100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
794 viewsHuawei ANR Management
Huawei ANR Management
Uploaded by
Talha Yasin1) The document describes ANR (Automatic Neighbor Relation) management in LTE networks. ANR automatically maintains neighbor cell lists to improve handover success rates without manual intervention.
2) ANR can be classified as intra-RAT ANR within the same radio access technology or inter-RAT ANR between different technologies. It manages neighbor lists including the NCL, NRT, temporary NRT, and handover blacklists and whitelists.
3) The process of detecting a missing neighbor cell involves the source cell requesting the UE to measure neighboring cells, the UE reporting any missing cells, and the source cell scheduling periods to retrieve more information about the missing cell from broadcasts to update its neighbor lists
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Huawei ANR Management
Huawei ANR Management
Uploaded by
Talha Yasin100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
794 views9 pages1) The document describes ANR (Automatic Neighbor Relation) management in LTE networks. ANR automatically maintains neighbor cell lists to improve handover success rates without manual intervention.
2) ANR can be classified as intra-RAT ANR within the same radio access technology or inter-RAT ANR between different technologies. It manages neighbor lists including the NCL, NRT, temporary NRT, and handover blacklists and whitelists.
3) The process of detecting a missing neighbor cell involves the source cell requesting the UE to measure neighboring cells, the UE reporting any missing cells, and the source cell scheduling periods to retrieve more information about the missing cell from broadcasts to update its neighbor lists
Original Description:
LTE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
1) The document describes ANR (Automatic Neighbor Relation) management in LTE networks. ANR automatically maintains neighbor cell lists to improve handover success rates without manual intervention.
2) ANR can be classified as intra-RAT ANR within the same radio access technology or inter-RAT ANR between different technologies. It manages neighbor lists including the NCL, NRT, temporary NRT, and handover blacklists and whitelists.
3) The process of detecting a missing neighbor cell involves the source cell requesting the UE to measure neighboring cells, the UE reporting any missing cells, and the source cell scheduling periods to retrieve more information about the missing cell from broadcasts to update its neighbor lists
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
794 views9 pagesHuawei ANR Management
Huawei ANR Management
Uploaded by
Talha Yasin1) The document describes ANR (Automatic Neighbor Relation) management in LTE networks. ANR automatically maintains neighbor cell lists to improve handover success rates without manual intervention.
2) ANR can be classified as intra-RAT ANR within the same radio access technology or inter-RAT ANR between different technologies. It manages neighbor lists including the NCL, NRT, temporary NRT, and handover blacklists and whitelists.
3) The process of detecting a missing neighbor cell involves the source cell requesting the UE to measure neighboring cells, the UE reporting any missing cells, and the source cell scheduling periods to retrieve more information about the missing cell from broadcasts to update its neighbor lists
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd.
www.huawei.com
HUAWEI Confidential
ANR Management
25
th
January, 2012
Objective
The object of below slides is to describe the ANR management for LTE system.
Overview of ANR
ANR is a self-optimization function. It automatically maintains the integrity and
effectiveness of Neighbor Cell Lists (NCLs) to increase handover success rates and
improve network performance. In addition, ANR does not require manual intervention,
which reduces the costs of network planning and optimization.
Concept related to ANR
Classification
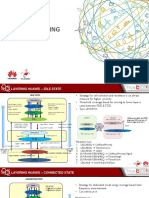
Based on neighbor relations, ANR is classified into intra-RAT ANR and inter-RAT ANR
Neighbor list management
1) NCL Neighbor cell list
2) NRT Neighbor relation table
3) TempNRT Temporary NRT
4) HO Blacklist Handover black list
5) HO Whitelist Handover white list
6) PCI Physical cell ID
7) Abnormal Neighboring Cell Coverage
Neighbor list management
NCL
An NCL contains the information about the neighboring cells of a cell. Each cell has an intra-RAT
NCL and inter-RAT NCLs. An NCL includes the E-UTRAN Cell Global Identifiers (ECGIs), PCIs,
and E-UTRA Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Numbers (EARFCNs) of the neighboring cells.
The eNodeB adds newly detected neighboring cells to the NCL.
NRT
An NRT contains the information about the neighbor relations between a cell and its
neighboring cells. NRTs are classified into intra-RAT NRTs and inter-RAT NRTs. Each cell has an
intra-RAT NRT and inter-RAT NRTs.
TempNRT
A TempNRT is a temporary NRT. It has the same data structure as the NRT. Each cell has an
intra-RAT TempNRT but does not have an inter-RAT TempNRT. After detecting a new intra-RAT
neighbor relation, the eNodeB adds it to the intra-RAT TempNRT. Then, the eNodeB regularly
analyzes the neighbor relation in the TempNRT. If the new neighbor relation is normal, the
eNodeB adds it to the intra-RAT NRT.
Neighbor list management
HO Blacklist
An HO black list contains the information about neighbor relations that cannot be removed
automatically from the NRT by ANR or used for a handover. The neighbor relations in the HO
Black list must meet the following conditions:
NO Remove = TRUE
NO HO = TRUE
HO Whitelist
An HO white list contains the information about neighbor relations that cannot be removed
automatically from the NRT by ANR but can be used for a handover. The neighbor relations in
the HO white list must meet the following conditions:
NO Remove = TRUE
NO HO = FALSE
Neighbor list management
PCI
A PCI is the identifier of a physical cell. A maximum of 504 PCIs are supported, therefore, PCI
collisions occur inevitably.
The PCI of an E-UTRAN cell corresponds to:
The Primary Scrambling Code (PSC) of a UTRAN FDD cell
The cell ID of a UTRAN TDD cell
The Base Station Identity Code (BSIC) of a GERAN cell
The Pseudo Number (PN) offset of a CDMA2000 cell
Abnormal Neighboring Cell Coverage
Abnormal neighboring cell coverage refers to the coverage of a cell that is not adjacent to
the serving cell but can be detected by a UE in the serving cell. The eNodeB regards this cell
as a neighboring cell of the serving cell and therefore attempts to add the neighbor relation
to the NRT. The signals of an abnormal neighboring cell are generally unstable and therefore
the success rate of handovers to this cell is low.
Procedure for detecting a missing neighboring cell
1) The source eNodeB delivers the
measurement configuration to the UE
and requests the UE to measure
neighboring cells that meet the
measurement configuration
2) The UE detects that the PCI of cell B
meets the measurement configuration
and reports it to the source eNodeB.
Then, the source eNodeB checks
whether the NCL of cell A includes the
PCI of cell B. If yes, the procedure ends.
If no, the following steps continue.
3) The source eNodeB instructs the UE, using the newly discovered PCI as a parameter, to read
the ECGI, Tracking Area Code (TAC), and Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) ID list of cell B.
4) The source eNodeB schedules appropriate idle periods to allow the UE to read the ECGI,
TAC, and PLMN ID list of cell B over the broadcast channel (BCH).
5) The UE reports the detected ECGI, TAC, and PLMN ID list of cell B to the source eNodeB.
You might also like
- LTE Mobility Strategy - HUAWEIxxDocument97 pagesLTE Mobility Strategy - HUAWEIxxmanson_dataNo ratings yet
- PDSCH Power Configuration Tool - V1.4Document9 pagesPDSCH Power Configuration Tool - V1.4CesarNo ratings yet
- Description: Huawei 3G To 4G ReselectionDocument2 pagesDescription: Huawei 3G To 4G Reselectioninfo vistaNo ratings yet
- Multi-Carrier Layer Management StrategiesDocument54 pagesMulti-Carrier Layer Management StrategiesHarsh BindalNo ratings yet
- 4G-4G Traffic Sharing For LTC (Low Throughput Cells) Improvement in Huawei LTEDocument3 pages4G-4G Traffic Sharing For LTC (Low Throughput Cells) Improvement in Huawei LTESofian HariantoNo ratings yet
- OPti ParameterDocument7 pagesOPti Parameteranil pathak100% (3)
- LTE Service KPIDocument102 pagesLTE Service KPIManuel_VINo ratings yet
- E-RAB Setup Failure CountersDocument12 pagesE-RAB Setup Failure CountersMehmet Can Kahraman33% (3)
- LTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and OptimizationFrom EverandLTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- BMW 335i Maint KM PDFDocument2 pagesBMW 335i Maint KM PDFTalha YasinNo ratings yet
- Deploying PDSCH Efficiency ImprovementDocument6 pagesDeploying PDSCH Efficiency ImprovementNizami Mammadaliyev100% (1)
- CQI Adjustment Based On BLER TargetDocument14 pagesCQI Adjustment Based On BLER TargetBettahar Mohamed100% (1)
- Huawei Cell Reselection ParametersDocument3 pagesHuawei Cell Reselection ParametersMohammad SelimNo ratings yet
- LTE SINR Principle & OptimizationDocument12 pagesLTE SINR Principle & OptimizationBrahim YEKHLEFNo ratings yet
- LTE Handover OptimizationDocument75 pagesLTE Handover OptimizationCamilo Bazan Heredia100% (3)
- ANR Delete OptimizationDocument6 pagesANR Delete OptimizationNak SandyNo ratings yet
- Congestion Lte CountersDocument38 pagesCongestion Lte CountersMuhammad Rizki0% (1)
- M1 LTE Cluster - 54 - Optimization Plan - 02052012Document49 pagesM1 LTE Cluster - 54 - Optimization Plan - 02052012Opeyemi DadaNo ratings yet
- CountersDocument6 pagesCountersGauravSwamiNo ratings yet
- LTE Breakdown CounterDocument63 pagesLTE Breakdown CounterAnonymous 1KI43V4d0% (1)
- Huawei LTE FormulaDocument10 pagesHuawei LTE Formulanathaniel07No ratings yet
- SJ-20131203170829-006-ZXSDR UniRAN FDD-LTE Base Station (V3.20.30) Radio Parameters Reference - 558739Document341 pagesSJ-20131203170829-006-ZXSDR UniRAN FDD-LTE Base Station (V3.20.30) Radio Parameters Reference - 558739moslem100% (1)
- UMTS Capacity Improvement SolutionDocument64 pagesUMTS Capacity Improvement SolutionSandeepNo ratings yet
- FDD TDD New LayeringDocument8 pagesFDD TDD New LayeringMuhammad Arif Wibowo100% (1)
- SDCCH Drop RateDocument4 pagesSDCCH Drop RateZeeNo ratings yet
- LTE Power ControlDocument34 pagesLTE Power ControlBimal Jhariat100% (2)
- IRAT Improvement HuaweiDocument4 pagesIRAT Improvement HuaweiSudheera Indrajith100% (3)
- Huawei LTE QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesHuawei LTE QuestionnaireJakir HossainNo ratings yet
- Downlink Throughput TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesDownlink Throughput TroubleshootingAbel MumaNo ratings yet
- Cluster Report LTE TSEL CIAMIS 02Document27 pagesCluster Report LTE TSEL CIAMIS 02IyesusgetanewNo ratings yet
- UMTS Multi-Carrier Strategy TrainingDocument25 pagesUMTS Multi-Carrier Strategy TrainingIshanWeera1982No ratings yet
- Huawei Parameter StrategyDocument22 pagesHuawei Parameter StrategyTùng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Kpi Counter and Cause of ProblemDocument17 pagesKpi Counter and Cause of Problemrfabre76100% (1)
- Top Level Optimization Solutions Access Failure & Call Drops UMTSDocument3 pagesTop Level Optimization Solutions Access Failure & Call Drops UMTSSeth Mawuli Dedzoe80% (5)
- FDD Parameter Audit - 20131201Document48 pagesFDD Parameter Audit - 20131201user_AlphaNo ratings yet
- Carrier Balancing Between Multiple Carriers/BI Sectors & DRD Issues IdentificationDocument19 pagesCarrier Balancing Between Multiple Carriers/BI Sectors & DRD Issues IdentificationMd Irfan HussainNo ratings yet
- GUL Interworking Principal & Solution Introduction PDFDocument54 pagesGUL Interworking Principal & Solution Introduction PDFheom123100% (1)
- Lte Drops:: Common Causes For Call DropsDocument6 pagesLte Drops:: Common Causes For Call DropsmohamedNo ratings yet
- Huawei CQI Parameter Improvement TopicDocument6 pagesHuawei CQI Parameter Improvement TopicmohammedNo ratings yet
- Huawei LTE ParametersDocument17 pagesHuawei LTE ParametersPRASHANT DIXIT100% (1)
- India VDF 4G MS Team Optimization Process v1.3Document19 pagesIndia VDF 4G MS Team Optimization Process v1.3Sandeep Singh Mehra100% (1)
- LTE Timing Advance PDFDocument6 pagesLTE Timing Advance PDFdtvt40No ratings yet
- Huawei Sharing Sessionn KPI ImprovementDocument54 pagesHuawei Sharing Sessionn KPI ImprovementmichaelNo ratings yet
- Guide To LTE Neighboring Cell and X2 Interface PlanningDocument132 pagesGuide To LTE Neighboring Cell and X2 Interface PlanningMiguel Diaz100% (2)
- Huawei Inter RAT HO OptimizationDocument23 pagesHuawei Inter RAT HO OptimizationNandhu NadhuNo ratings yet
- LTE Interoperability in Connection Mode (LTE-GU)Document152 pagesLTE Interoperability in Connection Mode (LTE-GU)Believer100% (2)
- LTE Uplink Throughput Problem and SolutionDocument5 pagesLTE Uplink Throughput Problem and SolutionpsquallNo ratings yet
- Huawei - LTE Network Tuning Issue - 1Document28 pagesHuawei - LTE Network Tuning Issue - 1NikNo ratings yet
- High RTWP Problem Troubleshooting and Optimization GuideDocument18 pagesHigh RTWP Problem Troubleshooting and Optimization GuideZouhir El Allaoui50% (2)
- Lte OptimizationDocument323 pagesLte Optimizationkumar100% (2)
- WCL Optimization & ActionsDocument14 pagesWCL Optimization & ActionssumitNo ratings yet
- UMTS Access and Retainability Performance Improvement Solution 01 (20120709)Document14 pagesUMTS Access and Retainability Performance Improvement Solution 01 (20120709)Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Lte Optimization StepDocument5 pagesLte Optimization StepGaurav MishraNo ratings yet
- Carrier Aggregation Trial CaseDocument15 pagesCarrier Aggregation Trial Casebrahiti3No ratings yet
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkFrom EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNo ratings yet
- Radio Network Planning and Optimisation for UMTSFrom EverandRadio Network Planning and Optimisation for UMTSJaana LaihoRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- LTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencyFrom EverandLTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencySeppo HämäläinenNo ratings yet
- Huawei ANR ManagementDocument9 pagesHuawei ANR ManagementmirsNo ratings yet
- Oeo102090 Lte Eran2.1 Anr Feature Issue 1.01Document39 pagesOeo102090 Lte Eran2.1 Anr Feature Issue 1.01Danny Segoro GenieNo ratings yet
- BSC: How To Dimension TRH in A Living BSC ExchangeDocument3 pagesBSC: How To Dimension TRH in A Living BSC Exchangeaamir_moshNo ratings yet
- SQL For MapinfoDocument7 pagesSQL For MapinfoTalha YasinNo ratings yet
- GSM Call Flow DIA (Motorola)Document19 pagesGSM Call Flow DIA (Motorola)Talha YasinNo ratings yet
- HUA 3G Capacity OptimizationDocument39 pagesHUA 3G Capacity Optimizationismail_hw91% (11)
- Hata Model CalculationDocument12 pagesHata Model CalculationTalha YasinNo ratings yet
- Para List For GSMDocument8,537 pagesPara List For GSMahmadtqNo ratings yet
- GSM RF Interview Questions and AnswersDocument21 pagesGSM RF Interview Questions and AnswersWA Khan100% (1)
- Hata Model CalculationDocument12 pagesHata Model CalculationTalha YasinNo ratings yet
- UrlImportTemplate 2 20240623205030Document192 pagesUrlImportTemplate 2 20240623205030ahmad aljarahNo ratings yet
- Dynamic DNSDocument56 pagesDynamic DNSasir gammer mohammad asirNo ratings yet
- Huawei ANR ManagementDocument9 pagesHuawei ANR ManagementTalha Yasin100% (1)
- Picture BibliographyDocument3 pagesPicture Bibliographyapi-201636665No ratings yet
- Blacklist Routes Test CasesDocument4 pagesBlacklist Routes Test CasesDwayneBravoNo ratings yet
- Arthur Miller PresentationDocument9 pagesArthur Miller Presentationapi-266422057No ratings yet
- SPF 2000 Calculation Sheet Rs 50Document8 pagesSPF 2000 Calculation Sheet Rs 50avk197565% (17)
- Andyihsan Lin3-TcrDocument82 pagesAndyihsan Lin3-TcrPurnama LestariNo ratings yet
- Arthur Miller PresentationDocument9 pagesArthur Miller PresentationEneyda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Why Do Blacks Ignore That Black Is A Badge of SlaveryDocument27 pagesWhy Do Blacks Ignore That Black Is A Badge of SlaveryMeru Muad'Dib Massey Bey100% (3)
- CSTP 2Document5 pagesCSTP 2api-622302174No ratings yet