Iveco 8000 Series Engine: Sec. 10 - Pg. 1/20
Iveco 8000 Series Engine: Sec. 10 - Pg. 1/20
Uploaded by
Daniel SaavedraCopyright:
Available Formats
Iveco 8000 Series Engine: Sec. 10 - Pg. 1/20
Iveco 8000 Series Engine: Sec. 10 - Pg. 1/20
Uploaded by
Daniel SaavedraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Iveco 8000 Series Engine: Sec. 10 - Pg. 1/20
Iveco 8000 Series Engine: Sec. 10 - Pg. 1/20
Uploaded by
Daniel SaavedraCopyright:
Available Formats
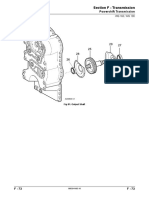
Iveco 8000 Series Engine
Sec. 10 - pg. 1/20
General specifications
TN70VA TN75VA TN95VA
TN60VA
TN70NA TN75NA TN95NA
Type 8035.05C 8035.25R 8035.25 8045.25S
Cylinders (nr.) 3 3 3 4
Sleeve dry dry dry dry
Piston diameter and stroke (mm) 104 x 115 104 x 115 104 x 115 104 x 115
Total displacement (cm³) 2930 2930 2930 3908
Compression ratio 17:1 17:1 16,5:1 16,5:1
Maximum power (KW/HP) 43,5 / 59 53 / 72 55,5 / 76 67,5 / 92
Maximum power speed (rpm) 2300 2300 2300 2300
Maximum torque speed (rpm) 1400 1400 1400 1400
Sec. 10 - pg. 2/20
General specifications
TN70VA TN75VA TN95VA
TN60VA
TN70NA TN75NA TN95NA
Valves clearance (mm) 0,30 ± 0,05 0,30 ± 0,05 0,30 ± 0,05 0,30 ± 0,05
BOSCH - VE3 BOSCH - VE3 BOSCH - VE3 BOSCH - VE4
Injection pump KSB KSB e LDA KSB e LDA KSB e LDA
Pump timing on engine
4° ± 0,5° (1,47 mm) 0° ± 0,5° (1,00 mm) 0° ± 0,5° (1,00 mm) 0° ± 0,5° (1,00 mm)
(plunger timing)
Injection order 1-2-3 1-2-3 1-2-3 1-3-4-2
Nozzles number 6 5 5 6
Injector pressure settings (bar) 260 ÷ 272 260 ÷ 272 260 ÷ 272 260 ÷ 272
Engine lubrification settings (bar) 2,9 ÷ 3,9 >= 2 >= 2 2,9 ÷ 3,9
3 row vertical pipes 3 row vertical pipes 4 row vertical pipes 4 row vertical pipes
Radiator type
with copper fins with copper fins with copper fins with copper fins
Sec. 10 - pg. 3/20
General specifications
TN75FA TN85FA TN95FA
Type 8045.05D 8045.25 8045.25S
Cylinders (nr.) 4 4 4
Sleeve dry dry dry
Piston diameter and stroke (mm) 104 x 115 104 x 115 104 x 115
Total displacement (cm³) 3908 3908 3908
Compression ratio 17:1 16,5:1 16,5:1
Maximum power (KW/HP) 54,5 / 74 61,5 / 84 67,5 / 92
Maximum power speed (rpm) 2300 2300 2300
Maximum torque speed (rpm) 1400 1400 1400
Sec. 10 - pg. 4/20
General specifications
TN75FA TN85FA TN95FA
Valves clearance (mm) 0,30 ± 0,05 0,30 ± 0,05 0,30 ± 0,05
BOSCH - VE4 BOSCH - VE4 BOSCH - VE4
Injection pump KSB KSB e LTC KSB e LDA
Pump timing on engine
4° ± 0,5° (1,47 mm) 1° ± 0,5° (1,12 mm) 0° ± 0,5° (1,00 mm)
(plunger timing)
Injection order 1-3-4-2 1-3-4-2 1-3-4-2
Nozzles number 6 6 6
Injector pressure settings (bar) 260 ÷ 272 260 ÷ 272 260 ÷ 272
Engine lubrification settings (bar) 2,9 ÷ 3,9 2,9 ÷ 3,9 2,9 ÷ 3,9
3 row vertical pipes 3 row vertical pipes 4 row vertical pipes
Radiator type
with copper fins with copper fins with copper fins
Sec. 10 - pg. 5/20
Engine type code
8035 05C XXX
4 25
XXX Bosch pump type
R Reduced
C
5 Bore/stroke 104x115
0 Suction
2 Turbo
5 CNH agricultural version
3 Number of cylinders
4
80 CNH engine with dry liners
Sec. 10 - pg. 6/20
Engine lubrification system (3 cylinders engine)
1 Plug 5 Dipstick
2 Filter by-pass valve 6 Pump
3 Filter 7 Lubrication relief valve
4 Engine oil low pressure switch 8 Screen filter
Sec. 10 - pg. 7/20
Engine lubrification system (4 cylinders engine)
1 Plug 5 Dipstick
2 Filter by-pass valve 6 Pump
3 Filter 7 Lubrication relief valve
4 Engine oil low pressure switch 8 Screen filter
Sec. 10 - pg. 8/20
Engine cooling system (3 cylinders engine)
1 Thermostat
2 Pump
3 Temperature
indicator
4 Temperature
sender
5 Fan
6 Radiator
a Coolant circulation
with thermostat
valve closed
b Coolant circulation
with thermostat
valve open
Sec. 10 - pg. 9/20
Engine cooling system (4 cylinders engine)
1 Thermostat
2 Pump
3 Temperature
indicator
4 Temperature
sender
5 Fan
6 Radiator
a Coolant circulation
with thermostat
valve closed
b Coolant circulation
with thermostat
valve open
Sec. 10 - pg. 10/20
KSB device
Heater Wax element Temperature switch
The KSB device acts to advance the injection of the fuel when beginning operations at low temperatures.
Sec. 10 - pg. 11/20
KSB device
When the wax is cold the piston (6) pulls the rod (5).
1 Lever The pin rotates the roller ring (4) of approx. 2.5°.
2 Spherical rod The pump increases the normal condition advance.
3 Pump housing When the temperature reaches approx. 30°C, the
4 Roller ring temperature stops of feeding the electric resistance
5 Rod
inside the wax thermostat system. The piston (6)
6 Piston
7 Spring doesn’t push anymore the rod (5). The spring (9)
8 Shaft rotates the lever and roller ring (4) goes back to the
9 Torque spring standard advance.
Sec. 10 - pg. 12/20
LDA device
Load-Dependent feed Adjustment
on all turbocharged engines.
Sec. 10 - pg. 13/20
LDA device
1 Membrane
2 Spring
3 Thrust washer
4 Controller pin
5 Conical mounting
6 Feeler pin
7 Stop lever
8 Axis
The LDA device adjusts the fuel throughput independent of the air pressure in the suction manifold. This
air pressure acts upon the membrane (1) which is rigidly connected to the controller pin (4). The lower
part of the controller pin (4) is provided with a conical mounting (5) with a feeler pin (6). By means of the
axial displacement of the controller pin (4) the feeler pin (6) is also displaced and acts upon the stop
lever (7). The stop lever rotates on its own axis (8) and acts upon the controller disk in such a way that
the fuel throughput is adjusted to the air quantity fed into the cylinders.
Sec. 10 - pg. 14/20
Injection pump timing
In order to obtain the proper pump timing,
the KSB device has to be powered at 12V.
Open the flywheel inspection window; turn the crank shaft so the
1st cylinder (fan side) reaches TDC (compression phase).
Sec. 10 - pg. 15/20
Injection pump timing
Unscrew plug (1), insert tool 380000914 (4) and dial gauge 380000228 (3)
pre-loading the rod by approx. 2.5 mm.
Slowly rotate counter-clockwise (fan side) the crank shaft so that the pumping element on the pump is at
BDC, shown by the dial gauge pointer stopping. Zero-set the dial gauge.
Sec. 10 - pg. 16/20
Injection pump timing
Rotate clockwise (fan side) the crank shaft
until the reference index corresponds with the pump advance degrees setting:
Using a dial gauge, check that the pumping element has moved by 1 (or 1.12 or 1.47) mm.
Sec. 10 - pg. 17/20
Injection pump timing
Rotate the pump:
counter-clockwise if travel is less than 1 (or 1.12 or 1.47) mm
clockwise if travel is more than 1 (or 1.12 or 1.47) mm
Lock the pump in position and close.
Sec. 10 - pg. 18/20
Counter-rotating weights
1 Counterweight rotation shafts 4 Counterweight gear
2 Counter-rotating weights 5 Driving gear
3 Idler gear 6 Idler gear
Sec. 10 - pg. 19/20
Counter-rotating weights - Timing
2 Counter-rotating weights
3 Idler gear
4 Counterweight gear
5 Driving gear
6 Idler gear
Reassemble, making the stamped marks coincide
(shown by the arrows).
Insert a pin in the hole (A).
Check that the 1st cylinder is at TDC.
Fit on the counterweights and screw down the bolts on
the crankcase.
Remove the pin from the hole (A).
Sec. 10 - pg. 20/20
You might also like
- Activate Adobe Photoshop CS5 Free Using Serial KeyDocument3 pagesActivate Adobe Photoshop CS5 Free Using Serial KeyLukmanto67% (30)
- D-155 D-179 D-206 D-239 D-246 D-268 D-310 D-358 DT-239 DT-358 DT-402 Engine Basic Engine Service ManualDocument108 pagesD-155 D-179 D-206 D-239 D-246 D-268 D-310 D-358 DT-239 DT-358 DT-402 Engine Basic Engine Service ManualDragos hirnia100% (3)
- Fiat 480 500 540 640 WSMDocument372 pagesFiat 480 500 540 640 WSMPeter TaylorNo ratings yet
- Tumosan Transmission and Gue FromDocument18 pagesTumosan Transmission and Gue FromДенис Сухарев100% (1)
- MF5400 Workshop Manual 03-EngineDocument42 pagesMF5400 Workshop Manual 03-EngineFerran Alfonso100% (4)
- 1091624R2-SM-ENG-IH International Diesel Engine-D-155, D-179, D-206, D-239, D-246, D-268, D-310, D-358, DT-239, DT-358Document108 pages1091624R2-SM-ENG-IH International Diesel Engine-D-155, D-179, D-206, D-239, D-246, D-268, D-310, D-358, DT-239, DT-358VìctorMqz91% (11)
- 334T, M2 NEF (Iveco) Engine F4CE0354A FAM #Document111 pages334T, M2 NEF (Iveco) Engine F4CE0354A FAM #MilAuto87100% (3)
- Silnik FPT F5AEDocument335 pagesSilnik FPT F5AERadek Babuszkiewicz100% (1)
- Ford BSD-444 4.4L 8V L4Document1 pageFord BSD-444 4.4L 8V L4ferran_alfonso33% (3)
- Massey Ferguson MF 174 CDocument133 pagesMassey Ferguson MF 174 Cjose cocoNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual: Shibaura Diesel EngineDocument75 pagesWorkshop Manual: Shibaura Diesel EngineVictor PinedoNo ratings yet
- Fendt 8300 8350Document662 pagesFendt 8300 8350Vladislav Markov РФ,ЗО100% (3)
- Parts Catalogue Farmtrac 9120 DT Iii ADocument306 pagesParts Catalogue Farmtrac 9120 DT Iii ADmytro Pichkur100% (5)
- Massey Ferguson Combine Service Manual MH S mf750 760Document12 pagesMassey Ferguson Combine Service Manual MH S mf750 760Devi RahmadaniNo ratings yet
- Engine F4CE9484 - F4HE9687 NEF Tier 3 AgricultureDocument6 pagesEngine F4CE9484 - F4HE9687 NEF Tier 3 AgricultureLuis Alberto Castillo Nieto50% (4)
- Fiat 55 60 65 70 80 66 DT Rep enDocument118 pagesFiat 55 60 65 70 80 66 DT Rep enSPRAYCROM TRADING100% (3)
- Pages From 9803-4160-17 - JCB 426, 435, 436, 446 Wheeled Loading Shovel Service ManualDocument5 pagesPages From 9803-4160-17 - JCB 426, 435, 436, 446 Wheeled Loading Shovel Service Manualعبدالغني القباطيNo ratings yet
- Training Manual - S8000 Complete (Tier 3) PDFDocument26 pagesTraining Manual - S8000 Complete (Tier 3) PDFJUNA RUSANDI S100% (7)
- Training Manual - S8000 Complete (Tier 3) PDFDocument26 pagesTraining Manual - S8000 Complete (Tier 3) PDFJUNA RUSANDI S100% (1)
- UseMaintanceManual 8000series Industrial L31022018E Jan05 PDFDocument39 pagesUseMaintanceManual 8000series Industrial L31022018E Jan05 PDFUmar Shamsudin100% (1)
- Eng Iveco PDFDocument36 pagesEng Iveco PDFdobas100% (1)
- NH - TM - Pumpa PDFDocument34 pagesNH - TM - Pumpa PDFBoštjan Šumenjak100% (1)
- Catalogo KMP John DeereDocument40 pagesCatalogo KMP John DeereAlexis Sanchez100% (1)
- Solis - 60N 75N 90N PDFDocument255 pagesSolis - 60N 75N 90N PDFkvsj2001No ratings yet
- TT75 T3A Parts CatalogDocument427 pagesTT75 T3A Parts CatalogMizoo Abbas100% (7)
- Skid Loader: Service Parts ManualDocument210 pagesSkid Loader: Service Parts Manualtriand87No ratings yet
- D05223ST - John DeereDocument4 pagesD05223ST - John DeereRamirez MaykolNo ratings yet
- Massey Ferguson MF 4270 TractorDocument60 pagesMassey Ferguson MF 4270 TractorArbanasi Bogdan50% (2)
- Kioti Daedong EX50CH Tractor Parts Catalogue Manual PDFDocument21 pagesKioti Daedong EX50CH Tractor Parts Catalogue Manual PDFfjjsekfkskeme100% (1)
- SoW Gallifrey PDFVerDocument595 pagesSoW Gallifrey PDFVerMysterysoup Productions100% (1)
- Parts Catalog: TT 55 Export Model (4WD)Document292 pagesParts Catalog: TT 55 Export Model (4WD)CENTURYBROTHER100% (2)
- 1104C 44taDocument8 pages1104C 44taWilmerNo ratings yet
- s8000 Engine SPC For Tb80 Models - DomesticDocument105 pagess8000 Engine SPC For Tb80 Models - DomesticNick100% (4)
- MF 200-Series Workshop Sec WatDocument0 pagesMF 200-Series Workshop Sec WatSelmirije2No ratings yet
- 24 Ford (New Holland) EEDocument223 pages24 Ford (New Holland) EEDanny Dan100% (3)
- Fiat NewHolland Catalogue 2013Document511 pagesFiat NewHolland Catalogue 2013Robert Ortega100% (3)
- Cloche TT490Document3 pagesCloche TT490winston sandoval100% (1)
- Perkins 1004-42Document2 pagesPerkins 1004-42Kft. Progép-TechnikaNo ratings yet
- 320-40009 Turbo 99HPDocument177 pages320-40009 Turbo 99HPIsa Yılmaz100% (2)
- Test Plan: 9320A210: Pump SpecificationDocument7 pagesTest Plan: 9320A210: Pump SpecificationBaytolgaNo ratings yet
- NH TD5.110 Catalog PDFDocument739 pagesNH TD5.110 Catalog PDFJohn Mendoza Pacheco100% (3)
- New Holland 8240Document78 pagesNew Holland 8240Zsombor GyergyaiNo ratings yet
- Ring Piston C6.4Document3 pagesRing Piston C6.4JebrodNo ratings yet
- Case 580 SleDocument4 pagesCase 580 SleDan Florin Lazăr75% (4)
- Diesel e in Spritz UngDocument82 pagesDiesel e in Spritz Ungrectificacionesvera100% (1)
- D41E, P-6 - Operation and MaintenanceDocument229 pagesD41E, P-6 - Operation and MaintenanceJEFERSON100% (1)
- 28 Renault DMA EEDocument128 pages28 Renault DMA EEtestas ciaNo ratings yet
- McCormick Cx75 Cx85 Cx95 Cx105 Service ManualDocument76 pagesMcCormick Cx75 Cx85 Cx95 Cx105 Service ManualMarek KłosNo ratings yet
- Zuidberg Pricelist 07062012Document147 pagesZuidberg Pricelist 07062012emmanolan100% (1)
- DIESEL ENGINES D-245S3A М, D-245.2S3A М, D-245.5 S3A М, D-245.43 S3A М PDFDocument89 pagesDIESEL ENGINES D-245S3A М, D-245.2S3A М, D-245.5 S3A М, D-245.43 S3A М PDFSecret64No ratings yet
- Catalogo PDF Tt55-Tt75Document424 pagesCatalogo PDF Tt55-Tt75joao11875% (4)
- TP07 - Brakes - Kocnice PDFDocument76 pagesTP07 - Brakes - Kocnice PDFSead KurtovićNo ratings yet
- Agco Sisu 420DS 4.4L 8V Ohv L4Document2 pagesAgco Sisu 420DS 4.4L 8V Ohv L4ferran_alfonso0% (1)
- Catalogo Motor KubotaDocument16 pagesCatalogo Motor KubotaLilly Novillo100% (1)
- Bar TablosuDocument34 pagesBar TablosuMükremin Songür100% (2)
- EPC FAULT CODES - EPC ERROR CODES - All Tractor ManualsDocument11 pagesEPC FAULT CODES - EPC ERROR CODES - All Tractor ManualsJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Specifications: Sec. 10.1 - Pg. 1/19Document19 pagesSpecifications: Sec. 10.1 - Pg. 1/19Petre LacatusuNo ratings yet
- Omc Cobra 86 93 Quick References DataDocument6 pagesOmc Cobra 86 93 Quick References DataJean-Baptiste Montfort100% (1)
- Force Feed Lubricator SystemDocument34 pagesForce Feed Lubricator SystemMOHANNo ratings yet
- Diesel Generator Technical DataDocument13 pagesDiesel Generator Technical DataRS Rajib sarkerNo ratings yet
- How To Build & Power Tune Weber & Dellorto DCOE, DCO/SP & DHLA Carburettors 3rd EditionFrom EverandHow To Build & Power Tune Weber & Dellorto DCOE, DCO/SP & DHLA Carburettors 3rd EditionNo ratings yet
- Control of Temperature and Aluminum Fluoride ConcentrationDocument6 pagesControl of Temperature and Aluminum Fluoride ConcentrationVibhav UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- IEED MCQs For MechanicalDocument8 pagesIEED MCQs For MechanicalZakyNo ratings yet
- EDFADocument2 pagesEDFATuấn Tươi TỉnhNo ratings yet
- Procuct Brochure PDFDocument11 pagesProcuct Brochure PDFspiritualbeing67% (3)
- Why Creativity and Innovation Is Important To MalaysiaDocument14 pagesWhy Creativity and Innovation Is Important To MalaysiaDr Bugs Tan100% (1)
- Microsoft Corp. v. AT & T CORP., 550 U.S. 437 (2007)Document30 pagesMicrosoft Corp. v. AT & T CORP., 550 U.S. 437 (2007)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Read The 2024 Republican Party PlatformDocument16 pagesRead The 2024 Republican Party PlatformOnPointRadio100% (1)
- Introduction To Business Nature & Scope of Business OrganizationsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Business Nature & Scope of Business OrganizationsRizwan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Great Expectations by Charles DickensDocument312 pagesGreat Expectations by Charles DickensBooks100% (9)
- RFUTicket Application Form 300509Document1 pageRFUTicket Application Form 300509Christ's SchoolNo ratings yet
- Removing Air Pollution With Nanogenerator-Enhanced Air FiltersDocument42 pagesRemoving Air Pollution With Nanogenerator-Enhanced Air Filtersraquel mallannnaoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet.: 1. Choose The Correct Answers To Complete The SentencesDocument2 pagesWorksheet.: 1. Choose The Correct Answers To Complete The SentencesJorge FroylanNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Document8 pagesHydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Gagay Villamor CañeteNo ratings yet
- Fanuc FA System For PC OperatorDocument381 pagesFanuc FA System For PC OperatorsunhuynhNo ratings yet
- Development of Bangla Spell and Grammar Checkers - Resource Creation and EvaluationDocument19 pagesDevelopment of Bangla Spell and Grammar Checkers - Resource Creation and Evaluationredwan.ahmed.khan.2023No ratings yet
- Monoclonal AntibodiesDocument14 pagesMonoclonal AntibodiesBrigitte ReyesNo ratings yet
- PVC Gravity Sewer PipeDocument1 pagePVC Gravity Sewer PipeDGWNo ratings yet
- Small 3Document24 pagesSmall 3Meetoo VikashNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment Receipt: GERZON B. BALAZO and Resident of Roxas ST., Corner San JoseDocument2 pagesAcknowledgment Receipt: GERZON B. BALAZO and Resident of Roxas ST., Corner San JoseGracelle Mae Oraller0% (1)
- Instalacion Transformadores de Corriente Externos PDFDocument8 pagesInstalacion Transformadores de Corriente Externos PDFVictor CisternaNo ratings yet
- Chromium Compounds: Historical. Chrome Iron Ore (Chromite) WasDocument15 pagesChromium Compounds: Historical. Chrome Iron Ore (Chromite) WasYusufNo ratings yet
- 2.30 - Arjun Batra - Indonesia Maritime Expo 06092013Document9 pages2.30 - Arjun Batra - Indonesia Maritime Expo 06092013poetoetNo ratings yet
- What Is Electrical Bus-Bar? - Definition & Types of Electrical Bus Bar - Circuit GlobeDocument9 pagesWhat Is Electrical Bus-Bar? - Definition & Types of Electrical Bus Bar - Circuit GlobeRazu AhmmedNo ratings yet
- BS en 10025 6 2004Document28 pagesBS en 10025 6 2004goalorchNo ratings yet
- A-Holistic-Assessment-of-Education-City-in-Doha - The-Borderless-Knowledge-HubDocument22 pagesA-Holistic-Assessment-of-Education-City-in-Doha - The-Borderless-Knowledge-HubAbdesslam FalsyNo ratings yet
- RAHULDocument24 pagesRAHULwadhwacommunisation0001No ratings yet
- Overview of Phil AgriDocument10 pagesOverview of Phil AgriJenny Lumain100% (3)