methods_of_reproduction_ppt-2 (1).ppt
- 1. Methods of Reproduction Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
- 2. Asexual Reproduction: requires only 1 parent and the offspring are an exact copy of the parent---a clone
- 3. Asexual Reproduction: • Organisms that reproduce asexually cannot develop much variety, because they are “copying” the original organism exactly. • This does not allow for evolution of the species. Each organism is the exact same as its parent. • This process take a relatively short period of time. And can produce 1-100s of offspring.
- 4. Methods of asexual reproduction: Binary fission Budding Fragmentation Parthenogenesis
- 5. Binary fission Single-celled organisms (Amoeba, paramecium, euglena) which use asexual reproduction can do so simply by dividing into two equal halves. This is called binary fission.
- 6. • When conditions are good, such as plenty of water, food, right temperatures, etc., binary fission is a very effective way of producing many, many offspring. • For example, the cell of a Paramecium can divide, grow, and divide again in the space of 8 hours.
- 7. Budding- an offspring grows out of the body of the parent. Hydra Budding offspring Cactus Budding
- 8. Budding cont. Green plants are quite sophisticated in their methods of asexual reproduction. Offspring may be produced by runners, bulbs, rhizomes or tubers.
- 9. Regeneration In this form, the body of the parent breaks into distinct pieces, each of which can produce an offspring. Pieces of coral broken off in storms can grow into new colonies. A new starfish can grow from one detached arm.
- 10. Fragmentation In this form, the organism fragments into smaller pieces and each piece forms a new organism identical to its parent. A flat worm will break into distinct pieces and each will regrow another smaller organism.
- 11. Fragmentation- plant cuttings Some plants can grow from cutting them up and replanting them.
- 12. Sporulation In this form, the parent organism produces tiny spores that it releases. They will then create an exact copy of the original organism without fertilization. The mushroom is releasing unfertilized spores
- 13. Parthenogenesis
- 14. Asexual Reproduction: Advantages of Asexual Reproduction • uses less energy (it is not necessary to find a partner) • offspring is usually well adapted to its environment because of the success of its parent
- 15. Asexual Reproduction: Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction • the species does not adapt at all or adapts very slowly when circumstances change • an asexual species runs the risk of suddenly disappearing because of a catastrophe that affects all organisms
- 27. What is sexual reproduction? • Requiring 2 parents – male and female (egg & sperm) • The egg and sperm join (zygote) to form an entirely new organism • Offspring are different from the parent organism. • This process creates a variety of genetic make-up which is the driving force behind evolution.
- 28. Sexual Reproduction • Sexual reproduction produces a greater chance of variation within a species than asexual reproduction would. • This variation improves the chances that a species will adapt to his environment and survive.
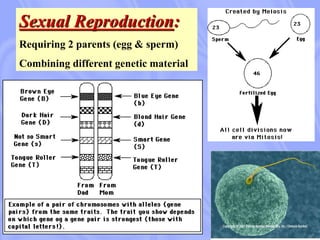
- 29. Sexual Reproduction: Requiring 2 parents (egg & sperm) Combining different genetic material
- 30. Sexual Reproduction: Requiring 2 parents (egg & sperm) Combining different genetic material
- 31. Sexual Reproduction Adv. • increases the genetic variability in organisms of the same species and even within the offspring of one couple • in the long run, allows the best adaptations to be widespread within a species, especially in changing circumstances
- 32. Sexual Reproduction Adv. • the variability of organisms within a species guarantees that a higher proportion will survive in perilous circumstances
- 33. Sexual Reproduction Dis. • finding a reproductive partner and producing gametes demands the output of a lot of energy • not only do you need two gametes for fertilization, one has to be male, the other Female • genetic “errors” happen more frequently because meiosis is more complex than mitosis and diploid organisms have more chromosomes to double
- 34. Methods of sexual reproduction: Pollination External Fertilization Internal Fertilization
- 35. Pollen is produced in the male organs of the flowers - anthers. Pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the anthers to the female organs by wind or by animals. If the female stigma is receptive to a pollen grain, the pollen produces a pollen tube, which grows through the female tissue to the egg, where fertilization takes place by the sperm nucleus. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- 36. External Fertilization • External fertilization usually requires a medium such as water, which the sperms can use to swim towards the egg cell. External fertilization usually occur in fish and amphibians. • The females lay the eggs in the water and the male squirts the sperm in the same area.
- 37. Internal Fertilization • Fertilization occurs within the female. • Internal fertilization occurs in mammals, insects, birds, reptiles. – Mammals (gorillas, lions, elephants, rats, zebras, and dolphins have live births) – Insects, birds, reptiles lay eggs
- 38. Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction • Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. • Sexual reproduction results in offspring that are genetically different from the parent organisms.