0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsModule 2
Module 2
Uploaded by
Josh LaxaThe document discusses the functions, skills, and roles of a manager. It defines a manager as someone who directs others and carries out management processes like planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources. Managers exist at different levels depending on the organization size. The key skills of a manager are technical skills, human skills, and conceptual skills. Managers fulfill important interpersonal roles like figurehead, leader, and liaison. They also serve informational roles as a monitor, disseminator, and spokesperson. Finally, managers take on decisional roles as an entrepreneur, disturbance handler, and resource allocator.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Module 2
Module 2
Uploaded by
Josh Laxa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views14 pagesThe document discusses the functions, skills, and roles of a manager. It defines a manager as someone who directs others and carries out management processes like planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources. Managers exist at different levels depending on the organization size. The key skills of a manager are technical skills, human skills, and conceptual skills. Managers fulfill important interpersonal roles like figurehead, leader, and liaison. They also serve informational roles as a monitor, disseminator, and spokesperson. Finally, managers take on decisional roles as an entrepreneur, disturbance handler, and resource allocator.
Original Title
Module-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document discusses the functions, skills, and roles of a manager. It defines a manager as someone who directs others and carries out management processes like planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources. Managers exist at different levels depending on the organization size. The key skills of a manager are technical skills, human skills, and conceptual skills. Managers fulfill important interpersonal roles like figurehead, leader, and liaison. They also serve informational roles as a monitor, disseminator, and spokesperson. Finally, managers take on decisional roles as an entrepreneur, disturbance handler, and resource allocator.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views14 pagesModule 2
Module 2
Uploaded by
Josh LaxaThe document discusses the functions, skills, and roles of a manager. It defines a manager as someone who directs others and carries out management processes like planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources. Managers exist at different levels depending on the organization size. The key skills of a manager are technical skills, human skills, and conceptual skills. Managers fulfill important interpersonal roles like figurehead, leader, and liaison. They also serve informational roles as a monitor, disseminator, and spokesperson. Finally, managers take on decisional roles as an entrepreneur, disturbance handler, and resource allocator.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
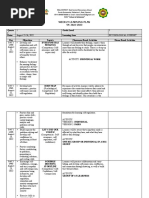
Module 2
MANAGER – Its Functions, Skills and Roles
Objectives: At the end of this lesson, you will
be able to:
• Explain the functions, roles and skills of a
manager.
Definition of Manager
and Its Levels
Manager
A manager is a person in the organization who directs the activities
of others (Venkatesh, 2020). A manager is someone whose primary
responsibility is to carry out the management process. In particular,
a manager is someone who plans and makes decisions, organizes,
leads, and controls human, financial, physical, and information
resources.
Levels of Managers
(by size of organization)
Skills of a Manager
Technical Skills
It is the ability to use special proficiency or expertise in performing
specific tasks. They refer to the use of tools, techniques, and
specialized knowledge..
Human Skills
It is the ability to work with people; it is cooperative efforts; it is
teamwork; it is the creation of an environment in which people feel
secure and free express their opinions.
Conceptual Skills – It is the ability of the
manager to see the organization as a whole and to
solve problems in ways that benefit the total system. Specifically,
the manager
who possess these skills is expected to analyzed and solve complex
problems.
Thus, the manager with good conceptual skills will have the mental
capacity to
perform the following:
a) identify problems and opportunity;
b) gather and interpret relevant information; and
c) c. execute problem-solving decisions that serve the organization’s
purpose.
Roles of a Manager
Interpersonal Roles:
Interpersonal Roles: These are the roles the managers plays when he interacts with
others. The specific roles under this category are:
a. Figurehead – When the manager performs this role, he acts as symbolic head of
the organization and as a result, he is expected to perform a number of duties of legal or
social nature. Examples: Cutting ceremonial ribbons of a company-sponsored projects.
b. Leader – He directs and motivates subordinates; counsel and communicate with
subordinates.
c. Liaison – In assuming the liaison role, the manager makes contacts with
individuals in and out of the organization to facilitate the accomplishment of work in his
department. Examples: activities like acknowledgement of mail, external board and other
activities involving outsiders.
Informational Roles
A very important aspect of manager’s job is to receive and communicate information.
On receiving and sharing information, the managers assumes three specific roles:
a. Monitor – In making the right decision concerning various aspects of an
organization, the manager is expected to collect information that will be useful in
performing his job. He maintains personal contact with stakeholders.
b. Disseminator – When the manager receives information from outsiders or
within the organization, he transmits them to the concerned members of the
organization. As information disseminator, the manager sees to it that relevant
incoming information is properly shared with members.
c. Spokesperson – There are times when outsiders seek information about
organization and as the manager, he acts as the spokesperson. The manager sees to it
that his views are heard and agreed upon by the members of the organization
specifically the board of directors.
Decisional Roles
The major part of the manager’s job is to make decisions. As such, he must use the
information he processes to make decisions that solve problems. As a decision
maker, the manager assumes the following roles:
a. Entrepreneur – In acting this role, the manager searches the organization
and its environment for opportunities and initiates projects to bring about positive
change.
b. Disturbance Handler – Sometimes, organizations face important but
unexpected disturbances such as striking employees dissatisfied with the
compensation, disagreement with the management, etc. As disturbance handler, the
manager is expected to respond to such unwelcome pressures by formulating
strategies.
c. Resource Allocator – As manager, he is responsible in deciding who gets
resources, he prepares budgets, and set schedules and determine priorities.
You might also like
- Function, Role and Skill of A ManagerDocument20 pagesFunction, Role and Skill of A ManagerChetan Choudhary91% (11)
- Self - Transcendence Theory in NursingDocument20 pagesSelf - Transcendence Theory in NursingRaveesh Kaimal100% (1)
- Cenms Vex Robotics FormDocument5 pagesCenms Vex Robotics Formapi-327552025No ratings yet
- Overview of Management and OrganizationDocument50 pagesOverview of Management and OrganizationDennisBrionesNo ratings yet
- University of Dhaka: Assignment On: Function, Role and Skill of A Manager Principles of Management Course Code: 102Document13 pagesUniversity of Dhaka: Assignment On: Function, Role and Skill of A Manager Principles of Management Course Code: 102teacherashleyNo ratings yet
- Functions, Roles and Skills of A ManagerDocument9 pagesFunctions, Roles and Skills of A ManagerMlyn100% (2)
- MBA - Unit 1 - MB20107 - Managerial Skills and CommunicationDocument21 pagesMBA - Unit 1 - MB20107 - Managerial Skills and CommunicationBalaji DNo ratings yet
- Roles of ManagerDocument7 pagesRoles of ManagerShubham KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Roles Skills of A ManagerDocument8 pagesRoles Skills of A ManagerDelina TedrosNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Management AND OrganizationDocument39 pagesAn Overview of Management AND Organizationhey JoguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (1111)Document19 pagesChapter 1 (1111)Abdallah ShamelNo ratings yet
- QuranDocument4 pagesQuranTahir AlyNo ratings yet
- Student Name - C.Buddhika Pahindra Student ID - Yet To Be Received Submission Date - 01/14/2021Document2 pagesStudent Name - C.Buddhika Pahindra Student ID - Yet To Be Received Submission Date - 01/14/2021Buddhi PahiNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management Module 2: Quarter 1 - Week 2Document15 pagesOrganization and Management Module 2: Quarter 1 - Week 2juvelyn luegoNo ratings yet
- What Are Managerial RolesDocument2 pagesWhat Are Managerial RolesBuddhi PahiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1editedDocument13 pagesChapter 1editedMuktar jiboNo ratings yet
- OBDocument7 pagesOBMelroy PereiraNo ratings yet
- Management Science Midterm HandoutsDocument30 pagesManagement Science Midterm Handoutsyennytobesa123No ratings yet
- Organizational ManagementDocument5 pagesOrganizational Managementmae ledesmaNo ratings yet
- Management RolesDocument4 pagesManagement RolesSaroj KumarNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Organization and OrganizationDocument52 pagesWeek 2 Organization and OrganizationFrancis Little AdventuresNo ratings yet
- Management: Definition, Nature, Importance and Functions of ManagementDocument41 pagesManagement: Definition, Nature, Importance and Functions of ManagementVasavi VaasuNo ratings yet
- Assignment Set-1 (60 Marks) Q.1 Write A Note On The Managerial Roles and Skills. Management Roles and SkillsDocument24 pagesAssignment Set-1 (60 Marks) Q.1 Write A Note On The Managerial Roles and Skills. Management Roles and SkillsAmbika RaoNo ratings yet
- MGT 1 - Management and OrganizationDocument20 pagesMGT 1 - Management and OrganizationVanessa AfableNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MGMT CH 1Document28 pagesIntroduction To MGMT CH 1kenoabebe9No ratings yet
- Managerial Roles & SkillsDocument4 pagesManagerial Roles & SkillsOghenetejiro ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management Summary Notes 2Document18 pagesIntroduction To Management Summary Notes 2danaietteklemariamNo ratings yet
- Managerial RolesDocument8 pagesManagerial RolesUmer Tariq Awan100% (1)
- Who Is A Manager?: Role of ManagersDocument64 pagesWho Is A Manager?: Role of ManagersMansiNo ratings yet
- Management NotesDocument21 pagesManagement NotesJoseph WanderaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document13 pagesLecture 3Sandhya Darshan DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Managing & ManagersDocument23 pagesChapter - 1: Managing & Managerscooldude690No ratings yet
- O&M Module PDF File-1Document177 pagesO&M Module PDF File-1Strewbary Barquio100% (1)
- Management Study BookDocument30 pagesManagement Study BookKaushal PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter-I MGTDocument24 pagesChapter-I MGTabdela83kasimNo ratings yet
- Essay Es27 NotesDocument10 pagesEssay Es27 NotesJake Lobrigas0% (1)
- 6 Mintzberg's Management RolesDocument12 pages6 Mintzberg's Management Roleshoney guptaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Chapter 1 and 2 NotesDocument14 pagesOrganizational Behavior Chapter 1 and 2 Notesfreakcricket80No ratings yet
- CHAPTER ONE MGDocument3 pagesCHAPTER ONE MGNikodimos yeshitilaNo ratings yet
- Omc ReviewerDocument16 pagesOmc ReviewersarahnicolejaconesbarsubiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Service Administration and Leadership.Document373 pagesNursing Service Administration and Leadership.Minlik-alew DejenieNo ratings yet
- Chapt-1-ManagementDocument5 pagesChapt-1-Managementarifhussainmalik12No ratings yet
- Principles of Management (HMM121)Document125 pagesPrinciples of Management (HMM121)ricardo njiniNo ratings yet
- Managerial Roles and SkillsDocument14 pagesManagerial Roles and SkillsAngela Loisse DawisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document31 pagesChapter 1Zemona SumalloNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument114 pagesChapter OneEden RobinNo ratings yet
- Intended Learning Outcomes: After Studying This Chapter, You Should Be Able To Do TheDocument4 pagesIntended Learning Outcomes: After Studying This Chapter, You Should Be Able To Do Thejestoni alvezNo ratings yet
- Role of A ManagerDocument12 pagesRole of A Managerrajdas000211No ratings yet
- Organization and Management ReviewerDocument2 pagesOrganization and Management ReviewerhlongNo ratings yet
- OB Assignment 1Document14 pagesOB Assignment 1RASHNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT AND MANAGERS IN THE WORKPLACEDocument4 pagesMANAGEMENT AND MANAGERS IN THE WORKPLACEmia.hrusikovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument14 pagesChapter Onetheeleadership.managementNo ratings yet
- MOB FinalDocument9 pagesMOB FinalSyeda TamzidaNo ratings yet
- The Roles of Manager 9 PagesDocument9 pagesThe Roles of Manager 9 PagesJobadzNo ratings yet
- Organizational Management: Management TheoriesDocument4 pagesOrganizational Management: Management TheoriesOSHIENo ratings yet
- Function, Role and Skill of A ManagerDocument7 pagesFunction, Role and Skill of A ManagerANUPAM KAPTINo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENTDocument24 pagesMANAGEMENTMónika NémethNo ratings yet
- CFLM - Final Examination Reviewer JANUARY 3 - 9, 2022 Characteristics of A Good ManagerDocument2 pagesCFLM - Final Examination Reviewer JANUARY 3 - 9, 2022 Characteristics of A Good ManagerLeonard MaestrocampoNo ratings yet
- MGT AssignmentDocument14 pagesMGT AssignmentigifariziNo ratings yet
- Mastering the Art of Management: A Comprehensive Guide to Becoming a Great ManagerFrom EverandMastering the Art of Management: A Comprehensive Guide to Becoming a Great ManagerNo ratings yet
- Advertisement Assessor Latest PDFDocument1 pageAdvertisement Assessor Latest PDFSeshagiri KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- Bulletin 12Document2 pagesBulletin 12api-563875898No ratings yet
- National Instructional Programmes Engineering BTELNPENDocument3 pagesNational Instructional Programmes Engineering BTELNPENtreyjonNo ratings yet
- Research Excellence Framework (REF) 2014 Equality Impact Assessment (EIA) - Coventry University PurposeDocument15 pagesResearch Excellence Framework (REF) 2014 Equality Impact Assessment (EIA) - Coventry University PurposeCekinNo ratings yet
- LECTURE Notes Baaba SillahDocument25 pagesLECTURE Notes Baaba SillahDemba BahNo ratings yet
- AP Literature and Composition Mr. Nerf 2019-2020: English Language and Composition Course Description (The "Acorn" Book)Document6 pagesAP Literature and Composition Mr. Nerf 2019-2020: English Language and Composition Course Description (The "Acorn" Book)Finnigan FallenNo ratings yet
- 1st Grade Narrative WritingDocument6 pages1st Grade Narrative WritingRamsha TjwNo ratings yet
- 4402 Internal Notification For Promotion Selection From Non Executive To Ex Pw6ziAvDocument6 pages4402 Internal Notification For Promotion Selection From Non Executive To Ex Pw6ziAvBccl LtdNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faceheatd When Changing CurriculumDocument11 pagesChallenges Faceheatd When Changing CurriculumMarshall-tendai Zifa-sire Zuku-chibikaNo ratings yet
- FIN201 CF - WSB - T3 2022 - Unit Guide - DR Vy LeDocument11 pagesFIN201 CF - WSB - T3 2022 - Unit Guide - DR Vy Lengân hà maNo ratings yet
- Trainee - S Record BookDocument4 pagesTrainee - S Record BookOgie Achilles D TestaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report On HrptaDocument7 pagesNarrative Report On HrptaBembem Quilang100% (1)
- SL - No 11 12 21 22 33 44 45 51 53 58 66 72 78 86 90 108 125 128 131 134 180 186 193 200 208 216 232 299 300 456Document8 pagesSL - No 11 12 21 22 33 44 45 51 53 58 66 72 78 86 90 108 125 128 131 134 180 186 193 200 208 216 232 299 300 456KOTESWARARAO PONGULETINo ratings yet
- Grade Staking BrochureDocument3 pagesGrade Staking BrochureGkou DojkuNo ratings yet
- E-Rubric To Measure Employability SkillsDocument10 pagesE-Rubric To Measure Employability SkillsHarunSaripNo ratings yet
- Lesson 24Document3 pagesLesson 24earthdestroyer55No ratings yet
- 00 AAPRINCIPLES - SyllabusDocument13 pages00 AAPRINCIPLES - SyllabusSamuel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management Project Itl 530Document14 pagesClassroom Management Project Itl 530api-406369287No ratings yet
- Teaching PortfolioDocument68 pagesTeaching PortfolioGSC100% (2)
- Mini Unit-Needs of Plants and AnimalsDocument21 pagesMini Unit-Needs of Plants and Animalsapi-509236392No ratings yet
- Unit 1: Society and EducationDocument5 pagesUnit 1: Society and EducationAngeline JuanilloNo ratings yet
- Placement Assessment ReportDocument4 pagesPlacement Assessment Reportapi-529553295No ratings yet
- WLP Week 1Document4 pagesWLP Week 1Dianne Villaflor SanchezNo ratings yet
- Marks Verification With Comments: Kamloops/Thompson South Kamloops SecondaryDocument7 pagesMarks Verification With Comments: Kamloops/Thompson South Kamloops SecondaryLinda DionNo ratings yet
- 2 Grade Diversity Lesson PlanDocument6 pages2 Grade Diversity Lesson Planapi-534599359No ratings yet
- Article CritiqueDocument6 pagesArticle Critiqueapi-652468450No ratings yet
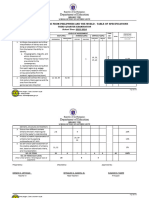
- 21st Century Tos - Sy - 2023-2024 - First QuarterDocument2 pages21st Century Tos - Sy - 2023-2024 - First QuarterKerwin100% (1)
- COT - DLP EPP 6 - ToolsDocument10 pagesCOT - DLP EPP 6 - ToolsGENALYN ACHANZAR100% (1)