Continue Statement in C
Last Updated :
20 Mar, 2023
The continue statement in C is a jump statement that is used to bring the program control to the start of the loop. We can use the continue statement in the while loop, for loop, or do..while loop to alter the normal flow of the program execution. Unlike break, it cannot be used with a C switch case.
What is continue in C?
The C continue statement resets program control to the beginning of the loop when encountered. As a result, the current iteration of the loop gets skipped and the control moves on to the next iteration. Statements after the continue statement in the loop are not executed.
Syntax of continue in C
The syntax of continue is just the continue keyword placed wherever we want in the loop body.
continue;
Use of continue in C
The continue statement in C can be used in any kind of loop to skip the current iteration. In C, we can use it in the following types of loops:
- Single Loops
- Nested Loops
Using continue in infinite loops is not useful as skipping the current iteration won’t make a difference when the number of iterations is infinite.
Example of continue in C
Example 1: C Program to use continue statement in a single loop.
The continue statement can be used in for loop, while loop, and do-while loop.
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++) {
if (i == 4) {
continue;
}
printf("%d ", i);
}
printf("\n");
int i = 0;
while (i < 8) {
i++;
if (i == 4) {
continue;
}
printf("%d ", i);
}
return 0;
}
|
Output
1 2 3 5 6 7 8
1 2 3 5 6 7 8
Example 2: C Program to use continue in a nested loop
The continue statement will only work in a single loop at a time. So in the case of nested loops, we can use the continue statement to skip the current iteration of the inner loop when using nested loops.
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= 4; j++) {
if (j == 3) {
continue;
}
printf("%d ", j);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
|
Output
0 1 2 4
0 1 2 4
0 1 2 4
The continue skips the current iteration of the inner loop when it executes in the above program. As a result, the program is controlled by the inner loop update expression. In this way, 3 is never displayed in the output.
How continue statement works?
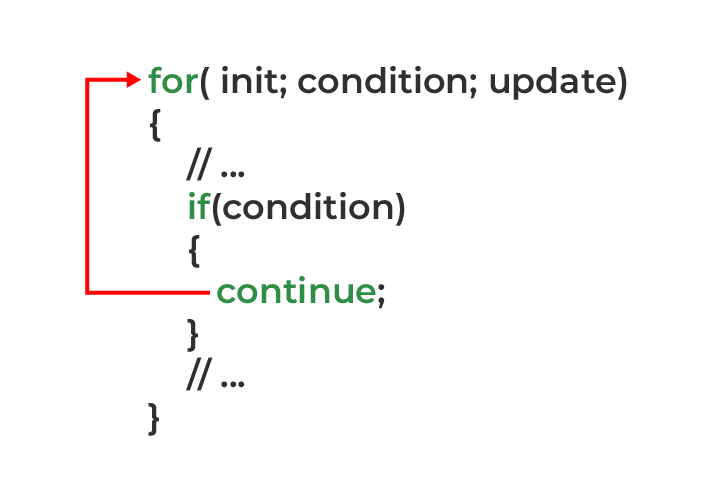
Working of C continue in for Loop
The working of the continue statement is as follows:
- STEP 1: The loop’s execution starts after the loop condition is evaluated to be true.
- STEP 2: The condition of the continue statement will be evaluated.
- STEP 3A: If the condition is false, the normal execution will continue.
- STEP 3B: If the condition is true, the program control will jump to the start of the loop and all the statements below the continue will be skipped.
- STEP 4: Steps 1 to 4 will be repeated till the end of the loop.
Flowchart of continue in C
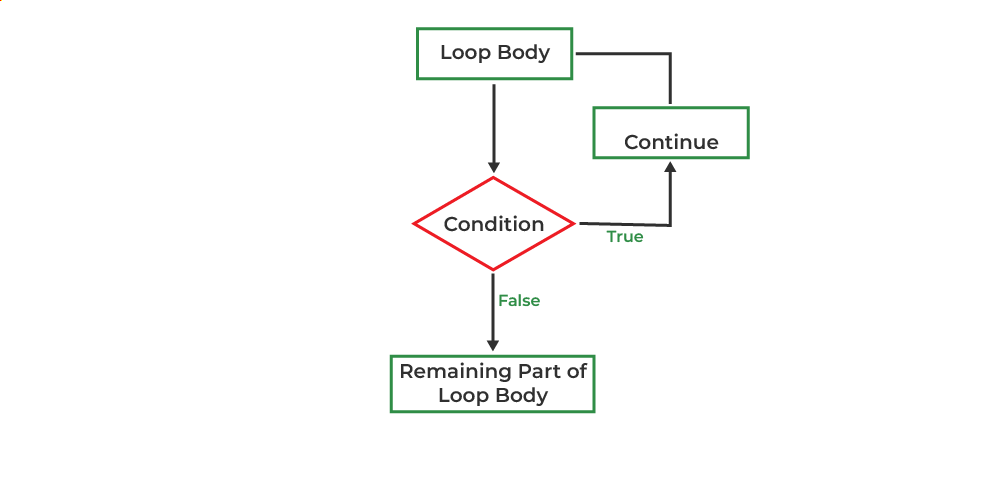
Flowchart of the continue Statement in C
C break and continue Statement Differences
break statement: By using break statement, we terminate the smallest enclosing loop (e.g, a while, do-while, for, or switch statement).
continue statement: By using the continue statement, the loop statement is skipped and the next iteration takes place instead of the one prior.
Example: C Program to demonstrate the difference between the working of break and continue statement in C.
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("The loop with break produces output as: \n");
for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) {
if (i == 3)
break;
else
printf("%d ", i);
}
printf("\nThe loop with continue produces output as: \n");
for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) {
if (i == 3)
continue;
printf("%d ", i);
}
return 0;
}
|
Output
The loop with break produces output as:
1 2
The loop with continue produces output as:
1 2 4 5 6 7
Explanation: In the above program, the first loop will print the value of i till 3 and will break the loop as we have used a break statement at i equal to 3. And in the second for loop program will continue but will not print the value of i when i will be equal to 3.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed continue statement which is one of the four jump statements in C. We also studied its syntax, working, and how we can use it to alter the normal flow of out C program.
FAQs on C continue statement
1. What is the use of continue statement in C?
The continue statement in C is used in loops to skip the current iteration and move on to the next iteration without executing the statements below the continue in the loop body.
2. What type of statements are break and continue?
The break and continue in C are jump statements that are used to alter the flow of the normal execution of the loops.
Please Login to comment...