900- 2000 the worl d s population went from
a) 1 bi l l ion to 7 bi l lion
b) 1. 5 bi l lion to 6 bi l l ion
c) 1. 6 bi l l ion to 6 bi l lion
d) 1. 6 bi l lion to 6.1 bi l lion
QUIZ!
You might also like
- Unit 1 Reading Guide Nat Geo Book (Ch. 1 & 2) APHUGNo ratings yetUnit 1 Reading Guide Nat Geo Book (Ch. 1 & 2) APHUG14 pages
- Ap Human Geography 2020 Practice Exam and Notes FRQNo ratings yetAp Human Geography 2020 Practice Exam and Notes FRQ21 pages
- 2018-2019 Ultimate Guide To AP Human Geography100% (1)2018-2019 Ultimate Guide To AP Human Geography14 pages
- Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 : Intro To Geo Pop & Migration Culture Political GeoNo ratings yetUnit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 : Intro To Geo Pop & Migration Culture Political Geo1 page
- AP Human Geography Chapter 1 Basic Concepts NotesNo ratings yetAP Human Geography Chapter 1 Basic Concepts Notes6 pages
- Have A Great Summer! See You in August!: Ms. Gutierrez's AP Human Geography Summer Assignment 2010-2011No ratings yetHave A Great Summer! See You in August!: Ms. Gutierrez's AP Human Geography Summer Assignment 2010-20117 pages
- AP Test Study Guide - AP Human GeographyNo ratings yetAP Test Study Guide - AP Human Geography34 pages
- APHG Unit 1 Review-Nature and Perspectives Multiple Choice PracticeNo ratings yetAPHG Unit 1 Review-Nature and Perspectives Multiple Choice Practice13 pages
- IB Urban Environments Option G (Latest 2024)No ratings yetIB Urban Environments Option G (Latest 2024)154 pages
- AP Human Geography Unit 1 Thinking Geographically100% (1)AP Human Geography Unit 1 Thinking Geographically5 pages
- ESS Grade 11 8.1 Human Population Dynamics Lesson 3No ratings yetESS Grade 11 8.1 Human Population Dynamics Lesson 317 pages
- Ap Human Geography Key Geography Concepts and ModelsNo ratings yetAp Human Geography Key Geography Concepts and Models3 pages
- Population and Settlement Geography UNIT-1No ratings yetPopulation and Settlement Geography UNIT-147 pages
- Ethnic Religions Vs Universalizing ReligionsNo ratings yetEthnic Religions Vs Universalizing Religions3 pages
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Layout and EMI (Electromagnetic I..100% (3)PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Layout and EMI (Electromagnetic I..2 pages
- Class 10 Ut-1 Date Sheet - Ut-1 SyllabusNo ratings yetClass 10 Ut-1 Date Sheet - Ut-1 Syllabus8 pages
- First Quarter LP in English July 30, Filling Out FormsNo ratings yetFirst Quarter LP in English July 30, Filling Out Forms5 pages
- Training Plan - 101769488 - TP - 61084 - V1No ratings yetTraining Plan - 101769488 - TP - 61084 - V14 pages
- CFD Modeling and Approaches For Calculating The Losses of A Subsea Pipeline Transporting HighPressurized FluidNo ratings yetCFD Modeling and Approaches For Calculating The Losses of A Subsea Pipeline Transporting HighPressurized Fluid7 pages
- Sample Weber Health Assessment Nursing 7th100% (1)Sample Weber Health Assessment Nursing 7th30 pages
- PR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 4 - October 4 - 8 2021No ratings yetPR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 4 - October 4 - 8 20214 pages
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 4 Revision Notes100% (1)Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 4 Revision Notes2 pages
- Apollo and Lumina - Crystal Wind™ - ElohimNo ratings yetApollo and Lumina - Crystal Wind™ - Elohim7 pages
- Learning Material 1-21st Century EducationNo ratings yetLearning Material 1-21st Century Education9 pages
- Aristophanes: Clouds, Women at The Thesmophoria, Frogs: A Verse Translation, With Introduction and Notes 1st Edition Stephen Halliwell100% (5)Aristophanes: Clouds, Women at The Thesmophoria, Frogs: A Verse Translation, With Introduction and Notes 1st Edition Stephen Halliwell62 pages
- Java Spring Boot Microservices Example - Step by Step Guide - GeNo ratings yetJava Spring Boot Microservices Example - Step by Step Guide - Ge13 pages
- Cell Line Profile: ECACC Catalogue No. 84113001No ratings yetCell Line Profile: ECACC Catalogue No. 841130012 pages
- Montague Blacksmith Supply 2009 CatalogNo ratings yetMontague Blacksmith Supply 2009 Catalog46 pages
- Health6 - Q4 - ImportanceOfConsumerHealthNo ratings yetHealth6 - Q4 - ImportanceOfConsumerHealth22 pages
- Unit 1 Reading Guide Nat Geo Book (Ch. 1 & 2) APHUGUnit 1 Reading Guide Nat Geo Book (Ch. 1 & 2) APHUG
- Ap Human Geography 2020 Practice Exam and Notes FRQAp Human Geography 2020 Practice Exam and Notes FRQ
- Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 : Intro To Geo Pop & Migration Culture Political GeoUnit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 : Intro To Geo Pop & Migration Culture Political Geo
- Have A Great Summer! See You in August!: Ms. Gutierrez's AP Human Geography Summer Assignment 2010-2011Have A Great Summer! See You in August!: Ms. Gutierrez's AP Human Geography Summer Assignment 2010-2011
- APHG Unit 1 Review-Nature and Perspectives Multiple Choice PracticeAPHG Unit 1 Review-Nature and Perspectives Multiple Choice Practice
- ESS Grade 11 8.1 Human Population Dynamics Lesson 3ESS Grade 11 8.1 Human Population Dynamics Lesson 3
- Ap Human Geography Key Geography Concepts and ModelsAp Human Geography Key Geography Concepts and Models
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Layout and EMI (Electromagnetic I..PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Layout and EMI (Electromagnetic I..
- First Quarter LP in English July 30, Filling Out FormsFirst Quarter LP in English July 30, Filling Out Forms
- CFD Modeling and Approaches For Calculating The Losses of A Subsea Pipeline Transporting HighPressurized FluidCFD Modeling and Approaches For Calculating The Losses of A Subsea Pipeline Transporting HighPressurized Fluid
- Aristophanes: Clouds, Women at The Thesmophoria, Frogs: A Verse Translation, With Introduction and Notes 1st Edition Stephen HalliwellAristophanes: Clouds, Women at The Thesmophoria, Frogs: A Verse Translation, With Introduction and Notes 1st Edition Stephen Halliwell
- Java Spring Boot Microservices Example - Step by Step Guide - GeJava Spring Boot Microservices Example - Step by Step Guide - Ge