Mobility characteristics, costs, and issues of the poor and vulnerable groups
- 1. RANDOLPH D. CARREON DONNA LOU O. MOSCARE-CARREON with generous support from
- 2. Objectives This Study sought to understand the nature of the transport needs, accessibility, mobility and transport costs of the poor and vulnerable groups. Specifically, this aimed to: establish the travel demand patterns of the poor and vulnerable groups; look qualitatively into the efficiency of the public transport system vis- à-vis the needs of the poor and the vulnerable groups; estimate the cost of transport of the poor; estimate the actual and desired cost of transport of those within the vulnerable groups; and examine other non–quantifiable costs, if any, incurred by the vulnerable groups.
- 3. Study Areas/Groups Poor Communities Purok Centro, Barangay Old Balara (414 Households) Area H, Barangay Bagong Pag-asa (1,415 Households) Purok 13, Barangay Payatas (197 Households) Vulnerable Groups Senior Citizens Persons With Disabilities Women BPO Workers
- 4. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Vehicle Ownership Rate Motorized Non–Motorized Study Area 4W 2W Bike Other Area H 3.03% 3.03% 0.00% 1.01% Purok Centro 5.43% 9.30% 6.98% 0.78% Purok 13 1.02% 8.16% 3.06% 0.00%
- 5. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Person Trip Generation Rate Per Household Total Person Home-Generated Person Trip per Study Area Trips per (HG) Trips HG Trip Household Area H 1.58 4.09 6.44 Purok Centro 1.90 4.06 7.70 Purok 13 1.89 3.66 6.90
- 6. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Person Trip Generation Per Area Daily Annual Study Area Home- Home- Home- Total Person Generated Generated Generated Trips Trips Trips Trips Area H 2,205 9,014 529,315 2,163,288 Purok Centro 786 3,189 188,600 765,440 Purok 13 372 1,360 89,307 326,457
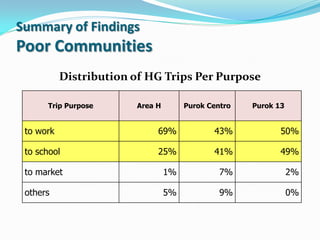
- 7. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Distribution of HG Trips Per Purpose Trip Purpose Area H Purok Centro Purok 13 to work 69% 43% 50% to school 25% 41% 49% to market 1% 7% 2% others 5% 9% 0%
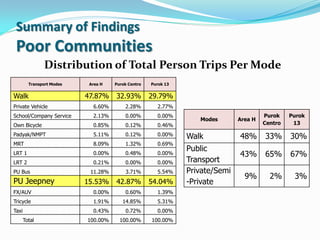
- 8. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Distribution of Total Person Trips Per Mode Transport Modes Area H Purok Centro Purok 13 Walk 47.87% 32.93% 29.79% Private Vehicle 6.60% 2.28% 2.77% School/Company Service 2.13% 0.00% 0.00% Purok Purok Modes Area H Own Bicycle 0.85% 0.12% 0.46% Centro 13 Padyak/NMPT 5.11% 0.12% 0.00% Walk 48% 33% 30% MRT 8.09% 1.32% 0.69% Public LRT 1 0.00% 0.48% 0.00% 43% 65% 67% LRT 2 0.21% 0.00% 0.00% Transport PU Bus 11.28% 3.71% 5.54% Private/Semi 9% 2% 3% PU Jeepney 15.53% 42.87% 54.04% -Private FX/AUV 0.00% 0.60% 1.39% Tricycle 1.91% 14.85% 5.31% Taxi 0.43% 0.72% 0.00% Total 100.00% 100.00% 100.00%
- 9. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Factors Considered in Mode Choice Rank Area H Purok Centro Purok 13 1 Affordability Affordability Affordability Short Travel Short Travel Short Travel 2 Duration Duration Duration / 3 Cleanliness Convenience Driving Style Availability of Availability of 4 Cleanliness Mode Mode 5 Driving Style Driving Style Convenience
- 10. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Percentage Share of Transport Cost to Total Expenses Rent-Free Renter Ownership Annual Average Area H (Barangay Bagong Pag-asa) Non Vehicle Owner 4.66% 5.75% Motor Vehicle Owner 10.97% 9.62% Purok Centro (Barangay Old Balara) Non Vehicle Owner 4.23% 6.39% Motor Vehicle Owner 12.24% 11.53% Purok 13 (Barangay Payatas) Non Vehicle Owner 7.67% - Motor Vehicle Owner 7.01% -
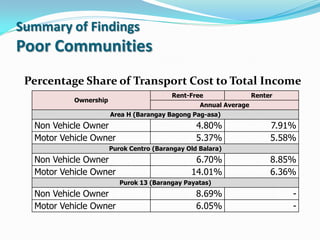
- 11. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Percentage Share of Transport Cost to Total Income Rent-Free Renter Ownership Annual Average Area H (Barangay Bagong Pag-asa) Non Vehicle Owner 4.80% 7.91% Motor Vehicle Owner 5.37% 5.58% Purok Centro (Barangay Old Balara) Non Vehicle Owner 6.70% 8.85% Motor Vehicle Owner 14.01% 6.36% Purok 13 (Barangay Payatas) Non Vehicle Owner 8.69% - Motor Vehicle Owner 6.05% -
- 12. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Non – Quantifiable Costs Safety Exposure to Pollution The need to sacrifice other necessities to meet transport cost requirements During times of financial difficulties, to meet transport requirement, households resort to sacrificing other cost items such as (i) food, (ii) electric and water bills, and (iii) health care.
- 13. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Primary Mobility Problems Purok Mobility Problems Area H Purok 13 Centro high transport cost 75.00% 97.35% 74.49% insufficient supply of public transport/MRT 2.00% 0.00% 2.04% lack of pedestrian facilities/sidewalks 1.00% 0.00% 1.02% non-operational stoplights 1.00% 0.00% 1.02% pollution 1.00% 0.88% 1.02% poorly maintained vehicles 3.00% 0.00% 3.06% traffic congestion 10.00% 1.77% 10.20% undisciplined loading and unloading of passengers 2.00% 0.00% 2.04% vehicle accidents 5.00% 0.00% 5.10%
- 14. Summary of Findings Poor Communities Proposed Solutions Purok Purok Proposed Solutions Area H Centro 13 work for additional income 28.57% 54.29% 29.41% borrow money 1.43% 11.43% 1.47% lower fare 14.29% 5.71% 11.76% proper budgeting 0.00% 11.43% 0.00% reduce other expenses 4.29% 4.76% 4.41% salary increase 2.86% 0.95% 2.94% save money 5.71% 2.86% 5.88% walk 5.71% 0.00% 5.88%
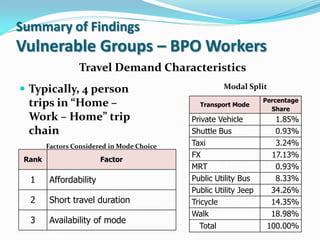
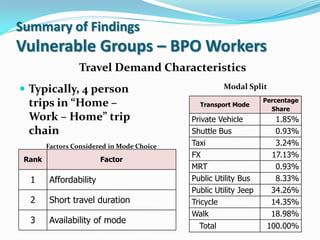
- 15. Summary of Findings Vulnerable Groups – BPO Workers Travel Demand Characteristics Typically, 4 person Modal Split Percentage trips in “Home – Transport Mode Share Work – Home” trip Private Vehicle 1.85% chain Shuttle Bus 0.93% Factors Considered in Mode Choice Taxi 3.24% FX 17.13% Rank Factor MRT 0.93% 1 Affordability Public Utility Bus 8.33% Public Utility Jeep 34.26% 2 Short travel duration Tricycle 14.35% Walk 18.98% 3 Availability of mode Total 100.00%
- 16. Summary of Findings Vulnerable Groups – BPO Workers Travel Demand Characteristics Typically, 4 person Modal Split Percentage trips in “Home – Transport Mode Share Work – Home” trip Private Vehicle 1.85% chain Shuttle Bus 0.93% Factors Considered in Mode Choice Taxi 3.24% FX 17.13% Rank Factor MRT 0.93% 1 Affordability Public Utility Bus 8.33% Public Utility Jeep 34.26% 2 Short travel duration Tricycle 14.35% Walk 18.98% 3 Availability of mode Total 100.00%
- 17. Summary of Findings Vulnerable Groups – BPO Workers Direct Costs Share of Transport Cost to Total Income Vehicle Owners: 5% Non Vehicle Owners: 13% Non – Quantifiable Costs Safety Exposure to Pollution
- 18. Summary of Findings Vulnerable Groups – PWDs Preferred Public Transport Modes: Tricycle, Taxis, and PUJ Tricycles and Taxis provide door-to-door service Incentives provided through section 27 of the Magna Carta for Persons with Disability (Republic Act 7277) Entitled to lower PT Fares (20% discount) However, not all PWDs are aware of this privilege
- 19. Summary of Findings Vulnerable Groups – PWDs PWDs view pedestrian facilities as inadequate in responding to their needs. On overpasses, PWDs think that: the locations are inappropriate and were selected mainly for the benefit of private establishments; the steps are too high making it difficult for them to climb; it needs cover; and the location is too distant.
- 20. Summary of Findings Vulnerable Groups – Senior Citizens Preferred Public Transport Modes: Tricycle, Taxis, and PUJ Tricycles and Taxis provide door-to-door service Incentives provided through Section 2 of the Expanded Senior Citizens Act of 2010 (Republic Act 9994) Entitled to lower PT Fares (20% discount)
- 21. Summary of Findings Vulnerable Groups – Senior Citizens They stated that it is hard to go up overpasses and it is not easy to walk along narrow sidewalks The law providing 20% discount to senior citizens is highly appreciated. However, concerns are raised on the implementation of the discount as some drivers refuse to accept the discounted fare.
- 22. Summary of Findings Vulnerable Groups – Women Preferred Public Transport Modes: Tricycle, PUJs, and walking Women are subject to the same cost of transport as any other regular commuter Issues on pedestrian facilities especially overpasses: height and steepness, location, condition and need for repair, lack of cover, and lack of lights at night
- 23. Summary of Findings Qualitative Assessment of Public Transport - Poor The residents on the three (3) study areas find the present public transport system as “somehow satisfactory”. PT terminals are generally regarded as accessible, clean, safe, and comfortable. There is, however, a general perception of lack of facilities in the PT terminals in terms of the inter–modal network, there is much to be desired. Based on these factors, walkability is viewed as “somehow satisfactory”
- 24. Summary of Findings Qualitative Assessment of Public Transport – BPO Workers BPO Workers generally view public transport as “just right” to “good”. Taxis and FX received the highest ratings. Public transport efficiency with consideration on the (i) fare, (ii) availability of mode, and (iii) travel time is generally regarded as “just right” PT terminals are generally regarded as accessible, clean, safe, and comfortable. There is a general perception of lack of facilities in the terminals In terms of connectivity, the public transport network is satisfactory Walkability is viewed as “generally satisfactory”.
- 25. Summary of Findings Qualitative Assessment of Public Transport – PWDs, Senior Citizens and Women PWDs, SCs, and Women generally view public transport modes as acceptable and ‘just right’ Some units, however, are already dilapidated, worn out and are in poor condition. The tricycles and taxis are the most preferred because these modes enable them to travel faster and offer door to door service. PUJs are also preferred due to the relatively low fare. PT terminals lack facilities except for terminals of mass transit systems such as the MRT and LRT.
- 26. Recommended Next Step further researches to expand the scope of this Study to other areas in Metro Manila to come up with a more comprehensive understanding of the mobility of the urban poor to address the mobility issues of the urban poor and the vulnerable groups