0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
135 viewsGen Bio 1 Cell Modification
Gen Bio 1 Cell Modification
Uploaded by
izy nicole bugalCell modifications are specialized cell structures that help cells perform various functions. There are three main types: apical modifications on the cell's top surface for functions like secretion and absorption; basal modifications on the bottom for attachment; and lateral modifications on the sides for connectivity between cells. Some key examples are cilia, flagella, villi, microvilli, desmosomes, tight junctions and adherens junctions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Gen Bio 1 Cell Modification
Gen Bio 1 Cell Modification
Uploaded by
izy nicole bugal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
135 views35 pagesCell modifications are specialized cell structures that help cells perform various functions. There are three main types: apical modifications on the cell's top surface for functions like secretion and absorption; basal modifications on the bottom for attachment; and lateral modifications on the sides for connectivity between cells. Some key examples are cilia, flagella, villi, microvilli, desmosomes, tight junctions and adherens junctions.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Cell modifications are specialized cell structures that help cells perform various functions. There are three main types: apical modifications on the cell's top surface for functions like secretion and absorption; basal modifications on the bottom for attachment; and lateral modifications on the sides for connectivity between cells. Some key examples are cilia, flagella, villi, microvilli, desmosomes, tight junctions and adherens junctions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
135 views35 pagesGen Bio 1 Cell Modification
Gen Bio 1 Cell Modification
Uploaded by
izy nicole bugalCell modifications are specialized cell structures that help cells perform various functions. There are three main types: apical modifications on the cell's top surface for functions like secretion and absorption; basal modifications on the bottom for attachment; and lateral modifications on the sides for connectivity between cells. Some key examples are cilia, flagella, villi, microvilli, desmosomes, tight junctions and adherens junctions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 35
CELL MODIFICATION
Cell modifications are specialized cell structures
or modifications re-acquired by the cell after cell
division that helps the cell in different ways. The
three types of cell modifications are apical, basal
and lateral cell modifications.
A. Apical Modification
Cell modification found on the apical surface of the cell.
It is specialized to carry out functions that occur at these
interfaces(interact), including secretion, absorption,
and movement of luminal contents. Examples are the
following;
Cilia are projections, usually
short, hairlike structures
and a type of organelle seen
on the apical surface of
epithelial cells. This assists in
the movement of material over
the epithelial surface in a
manner parallel with the
surface of the epithelium.
Flagella are long, whip-like
structure that are formed by
microtubules protruding from
the cell body of bacteria and
some eukaryotic cells. The
primary function of a flagellum
is that of
locomotion(movement), but it
also functions as sensory
organelle.
Villi are finger-like
projections that arise
from the epithelial layer
in some organs. They
help to increase surface
area, allowing faster
and more efficient
absorption.
Microvilli are smaller projections than villi
which functions primarily on the efficient
absorption of molecules. Microvilli are present
on the apical aspect of the columnar epithelium
of the duodenum .
PLANT CELL MODIFICATION:
Root hairs
These are cylindrical
extensions of root epidermal
cells that are important for
absorption of nutrients.
Pseudopods – Temporary, irregular lobes formed
by amoebas and some other eukaryotic cells. It
bulges outward to move the cell or engulf the
prey. It primarily consist of actin filaments and
may also contain microtubules and intermediate
filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and
ingestion
Extra Cellular Matrix (ECM) –
They act as barriers that
regulate the movement of
water and solutes between
epithelial layers wall is the
extracellular structure in plant
cells that distinguishes them
from animal cells. The plant cell
wall is made up of molecules
secreted by the cell called
cellulose, a polysaccharide
compose of glucose units.
B. Basal Modification – Cell modification
found on the basal surface of the cell
basement membrane.
Desmosomes/ Hemidesmosomes – These allow for
strong attachment between cells or to a basement
membrane. Desmosomes attach to the microfilaments of
cytoskeleton made up of keratin protein.
Hemidesmosomes are similar to desmosomes in terms of
function, however, they attach the epithelial cell to the
basement membrane rather than the adjacent cell.
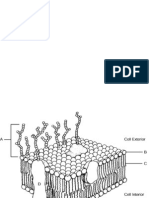
C. Lateral Modification
Cell modification found on the basal surface of the
cell.These are tight junctions, adhering junctions
and gap junctions. These structures consist of protein
complexes and induce connectivity between adjacent
epithelial cells, between cell and ECM. They can
contribute to the barrier function of epithelia and
control the paracellular transport.
Adherens Junctions –
Protein complexes that
occur in cell to cell
junctions in epithelial and
endothelial tissues (help
hold animal cells
together), usually more
basal than tight junctions.
Gap Junctions- It is also known
as communicating
junctions(small tunnels). These
are especialized intercellular
connections between multitude of
animal cell-types. They directly
connect the cytoplasm of two
cells, which allows various
molecules, ions and electrical
impulses to directly pass
through a regulated gate
between cells
Tight Junctions – They
are transmembrane
proteins fused on
outer plasma
membrane . They act
as barriers that
regulate the movement
of water and solutes
between epithelial
layers
1. These are projections, usually
short, hair like structures and a
type of organelle seen on the
apical surface of epithelial cells.
2. What are finger-like
projections that arise from the
epithelial layer in some
organs?
3.These are long, whip-like
structure that are formed by
microtubules protruding from the
cell body of bacteria and some
eukaryotic cells.
4. These are cylindrical extensions of
root epidermal cells that are important
for absorption of nutrients.
5. These are smaller projections than
villi which functions primarily on the
efficient absorption of molecules.
6. It is also known as
communicating
junctions(small tunnels).
7. They act as barriers that
regulate the movement of
water and solutes between
epithelial layers
8. Temporary, irregular lobes
formed by amoebas and some
other eukaryotic cells.
9. These allow for strong
attachment between cells or
to a basement
10. Protein complexes that
occur in cell to cell junctions in
epithelial and endothelial
tissues
Activity: Sing and rhyme!
-8 members / Group
-choose one from the five cell
modifications which are the cilia,
flagella, villi, microvilli, roothair
-use the cell modifications on your
chosen song
You have 5 minutes to prepare
Each group will be graded by the leaders of
the other groups(use ¼ sheet of paper)
Each group will have 1-2 minutes to
perform
Criteria
5 points - choice of song
5 points - correct rhyme
5 points – correct tune/clarity of the
song
5 points – originality
5 points -performance
THANK YOU!
1. Cilia
2. Villi
3. Flagella
4. Roothair
5. Microvilli
6. Gap junctions
7. Tight junctions
8. Pseudopods
9. Desmosomes/hemidesmosomes
10. Adherens junctions
You might also like
- Introduction To Life ScienceDocument53 pagesIntroduction To Life Sciencerufino delacruzNo ratings yet
- Gen. Bio 2 Enrichment ActivitiesDocument3 pagesGen. Bio 2 Enrichment Activitiesjulzhaide100% (1)
- Cell ModificationDocument28 pagesCell ModificationIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.No ratings yet
- Cell ModificationsDocument35 pagesCell ModificationsIvan Galleto100% (1)
- Cell ModificationDocument2 pagesCell ModificationArwen GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cell ModificationsDocument38 pagesCell ModificationsMarlennete Urbano Ligas100% (1)
- Biology Module 1Document15 pagesBiology Module 1Joemmel MagnayeNo ratings yet
- STEM Gen Bio 1 Q1 M3Document14 pagesSTEM Gen Bio 1 Q1 M3Roland Agra100% (1)
- Gen Bio 1 Lesson 4Document2 pagesGen Bio 1 Lesson 4Ric Santos100% (1)
- My Daily Lesson Plan: STEM - BIO11/12-Ig-h-13Document5 pagesMy Daily Lesson Plan: STEM - BIO11/12-Ig-h-13Romel Christian Zamoranos MianoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 1: Energy TransformationDocument37 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 1: Energy TransformationNikki AlquinoNo ratings yet
- General Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GJackylyn Evangelista100% (2)
- Gen Bio 1 - PretestDocument3 pagesGen Bio 1 - PretestApz venturaNo ratings yet
- Concept of LifeDocument28 pagesConcept of LifeJesh RishNo ratings yet
- Q3 Week 2 Stem G11 General Biology Las W2Document15 pagesQ3 Week 2 Stem G11 General Biology Las W2John Erniest Tabungar AustriaNo ratings yet
- LP1 The Cell TheoryDocument3 pagesLP1 The Cell TheoryPaulus VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Prepared By: Pamela May L. Raposa RN, LPTDocument21 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prepared By: Pamela May L. Raposa RN, LPTJean Raziel Mantes100% (1)
- Genbio1q1 Module 12 Transport Mechanisms in CellDocument24 pagesGenbio1q1 Module 12 Transport Mechanisms in CelljoveljanerNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in General Biology 1Document1 pageActivity Sheet in General Biology 1Janin CodillaNo ratings yet
- General Biology q1 w2 Mod2Document40 pagesGeneral Biology q1 w2 Mod2Karen Mae Castillo100% (1)
- Sample DLL For SHSDocument5 pagesSample DLL For SHSBonsai Cabana BasilanNo ratings yet
- Cell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationDocument1 pageCell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationJohn Barry Ibanez80% (15)
- DLL Bio LatestDocument4 pagesDLL Bio LatestGlenda AstodilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Cell TheoryDocument26 pagesLesson 1 - Cell TheoryJoy's Faith Marata100% (3)
- General Biology 1 Stem 12: Test L. Multiple Choice. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Stem 12: Test L. Multiple Choice. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerJohnson FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9.2 Biological DiversityDocument25 pagesLesson 9.2 Biological DiversityJohn Cesar CastilloNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: The CellsDocument71 pagesGeneral Biology 1: The CellsPaula Marie Llido100% (3)
- Subject Orientation Grade 11 Gen Bio UpdatedDocument2 pagesSubject Orientation Grade 11 Gen Bio UpdatedArlance Sandra Marie Medina100% (1)
- Bio 2Document49 pagesBio 2Rey EncisoNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 3rd Quarter Biology PDFDocument20 pagesGrade 11 3rd Quarter Biology PDFjosephNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Module 4Document13 pagesGen Bio 1 Module 4Ante,Glainry Rose Basan100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Cell Cycle: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument34 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Cell Cycle: Mitosis and MeiosisnanaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 5 & 6, GenBio1, PDFDocument8 pagesActivity Sheet 5 & 6, GenBio1, PDFMarlou GayaneloNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam in General Biology 1Document1 pagePrelim Exam in General Biology 1JaneRobledoNo ratings yet
- Modifications To Mendel's Classic Ratio. GenBio 2Document20 pagesModifications To Mendel's Classic Ratio. GenBio 2Hannah Charis L. BarabatNo ratings yet
- Descent With ModificationDocument40 pagesDescent With ModificationNanami MumuzunoNo ratings yet
- Biology1 Final Teaching GuideDocument196 pagesBiology1 Final Teaching GuideGissele AbolucionNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 - Module 7-MitosisandmeiosisDocument32 pagesGeneral Biology 1 - Module 7-Mitosisandmeiosisエアーア ラシブ100% (1)
- General Biology 2Document33 pagesGeneral Biology 2Treshia Jazmin EguinNo ratings yet
- GenBio 1 Lesson 1 ATP and ADP CycleDocument2 pagesGenBio 1 Lesson 1 ATP and ADP CycleLlaban MunicaNo ratings yet
- Module General Biology 1 Week 2 SHS 2Document35 pagesModule General Biology 1 Week 2 SHS 2yeon gyuuNo ratings yet
- 5.transport MechanismDocument10 pages5.transport Mechanismdiane recintoNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 11 3rd Quarter DLLDocument21 pagesBiology Grade 11 3rd Quarter DLLkyru Schatten100% (2)
- General Biology 2Document35 pagesGeneral Biology 2Claries Cuenca100% (1)
- Quipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellDocument17 pagesQuipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellPhil Christian MerinoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Module 1Document30 pagesGen Bio 1 Module 1Louise Gabriel Lozada100% (2)
- Learning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - Lessons 3 and 4) The Organ Systems of Plants and AnimalsDocument12 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - Lessons 3 and 4) The Organ Systems of Plants and AnimalsJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- DLL Shs Stem Grade 12general Biology1 Quarter1 Week1 Palawan Division 1 PDF FreeDocument13 pagesDLL Shs Stem Grade 12general Biology1 Quarter1 Week1 Palawan Division 1 PDF FreeJinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Feedback MechanismDocument36 pagesHomeostasis Feedback MechanismJessmay OlivarNo ratings yet
- Unit 15 Introduction To Life Science Grade 11 WorksheetDocument1 pageUnit 15 Introduction To Life Science Grade 11 Worksheetwiz wiz100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Cell Theory Gen. Bio 1Document27 pagesLesson 1 Cell Theory Gen. Bio 1Trisha Anthony Cortaz100% (1)
- Gen Bio 1 Le Week 4 - Quarter 2Document8 pagesGen Bio 1 Le Week 4 - Quarter 2Cassy Joy RellamaNo ratings yet
- ATP-ADP CycleDocument15 pagesATP-ADP CycleMay PaviaNo ratings yet
- Shs Stem - Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 14Document21 pagesShs Stem - Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 14Grace Relloso100% (1)
- Module I - GeneticsDocument20 pagesModule I - GeneticsJhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsEarl Caesar Quiba Pagunsan100% (2)
- Bio1 Q2 M5 RevisedDocument13 pagesBio1 Q2 M5 RevisedgrizNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module 5Document21 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 5Vienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- Cell ModificationsDocument35 pagesCell ModificationsJames Paul VelascoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Cell ModificationsDocument21 pagesModule 5 Cell ModificationsnodzzkarbNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanisms M9 10Document26 pagesTransport Mechanisms M9 10izy nicole bugalNo ratings yet
- Peter and WendyDocument331 pagesPeter and Wendyizy nicole bugalNo ratings yet
- Distance Education During The COVID 19 PDocument8 pagesDistance Education During The COVID 19 Pizy nicole bugalNo ratings yet
- Article Text 506345 1 10 20201214Document7 pagesArticle Text 506345 1 10 20201214izy nicole bugalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Scientific InquiryDocument19 pagesLesson 1 Scientific Inquiryizy nicole bugalNo ratings yet
- Antigen-Stimulated PBMC Transcriptional Protective Signatures For Malaria ImmunizationDocument18 pagesAntigen-Stimulated PBMC Transcriptional Protective Signatures For Malaria Immunizationyowan wandikboNo ratings yet
- 9 Bio Mcqs Full BookDocument5 pages9 Bio Mcqs Full BookShahzad Meo MeoNo ratings yet
- DR Fatima Abid Assistant Professor Physiology DepartmentDocument49 pagesDR Fatima Abid Assistant Professor Physiology Departmentwarda farooqNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Cycle TransitionsDocument8 pagesPlant Cell Cycle TransitionsakNo ratings yet
- UST-FMS Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Nutrition Academic Year 2019-2020 Problem Set For Case Discussion (Students ' Guide)Document2 pagesUST-FMS Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Nutrition Academic Year 2019-2020 Problem Set For Case Discussion (Students ' Guide)Gail HamtigNo ratings yet
- Generation of Antibody DiversityDocument12 pagesGeneration of Antibody DiversityAltaf khan100% (1)
- MB ReviewerDocument77 pagesMB ReviewerJohn Rey DecanoNo ratings yet
- Aqa Unit 1 June 2002 MsDocument6 pagesAqa Unit 1 June 2002 MsYanahan ParamalingamNo ratings yet
- Sandip BambhaniyaDocument13 pagesSandip BambhaniyaAnyone Can CookNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells LessonDocument4 pagesStem Cells Lessonapi-372328325No ratings yet
- Food Microbiology and Food Safety: Series EditorDocument588 pagesFood Microbiology and Food Safety: Series EditorAlejandra LópezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Chapter 3Document82 pagesAnatomy Chapter 3Jess WhiteNo ratings yet
- Book - MicrobiologyDocument2,119 pagesBook - Microbiologyfusheng zhangNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Reinforcement: Key ConceptDocument1 page8.3 Reinforcement: Key Concepthanooaa2008No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Chaper12Document24 pagesCell Cycle, Mitosis, Chaper12prehealthhelp43% (7)
- Blood and Body FluidsDocument24 pagesBlood and Body FluidsQasim NaeemNo ratings yet
- 2.5 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument7 pages2.5 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylationlovelots1234100% (2)
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Bio Lab-131 Session-Fall 2021 Section-001Document27 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Bio Lab-131 Session-Fall 2021 Section-001Satya NadellaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of AntimicrobialsDocument15 pagesMechanism of AntimicrobialsHassan.shehri100% (6)
- Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Synaptophysin: Novocastra LiquidDocument2 pagesMouse Monoclonal Antibody Synaptophysin: Novocastra LiquidNST MtzNo ratings yet
- Biology 3 Tuto 1Document43 pagesBiology 3 Tuto 1Firdaus ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Mags Matatag Lesson Plan C o DivisionDocument12 pagesMags Matatag Lesson Plan C o DivisionJerum PalahangNo ratings yet
- Bio Inorganic ChemistryDocument106 pagesBio Inorganic ChemistryUmendra Kumar KhokharNo ratings yet
- Practice Test - Chapter 11 - Urry Et Al., Campbell Biology, 11-EDocument22 pagesPractice Test - Chapter 11 - Urry Et Al., Campbell Biology, 11-E113110106No ratings yet
- Topic:: Igcse / O'Level Biology TopicDocument19 pagesTopic:: Igcse / O'Level Biology TopicCollins JimNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PDFDocument15 pagesCellular Respiration PDFJovicaNo ratings yet
- Chan Et Al 2015 (Biocontainment 01)Document7 pagesChan Et Al 2015 (Biocontainment 01)Felix Moronta BarriosNo ratings yet
- Intro To Biology: Cell TheoryDocument2 pagesIntro To Biology: Cell TheoryMarcos Palaca Jr.No ratings yet
- PrionDocument22 pagesPrionAnushkaNo ratings yet
- Biology Review Game - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesBiology Review Game - Print - QuizizzrubelliteNo ratings yet