Sem 3 size reduction
- 1. SIZE REDUCTION By Yogeshwary Bhongade Assistant Professor Gondia College of Pharmacy, Gondia.
- 2. CONTENTS Introduction Objectives Methods of size reduction Advantages of size reduction Disadvantages of size reduction Mechanism of size reduction Laws governing to the size reduction Principle of Size Reduction, Construction, working and uses of following- Hammer mill Ball mill Fluid Energy Mill Edge Runner Mill End Runner Mill
- 3. SIZE REDUCTION Definition: Size reduction is the process of reducing large solid units or substances into the smaller unit mass, course particles or fine particles. The process also termed as comminution or diminution or pulverisation Reduction of particle size above 40 mm- machine known as Crushers and below it machine known as Mill
- 4. CONT. Degree of size reduction depends upon the machinery, methods, duration to which size of particle is reduced. Eg. To reduce particle in very small size then longer duration will be required and vice versa.
- 5. CONT. Usually size reduction in material processing industry carry out in order to- To increase the surface area Break material into very small particles in order to separate the desired particle from the mixture of two constituent To achieve the intimate mixing
- 6. OBJECTIVES OF SIZE REDUCTION Size reduction leads to increase of surface area. Pharmaceutical capsules, insufflations (i.e. powders inhaled directly into the lungs), suppositories and ointments require particles size to be below 60 mm size. To increase the therapeutic effectiveness of certain drugs by reducing the particle size. Eg. Griseofulvin (half of the dose of drug required after size reduction) Size reduction produces particles in narrow size range. Mixing of powders with narrow size range is easier. The mixing of several solid ingredients is easier and more uniform if the ingredients are reduced to same particle size.
- 7. CONT. Pharmaceutical suspensions require finer particle size. It reduces rate of sedimentation. The stability of emulsions is increased by decreasing the size of the oil globules. All the ophthalmic preparations and preparations meant for external application to the skin must be free from gritty particles to avoid irritation of the area to which they are applied. The rate of absorption of a drug depends on the dosage form, route of administration and particle size. The smaller the particle size, quicker and greater will be rate of absorption. The physical appearance of ointments, pastes and creams can be improved by reducing its particle size
- 8. METHOD OF SIZE REDUCTION Grinding and cutting This method employed for the solid substances Emulsification or Atomization This method employed for the for liquid phase
- 9. ADVANTAGES Effective particle size mixing Increase surface area Increase flow of powder material Effective Extraction Effective drying Enhance the viscosity Improve bioavailability of drug
- 10. DISADVANTAGES Decomposition of thermo labile substances Chances of contamination Poor mixing Noisy environment
- 11. MECHANISM OF SIZE REDUCTION Impact - A sudden force occurring when one object collides with another Attrition - Frictional force applied to the material due to the opposing motion of two hard surfaces Shear - A force applied when the material is compressed between the edges of two hard surfaces moving tangentially Compression - Force applied by the faces of hard surfaces moving towards each other.
- 12. LAWS GOVERNING SIZE REDUCTION Various theories are there to establish a relationship between energy input and the degree of size reduction. Theories of size reduction Kick’s Law Rittinger’s Law Bond’s Law
- 13. KICK’S LAW According to Kick’s Law- Energy require to reduce size of particle is proportional to ratio of initial size of a typical dimension to the final size of dimension. Where E : Energy require per mass of feed Kk : Kick’s Constant di : Diameter of initial particles dn : Diameter of new particles di/dn : Ratio of size reduction
- 14. APPLICATION For compression of large particle Kick’s theory is useful
- 15. RITTINGER’S LAW According to this law- The energy (E) required for reduction in particle size of a solid is directly proportional to the increase in surface area. E= KR (Sn- Si) Where, E - Amount of energy KR - Rittinger’ constant Sn - New specific surface area Si - Initial surface area
- 16. APPLICATION Applicable to brittle material under going fine milling This theory ignore deformation before fracture
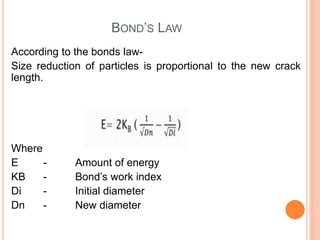
- 17. BOND’S LAW According to the bonds law- Size reduction of particles is proportional to the new crack length. Where E - Amount of energy KB - Bond’s work index Di - Initial diameter Dn - New diameter
- 18. APPLICATIONS The theory is useful for rough mill The work index is useful for comparing efficient milling operations
- 19. CLASSIFIATION OF SIZE REDUCTION EQUIPMENTS Machines Crusher Grinder Ultrafine Grinders Cutting Machine
- 20. A. Crusher ex. Edge runner mill. End runner mill. B. Grinder 1)Impact mill. ex-Hammer mill. 2)Rolling-compression. ex-Roller mill. 3)Attrition mills ex-Attrition mill. 4)Tumbling mills. ex-Ball mill. C. Ultrafine grinder ex-Fluid energy mill. D.Cutting machine ex- Cutter mill.
- 21. HAMMER MILL Principle: It work on principle of impact (material is more or less stationary and is hit by objeect moving in high speed) Construction
- 22. CONT. It consist of stout metal casing enclosed a centre shaft to which more than four swinging hammers are attached lower part of the casing consist of screen, through which material can pass in receiver. Working: Material is put into hopper. Due to rotation rotation of hammer,he material is powdered into desired size. https://youtu.be/Y93rf2cNloI
- 23. PHARMACEUTICAL USES OF HAMMER MILL 1. It is used in pharmaceutical industries to process wet or dry granulations and disperse powder mixtures. 2. It is used in milling pharmaceutical raw materials, herbal medicine, and sugar. 3. It is used in powdering of barks, leaves, and roots of medicinal plants. 4. It is applied in the milling of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API), excipients, etc.
- 24. ADVANTAGES OF HAMMER MILL 1. It produces specified top size without the need for a closed- circuit crushing system. 2. It produces relatively numerous size distributions with a minimum of fines due to self-classification. 3. It has a high reduction ratio and high capacity whether used for primary, secondary or tertiary grinding. 4. Relatively reasonable energy requirements. 5. Brittle materials are best fractured by impact from blunt hammers. 6. It is capable of grinding many different types of materials 7. The machine is easy to install and operate and its operation is continuous.
- 25. CONT. 8. It occupies small space. 9. It is easy to maintain and clean. 10. It is inexpensive. 11. Its ease of manufacture allows easier local construction.
- 26. DISADVANTAGES OF HAMMER MILL 1. Not recommended for the fine grinding of very hard and abrasive material due to excessive wear. 2. Not suitable for low-melting sticky or plastic-like material due to heat generation in the mill head as a result of mill fouling. 3. The mill may be choked if the feed rate is not controlled, leading to damage. 4. Presence of foreign materials like stone or metals which finds its way into the material due to inadequate garbling process 5. There is a possibility of clogging of the screen.
- 27. BALL MILL Principle: it work on principle of impact and attrition A ball mill also known as pebble mill or tumbling mill is a milling machine that consists of a hallow cylinder containing balls mounted on a metallic frame such that it can be rotated along its longitudinal axis. The balls which could be of different diameter occupy 30 – 50 % of the mill volume and its size depends on the feed and mill size. The large balls tend to break down the coarse feed materials and the smaller balls help to form fine product by reducing void spaces between the balls. Ball mills grind material by impact and atrrition.
- 28. BALL MILL Construction: consist of two hollow cylinder which is mounted on metallic frame in such a way that it can be rotated on its longitudinal axis.
- 29. BALL MILL Working drug to be ground put into the cylinder of mill and rotated. speed of rotation is very important low speed-mass od ball is side or role over each other only negligible ammount of size reduction occures.(a) high speed- balls will be thrown out to the wall by centrifugation(b) 2/3rd speed- centrifugal force occures, ball are carried almost to the top of the mill and then fall in.(c) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zUtQZtfVJN8
- 30. CONT. The degree of milling in a ball mill is influenced by; a. Residence time of the material in the mill chamber. b. The size, density, and number of the balls. c. The nature of the balls (hardness of the grinding material) d. Feed rate and feed level in the vessel. e. Rotation speed of the cylinder.
- 31. PHARMACEUTICAL USES OF BALL MILL 1. The small and average capacity ball mills are used for the final grinding of drugs or for grinding suspensions. 2. The maximum capacity ball mills are used for milling ores prior to manufacture of pharmaceutical chemicals.
- 32. ADVANTAGES OF BALL MILLS 1. It produces very fine powder (particle size less than or equal to 10 microns). 2. It is suitable for milling toxic materials since it can be used in a completely enclosed form. 3. Has a wide application. 4. It can be used for continuous operation.
- 33. DISADVANTAGES OF BALL MILLS 1. Contamination of product may occur as a result of wear and tear which occurs principally from the balls and partially from the casing. 2. High machine noise level especially if the hollow cylinder is made of metal, but much less if rubber is used. 3. Relatively long milling time. 4. It is difficult to clean the machine after use.
- 34. FLUID ENERGY MILL Principle: Works on the principle of Impact and Attrition Construction: consist of loop of pipe (20- 200 mm diameter depending on height of loop which may be upto 2 m) There are an inlet for food and series of nozel for inlet of air or an ineret gas also have outlet with classifier which allow the aie to escap but prevent the particles to pass until they become sufficiently fine
- 35. FLUID ENERGY MILL Working through nozzles air or intert gas introduce at very high pressure. solids are introduce through the inlet. Due to high degree of turbulence, impact and attritional forces occurse between the particles. The fine particles are collected through a classifier. Fluid energy mill reduces the partile to 1 to 20 micron. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iWgRm5LSJek
- 36. PHARMACEUTICAL USES OF FLUIDIZED ENERGY MILL a. Fluidized energy is used in milling thermolabile materials b. It is the choice of mill when a higher degree of drug purity is required c. Fluidized energy mill is used for the fine grinding of frits, Kaolin, Zircon, titanium, and calcium, alumina.
- 37. ADVANTAGES OF FLUIDIZED ENERGY MILL 1. The machine has no moving parts and thus the tendency of contamination due to wear of parts is minimized. 2. The equipment is easily sterilized. 3. Small particle size (between 2 and 10) is usually obtained at the end of milling. 4. Thermolabile materials can be milled with little degradation since the heat produced by the process is nullified by the cooling effect of the expansion of the compressed gas
- 38. DISADVANTAGES OF FLUIDIZED ENERGY MILL 1. Tendency of forming aggregates or agglomerates after milling. 2. Generation of amorphous content due to high energy impact. 3. Formation of ultra-fine particles
- 39. EDGE RUNNER MILL Principle: Crushing is the principle for edge runner mill. Edge runner mill, also known as Chilean mill or Roller stone mill. Construction Consists of one or two heavy steel or granite rollers mounted on a horizontal shaft and turned round a central vertical shaft on a bed of steel or granite and they revolved on axis of central shaft. The stones may vary from 0.5 to 2.5 m in diameter, the larger size weighing up to about 6 tonnes.
- 40. EDGE RUNNER MILL Working The material to be ground is kept in the path of the runner by scrapers. The reduction is partly due to crushing: by the weight of the stones, but more to friction between the surfaces of contact between the runners and the bed stone.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DPggUMaktjk
- 41. EDGE RUNNER MILL Uses Although the edge runner mills are gradually being replaced by more sophisticated machines they are still used, particularly for reducing extremely tough and fibrous materials – roots and barks to the form of powder. used to grind most of drugs to fine poweder but require more floor space
- 42. END RUNNER MILL Principle: Impact and shear is the principle of end runner mill Construction: The end-runner mill consists of a weighted pestle mounted eccentrically in a ceramic, granite or metal mortar, which is rotated by a motor.
- 43. END RUNNER MILL Working End runer mill provides moderately fine powder and operates successfully with fibrous materials, bark, woods fruits, leaves, etc. The pestle rotates by friction and is free to rise and fall in the mortar so that its grinding action involves both impact and shear, the material being crushed and rubbed between it and the rotating mortar. Spring-loaded scrapers ensure that material is constantly returned to the grinding area and at the end of the operation the pestle can be swung clear of the mortar to facilitate emptying and cleaning.
- 44. END-RUNNER MILL AND EDGE-RUNNER MILL Advantages of End-runner mill and Edge-runner mill 1. It produces fine particles 2. Requires less attention during the milling operation Disadvantages of End-runner mill and Edge-runner mill 1. It is not suitable for milling sticky materials 2. Machine noise leading to noise pollution
- 45. FACTOR AFFECTING SIZE REDUCTION Hardness It is easier to break soft material than hard materials. Toughness Fibrous materials are tough. These are tough in nature. A soft, tough material has more difficulty than a hard, brittle substance. Ex: Rauwlfia, Ginger. Here cutters can be used. Stickiness Stickiness causes lots of difficulties during size reduction. This is due to adhesion of material to grinding surface or sieve surface of mill.
- 46. FACTOR AFFECTING SIZE REDUCTION Material Structure Material having special structure shows problem during size reduction eg. Vegetable produce circular structure produce large fibrous particle on size reduction Softening Temperature Waxy substances such as steric acids or drugs containing oil or fat, become softened during the size reduction. So if heat generated this can be avoided by cooling mill.
- 47. FACTOR AFFECTING SIZE REDUCTION Friable material. These tend to fracture along well defined planes. Purity Required Various mills used for size reduction often cause the grinding surfaces to wear off and thus impurities come in the powder.
- 48. FACTOR AFFECTING SIZE REDUCTION Melting point Waxy substances, fats and oils are softened during size reduction due to heat generated. This is avoided by cooling the mill and the substance. Moisture Content Hygroscopic - Certain substances absorb moisture content rapidly. This wet mass hampers the milling process. Ex: Potassium carbonate. Closed system such as porcelain ball mill is used.
- 49. FACTOR AFFECTING SIZE REDUCTION Physiological effect Some drugs are very potent. During their particle size reduction in mill dust may have produce which may have effect on operator. To avoid dust closed mill can be used Ratio of feed size to product size Small feed size required to get fine particle. Bulk density Output of size reduction of material in a machine, depends on bulk density of substances.
- 50. GENETRAL CHARACTERISTICS OF MILLS Sr. No. Name of mill Action/ Principle Product size Uses Not used for 1 Cutter Mill Cutting 20- 80 Mesh Fribrous, Crude(Animal and Vegetavle Drug) Friable Material 2 Roller Mill Compression 20- 200 Mesh Soft Matrial Abrasive material 3 Hammer Mill Impact 4-325 Mesh Almost all ddrug Abrasive material 4 Ball Mill Attrition & Impact 20- 200 Mesh Brittle Drug Soft material 5 Fluid Energy Mill Attrition & Impact 1-30 Mesh Moderately hard and friabl material Soft & sticky material 6 Edge Runner Mill Crushing & Sharing 20-80 Mesh Almost all drug Sticky Material
- 51. THANK YOU