Let’s create an ArrayList object named elements which stores string elements:
import java.util.ArrayList; // Importing the ArrayList class from the java.util package
// Creating an ArrayList to store String elements
ArrayList<String> elements = new ArrayList<String>();
Java ArrayList is a part of the Java collections framework and it is a class of java.util package. It provides us with dynamic arrays in Java. Though, it may be slower than standard arrays but can be helpful in programs where lots of manipulation in the array is needed. This class is found in java.util package. The main advantage of ArrayList in Java is, that if we declare an array then we need to mention the size, but in ArrayList, it is not needed to mention the size of ArrayList. If you want to mention the size then you can do it.
What is ArrayList in Java?
ArrayList is a Java class implemented using the List interface. Java ArrayList, as the name suggests, provides the functionality of a dynamic array where the size is not fixed as an array. Also, as a part of the Collections framework, it has many features not available with arrays.
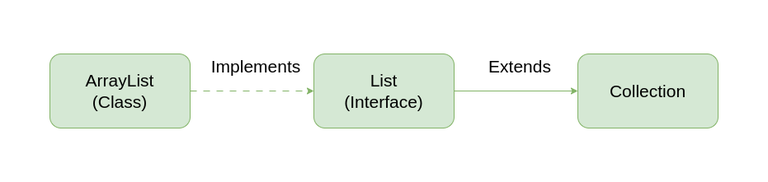
Illustration:
Let us check on the ArrayList with the Integer Object type Stored in it with a image.

Java ArrayList Example
Example 1: The following implementation demonstrates how to create and use an ArrayList with a mention of its size.
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// working of ArrayList
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class ArrayListExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Size of the
// ArrayList
int n = 5;
// Declaring the ArrayList with
// initial size n
ArrayList<Integer> arr1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(n);
// Declaring the ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer> arr2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Printing the ArrayList
System.out.println("Array 1:" + arr1);
System.out.println("Array 2:" + arr2);
// Appending new elements at
// the end of the list
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
arr1.add(i);
arr2.add(i);
}
// Printing the ArrayList
System.out.println("Array 1:" + arr1);
System.out.println("Array 2:" + arr2);
}
}
OutputArray 1:[]
Array 2:[]
Array 1:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Array 2:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Explanation of the above Program:
ArrayList is a dynamic array and we do not have to specify the size while creating it, the size of the array automatically increases when we dynamically add and remove items. Though the actual library implementation may be more complex, the following is a very basic idea explaining the working of the array when the array becomes full and if we try to add an item:
- Creates a bigger-sized memory on heap memory (for example memory of double size).
- Copies the current memory elements to the new memory.
- The new item is added now as there is bigger memory available now.
- Delete the old memory.
Important Features of ArrayList in Java
- ArrayList inherits AbstractList class and implements the List interface.
- ArrayList is initialized by size. However, the size is increased automatically if the collection grows or shrinks if the objects are removed from the collection.
- Java ArrayList allows us to randomly access the list.
- ArrayList can not be used for primitive types, like int, char, etc. We need a wrapper class for such cases.
- ArrayList in Java can be seen as a vector in C++.
- ArrayList is not Synchronized. Its equivalent synchronized class in Java is Vector.
Let’s understand the Java ArrayList in depth. Look at the below image:

In the above illustration, AbstractList, CopyOnWriteArrayList, and AbstractSequentialList are the classes that implement the list interface. A separate functionality is implemented in each of the mentioned classes. They are:
- AbstractList: This class is used to implement an unmodifiable list, for which one needs to only extend this AbstractList Class and implement only the get() and the size() methods.
- CopyOnWriteArrayList: This class implements the list interface. It is an enhanced version of ArrayList in which all the modifications(add, set, remove, etc.) are implemented by making a fresh copy of the list.
- AbstractSequentialList: This class implements the Collection interface and the AbstractCollection class. This class is used to implement an unmodifiable list, for which one needs to only extend this AbstractList Class and implement only the get() and the size() methods.
Constructors in ArrayList in Java
In order to Create an ArrayList, we need to create an object of the ArrayList class. The ArrayList class consists of various constructors which allow the possible creation of the array list. The following are the constructors available in this class:
1. ArrayList()
This constructor is used to build an empty array list. If we wish to create an empty ArrayList with the name arr, then, it can be created as:
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList();
2. ArrayList(Collection c)
This constructor is used to build an array list initialized with the elements from the collection c. Suppose, we wish to create an ArrayList arr which contains the elements present in the collection c, then, it can be created as:
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(c);
3. ArrayList(int capacity)
This constructor is used to build an array list with the initial capacity being specified. Suppose we wish to create an ArrayList with the initial size being N, then, it can be created as:
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(N);
Java ArrayList Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|
| add(int index, Object element) | This method is used to insert a specific element at a specific position index in a list. |
| add(Object o) | This method is used to append a specific element to the end of a list. |
| addAll(Collection C) | This method is used to append all the elements from a specific collection to the end of the mentioned list, in such an order that the values are returned by the specified collection’s iterator. |
| addAll(int index, Collection C) | Used to insert all of the elements starting at the specified position from a specific collection into the mentioned list. |
| clear() | This method is used to remove all the elements from any list. |
| clone() | This method is used to return a shallow copy of an ArrayList in Java. |
| contains? (Object o) | Returns true if this list contains the specified element. |
| ensureCapacity?(int minCapacity) | Increases the capacity of this ArrayList instance, if necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. |
| forEach?(Consumer<? super E> action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| get?(int index) | Returns the element at the specified position in this list. |
| indexOf(Object O) | The index the first occurrence of a specific element is either returned or -1 in case the element is not in the list. |
| isEmpty?() | Returns true if this list contains no elements. |
| lastIndexOf(Object O) | The index of the last occurrence of a specific element is either returned or -1 in case the element is not in the list. |
| listIterator?() | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence). |
| listIterator?(int index) | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence), starting at the specified position in the list. |
| remove?(int index) | Removes the element at the specified position in this list. |
| remove? (Object o) | Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, if it is present. |
| removeAll?(Collection c) | Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection. |
| removeIf?(Predicate filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| removeRange?(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. |
| retainAll?(Collection<?> c) | Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the specified collection. |
| set?(int index, E element) | Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element. |
| size?() | Returns the number of elements in this list. |
| spliterator?() | Creates a late-binding and fail-fast Spliterator over the elements in this list. |
| subList?(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. |
| toArray() | This method is used to return an array containing all of the elements in the list in the correct order. |
| toArray(Object[] O) | It is also used to return an array containing all of the elements in this list in the correct order same as the previous method. |
| trimToSize() | This method is used to trim the capacity of the instance of the ArrayList to the list’s current size. |
Note: You can also create a generic ArrayList:
// Creating generic integer ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer> arrli = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Some Key Points of ArrayList in Java
- ArrayList is Underlined data Structure Resizable Array or Growable Array.
- ArrayList Duplicates Are Allowed.
- Insertion Order is Preserved.
- Heterogeneous objects are allowed.
- Null insertion is possible.
Let’s see how to perform some basic operations on the ArrayList as listed which we are going to discuss further alongside implementing every operation.
- Adding element to List/ Add element
- Changing elements/ Set element
- Removing elements/Delete element
- Iterating elements
- get elements
- add elements in between two number
- Sorting elements
- ArrayList size
1. Adding Elements
In order to add an element to an ArrayList, we can use the add() method. This method is overloaded to perform multiple operations based on different parameters. They are as follows:
- add(Object): This method is used to add an element at the end of the ArrayList.
- add(int index, Object): This method is used to add an element at a specific index in the ArrayList.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
Java
// Java Program to Add elements to An ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an Array of string type
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to ArrayList
// Custom inputs
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Here we are mentioning the index
// at which it is to be added
al.add(1, "For");
// Printing all the elements in an ArrayList
System.out.println(al);
}
}
Output[Geeks, For, Geeks]
2. Changing Elements
After adding the elements, if we wish to change the element, it can be done using the set() method. Since an ArrayList is indexed, the element which we wish to change is referenced by the index of the element. Therefore, this method takes an index and the updated element which needs to be inserted at that index.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
Java
// Java Program to Change elements in ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an Arraylist object of string type
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to Arraylist
// Custom input elements
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Adding specifying the index to be added
al.add(1, "Geeks");
// Printing the Arraylist elements
System.out.println("Initial ArrayList " + al);
// Setting element at 1st index
al.set(1, "For");
// Printing the updated Arraylist
System.out.println("Updated ArrayList " + al);
}
}
OutputInitial ArrayList [Geeks, Geeks, Geeks]
Updated ArrayList [Geeks, For, Geeks]
3. Removing Elements
In order to remove an element from an ArrayList, we can use the remove() method. This method is overloaded to perform multiple operations based on different parameters. They are as follows:
- remove(Object): This method is used to simply remove an object from the ArrayList. If there are multiple such objects, then the first occurrence of the object is removed.
- remove(int index): Since an ArrayList is indexed, this method takes an integer value which simply removes the element present at that specific index in the ArrayList. After removing the element, all the elements are moved to the left to fill the space and the indices of the objects are updated.
Example:
Java
// Java program to Remove Elements in ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of arraylist class
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to ArrayList
// Custom addition
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
// Adding element at specific index
al.add(1, "For");
// Printing all elements of ArrayList
System.out.println("Initial ArrayList " + al);
// Removing element from above ArrayList
al.remove(1);
// Printing the updated Arraylist elements
System.out.println("After the Index Removal " + al);
// Removing this word element in ArrayList
al.remove("Geeks");
// Now printing updated ArrayList
System.out.println("After the Object Removal "
+ al);
}
}
OutputInitial ArrayList [Geeks, For, Geeks]
After the Index Removal [Geeks, Geeks]
After the Object Removal [Geeks]
4. Iterating the ArrayList
There are multiple ways to iterate through the ArrayList. The most famous ways are by using the basic for loop in combination with a get() method to get the element at a specific index and the advanced for a loop.
Example
Java
// Java program to Iterate the elements
// in an ArrayList
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an Arraylist of string type
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to ArrayList
// using standard add() method
al.add("Geeks");
al.add("Geeks");
al.add(1, "For");
// Using the Get method and the
// for loop
for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(al.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// Using the for each loop
for (String str : al)
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
}
OutputGeeks For Geeks
Geeks For Geeks
5. Get Elements
Java
// Java program to get the elemens in ArrayList
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main (String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
// add the number
list.add(9);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
System.out.println(list);
// get method
Integer n= list.get(1);
System.out.println("at indext 1 number is:"+n);
}
}
Output[9, 5, 6]
at indext 1 number is:5
6. Add Elements Between Two Numbers
Java
// Java program to add the elements
// between two numbers in ArrayList
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(4);
System.out.println(list);
// insert missing element 3
list.add(2, 3);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
Output[1, 2, 4]
[1, 2, 3, 4]
7. ArrayList Sort
Java
// Java Program for ArrayList Sorting
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
list.add(2);
list.add(4);
list.add(3);
list.add(1);
System.out.println("Before sorting list:");
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println("after sorting list:");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
OutputBefore sorting list:
[2, 4, 3, 1]
after sorting list:
[1, 2, 3, 4]
8. Size of Elements
Java
// Java program to find the size
// of elements of an ArrayList
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
int b = list.size();
System.out.println("The size is :" + b);
}
}
Complexity of Java ArrayList
Operation
| Time Complexity
| Space Complexity
|
|---|
Inserting Element in ArrayList
| O(1)
| O(N)
|
Removing Element from ArrayList
| O(N)
| O(1)
|
Traversing Elements in ArrayList
| O(N)
| O(N)
|
Replacing Elements in ArrayList
| O(1)
| O(1)
|
ArrayList in Java is a class in the Java Collections framework that implements the List interface. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of using ArrayList in Java.
Advantages of Java ArrayList
- Dynamic size: ArrayList can dynamically grow and shrink in size, making it easy to add or remove elements as needed.
- Easy to use: ArrayList is simple to use, making it a popular choice for many Java developers.
- Fast access: ArrayList provides fast access to elements, as it is implemented as an array under the hood.
- Ordered collection: ArrayList preserves the order of elements, allowing you to access elements in the order they were added.
- Supports null values: ArrayList can store null values, making it useful in cases where the absence of a value needs to be represented.
Disadvantages of Java ArrayList
- Slower than arrays: ArrayList is slower than arrays for certain operations, such as inserting elements in the middle of the list.
- Increased memory usage: ArrayList requires more memory than arrays, as it needs to maintain its dynamic size and handle resizing.
- Not thread-safe: ArrayList is not thread-safe, meaning that multiple threads may access and modify the list concurrently, leading to potential race conditions and data corruption.
- Performance degradation: ArrayList’s performance may degrade as the number of elements in the list increases, especially for operations such as searching for elements or inserting elements in the middle of the list.
Conclusion
Points to be remembered from this article are mentioned below:
- ArrayList is the part of Collections framework. It inherits the AbstractList class and implements the List interface.
- ArrayList is the implementation of a dynamic array.
- ArrayList can be initialized used using different constructor types like without parameters, passing collection as a parameter, and passing integer as a parameter.
- Operations can be performed in ArrayList as follows Adding, removing, iterating, and sorting.
FAQs of ArrayList
What is an ArrayList in Java?
An ArrayList is a resizable array that is part of the Java Collections Framework. It can dynamically grow and shrink as elements are added or removed.
How is ArrayList different from an Array in Java?
An ArrayList can resize dynamically, while a traditional array has a fixed size. ArrayList also provides many useful methods like add(), remove(), and size().
How to Create an ArrayList in Java?
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Can ArrayList hold primitive types like int or char?
No, ArrayList can only hold objects. You must use wrapper classes like Integer or Character.
How to Add elements to an ArrayList?
We can add elements using the add() method:
list.add(“Hello”);
How to Access elements in an ArrayList?
Elements can be accessed using the get() method:
String element = list.get(0);
How to Remove an element from an ArrayList?
Use the remove() method to remove elements by index:
list.remove(0);
Is ArrayList Synchronized?
No, ArrayList is not synchronized. Use Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()) for thread-safe operations.
Can we Store null elements in an ArrayList?
Yes, ArrayList can store null elements.
How to convert an ArrayList to an Array?
We can convert an ArrayList to an array using the toArray() method:
String[] array = list.toArray(new String[0]);
How is data stored in ArrayList?
ArrayList can store data till the ArrayList size is full, after that the size of ArrayList is doubled if we want to store any more elements.
Does ArrayList allow Duplicates?
Yes, ArrayList allows duplicate values to be stored.
Please Login to comment...