Meckenzie approach
- 2. CONTENTS • Introduction • History • Phenomenon of centralization • Progression of forces • Mechanical diagnosis - Spine - Extremities • Predisposing and precipitating factors • Precautions • Physical examination • Procedures and techniques • Management of syndromes • Summary • Evidence
- 3. INTRODUCTION • A progression of mechanical forces applied by or to the patient in such a way that a minimal amount is utilized to effect a therapeutic change in the presenting mechanical syndrome. ( Robin Mckenzie, 1981)
- 4. HISTORY • Accidental discovery by Robin Mckenzie
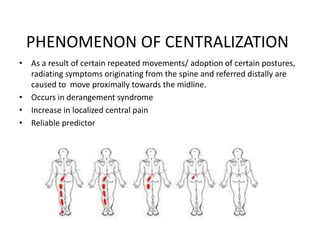
- 5. PHENOMENON OF CENTRALIZATION • As a result of certain repeated movements/ adoption of certain postures, radiating symptoms originating from the spine and referred distally are caused to move proximally towards the midline. • Occurs in derangement syndrome • Increase in localized central pain • Reliable predictor
- 6. Evidence • A study was conducted on 289 patients to determine the centralization phenomenon with acute neck and back pain. • During repeated movement testing 31% subjects had their pain centralized or abolition of symptoms in 4 sessions. • 46% subjects showed centralization on 8 sessions • 23% showed no change in symptoms site or intensity in 8 sessions.
- 7. PROGRESSION OF FORCES • Static patient-generated force positioning in mid-range positioning at end-range • Dynamic patient-generated force patient motion in mid range patient motion to end range patient motion to end range with overpressure • Therapist generated forces patient motion to end range with therapist overpressure therapist overpressure- mobilization therapist overpressure- manipulation traction- manual, intermittent or sustained
- 8. THE THREE LIGHTS • Red light - Pain in derangement & dysfunction is produced/ increased & remains worsened (not centralized) • Green - Pain in derangement is reduced/ abolished and remains better. - Pain in dysfunction produced at the end range disappears when stretch is released. • Amber - pain is not worsened nor better.
- 9. MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS 1. Postural syndrome 2. Dysfunctional syndrome 3. Derangement syndrome Syndrome ? A characteristic group of symptoms & pattern of happenings typical of a particular problem. ( Chamber’s dictionary)
- 10. POSTURAL SYNDROME • Definition: mechanically deformed soft tissues due to sustaining end range postures and positions. • Mechanism of pain: - Prolonged static loading of soft tissues within/adjacent to spine - Causes overstretching & mechanical deformation - Ligamentous followed by muscle fatigue - Bent finger syndrome • Clinical picture - age< 30 yrs - Sedentary occupation - Insidious onset, gradually worsens - Local, intermittent & symmetrical pain - Associated with headaches for Cx spine - Active pain free movements - Worsens at the end of day - No radiating pain
- 11. DYSFUNCTION SYNDROME • Definition: shortened tissues are mechanically deformed by overstretching at end range • Mechanism of pain: - Adaptive shortening, scarring, contracture, adherence/ fibrosis - Reduced extensibility of soft tissues - Static/ dynamic loading in end range ->mechanical stress on abnormal soft tissues-> mechanical deformation-> pain - Causes: trauma, degeneration, posture/ derangement • Clinical picture: - age: >30 yrs - Past h/o trauma or derangement - Poor posture - Intermittent pain at end range - No radiating pain - Reduced spinal mobility - Early morning stiffness & pain - Structural deformities - Asymmetrical movement loss
- 12. DERANGEMENT SYNDROME • Definition: disruption or displacement of structures within the intervertebral segment • Mechanism of pain - Unequal loading of IV disc-> nucleus purposes in eccentric position ->asymmetric compression->disruption in normal resting position of vertebrae-> discomfort-> pain • Types -> anterior - > posterior • Clinical picture - age: 20-55 yrs 12-55 yrs - Sudden onset - Asymmetrical - Radiating symptoms - Pain alters & differs - Constant in nature - Painful ROM - Structural deformities
- 14. For extremities: POSTURAL SYNDROME • Pain caused by mechanical deformation/ vascular deprivation of soft tissues due to prolonged postures • Affects articular structures / contractile tissues, tendons / periosteul insertions • Joint capsule/ ligament pain-> prolonged end range position • Contractile tissue pain-> prolonged static mid range loading • Leads to CTDs
- 15. DYSFUNCTION SYNDROME • Definition • Cause of pain: d/t mechanical deformation of structurally impaired tissues seen in previous h/o trauma/ inflammation/ degenerative processes. • These events cause scarring, contraction, adherence/ adaptive shortening. • capsule/ligaments affected-> painful restriction at end-range • Contractile tissues affected-> pain during resisted movements/ loading at any point of range • Articular structures-> restricted end range & intermittent pain • Pain in contraction & stretching
- 16. DERANGEMENT SYNDROME • Internal derangement is a common of pain in extremities. (Cyriax,1981) • Commonly seen in knee with meniscoid cartilage tear/ displacement of deranged menisci. • Causes locking/ restricted ROM. • Internal derangement disturbs normal resting position of joint Deforms capsule & periarticular ligaments pain
- 17. PREDISPOSING AND PRECIPIATING FACTORSPredisposing: Precipitating: • Prolonged sitting - Movements • Frequency of flexion - trauma - lifting - lateral flexion or rotation
- 18. PRECAUTIONS • Increase in central pain, decrease in distal pain. • The increased spinal pain may be disconcerting to clients. • Hence, prior to treatment they must be explained & fully assured. • Stop the exercises if distal pain/ centralization worsens which should occur during and not after several hours. • If symptoms occur after several hours, cause is posture. • Unused to exs clients may have new pains in thoracic, extremities d/t new positions movements. • In dysfunction, be cautious with clients recovered from a recent derangement. Exs should not provoke pain. • Manipulation may cause minor trauma & perpetuate the cycle of repair & failure to remodel.
- 19. RED FLAGS • Cauda equina syndrome • Possible cancer • Inflammatory disorders • Stenosis • Serious spinal pathology • Hip pathology • Symptomatic SIJ • Symptomatic spondylolisthesis • Mechanically inconclusive • Chronic pain state
- 20. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION • History • Physical examination Aims of physical examination:- 1. Usual posture 2. Symptomatic response to posture correction 3. Deformities/ asymmetries related to episode 4. Neurological examination 5. Baseline measures of mechanical presentation 6. Symptomatic & mechanical response to repeated movements Conclusion:- 1. Syndrome classification 2. Appropriate therapeutic loading strategy 3. Appropriate testing loading strategy
- 21. 1. POSTURE: i) Sitting ii) Standing iii) Leg length discrepancy 2. NEUROLOGICAL TESTS i) Sensations ii) Muscle power iii) Reflexes iv) Nerve tension tests 3. Movement loss i) Flexion ii) Extension iii) Rotation iv) Side flexion v) Side gliding
- 22. 4. MOVEMENTS IN RELATION TO PAIN - Standing - Lying 5. REPEATED MOVEMENTS - Diagnostic in derangement and dysfunction syndromes - In derangement: movement towards painful side - derangement & peripheralising pain movement away from painful side- derangement/ centralization - In dysfunction: pain is produced at end range of movement & does not worsen - In postural: pain not produced with movement aggravates on sustained positioning
- 25. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION FOR EXTREMITIES: • Active movements • Passive movements • Passive movement with overpressure • Resisted tests • Repeated movements - Postural syndrome - Dysfunction syndrome - Derangement syndrome • Neurological examination
- 26. PROCEDURES CERVICAL SPINE • Retraction • Retraction with extension (sitting/ standing) • Retraction with extension (lying/prone) • Retraction with extension with traction or rotation • Extension mobilization (lying prone/ supine) • Retraction and lateral flexion • Lateral flexion mobilization and manipulation • Retraction and rotation • Retraction mobilization and manipulation • Flexion • Flexion mobilization • Traction
- 29. THORACIC • Erect sitting flexion • Extension in lying • Extension mobilization/ manipulation • Erect sitting rotation • Rotation mobilization/ manipulation
- 31. LUMBAR • Lying prone • Lying prone in extension • Extension in lying • Extension in lying with belt fixation • Sustained extension • Extension in standing • Extension mobilization • Extension manipulation • Rotation mobilization in extension • Rotation manipulation in extension • Sustained rotation/ mobilization in flexion • Rotation manipulation in flexion • Flexion in lying • Flexion in step standing • Correction of lateral shift • Self-correction of lateral shift
- 34. MANAGEMENT OF SYNDROMES • DERANGEMENT SYNDROME: Stages – 1. Reduction 2. Maintenance of reduction 3. Recovery of function 4. Prophylaxis Treatment principles – 1. Extension 2. Flexion 3. Lateral 4. Combination 5. Irreducible
- 35. • DYSFUNCTION SYNDROME • Process is lengthy & measured in week/months • Frustration d/t lack of apparent change • Exercises performed repeatedly every 2-3 hours • Each session of 10-15 stretches • Do not strain and cause micro trauma • If pain persist after treatment: i) Overstretching ii) Micro trauma iii) wrong diagnosis • Pain is mandatory but subsides after 10 mins • Stop exs if pain spreads distally/ deteriorates
- 36. POSTURAL SYNDROME • Explain the correlation between posture & symptoms • Educate on posture correction - Attain posture - Maintain posture • Educate on avoidance of aggravating postures • Correct posture
- 37. • EXTREMITIES: 1. POSTURAL SYNDROME - Education in self management - Exs can be performed 10 times 3-4 times daily - repeated end range active movements progress with self applied overpressure Resistance towards/ away from direction of limitation at end range Resistance throughout the movement
- 38. • DYSFUNCTION SYNDROME a) Articular dysfunction - End range self mobilizations - Client moves the joint actively towards restriction until pain is felt - Repetitions:10-12 - Frequency: 3-4 times/day - Review in 2 days & at the end of 1 week - Progress with resisted exercises b) Musculotendinous/ contractile dysfunction - static/ dynamic loading - Target zone identified - Active movements, static resisted movements, concentric & eccentric loading given in inner, outer or in the target zone - Frequency: 3-4 times/day
- 40. • DERANGEMENT SYNDROME - Repeated end range movement loading in pain free direction - Active exercises at end range overpressure ( progression) Resistance towards/ away from direction of limitation at end range
- 42. SUMMARY • Definition: Mckenzie approach - a progression of mechanical forces from patient to therapist generated. Centralization- radiating symptoms originating from the spine and referred distally are caused to move proximally towards the midline due to adaption to certain postures. • History: Accidental discovery of Robin Mckenzie • Forces: 1) Static 2) Dynamic 3) Therapist generated
- 43. Postural Dysfunction Derangement Definition Deformation d/t sustained postures Deformation d/t shortened structures Disruption/displacemen t of structures Mechanism of pain Overstretching & mechanical deformation Scarring, adherence, contracture, fibrosis Unequal loading Clinical features Age: < 30 Age: > 30 Age: 20-55(Cx) 12-55 (Lx) Insidious onset insidious/ aware about onset Sudden onset No referred pain No referred pain Referred to arm/ leg Local & symmetrical Symmetrical/ asymmetrical Asymmetrical Intermittent Intermittent Constant Worsens at the end of the day Worsens in morning Worsens in morning Sedentary occupation Poor posture occupation Repetitive/strainousmo vements
- 44. • Examination: History Physical examination SPINE EXTREMITIES - Posture - Active movements - Neurological examination - neurological examination - Movements - resisted movements - Repeated movements - repeated movements - Painful movements - passive movements • Procedures: - Cervical - Thoracic - Lumbar
- 45. • Management: Derangement Dysfunction Postural posture correction Extension flexion principle lateral principle principle • Postural syndrome: - Educate - Correct - Avoid
- 46. • Dysfunction syndrome - Stretch - Maintain • Derangement syndrome - Reduction - Maintain - Recovery - Prophylaxis
- 47. EVIDENCES • A RCT study was conducted by Rosedale et al on the efficacy of exercise intervention in patients with knee OA based on Mckenzie’s mechanical diagnosis. • 180 patients were assigned to MDT and a control group. • Pain & function were assessed after 3 months of intervention • The study concluded that MDT group showed superior outcomes than the control groups
- 48. • Stanish et al conducted a study on the effect of eccentric exercises on 200 chronic tendononitis subjects. • Eccentric strength training program was given daily over a six week period. • Among 200 patients, 44% had complete relief of symptoms & return to normal function. • 43% had a marked decrease in pain & function • 9% had their problems unchanged • 2% had worse outcomes at the end of treatment. • Study concluded that eccentric loading in particular was extremely useful in rehabilitation of chronic tendonitis.
- 49. • Kjellman & Oberg in 2002 conducted a RCT on 77 patients to find out the effect of general exercises, Mckenzie group and control group. • Pain intensity & NDI were calculated. • Pain intensity and disability scale showed improvements in all groups with no significant difference. • But, there was significant difference in Mckenzie group than the control group & general mobility exercise group.
- 50. REFERENCES • Jeffrey Boyling, Nigel Palastanga; GRIEVE’S modern manual therapy, chap 28, 42, 55; 2nd edition, the vertebral column.; Churchil Livingstone. • Robin Mckenzie, Stephan May; The lumbar spine: mechanical diagnosis & therapy. Volume I, II. 2nd edition, Spinal publications. • Robin Mckenzie, Stephan May; The cervical & thoracic spine: mechanical diagnosis & therapy. Volume I, II. 2nd edition, Spinal publications. • Robin Mckenzie, Stephan May; Human extremities: mechanical diagnosis & therapy. Volume I, II. 2nd edition, Spinal publications. • Stanish WD, Rubinovich RM. Eccentric exercises in chronic tendonitis. Clinical Ortho & Rel Res 208. 65-68. • Rosedale R et al. efficacy of exercise intervention as determined by Mckenzie system of mechanical Diagnosis & therapy for knee osteoarthritis: aRCT. Journal of orthopaedic and sports physiotherapy; 44(3).
- 51. • Werenke M, Hart DL, Cook D. Descriptive study of the phenomenon. A prospective analysis. Spine 1999; 24(7): 676-83. • Kjellman, Oberg B. a critical analysis of randomized clinical trials on neck pain and treatment efficiency. A review of literature. Scand J rehab Med 31. 139-152. • Stanish WD, Rubinovich RM, Curvin S. eccentric exercise in chronic tendonitis. Clinical ortho & rel res 208.65-68.