0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Unit III Dobby
Unit III Dobby
Uploaded by
vasineystudy dobby mechanism
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
Unit III Dobby
Unit III Dobby
Uploaded by
vasiney0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
study dobby mechanism
Original Title
unit iii dobby
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
study dobby mechanism
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Unit III Dobby
Unit III Dobby
Uploaded by
vasineystudy dobby mechanism
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1/ 32
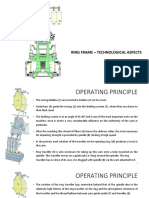
DOBBY
Dobby is a shedding mechanism placed on the top of the loom in
order to produce figured patterns by using large number of
healds than the capacity of a tappet.
Scope of a dobby:
• The scope of dobby is limited between a tappet and a jacquard.
• The number of shafts that can be actuated by a dobby varies
between 6 and 40.
• Theoretically dobby can control 48 shafts (maximum).
• However, practically it can control 36 shafts in case of wool
and allied fibres.
• Again, for cotton and allied fibers, it can control maximum 24
heald shafts.
S.N Tappet Shedding Dobby shedding
Tappet shedding is simple and Dobby shedding is relatively
1.
cheap in construction. complicated.
Tappets produce simple and A dobby can produce small
basic designs using a motifs using many more heald
2.
maximum of only 8 heald shafts up to a maximum of 40
shafts. heald shafts.
A tappet loom consumes less A dobby loom consumes more
3.
power. power.
A tappet loom can be run at A dobby loom cannot be run at
high speed with less machine high speed because of more
4.
vibration. machine vibration and excessive
friction between moving parts.
Tappets are required to be The designs can be modified
changed for altering the easily. Change over is
5. design. Gearings on the bottom brought about quickly and does
and counter shaft are to be not require any major alterations.
altered.
The number of heald shafts The number of healds and picks/
used and picks/repeat cannot repeat can be easily altered.
6.
be changed for a given set of
tappet.
In tappet shedding dwell In swing lever dobbies there is
7. period is maintained for the no dwell period. In a cam dobby,
safe passage of shuttle. a dwell is maintained.
The dobby consists of three principal mechanisms:
• The drive mechanism:
• The selection mechanism:.
• The lifting mechanism
• Dobby mechanisms are classified as negative, positive
and rotary dobbies, they can be mechanical or
electronic.
• In negative dobby shedding, the harnesses are lifted by
the dobby and lowered by a spring reversing motion.
• In positive dobby shedding, the dobby both raises and
lowers the shafts.
Single-lift dobbies are the oldest.
• All system elements perform their function once every
weaving cycle to open a shed, and then they return to
their original positions before a new cycle.
• The shed is closed after every weft insertion and the
pick is beaten up at the closed shed (center-closed
shed).
• The speed of single-lift dobbies is limited to 160 to
180 rpm.
Double-lift dobbies:
• All new type dobbies are double-lift in their action.
• Its cycle occupies two picks.
• System elements operate once every two weaving
cycles, but the shed opening is achieved every pick.
• Most of the motions in dobby occur at half time
loom speed.
• Open shed is produced; unnecessary, wasted
movements are eliminated.
• Suitable for high speed operations.
Characteristics of a Double-lift Dobby
1. A double-lift dobby forms an open shed.
2. The weft is beaten up in a crossed shed.
3. Each heald frame is controlled independently by a pair
of hooks, one at the top and the other at the bottom.
4. Drive from the bottom shaft of the loom activates the
dobby.
S.No Single-lift Dobby Double-lift Dobby
1. The dobby operates once for A double-lift dobby operates
every pick. once for every two picks.
2. The dobby is connected to the The dobby is connected to the
crankshaft. bottom shaft.
3. The dobby gives a stationary, botThis dobby gives an open
tom-closed shed. shed.
4. The dobby systems are very slow Double-lift dobby systems
and cause more wear and tear operate faster with less wear
and vibration of parts. tear of the parts.
5. They are used for weaving light These systems are used for
and medium weight fabric of weaving cotton fabric.
silk, rayon, etc.
Definition of Right handed dobby:
• A right-hand dobby is one that is placed at the left-hand side
of a right-hand loom; it gets its drive from the left-hand end
of the loom.
Definition of Left handed dobby:
• A left-hand dobby is one placed at the right-hand side of a
left-hand loom. A left-hand dobby gets its drive from the
right-hand end of the loom.
Definition of Positive dobby:
• A positive dobby moves the heald shafts in both the
directions, up and down. It is used for producing heavy
fabric in woolen and worsted weaving.
• Positive dobby: Positive Cam dobby – Used mostly on
Shuttle-less looms
Definition of Negative dobby:
• A negative dobby moves the heald frames in only
one direction, i.e. either upward or downward.
• The heald frames are reversed by means of
reversing motions using springs or elastic bands.
• A negative dobby is used for the production of
light and medium-weight fabric in cotton, silk or
synthetic yarn weaving.
• Negative dobby: Climax dobby, Paper dobby etc.
– Used in Shuttle looms
Keighley Dobby:
• Keighley dobby is known to be a double acting dobby
as most of the operations is done at half speed as
compared to the loom speed.
• The basic components of Keighley dobby are as
follows:
– Stop bars
– Baulk
– Hooks (two per heald)
– Knives (two for the entire dobby)
– Pegs on pattern chain
Climax Dobby
• The climax dobby is placed at one end of the
loom at a suitable height for convenient
handling by the weaver.
The timing circle for a climax dobby loom is shown above.
0° or 360°
1. Heald shafts are level; draw knives are in the midway position
2. The dobby T-lever is horizontal.
Dobby Weaving
150° to 210° Dwell period of the dobby.
• The heald shafts are stationary.
• The shed is open.
180°
1. One arm of the dobby T-lever is outside, and the other inside.
2. The bottom shaft crank or L-lever is at the top or bottom centre.
3. Shed remains open.
210° to 150°
- Change periods of heald shafts.
Cam dobby
The more recent trend is to actuate the knives by
means of cams mounted on a shaft in the dobby
system, the shaft being driven by a set of bevel gears
or by a chain and sprocket arrangement attached to
the crankshaft.
The cams can be designed to give any required period
of dwell, which is usually about one third of a pick.
Cam dobby systems were originally introduced for
weaving continuous filament yarn, for which a period
of dwell is particularly desirable in order to minimize
abrasion and filamentation of warp by the shuttle.
Advantages of Modern Cam Dobby Systems
• The elements of a cam dobby are precise and work smoothly and
accurately.
• They work with much less vibration than Keighley-type or climax
dobby.
• The dobby is placed at one side of the loom and hence allows
maximum light to fall on the fabric.
• The problem of oil drops falling on the cloth, found commonly in the
climax dobby, is not found in a modern cam dobby.
• In modern cam dobby systems the drive is derived from the crank
shaft by means of a suitable reduction gear arrangement like a chain-
sprocket or a bevel and bevel-wheel combination, which makes
smooth, running.
• The pick-finding mechanism in a modern cam dobby is controlled by
a clutch arrangement. So the dobby can be completely disengaged
from the crankshaft and turned in any direction, forward or backward,
by rotating a handle. This is advantageous when defects are to be
removed from the fabric, with the dobby conveniently out of the way.
• Modern cam dobby systems are provided with a heald-leveling
attachment by means of which all the heald shafts can be brought
to the same level for piecing up.
• The worm-and-worm-wheel arrangement for the pattern cylinder
drive gives a smooth and precise action.
• Modern cam dobby systems uses endless paper roll instead of
wooden lags and pegs. A bulky length of the pattern chain for long
repeats is thus avoided.
• Paper rolls that have been used once can be stored and reused
which is practically impossible in a climax dobby working with
lags and pegs.
Pick-Finding Device
• A pick-finding device is a part of a cam dobby to avoid variations
in pick spacing, when broken picks are repaired.
Positive Dobby Systems
• A positive dobby is one in which the heald shaft is moved
positively in both the directions, upwards or downwards.
• The heald shafts are raised or lowered directly by appropriate
lever arrangements without the use of any spring or other
under-motion or over-motion.
• Positive dobby systems are preferred for heavy fabric and are
suitable for high-speed or wider width looms.
Rotary dobby
You might also like
- Winding: Md. Touhidul Islam Faculty of Department of Textile Engineering Green University of Bangladesh100% (1)Winding: Md. Touhidul Islam Faculty of Department of Textile Engineering Green University of Bangladesh67 pages
- Textile Mill: - Spinning Mill - Weaving - Loom MotorsNo ratings yetTextile Mill: - Spinning Mill - Weaving - Loom Motors11 pages
- Lecture 1 Shedding - Cam Sheddiing - Dobby SheddingNo ratings yetLecture 1 Shedding - Cam Sheddiing - Dobby Shedding68 pages
- Weaving Technology 3rd Sem Unit - II DHTTNo ratings yetWeaving Technology 3rd Sem Unit - II DHTT59 pages
- Group-6 LAB REPORT 2 TEX3104 ID 191-267-801No ratings yetGroup-6 LAB REPORT 2 TEX3104 ID 191-267-8017 pages
- Factors Affecting Production in Spinning Mill67% (3)Factors Affecting Production in Spinning Mill38 pages
- Faculty of Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department: Drilling Engineering I Third StageNo ratings yetFaculty of Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department: Drilling Engineering I Third Stage24 pages
- General Factors Influencing Opening and CleaningNo ratings yetGeneral Factors Influencing Opening and Cleaning21 pages
- Complete Book of Sewing Techniques: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to MasterFrom EverandComplete Book of Sewing Techniques: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to Master3/5 (2)
- FABRIC MANUFACTURE Two Marks Question With AnswerNo ratings yetFABRIC MANUFACTURE Two Marks Question With Answer12 pages
- Linguamarina-Grammarbook To Help Boost EnglishNo ratings yetLinguamarina-Grammarbook To Help Boost English58 pages
- Nouns and Agreement: (Piece) (Every) (Earnings) (Litter) (Food) (Pair) (Book) (Glass) (Two)100% (1)Nouns and Agreement: (Piece) (Every) (Earnings) (Litter) (Food) (Pair) (Book) (Glass) (Two)2 pages
- Get (Ebook) Design of Reinforced Concrete by Jack C. McCormac, James K. Nelson ISBN 9780471761327, 047176132X free all chapters100% (2)Get (Ebook) Design of Reinforced Concrete by Jack C. McCormac, James K. Nelson ISBN 9780471761327, 047176132X free all chapters67 pages
- Unit Three: The Secondary Level: The Producers of ApparelNo ratings yetUnit Three: The Secondary Level: The Producers of Apparel37 pages
- Aspire - Pre-Intermediate - Teacher - 39 - S - Book (1) - 220-221No ratings yetAspire - Pre-Intermediate - Teacher - 39 - S - Book (1) - 220-2212 pages
- Women S Style Trend Concepts A W 21 22 PhantasmagoriaNo ratings yetWomen S Style Trend Concepts A W 21 22 Phantasmagoria19 pages
- Ket Schools Vocabulary List Các Trang Đã XóaNo ratings yetKet Schools Vocabulary List Các Trang Đã Xóa11 pages
- Winding: Md. Touhidul Islam Faculty of Department of Textile Engineering Green University of BangladeshWinding: Md. Touhidul Islam Faculty of Department of Textile Engineering Green University of Bangladesh
- Textile Mill: - Spinning Mill - Weaving - Loom MotorsTextile Mill: - Spinning Mill - Weaving - Loom Motors
- Lecture 1 Shedding - Cam Sheddiing - Dobby SheddingLecture 1 Shedding - Cam Sheddiing - Dobby Shedding
- Faculty of Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department: Drilling Engineering I Third StageFaculty of Engineering Petroleum Engineering Department: Drilling Engineering I Third Stage
- Complete Book of Sewing Techniques: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to MasterFrom EverandComplete Book of Sewing Techniques: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to Master
- Nouns and Agreement: (Piece) (Every) (Earnings) (Litter) (Food) (Pair) (Book) (Glass) (Two)Nouns and Agreement: (Piece) (Every) (Earnings) (Litter) (Food) (Pair) (Book) (Glass) (Two)
- Get (Ebook) Design of Reinforced Concrete by Jack C. McCormac, James K. Nelson ISBN 9780471761327, 047176132X free all chaptersGet (Ebook) Design of Reinforced Concrete by Jack C. McCormac, James K. Nelson ISBN 9780471761327, 047176132X free all chapters
- Unit Three: The Secondary Level: The Producers of ApparelUnit Three: The Secondary Level: The Producers of Apparel
- Aspire - Pre-Intermediate - Teacher - 39 - S - Book (1) - 220-221Aspire - Pre-Intermediate - Teacher - 39 - S - Book (1) - 220-221
- Women S Style Trend Concepts A W 21 22 PhantasmagoriaWomen S Style Trend Concepts A W 21 22 Phantasmagoria