0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
192 viewsGlyoxylate Cycle
Glyoxylate Cycle
Uploaded by
Utkarsh SharmaThe glyoxylate cycle is a metabolic pathway that allows organisms like plants and microbes to convert acetate and fatty acids into carbohydrates. In vertebrates, acetate produced from fatty acids is lost as carbon dioxide during the TCA cycle. But the glyoxylate cycle allows other organisms to bypass these two decarboxylation steps, instead converting acetate into the TCA cycle intermediate succinate and then into carbohydrates through gluconeogenesis. This pathway occurs in specialized organelles called glyoxysomes in plants, which contain enzymes that catalyze both fatty acid breakdown and the glyoxylate cycle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Glyoxylate Cycle
Glyoxylate Cycle
Uploaded by
Utkarsh Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
192 views14 pagesThe glyoxylate cycle is a metabolic pathway that allows organisms like plants and microbes to convert acetate and fatty acids into carbohydrates. In vertebrates, acetate produced from fatty acids is lost as carbon dioxide during the TCA cycle. But the glyoxylate cycle allows other organisms to bypass these two decarboxylation steps, instead converting acetate into the TCA cycle intermediate succinate and then into carbohydrates through gluconeogenesis. This pathway occurs in specialized organelles called glyoxysomes in plants, which contain enzymes that catalyze both fatty acid breakdown and the glyoxylate cycle.
Original Title
Glyoxylate Cycle.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The glyoxylate cycle is a metabolic pathway that allows organisms like plants and microbes to convert acetate and fatty acids into carbohydrates. In vertebrates, acetate produced from fatty acids is lost as carbon dioxide during the TCA cycle. But the glyoxylate cycle allows other organisms to bypass these two decarboxylation steps, instead converting acetate into the TCA cycle intermediate succinate and then into carbohydrates through gluconeogenesis. This pathway occurs in specialized organelles called glyoxysomes in plants, which contain enzymes that catalyze both fatty acid breakdown and the glyoxylate cycle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
192 views14 pagesGlyoxylate Cycle
Glyoxylate Cycle
Uploaded by
Utkarsh SharmaThe glyoxylate cycle is a metabolic pathway that allows organisms like plants and microbes to convert acetate and fatty acids into carbohydrates. In vertebrates, acetate produced from fatty acids is lost as carbon dioxide during the TCA cycle. But the glyoxylate cycle allows other organisms to bypass these two decarboxylation steps, instead converting acetate into the TCA cycle intermediate succinate and then into carbohydrates through gluconeogenesis. This pathway occurs in specialized organelles called glyoxysomes in plants, which contain enzymes that catalyze both fatty acid breakdown and the glyoxylate cycle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Glyoxylate Cycle
Glyoxylate Cycle
• Vertebrates can’t convert fatty acids, or acetate
derived from them, to carbohydrates
• In vertebrates, for every two carbons that enter TCA
as acetyl-CoA, two CO2 leave
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 2
Glyoxylate Cycle
In many organisms other than vertebrates, glyoxylate
cycle serves as a mechanism for converting acetate to
carbohydrates
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 3
Quiz
Glyoxylate cycle helps the conversion of
A. Fats to lipids
B. Fats to Acetyl CoA
C. Acetate to carbs
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 4
Glyoxylate Cycle
In plants, certain invertebrates, and some
microorganisms (E. coli and yeast) acetate can serve
both as
• An energy rich fuel and
• Source for carbohydrate synthesis
In these organisms, glyoxylate cycle catalyzes the net
conversion of acetate to succinate
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 5
Quiz
Glyoxylate cycle usually does not happen in
A. Vertebrates
B. Plants
C. Invertebrates
D. Microbes
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 6
2 Acetyl-CoA + NAD+ + 2H2O
succinate + 2CoA + NADH + H+
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 8
Quiz
Glyoxylate cycle happens in
A. Nucleus
B. Cytosol
C. Glyoxysomes
D. Mitochondria
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 9
Glyoxylate Cycle
In plants, enzymes of glyoxylate cycle are sequestered
in membrane-bounded organelles called glyoxysomes
(specialized peroxisomes)
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 10
Glyoxylate Cycle
• Glyoxysomes are not present in all plant tissues at all
times
• They develop in lipid-rich seeds during germination
• In addition to glyoxylate cycle enzymes, glyoxysomes
contain all the enzymes needed for degradation of
fatty acids
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 11
Glyoxylate Cycle
• Acetyl-CoA formed from fatty acids converted to
succinate
• Succinate exported to mitochondria, TCA enzymes
transform it to malate
• Cytosolic isozyme of MDH oxidizes malate to OAA,
precursor for gluconeogenesis
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 12
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 13
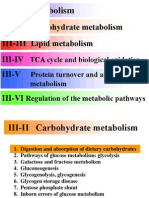
Glyoxylate Cycle
Four distinct pathways participate in these
conversions:
• Fatty acid breakdown to acetyl-CoA (in glyoxysomes)
• GlyoxyIate cycle (in glyoxysomes)
• Citric acid cycle (in mitochondria) and
• Gluconeogenesis (in the cytosol)
10/15/2020 Biochemistry for medics 14
You might also like
- Carbohydrate - Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesCarbohydrate - Lecture NotesKate Taylor100% (1)
- Beta Oxidation of FattyacidDocument26 pagesBeta Oxidation of FattyacidLipsa Rani Panda100% (1)
- Handbook of Industrial Chemistry and Biotechnolog Y: Kent and Riegel'sDocument10 pagesHandbook of Industrial Chemistry and Biotechnolog Y: Kent and Riegel'sJulián MelendrezNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Slide-2 PHARM-D, SALUDocument85 pagesCarbohydrates Slide-2 PHARM-D, SALUShahid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Modulator: Dr. P.B.Desai HOD, Dept of Biochemistry. Presenter: DR Vijayetha S. KagwadDocument68 pagesModulator: Dr. P.B.Desai HOD, Dept of Biochemistry. Presenter: DR Vijayetha S. KagwadvijayethaNo ratings yet
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntDocument18 pagesHexose Monophosphate ShuntAbdul Jabbar Abdul JabbarNo ratings yet
- Reactions of MonosaccharidesDocument15 pagesReactions of Monosaccharidesvishnudurga88% (8)
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument17 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYEthel May Granil100% (1)
- Lec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCDocument12 pagesLec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCJonah Micah MangacoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Lipid Metabolism Iii-IvDocument124 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Lipid Metabolism Iii-Ivomarou18100% (1)
- Lab Manual of BiochemistryDocument19 pagesLab Manual of BiochemistryUsama Javed0% (1)
- 2.metabolism of LipidsDocument159 pages2.metabolism of LipidsChristian Tham100% (1)
- Carbohydrates (CHO)Document190 pagesCarbohydrates (CHO)Mustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates SummaryDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates SummaryHarold NagunaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 140 Unit 8 Lec 1 LipidsDocument93 pagesCHEM 140 Unit 8 Lec 1 LipidsMevil Jane MabrasNo ratings yet
- Glycogenesis & GlycogenolysisDocument68 pagesGlycogenesis & GlycogenolysisAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 4. Chemistry CarbohydratesDocument45 pagesUnit-4 4. Chemistry CarbohydratesKiya Alemu100% (1)
- Cell Biology Lecture NotesDocument52 pagesCell Biology Lecture NotesSheh ZadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument23 pagesChemistry of Lipidsbrian mgabiNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Lipid MembraneDocument50 pagesBiosynthesis of Lipid MembraneJoshua De LeonNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry VivaDocument8 pagesBiochemistry VivaNazia WasimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Lecture Notes: Nucleic Acids: Educational GoalsDocument48 pagesChapter 14 Lecture Notes: Nucleic Acids: Educational GoalsZahid Gul AsceticNo ratings yet
- Subject: Biochemistry Topic:Lipid Metabolism 2 Lecturer: Dr. Laygo DATE: NOV. 2010Document11 pagesSubject: Biochemistry Topic:Lipid Metabolism 2 Lecturer: Dr. Laygo DATE: NOV. 2010Std DlshsiNo ratings yet
- Nuclei C Acids: BSN 1y0-5Document25 pagesNuclei C Acids: BSN 1y0-5joevette_30No ratings yet
- Chapter V: LIPIDSDocument23 pagesChapter V: LIPIDSGwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- HMP-shunt MEDDocument37 pagesHMP-shunt MEDAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Fatty AcidsDocument10 pagesLipids: Fatty AcidsRhealyn IliganNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of DisaccharidesDocument15 pagesMetabolism of DisaccharidesminaNo ratings yet
- BIOC 307 Old Exam 1Document17 pagesBIOC 307 Old Exam 1Katie RoseNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS D PharmDocument65 pagesLIPIDS D PharmMadhuri poulkarNo ratings yet
- MCQ MembranesDocument10 pagesMCQ MembranesMarilyne RizkNo ratings yet
- Starch and Sucrose MetabolismDocument41 pagesStarch and Sucrose MetabolismSanaur Rahman0% (1)
- Biochemistry - Final Exam Biology 020.305 December 15, 2011 Instructions For ExaminationDocument11 pagesBiochemistry - Final Exam Biology 020.305 December 15, 2011 Instructions For ExaminationJenna ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Paul D. Adams - University of ArkansasDocument27 pagesChapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Paul D. Adams - University of ArkansasSheila GarciaNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis Metabolic PathwayDocument36 pagesGluconeogenesis Metabolic PathwayDayledaniel Sorveto0% (1)
- BIOCHEM - 2S05 - Nucleotide MetabolismDocument10 pagesBIOCHEM - 2S05 - Nucleotide MetabolismRonak UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 05 01 Lipid Metabolism I 2012Document125 pages05 01 Lipid Metabolism I 2012anthony.johNo ratings yet
- 3 3 Cell Organelles PPT 1193949429900273 1Document19 pages3 3 Cell Organelles PPT 1193949429900273 1kikkabuttigieg1466100% (1)
- 2.2 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Carbohydrate Chemistry and MetabolismDocument8 pages2.2 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Carbohydrate Chemistry and Metabolismlovelots1234No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates MetabolismDocument33 pagesCarbohydrates MetabolismGungun FalguniNo ratings yet
- Terms For A Medical Student:: 1. GlycolysisDocument24 pagesTerms For A Medical Student:: 1. Glycolysischarmin_limNo ratings yet
- Integration of Metabolism Integration of MetabolismDocument10 pagesIntegration of Metabolism Integration of MetabolismEdison Luciano100% (1)
- Practical BiochemistryDocument35 pagesPractical BiochemistryMockinjay100% (1)
- Glycogenesis: DR Nazakat HussainDocument16 pagesGlycogenesis: DR Nazakat HussainMuhammad Jamal100% (1)
- BIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDDocument73 pagesBIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDJowe Varnal100% (1)
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument10 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwaySania SaeedNo ratings yet
- Photoperiodism in Plants: The Department of Botany Punjab University LahoreDocument12 pagesPhotoperiodism in Plants: The Department of Botany Punjab University LahorewertyuiodfghjklNo ratings yet
- Hydropathic PlotsDocument14 pagesHydropathic PlotsKrithika Balasubramanian100% (2)
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: By:-Dr - Priyanka Sharma 1 Year MDS Dept. of Public Health DentistryDocument93 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: By:-Dr - Priyanka Sharma 1 Year MDS Dept. of Public Health DentistrySimham Venu50% (2)
- Amino SugarsDocument2 pagesAmino SugarsNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Checkpoints PPT by EasybiologyclassDocument22 pagesCell Cycle Checkpoints PPT by EasybiologyclassMaryNo ratings yet
- Neuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesNeuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisPradyut BiswasNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry & Clinical PathologyDocument46 pagesBiochemistry & Clinical PathologyParjinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle RegulationDocument23 pagesCell Cycle RegulationShikhaj ArmaanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.2. GlycoconjugatesDocument4 pagesLesson 4.2. GlycoconjugatesGemma CabañasNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument13 pagesProteinapi-272775120No ratings yet
- BCH 401 - Advanced EnzymologyDocument15 pagesBCH 401 - Advanced EnzymologyOLUWASEGUN K Afolabi100% (2)
- LIPIDS D.PharmDocument60 pagesLIPIDS D.PharmDavid patel100% (6)
- HMPDocument44 pagesHMPraanja2No ratings yet
- Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids: Chapter 8 Lehninger 5 EdDocument17 pagesNucleotides and Nucleic Acids: Chapter 8 Lehninger 5 Edarun231187No ratings yet
- A, B and Z DnaDocument24 pagesA, B and Z DnaUtkarsh Sharma100% (1)
- Fatty Acid OxidationDocument32 pagesFatty Acid OxidationUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument40 pagesElectron Transport ChainUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Classes of Proteins and EnzymesDocument40 pagesClasses of Proteins and EnzymesUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anomers and Ring Form PDFDocument26 pagesAnomers and Ring Form PDFUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Protein Structure PDFDocument50 pagesAmino Acids and Protein Structure PDFUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Death and Have Been Associated With Insulin ResistanceDocument3 pagesDeath and Have Been Associated With Insulin ResistanceJanine ImeeNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesDifferences Between Mitosis and MeiosisNanashiNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets Biotechnology 8 (Q4-Lesson 5 & 6) Application of Biotechnology in Industry and EnvironmentDocument16 pagesLearning Activity Sheets Biotechnology 8 (Q4-Lesson 5 & 6) Application of Biotechnology in Industry and Environmentms. dlcrzNo ratings yet
- 2019-Exosomes, New Biomarkers in Early Cancer DetectionDocument47 pages2019-Exosomes, New Biomarkers in Early Cancer Detectionvivitri.dewiNo ratings yet
- Banasthali Vidyapith: Internal Research SupervisorsDocument10 pagesBanasthali Vidyapith: Internal Research SupervisorsasanyogNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument57 pagesPreviewpdfAISHANo ratings yet
- MethodsDocument20 pagesMethodsRuzdee HarimanNo ratings yet
- A CRISPR Way To Block PERVs - Engineering OrgansDocument3 pagesA CRISPR Way To Block PERVs - Engineering OrgansFrancisco Baca DejoNo ratings yet
- PCR Master Mix ProtocolDocument2 pagesPCR Master Mix ProtocolDo Thi Van AnhNo ratings yet
- RahulDocument3 pagesRahulCOVID-19 ProjectNo ratings yet
- Cover Lab Report Ujian Amali Semester 1 Sesi 2023 2024 PDFDocument4 pagesCover Lab Report Ujian Amali Semester 1 Sesi 2023 2024 PDFaleeyasafiy28No ratings yet
- T3 Rapid Quantitative Test COA - F2311630AADDocument1 pageT3 Rapid Quantitative Test COA - F2311630AADg64bt8rqdwNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1A - Producing GMOsDocument50 pagesLesson 1A - Producing GMOsBeng QuinnNo ratings yet
- Supercoiling of DNADocument40 pagesSupercoiling of DNAstevensb055No ratings yet
- Is Nutri-Epigenetics The Future of Atherosclerosis?: ResultsDocument1 pageIs Nutri-Epigenetics The Future of Atherosclerosis?: ResultsAhmed SalamaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Stem Cell Therapy: An Overview: AKM M Islam, AAS Majumder, F Doza, MM Rahman, H JesminDocument15 pagesCardiac Stem Cell Therapy: An Overview: AKM M Islam, AAS Majumder, F Doza, MM Rahman, H JesminNavojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: Isbn Title Author Year PriceDocument61 pagesAgriculture: Isbn Title Author Year Pricefunmehdi99No ratings yet
- Synthetic Genomics: Building A Better BacteriumDocument3 pagesSynthetic Genomics: Building A Better BacteriumNabilah100% (2)
- Biology 11th 14 - 01 - 2024 - 001525Document9 pagesBiology 11th 14 - 01 - 2024 - 001525zabiu8926No ratings yet
- Assessment of Microbial Community Structure Changes by Amplified Ribosomal DNA Restriction Analysis (ARDRA)Document4 pagesAssessment of Microbial Community Structure Changes by Amplified Ribosomal DNA Restriction Analysis (ARDRA)Aditi Patil100% (1)
- Mahatma Gandhi University, NALGONDA-508 254Document2 pagesMahatma Gandhi University, NALGONDA-508 254Champati SrivarmaNo ratings yet
- Genome Editing-A Review of LiteratureDocument54 pagesGenome Editing-A Review of LiteraturePaulo PeraltaNo ratings yet
- PharmacogeneticsDocument18 pagesPharmacogeneticsHafsah ShoaibNo ratings yet
- How To Use BLASTDocument18 pagesHow To Use BLASTColleen DejanNo ratings yet
- Replication in EukaryotesDocument8 pagesReplication in EukaryotesnaliniNo ratings yet
- DNA: The Genetic MaterialDocument3 pagesDNA: The Genetic MaterialRobert WalusimbiNo ratings yet
- 1st Lec IntroductionDocument11 pages1st Lec IntroductionArslan AliNo ratings yet
- Phet - Activity 1Document4 pagesPhet - Activity 1api-306913723No ratings yet
- Antisence TechnologyDocument4 pagesAntisence TechnologyAlishan BangashNo ratings yet