Chapter 10
•Download as PPT, PDF•
3 likes•1,709 views
This document discusses energy transfer and heat, defining key concepts like temperature, heat capacity, enthalpy, and calorimetry. It explains that enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a system and can be used to calculate the energy change of chemical reactions using Hess's law by adding the enthalpy changes of individual steps. Calorimetry is used to experimentally measure enthalpy changes.
Report
Share
Report
Share
More Related Content
What's hot
Tang 03 enthalpy of formation and combustion

The document defines standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) as the amount of heat absorbed or released when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements in their standard states at 25°C and 100kPa. ΔHf° values are used to calculate the enthalpy change (ΔH°) of a chemical reaction. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to determine the ΔHf° of a compound from combustion reactions and how to calculate ΔH° from the ΔHf° values of reactants and products.
Hess's law

Hess's law states that the total enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the pathway between the initial and final states. To calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction, standard enthalpy change values can be used for the elementary steps that add up to the overall reaction through algebraic manipulation. For the reaction of 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g), using standard enthalpy change values for the elementary steps gives an overall exothermic enthalpy change of -906.3 kJ.
Tang 01 reversible reactions 2

The document discusses reversible reactions and chemical equilibrium. It provides examples of reversible reactions and how changing temperature affects the rates of the forward and reverse reactions. Equilibrium is reached when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. Factors like temperature, concentration, and entropy can affect whether a reaction proceeds to completion or reaches an equilibrium state.
05c reversible reactions

This document discusses reversible chemical reactions and chemical equilibrium. It defines key terms like activation energy, exothermic and endothermic reactions, and how factors like temperature, concentration, and catalysts affect the rate and direction of reversible reactions. Specifically, it explains that at chemical equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal and application of Le Chatelier's principle describes how the system responds to changes to relieve stress.
AP Chemistry Chapter 3 Outline

This document summarizes key concepts in stoichiometry including:
1) Chemical equations represent chemical reactions and include reactants, products, and coefficients to balance the equation.
2) Reaction types include combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions.
3) Formula weights, molecular weights, moles, molar mass, and limiting reactants are important concepts for solving stoichiometry problems quantitatively.
4) Empirical formulas can be calculated from elemental composition data using mole ratios.
AP Chemistry Chapter 5 Outline

This document summarizes key concepts in thermochemistry, including:
1) Energy can be transferred as heat or work. The SI unit of energy is the joule. Internal energy is the sum of kinetic and potential energies within a system.
2) Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a system at constant pressure. It can be used to determine whether chemical reactions are endothermic or exothermic.
3) Calorimetry allows the measurement of heat and enthalpy changes through experiments on chemical reactions. Hess's law states that the enthalpy change of an overall reaction is the sum of enthalpy changes for individual steps.
Chemical Equilibrium

The fundamentals of chemical equilibrium including Le Chatier's Principle and solved problems for heterogeneous and homogeneous equilibrium.
**More good stuff available at:
www.wsautter.com
and
http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=wnsautter&aq=f
Kinetics pp

This document discusses chemical kinetics and reaction rates. It explains that kinetics studies how fast chemical reactions occur. The rate of a reaction depends on factors like the concentrations of reactants, temperature, and presence of catalysts. Reaction rates can be determined by measuring changes in concentration over time. The order of a reaction indicates how the rate depends on reactant concentrations. First-order and second-order reactions follow distinct rate laws that allow calculation of rate constants from experimental data. Reaction mechanisms involve elementary steps that may be fast or slow, with the overall rate determined by the slowest step.
Tang 03 enthalpy of formation and combustion

The document discusses standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°), which is the amount of heat absorbed or released when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements in their standard states. Examples are provided of writing balanced chemical equations for formation reactions and using ΔHf° values to calculate the enthalpy change (ΔH°) of chemical reactions. The standard heat of combustion (ΔHc°) is also introduced, which is the enthalpy change when a substance undergoes complete combustion.
Entropy ok1294987599

This document discusses thermodynamics concepts including entropy, spontaneity, Gibbs free energy, and how to use thermodynamic data to determine if chemical reactions are spontaneous. It provides examples of calculating entropy changes, Gibbs free energy changes, and using these values along with enthalpy changes to predict spontaneity. Standard enthalpy and entropy values are used from data tables to perform sample calculations for reactions.
8.0 thermochemistry (student's copy)

This document discusses thermo chemistry and key concepts like enthalpy, calorimetry, and Hess's law. It begins by defining open, closed, and isolated systems and explains endothermic and exothermic reactions using energy profile diagrams. It then discusses enthalpy and defines standard enthalpy. Various types of enthalpies are defined like enthalpy of formation, combustion, atomization, and more. Calorimetry is explained as a method to measure heat changes in reactions using calorimeters. Hess's law is introduced as the principle that the enthalpy change of a reaction is the same whether it occurs in one step or multiple steps.
Equilibrium

This document covers various topics related to chemical equilibrium including:
1. Irreversible and reversible reactions, and examples of each.
2. Types of equilibrium including homogeneous, heterogeneous, physical, and chemical equilibrium.
3. The law of mass action and how equilibrium constants are calculated.
4. How changing conditions like temperature, pressure, and concentration affects chemical equilibria.
5. Additional topics like acid-base theories, buffer solutions, and solubility products are also briefly discussed.
Chemical Equilibrium

The document discusses chemical equilibrium, including:
1) All physical and chemical changes tend toward a state of equilibrium according to Le Chatelier's principle.
2) At dynamic equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal and the reaction quotient equals the equilibrium constant.
3) Equilibrium constants can be calculated using concentration values and reaction quotients can indicate the direction a reaction will proceed to reach equilibrium.
Standard Enthalpy Formation

This document discusses standard enthalpies of formation (ΔHf°) and how to calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction (ΔH°) using ΔHf° values. Standard enthalpies of formation are defined as the enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of a compound from its constituent elements in their standard states. ΔHf° values are tabulated at 298 K and 1 atm and can be looked up in tables. The standard enthalpy of reaction can be calculated using the equation ΔH° = ΣΔHf°(products) - ΣΔHf°(reactants). An example reaction of N2O4(g) → 2NO2(g
Equilibrium 

The document discusses chemical equilibrium and reversible reactions. It defines chemical equilibrium as a state where the forward and reverse reactions are proceeding at the same rate, such that the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. It describes characteristics of equilibrium such as it being dynamic, having equal forward and reverse reaction rates, and requiring a closed system. It also introduces Le Châtelier's principle, which states that disturbances to a system at equilibrium cause the equilibrium to shift in a direction that counteracts the applied stress.
Equilibrium and types of equilibrium

There are two types of equilibrium: physical and chemical. Physical equilibrium occurs when a system's physical state does not change over time, such as when a solid melts at a fixed temperature. Chemical equilibrium is reached when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal and the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. The equilibrium constant (K) is a ratio of product to reactant concentrations raised to their stoichiometric coefficients that remains constant at equilibrium. K can be used to determine whether the equilibrium favors reactants or products.
Tang 05 bond energy

This document discusses bond energy and how it relates to chemical reactions. It states that bond breaking is endothermic while bond formation is exothermic. A table of average bond energies is provided. The bond energies can be used to calculate the change in enthalpy (ΔH°) of reactions. Examples are given showing how to set up calculations using bond energies to find the ΔH° of reactions, including combustion reactions of ethanol and methoxymethane. Bond dissociation energy is also introduced as another measure of bond strength.
Thermodynamics

The document discusses various types of enthalpy changes including:
- Standard enthalpy of reaction is the enthalpy change when reactants and products are in their standard states.
- Enthalpy of fusion/melting is the energy required to melt 1 mole of a solid.
- Enthalpy of vaporization is the energy required to vaporize 1 mole of a liquid.
- Enthalpy of sublimation is the energy change of a solid transforming directly to a gas.
- Standard enthalpy of formation is the energy change to form 1 mole of a compound from its elements.
- Examples are provided to illustrate the different types of enthalpy changes.
Equilibrium student 2014 2

The document discusses chemical equilibrium. It begins by defining chemical equilibrium as a state where the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal, but the reactions are still occurring dynamically. It also notes that at equilibrium, the concentrations or pressures of all species remain constant over time. The document then provides the definitions and expressions for equilibrium constants Kc and Kp, which relate the concentrations or pressures of reactants and products at equilibrium. It also discusses how equilibrium positions can be manipulated by changing conditions based on Le Chatelier's principle.
Standard Enthalpy Changes of Reactions

1) Enthalpy is a measure of the heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction at constant pressure. It is equal to the change in internal energy of the system plus the product of pressure and change in volume.
2) The standard enthalpy change of a reaction is the enthalpy change that occurs under standard state conditions of 1 atm pressure and 25°C temperature.
3) Standard enthalpy changes of formation, combustion, atomization, neutralization, and solution can be defined based on specific chemical processes occurring under standard state conditions.
What's hot (20)
Viewers also liked
Chapter 15 review

The document defines key optics terms including: plane, convex, and concave mirrors and lenses and how they affect light rays and images. It discusses the differences between convex and concave lenses and mirrors, and how they produce upright or inverted, magnified or minified images. The document also briefly mentions far-sightedness and near-sightedness in relation to convex and concave lenses.
Science Facts

Science Facts - Check our astonishing compiliation of random and science facts.
Visit us at http://mesmerizeus.com or follow us at https://www.facebook.com/mesmerizerz
Chpt.2.2

The flow of energy in an ecosystem begins with autotrophs, such as plants, which use energy from the sun to produce their own food through photosynthesis. Heterotrophs, including herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and decomposers then obtain energy by consuming autotrophs and other organisms. This energy is transferred between trophic levels in a food chain and food web, with less energy being available at higher trophic levels due to energy being lost as heat at each transfer.
Electromagnetic Spectrum

This document discusses the electromagnetic spectrum and properties of light. It explains that light can be described as both a wave and particle. The visible light spectrum is a small portion of the full electromagnetic spectrum. Different frequencies of light correspond to different colors, from red to violet. The speed of light is constant, and the frequency and wavelength of a light wave are related by the equation c=λν. Spectral lines allow scientists to identify elements and study distant stars and galaxies.
Light

Myopia can be corrected using concave lenses and hypermetropia can be corrected using convex lenses. Crabs have small eyes but can see all around using them. Owls have large corneas and pupils to let in more light as their retinas have more rods than cones, unlike day birds which have more cones and less rods.
Reflection refraction

Reflection and Refraction of Optical Rays.
For comments, please contact me at solo.hermelin@gmail.com.
For more presentations on different topics visit my website at http://www.solohermelin.com.
This presentation is in the Optics folder.
Light reflaction and refraction

This document provides a summary of light reflection and refraction. It begins by explaining that light travels in a straight line until it meets a boundary, where it can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed. It then discusses the laws of reflection, including that the incident, reflected, and normal rays lie in the same plane and that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Next, it explains refraction when light passes from one medium to another and discusses the relationship between incident and refracted angles. The remainder of the document analyzes light reflection and refraction using spherical mirrors and lenses through diagrams and explanations of six cases for each. It concludes by thanking various resources used to create the summary.
Trivia Questions For Science 8 Review Optics Quiz #2

According to the ray model of light, light travels in a straight line. When light hits a translucent surface it is scattered, and transparent materials let light pass through unobscured. Cardboard is opaque as it does not let light pass through, while wax paper is translucent since it scatters light. The object with the larger shadow is closer to the light source.
Optics

Optics involves the reflection and refraction of light. Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface, following the law of reflection where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction is when light changes speed and direction when passing from one medium to another due to a change in index of refraction. Refraction is described by Snell's law, where the ratio of sines of the incident and refracted angles is equal to the ratio of the indices of refraction. Total internal reflection occurs when light passes from a higher to lower index of refraction beyond the critical angle and is completely reflected rather than refracted.
6. 10. lightreflectionandrefraction

This document provides information about light reflection and refraction. It discusses the laws of reflection and refraction, and how light behaves when interacting with spherical mirrors and lenses. Key points covered include:
- The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
- Reflection and refraction of light can be used to form real or virtual images with mirrors and lenses.
- Spherical mirrors and lenses have a focal point where light rays converge or appear to diverge, depending on whether the surface is convex or concave.
- Mirror and lens formulas relate the focal length to the object and image distances.
11 4 refraction-of_light

Here is a ray diagram showing why the chopstick looks bent when dipped into water:
air
water
incident ray refracted ray
normal
The diagram shows a ray of light traveling from air into water at the tip of the chopstick. Due to the change in refractive index, the light ray bends towards the normal as it enters the water. This makes the tip of the chopstick appear higher and causes the illusion that the chopstick is bent.
The Human Life And The Colourful World

The five sense organs are
Eyes ,ears , nose, tongue and skin.
Among these the most important one are the eyes. It is one of the most valuable and sensitive organs .It helps us to identify colours. This allows us to see the beautiful world around us.
Notes on Optics

Optics is the study of light and how it interacts with mirrors and lenses. Light travels in straight lines and can be reflected or refracted when it hits a surface. Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface at the same angle, while refraction causes light to bend when moving between materials of different densities. Plane mirrors produce virtual images using the law of reflection. Spherical mirrors can produce virtual or real images depending on whether the object is inside or outside the focal length. Refraction is governed by Snell's law and causes light to bend when passing through materials like glass or water.
\\Vfs2\Mey9269$\Lenses

Convex lenses bend light toward a focal point and are used by farsighted patients in eyeglasses. Concave lenses spread out light and are used by nearsighted patients. Camera lenses and telescope lenses evolved from optical lenses developed for eyeglasses and help focus images. The Fresnel lens, invented in the 1800s, helped project light across seas for lighthouses. Convex and concave lenses have been instrumental in scientific discoveries since their invention in the 1300s and were a key part of Galileo's telescope inventions in the 1600s that helped launch the scientific revolution.
Convex concave ray diagrams

This document provides information about ray diagrams and image formation using spherical mirrors. It discusses the key terms including principal axis, focus, center of curvature and explains how to use ray diagrams to determine the location, orientation, size and type of images formed by concave and convex mirrors in different configurations. Five cases of image formation using a concave mirror and one case using a convex mirror are described through diagrams and explanations of how the light rays behave. The document also includes examples for readers to practice locating and describing images.
Ophthalmology 5th year, 3rd lecture (Dr. Tara)

The document discusses the properties and behavior of light, including reflection, refraction, and how different materials and optical components like lenses interact with light. It explains how lenses can refract light to form real or virtual images, and the factors that determine the type of image formed such as whether the object is between the focal point and lens or beyond it. Different lens shapes and cylindrical lenses are also described.
Refraction

This document provides information about conducting an eye exam, including:
1) Taking a case history to understand a patient's vision needs, eye health history, and general health conditions.
2) Performing objective and subjective refraction tests to determine a patient's prescription for distance and near vision.
3) Evaluating binocular vision by testing motor and sensory functions like eye movements, stereopsis, and fusional reserves.
4) Prescribing corrective lenses or prisms as needed based on the refraction and binocular vision results.
Light reflection and refaraction

This document discusses the properties of reflection and refraction of light by spherical mirrors and lenses. It defines key terms like focal length, pole, principal axis, image formation, magnification, and sign conventions. The laws of reflection and refraction are described, including the mirror formula, lens formula, and definitions of refractive index. Image formation diagrams are presented for concave and convex mirrors and lenses. Common uses of these optical components are also noted.
Reflection of light (Physics)

Light propagates in straight lines and can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted when interacting with matter. Reflection occurs when light hits a smooth surface and bounces back into the same medium at the same angle. Regular reflection occurs from plane mirrors where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Spherical mirrors can be concave or convex. Concave mirrors form real, inverted images, while convex mirrors form virtual, upright images. The mirror equation relates the focal length and distances of the object and image.
Concave mirrors

Concave mirrors reflect light inwards like the inside of a bowl. Rays of light hitting any point on the curved mirror behave as if they are hitting a flat plane at that point. All the imaginary normal lines drawn from points on the curved surface meet at the center of curvature. Rays parallel to the principal axis, which runs through the vertex and center of curvature, meet at the focal point. The location and orientation of the mirror's image depends on where the object is placed relative to the focal point and center of curvature.
Viewers also liked (20)
Trivia Questions For Science 8 Review Optics Quiz #2

Trivia Questions For Science 8 Review Optics Quiz #2
Similar to Chapter 10
ENERGY AS HEAT

1) Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between objects at different temperatures. Heat transfer occurs when samples are in contact and energy moves from the higher temperature sample to the lower temperature sample.
2) Enthalpy is a measurement of the total energy of a system and includes both the internal energy and pressure-volume work term. The enthalpy change of a reaction can be determined from standard enthalpies of formation values.
3) Hess's law states that the enthalpy change of an overall chemical process is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes of the individual steps in that process.
Inorganic Chemistry: Thermochemistry

This document provides an introduction to thermochemistry and the key concepts of enthalpy, enthalpy change, and standard enthalpy of formation. It defines system and surroundings, and the three types of systems - open, closed, and isolated. The key points are:
- Enthalpy change (ΔH) is the difference in enthalpies between products and reactants and indicates whether a reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
- Standard enthalpy of formation (H°f) is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is formed from its elements under standard conditions.
- Enthalpy of combustion (H°c) is the enthalpy change when 1 mole
AP_Chem_Thermodynamics.pptx

Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the subdiscipline involving chemical reactions and energy changes. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved as it transforms between forms. Energy exists in kinetic and potential forms. Kinetic energy is associated with motion, while potential energy is stored energy due to position or composition. Heat is the transfer of kinetic energy between objects of different temperatures until they reach equilibrium. Exothermic processes release heat from a system, while endothermic processes absorb heat into a system. Enthalpy changes (ΔH) quantify the heat absorbed or released by chemical reactions. Spontaneous processes are those that proceed without outside intervention, as dictated by a negative change
Chapter 10-Holt causes of change

This document discusses energy transfer and heat. It defines heat as energy transferred between objects at different temperatures. Temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, and heat is transferred from hotter to colder objects. Enthalpy is a measure of total energy in a system and can increase or decrease in chemical reactions, which can be exothermic or endothermic. The enthalpy change of a reaction depends on variables like temperature and can be determined through calorimetry experiments or by applying Hess's law.
Test Document

This document provides instructions for an experiment to determine the heat of neutralization (ΔH) for acid-base reactions using calorimetry. It discusses key concepts like enthalpy, Hess' Law, and heat capacity. The procedure involves first calibrating thermometers and determining the heat capacity of the calorimeter. Then neutralization reactions between acids and bases are carried out in the calorimeter, and the temperature change is used to calculate the heat of reaction (ΔH) based on the calorimeter's heat capacity.
Thermochemistry ok1294993378

The document discusses energy changes that occur during chemical reactions. It defines exothermic and endothermic reactions, and standard enthalpy change. It provides examples of how to calculate enthalpy changes from experimental temperature change data using concepts like specific heat capacity. Hess's law, which states the enthalpy change of a reaction is equal to the sum of enthalpy changes of the steps in a reaction mechanism, is also introduced.
2016 topic 5.1 measuring energy changes

This document provides an overview of exothermic and endothermic reactions, calorimetry, and how to calculate enthalpy changes. The key points are:
- Exothermic reactions release heat while endothermic reactions absorb heat.
- Enthalpy change (ΔH) is the quantity of heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction.
- Calorimetry experiments allow calculation of ΔH by measuring the temperature change of a reaction mixture.
- Sample problems demonstrate how to use calorimetry data like mass changes and temperature differences to calculate the enthalpy change for a reaction.
Chapter 17.1 : Thermochemistry

The document discusses thermochemistry and concepts related to heat, temperature, enthalpy, and thermochemical equations. It provides definitions and examples of:
- Specific heat and how to calculate it using the formula q=m*c*ΔT
- Enthalpy change (ΔH), enthalpy of reaction, enthalpy of formation (ΔHf), and enthalpy of combustion (ΔHc)
- How to use Hess's law to calculate enthalpy changes from individual reaction steps
Ch05 outline

This document summarizes key concepts in thermochemistry, including:
1) Energy can be transferred as heat or work. The SI unit of energy is the joule. Internal energy is the sum of kinetic and potential energies within a system.
2) Enthalpy is a measurement of energy for chemical reactions that takes into account heat and pressure-volume work. It can be used to determine if a reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
3) Calorimetry is used to measure enthalpy changes through determining heat flows during chemical reactions. Hess's law allows calculation of enthalpy changes for reactions using known enthalpies of individual steps.
Thermochemistry PowerPoint.ppt

1. Thermochemistry is the study of heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. It uses concepts such as exothermic and endothermic reactions, enthalpy, and calorimetry.
2. Hess's law states that the heat change of a reaction is equal to the sum of the heat changes of the steps forming that reaction. This allows for calculation of heats of reaction from standard heats of formation.
3. Calorimetry is used to directly measure heat changes through the use of calorimeters. Thermochemical equations contain the balanced chemical equation and associated heat change.
Chemistry- JIB Topic 9 Thermochemistry

The document defines key terms in thermodynamics including system, surroundings, open system, closed system, isolated system, exothermic, endothermic, enthalpy, kinetic energy, potential energy, heat, work, state functions, standard enthalpy of formation, standard enthalpy of combustion, and entropy. It also discusses the first and second laws of thermodynamics, Gibbs free energy, and how to calculate thermodynamic properties using standard enthalpies of formation.
Chapter5.pdf

The document discusses thermochemistry and the following key points:
- Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes in chemical reactions, especially the heat evolved or absorbed.
- Enthalpy (H) is a state function that equals the internal energy (E) plus pressure-volume work (PV) for a chemical reaction. The enthalpy change (ΔH) of a reaction is the heat absorbed or released under constant pressure.
- Hess's law states that the enthalpy change for an overall reaction is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps of that reaction. This allows for calculation of enthalpy changes from standard enthalpy of formation values.
Enthalpy

Enthalpy is an important concept in thermochemistry that represents the heat transferred during a chemical reaction under constant pressure. It can be used to determine if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic based on the sign of ΔH. Hess's law states that the enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the pathway and can be calculated from the enthalpies of the steps. Properties of enthalpy include it being a state function, extensive property, and dependent on the states of the reactants and products.
Lect w10 abbrev_ thermochemistry_alg

The document provides information about thermochemistry and how to calculate the change in enthalpy (ΔH) of chemical reactions using standard enthalpy values and bond energies. It discusses how ΔH is measured experimentally using calorimetry and how Hess's law allows calculating ΔH from multiple reaction steps. Standard enthalpy values and bond dissociation energies allow predicting if reactions are endothermic or exothermic without direct experimentation.
Chemical Reactions: Thermochemistry

This document discusses various topics in thermochemistry including:
- Enthalpy changes in chemical reactions and how they are measured using calorimetry. Exothermic and endothermic reactions are explained.
- Hess's law, which states that the enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the reaction pathway. It can be used to calculate enthalpy changes.
- Standard enthalpies of formation and how they allow calculation of enthalpy changes using Hess's law and bond dissociation enthalpies.
- Measuring enthalpy changes using bomb calorimetry and coffee cup calorimetry. Limitations of each method are discussed.
005 lecture f

This document discusses thermochemistry and calorimetry. It defines key concepts in thermochemistry including the various forms of energy, exothermic and endothermic processes, and systems and surroundings. It introduces the first law of thermodynamics and defines state functions. It also discusses enthalpy, thermochemical equations, and calculations involving enthalpy changes. The document explains calorimetry concepts like heat capacity, specific heat, and how to perform calculations using bomb and coffee cup calorimetry.
1422 chapt-15-thermodynamics

This document provides an overview of thermodynamic concepts including:
- Definitions of system, surroundings, isothermal process, heat capacity, calorie, and specific heats
- Tables listing specific heats and molar heat capacities of various substances
- Explanations and examples of standard enthalpy of formation (ΔH°f), Hess's law, and bomb calorimetry
- Relationships between internal energy (ΔE), enthalpy (ΔH), heat (q), and work (w)
Thermochemistry

Thermochemistry is the study of heat changes in chemical reactions. Exothermic reactions evolve heat while endothermic reactions absorb heat. The enthalpy of a reaction is the quantity of heat absorbed or evolved. Standard enthalpy of reaction is measured under standard conditions. Hess's law states that the enthalpy change of a reaction is the same regardless of the reaction pathway. Thermochemistry is applied in pyrometallurgy which involves processes like calcination, roasting, smelting, and refining to extract metals from ores.
DE_-_Chapter_16_-_Free_Energy_and_Spontaneity.ppt

This document provides information on thermodynamics and spontaneity of chemical reactions. It defines key concepts such as the first and second laws of thermodynamics, entropy, free energy, and Gibbs free energy. Equations for calculating entropy, enthalpy, and Gibbs free energy changes in chemical reactions are presented. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to apply these equations and determine if reactions are spontaneous based on the sign and value of their Gibbs free energy changes. The dependence of spontaneity on temperature is also discussed.
Similar to Chapter 10 (20)
Chemistry_Energetics_Lecture_1.Chemistry_Energetics_Lecture

Chemistry_Energetics_Lecture_1.Chemistry_Energetics_Lecture
More from ChemistryFun
Chapter 13

The document discusses solutions, acids, bases and pH. It defines a solution as a homogeneous mixture where a solute is dissolved in a solvent. Acids are defined as substances that produce hydronium (H3O+) ions in water, lower pH, and conduct electricity. Bases are defined as substances that produce hydroxide (OH-) ions in water, raise pH and feel slippery. pH is a measure of acidity/basicity defined as the negative log of the hydronium ion concentration.
Chapter 20

The document provides information about carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and energy and living systems. It defines monomers, polymers, and important biomolecules like ATP. It describes key processes like photosynthesis and cellular respiration that living things use to obtain and use energy. Gene technology techniques like DNA fingerprinting and cloning are also summarized.
Chapter 4

This document provides an overview of how elements are organized in the periodic table. It discusses early classification systems developed by Newlands and Mendeleev and how Moseley later determined that atomic number, not atomic mass, is the basis for organization. Key periodic properties like valence electrons and how they determine chemical properties are explained. Finally, it gives a brief tour of different groups of elements and trends seen in the periodic table.
Chapter 5 and 6

This document summarizes key concepts about ions, ionic bonding, and covalent bonding from chemistry. It defines ions as atoms that have gained or lost electrons, and discusses how ions bond to form ionic compounds like sodium chloride. It also explains how atoms can bond by sharing electrons in covalent bonds, including how bond polarity and molecular shape are determined. Chemical formulas and naming conventions for ionic and covalent compounds are presented.
Chapter 3

The document discusses the history of atomic theory from ancient Greek philosophers to modern atomic structure. It introduces key figures like Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, and Rutherford and their contributions to understanding that all matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. The document also describes the discovery of subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons, and how electrons occupy distinct energy levels around the nucleus in an atom.
More from ChemistryFun (7)
Recently uploaded
UiPath Community Day Kraków: Devs4Devs Conference

We are honored to launch and host this event for our UiPath Polish Community, with the help of our partners - Proservartner!
We certainly hope we have managed to spike your interest in the subjects to be presented and the incredible networking opportunities at hand, too!
Check out our proposed agenda below 👇👇
08:30 ☕ Welcome coffee (30')
09:00 Opening note/ Intro to UiPath Community (10')
Cristina Vidu, Global Manager, Marketing Community @UiPath
Dawid Kot, Digital Transformation Lead @Proservartner
09:10 Cloud migration - Proservartner & DOVISTA case study (30')
Marcin Drozdowski, Automation CoE Manager @DOVISTA
Pawel Kamiński, RPA developer @DOVISTA
Mikolaj Zielinski, UiPath MVP, Senior Solutions Engineer @Proservartner
09:40 From bottlenecks to breakthroughs: Citizen Development in action (25')
Pawel Poplawski, Director, Improvement and Automation @McCormick & Company
Michał Cieślak, Senior Manager, Automation Programs @McCormick & Company
10:05 Next-level bots: API integration in UiPath Studio (30')
Mikolaj Zielinski, UiPath MVP, Senior Solutions Engineer @Proservartner
10:35 ☕ Coffee Break (15')
10:50 Document Understanding with my RPA Companion (45')
Ewa Gruszka, Enterprise Sales Specialist, AI & ML @UiPath
11:35 Power up your Robots: GenAI and GPT in REFramework (45')
Krzysztof Karaszewski, Global RPA Product Manager
12:20 🍕 Lunch Break (1hr)
13:20 From Concept to Quality: UiPath Test Suite for AI-powered Knowledge Bots (30')
Kamil Miśko, UiPath MVP, Senior RPA Developer @Zurich Insurance
13:50 Communications Mining - focus on AI capabilities (30')
Thomasz Wierzbicki, Business Analyst @Office Samurai
14:20 Polish MVP panel: Insights on MVP award achievements and career profiling
Coordinate Systems in FME 101 - Webinar Slides

If you’ve ever had to analyze a map or GPS data, chances are you’ve encountered and even worked with coordinate systems. As historical data continually updates through GPS, understanding coordinate systems is increasingly crucial. However, not everyone knows why they exist or how to effectively use them for data-driven insights.
During this webinar, you’ll learn exactly what coordinate systems are and how you can use FME to maintain and transform your data’s coordinate systems in an easy-to-digest way, accurately representing the geographical space that it exists within. During this webinar, you will have the chance to:
- Enhance Your Understanding: Gain a clear overview of what coordinate systems are and their value
- Learn Practical Applications: Why we need datams and projections, plus units between coordinate systems
- Maximize with FME: Understand how FME handles coordinate systems, including a brief summary of the 3 main reprojectors
- Custom Coordinate Systems: Learn how to work with FME and coordinate systems beyond what is natively supported
- Look Ahead: Gain insights into where FME is headed with coordinate systems in the future
Don’t miss the opportunity to improve the value you receive from your coordinate system data, ultimately allowing you to streamline your data analysis and maximize your time. See you there!
Recent Advancements in the NIST-JARVIS Infrastructure

Recent advancements in the NIST-JARVIS infrastructure: JARVIS-Overview, JARVIS-DFT, AtomGPT, ALIGNN, JARVIS-Leaderboard
@Call @Girls Guwahati 🚒 XXXXXXXXXX 🚒 Priya Sharma Beautiful And Cute Girl any...

@Call @Girls Guwahati 🚒 XXXXXXXXXX 🚒 Priya Sharma Beautiful And Cute Girl any Time
For Ad post Mail : adityaroy0215@gmail.com
MYIR Product Brochure - A Global Provider of Embedded SOMs & Solutions

This brochure gives introduction of MYIR Electronics company and MYIR's products and services.
MYIR Electronics Limited (MYIR for short), established in 2011, is a global provider of embedded System-On-Modules (SOMs) and
comprehensive solutions based on various architectures such as ARM, FPGA, RISC-V, and AI. We cater to customers' needs for large-scale production, offering customized design, industry-specific application solutions, and one-stop OEM services.
MYIR, recognized as a national high-tech enterprise, is also listed among the "Specialized
and Special new" Enterprises in Shenzhen, China. Our core belief is that "Our success stems from our customers' success" and embraces the philosophy
of "Make Your Idea Real, then My Idea Realizing!"
Implementations of Fused Deposition Modeling in real world

The presentation showcases the diverse real-world applications of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) across multiple industries:
1. **Manufacturing**: FDM is utilized in manufacturing for rapid prototyping, creating custom tools and fixtures, and producing functional end-use parts. Companies leverage its cost-effectiveness and flexibility to streamline production processes.
2. **Medical**: In the medical field, FDM is used to create patient-specific anatomical models, surgical guides, and prosthetics. Its ability to produce precise and biocompatible parts supports advancements in personalized healthcare solutions.
3. **Education**: FDM plays a crucial role in education by enabling students to learn about design and engineering through hands-on 3D printing projects. It promotes innovation and practical skill development in STEM disciplines.
4. **Science**: Researchers use FDM to prototype equipment for scientific experiments, build custom laboratory tools, and create models for visualization and testing purposes. It facilitates rapid iteration and customization in scientific endeavors.
5. **Automotive**: Automotive manufacturers employ FDM for prototyping vehicle components, tooling for assembly lines, and customized parts. It speeds up the design validation process and enhances efficiency in automotive engineering.
6. **Consumer Electronics**: FDM is utilized in consumer electronics for designing and prototyping product enclosures, casings, and internal components. It enables rapid iteration and customization to meet evolving consumer demands.
7. **Robotics**: Robotics engineers leverage FDM to prototype robot parts, create lightweight and durable components, and customize robot designs for specific applications. It supports innovation and optimization in robotic systems.
8. **Aerospace**: In aerospace, FDM is used to manufacture lightweight parts, complex geometries, and prototypes of aircraft components. It contributes to cost reduction, faster production cycles, and weight savings in aerospace engineering.
9. **Architecture**: Architects utilize FDM for creating detailed architectural models, prototypes of building components, and intricate designs. It aids in visualizing concepts, testing structural integrity, and communicating design ideas effectively.
Each industry example demonstrates how FDM enhances innovation, accelerates product development, and addresses specific challenges through advanced manufacturing capabilities.
Fluttercon 2024: Showing that you care about security - OpenSSF Scorecards fo...

Have you noticed the OpenSSF Scorecard badges on the official Dart and Flutter repos? It's Google's way of showing that they care about security. Practices such as pinning dependencies, branch protection, required reviews, continuous integration tests etc. are measured to provide a score and accompanying badge.
You can do the same for your projects, and this presentation will show you how, with an emphasis on the unique challenges that come up when working with Dart and Flutter.
The session will provide a walkthrough of the steps involved in securing a first repository, and then what it takes to repeat that process across an organization with multiple repos. It will also look at the ongoing maintenance involved once scorecards have been implemented, and how aspects of that maintenance can be better automated to minimize toil.
20240705 QFM024 Irresponsible AI Reading List June 2024

Everything that I found interesting last month about the irresponsible use of machine intelligence
AC Atlassian Coimbatore Session Slides( 22/06/2024)

This is the combined Sessions of ACE Atlassian Coimbatore event happened on 22nd June 2024
The session order is as follows:
1.AI and future of help desk by Rajesh Shanmugam
2. Harnessing the power of GenAI for your business by Siddharth
3. Fallacies of GenAI by Raju Kandaswamy
Transcript: Details of description part II: Describing images in practice - T...

This presentation explores the practical application of image description techniques. Familiar guidelines will be demonstrated in practice, and descriptions will be developed “live”! If you have learned a lot about the theory of image description techniques but want to feel more confident putting them into practice, this is the presentation for you. There will be useful, actionable information for everyone, whether you are working with authors, colleagues, alone, or leveraging AI as a collaborator.
Link to presentation recording and slides: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/details-of-description-part-ii-describing-images-in-practice/
Presented by BookNet Canada on June 25, 2024, with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
“Intel’s Approach to Operationalizing AI in the Manufacturing Sector,” a Pres...

“Intel’s Approach to Operationalizing AI in the Manufacturing Sector,” a Pres...Edge AI and Vision Alliance
For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2024/07/intels-approach-to-operationalizing-ai-in-the-manufacturing-sector-a-presentation-from-intel/
Tara Thimmanaik, AI Systems and Solutions Architect at Intel, presents the “Intel’s Approach to Operationalizing AI in the Manufacturing Sector,” tutorial at the May 2024 Embedded Vision Summit.
AI at the edge is powering a revolution in industrial IoT, from real-time processing and analytics that drive greater efficiency and learning to predictive maintenance. Intel is focused on developing tools and assets to help domain experts operationalize AI-based solutions in their fields of expertise.
In this talk, Thimmanaik explains how Intel’s software platforms simplify labor-intensive data upload, labeling, training, model optimization and retraining tasks. She shows how domain experts can quickly build vision models for a wide range of processes—detecting defective parts on a production line, reducing downtime on the factory floor, automating inventory management and other digitization and automation projects. And she introduces Intel-provided edge computing assets that empower faster localized insights and decisions, improving labor productivity through easy-to-use AI tools that democratize AI.What’s New in Teams Calling, Meetings and Devices May 2024

This is a powerpoint that features Microsoft Teams Devices and everything that is new including updates to its software and devices for May 2024
INDIAN AIR FORCE FIGHTER PLANES LIST.pdf

These fighter aircraft have uses outside of traditional combat situations. They are essential in defending India's territorial integrity, averting dangers, and delivering aid to those in need during natural calamities. Additionally, the IAF improves its interoperability and fortifies international military alliances by working together and conducting joint exercises with other air forces.
Running a Go App in Kubernetes: CPU Impacts

Understanding the impacts of running a containerized Go application inside Kubernetes with a focus on the CPU.
HTTP Adaptive Streaming – Quo Vadis (2024)

Video traffic on the Internet is constantly growing; networked multimedia applications consume a predominant share of the available Internet bandwidth. A major technical breakthrough and enabler in multimedia systems research and of industrial networked multimedia services certainly was the HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) technique. This resulted in the standardization of MPEG Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (MPEG-DASH) which, together with HTTP Live Streaming (HLS), is widely used for multimedia delivery in today’s networks. Existing challenges in multimedia systems research deal with the trade-off between (i) the ever-increasing content complexity, (ii) various requirements with respect to time (most importantly, latency), and (iii) quality of experience (QoE). Optimizing towards one aspect usually negatively impacts at least one of the other two aspects if not both. This situation sets the stage for our research work in the ATHENA Christian Doppler (CD) Laboratory (Adaptive Streaming over HTTP and Emerging Networked Multimedia Services; https://athena.itec.aau.at/), jointly funded by public sources and industry. In this talk, we will present selected novel approaches and research results of the first year of the ATHENA CD Lab’s operation. We will highlight HAS-related research on (i) multimedia content provisioning (machine learning for video encoding); (ii) multimedia content delivery (support of edge processing and virtualized network functions for video networking); (iii) multimedia content consumption and end-to-end aspects (player-triggered segment retransmissions to improve video playout quality); and (iv) novel QoE investigations (adaptive point cloud streaming). We will also put the work into the context of international multimedia systems research.
Quality Patents: Patents That Stand the Test of Time

Is your patent a vanity piece of paper for your office wall? Or is it a reliable, defendable, assertable, property right? The difference is often quality.
Is your patent simply a transactional cost and a large pile of legal bills for your startup? Or is it a leverageable asset worthy of attracting precious investment dollars, worth its cost in multiples of valuation? The difference is often quality.
Is your patent application only good enough to get through the examination process? Or has it been crafted to stand the tests of time and varied audiences if you later need to assert that document against an infringer, find yourself litigating with it in an Article 3 Court at the hands of a judge and jury, God forbid, end up having to defend its validity at the PTAB, or even needing to use it to block pirated imports at the International Trade Commission? The difference is often quality.
Quality will be our focus for a good chunk of the remainder of this season. What goes into a quality patent, and where possible, how do you get it without breaking the bank?
** Episode Overview **
In this first episode of our quality series, Kristen Hansen and the panel discuss:
⦿ What do we mean when we say patent quality?
⦿ Why is patent quality important?
⦿ How to balance quality and budget
⦿ The importance of searching, continuations, and draftsperson domain expertise
⦿ Very practical tips, tricks, examples, and Kristen’s Musts for drafting quality applications
https://www.aurorapatents.com/patently-strategic-podcast.html
BLOCKCHAIN FOR DUMMIES: GUIDEBOOK FOR ALL

Blockchain technology is transforming industries and reshaping the way we conduct business, manage data, and secure transactions. Whether you're new to blockchain or looking to deepen your knowledge, our guidebook, "Blockchain for Dummies", is your ultimate resource.
DealBook of Ukraine: 2024 edition

The DealBook is our annual overview of the Ukrainian tech investment industry. This edition comprehensively covers the full year 2023 and the first deals of 2024.
Recently uploaded (20)
Recent Advancements in the NIST-JARVIS Infrastructure

Recent Advancements in the NIST-JARVIS Infrastructure
@Call @Girls Guwahati 🚒 XXXXXXXXXX 🚒 Priya Sharma Beautiful And Cute Girl any...

@Call @Girls Guwahati 🚒 XXXXXXXXXX 🚒 Priya Sharma Beautiful And Cute Girl any...
MYIR Product Brochure - A Global Provider of Embedded SOMs & Solutions

MYIR Product Brochure - A Global Provider of Embedded SOMs & Solutions
Implementations of Fused Deposition Modeling in real world

Implementations of Fused Deposition Modeling in real world
Fluttercon 2024: Showing that you care about security - OpenSSF Scorecards fo...

Fluttercon 2024: Showing that you care about security - OpenSSF Scorecards fo...
20240705 QFM024 Irresponsible AI Reading List June 2024

20240705 QFM024 Irresponsible AI Reading List June 2024
AC Atlassian Coimbatore Session Slides( 22/06/2024)

AC Atlassian Coimbatore Session Slides( 22/06/2024)
Transcript: Details of description part II: Describing images in practice - T...

Transcript: Details of description part II: Describing images in practice - T...
“Intel’s Approach to Operationalizing AI in the Manufacturing Sector,” a Pres...

“Intel’s Approach to Operationalizing AI in the Manufacturing Sector,” a Pres...
What’s New in Teams Calling, Meetings and Devices May 2024

What’s New in Teams Calling, Meetings and Devices May 2024
Quality Patents: Patents That Stand the Test of Time

Quality Patents: Patents That Stand the Test of Time
Chapter 10
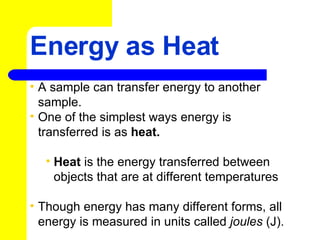
- 1. Energy as Heat A sample can transfer energy to another sample. One of the simplest ways energy is transferred is as heat. Heat is the energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures Though energy has many different forms, all energy is measured in units called joules (J).
- 2. Temperature is a measure of how hot (or cold) something is; specifically, a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in an object. When samples of different temperatures are in contact, energy is transferred from the sample that has the higher temperature to the sample that has the lower temperature.
- 3. Temperature is an intensive property, which means that the temperature of a sample does not depend on the amount of the sample. Heat is an extensive property, which means that the amount of energy transferred as heat by a sample depends on the amount of the sample.
- 4. Changes in energy content can be determined. If 73 J of energy enter a piece of silver and no change in pressure occurs, we know that the enthalpy of the silver has increased by 73 J. Enthalpy, which is represented by the symbol H, is the total energy content of a sample.
- 5. Enthalpy is the sum of the internal energy of a system plus the product of the system’s volume multiplied by the pressure that the system exerts on its surroundings.
- 6. The particles in a sample are in constant motion. The enthalpy of a sample includes the total kinetic energy of its particles. Both the total and average kinetic energies of a substance’s particles are important to chemistry, because these quantities account for every particle’s kinetic energy.
- 7. Molar heat capacity can be used to determine the enthalpy change of a sample. The molar heat capacity of a pure substance is the energy as heat needed to increase the temperature of 1 mol of the substance by 1 K. Molar heat capacity has the symbol C and the unit J/K mol.
- 8. When a substance receives energy in the form of heat, its enthalpy increases and the kinetic energy of the particles that make up the substance increases. The direction in which any particle moves is not related to the direction in which its neighboring particles move. The motions of these particles are random .
- 9. Because enthalpy is the total energy of a system, it is an important quantity. The only way to measure energy is through a change. Absolute values cannot be measured. The enthalpy change for one mole of a pure substance is called molar enthalpy change.
- 10. When a pure substance is only heated or cooled, the amount of heat involved is the same as the enthalpy change. H = q for the heating or cooling of substances
- 11. A change in enthalpy during a reaction depends on many variables. Temperature is one of the most important variables. To standardize the enthalpies of reactions, data are often presented for reactions in which both reactants and products have the standard thermodynamic temperature of 25.00 C or 298.15 K.
- 12. Chemists usually present a thermodynamic value for a chemical reaction by using the chemical equation. This equation shows that when 0.5 mol of H 2 reacts with 0.5 mol of Br 2 to produce 1 mol HBr and all have a temperature of 298.15 K, the enthalpy decreases by 36.4 kJ.
- 13. For the H 2 and Br 2 reaction, in which H is negative, the total energy of the reaction decreases. The energy is released as heat by the system. If the reaction was endothermic, energy in the form of heat would be absorbed by the system and the enthalpy would increase.
- 14. The experimental measurement of an enthalpy change for a reaction is called calorimetry. Calorimetry is the measurement of heat-related constants, such as specific heat or latent heat Combustion reactions are always exothermic. The enthalpy changes of combustion reactions are determined using a bomb calorimeter. A calorimeter Is a device used to measure the heat absorbed or released in a chemical or physical change
- 16. Inside the pressurized oxygen atmosphere of a bomb calorimeter, most organic matter, including food, fabrics, and plastics, will ignite easily and burn rapidly. Sample sizes are chosen so that there is excess oxygen during the combustion reactions. Under these conditions, the reactions go to completion and produce carbon dioxide, water, and possibly other compounds.
- 17. Any two processes that both start with the same reactants in the same state and finish with the same products in the same state will have the same enthalpy change. Hess’s law states that the overall enthalpy change in a reaction is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps in the process.
- 18. When phosphorus is burned in excess chlorine 4 mol of phosphorus pentachloride, PCl 5 , is synthesized. P 4 ( s ) + 10Cl 2 ( g ) 4PCl 5 ( g ) H = -1596 kJ Phosphorus pentachloride may also be prepared in a two-step process. Step 1: P 4 ( s ) + 6Cl 2 ( g ) 4PCl 3 ( g ) H = -1224 kJ Step 2: PCl 3 ( g ) + Cl 2 ( g ) PCl 5 ( g ) H = -93 kJ
- 19. The second reaction must take place four times for each occurrence of the first reaction in the two-step process. This two-step process is more accurately described by the following equations. P 4 ( s ) + 6Cl 2 ( g ) 4PCl 3 ( g ) H = -1224 kJ 4PCl 3 ( g ) + 4Cl 2 ( g ) 4PCl 5 ( g ) H = 4(-93 kJ) = -372 kJ
- 20. So, the total change in enthalpy by the two-step process is as follows: (-1224 kJ) + (-372 kJ) = -1596 kJ This enthalpy change, H, for the two-step process is the same as the enthalpy change for the direct route of the formation of PCl 5 . This example is in agreement with Hess’s law.
- 21. The enthalpy of the formation of CO, when CO 2 and solid carbon are reactants, is found using the equations below. 2C( s ) + O 2 ( g ) 2CO( g ) H = -221 kJ C( s ) + O 2 ( g ) CO 2 ( g ) H = -393 kJ You cannot simply add these equations because CO 2 would not be a reactant.
- 22. Adding the two equations gives the equation for the formation of CO by using CO 2 and C. 2C( s ) + O 2 ( g ) 2CO( g ) H = – 221 kJ CO 2 ( g ) C( s ) + O 2 ( g ) H = 393 kJ 2C( s ) + O 2 ( g ) + CO 2 ( g ) 2CO( g ) + C( s ) + O 2 ( g ) H = 172 kJ Oxygen and carbon that appear on both sides of the equation can be canceled. C( s ) + CO2( g ) 2CO( g ) H = 172 kJ
- 23. The enthalpy change in forming 1 mol of a substance is called the standard enthalpy of formation of the substance, The values of the standard enthalpies of formation for elements are 0. The following equation is used to determine the enthalpy change of a chemical reaction from the standard enthalpies of formation. H reaction = H products - H reactants