Cytoplasm and Nucleus – Overview, Structure, Functions, Examples
Last Updated :
07 Jun, 2024
The cytoplasm and nucleus of a cell together make up the protoplasm. The cytoplasm and nucleus are present inside the cell. Understanding the function and structure of cytoplasm and nucleus helps learn cellular processes, including metabolism and protein synthesis.
In this article, we will cover the cytoplasm and nucleus in detail.
Cytoplasm and Nucleus Relationship
The cytoplasm and nucleus are integral components of eukaryotic cells. They work together to support various cellular functions. The nucleus contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes. These contain the instructions for protein synthesis and cellular activities. The nucleus acts as the command centre which regulates gene expression, DNA replication, and RNA synthesis.
Meanwhile, the cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell’s interior. Cytoplasm plays a crucial role as the site for many cellular activities. It contains cellular organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes, which are involved in energy production, protein synthesis, and cellular transport processes.
The relationship between the cytoplasm and nucleus is based on interdependence and coordination. The nucleus directs cellular activities by sending out signals in the form of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules, which travel to the cytoplasm, where ribosomes translate them into proteins. These proteins then fulfill various functions, including structural support, enzymatic reactions, and cell signaling.
Conversely, the cytoplasm provides essential resources and support for nuclear functions. It supplies the raw materials required for DNA replication and transcription, such as nucleotides and enzymes. Additionally, it maintains the necessary conditions for nuclear activities, including appropriate pH levels and ion concentrations.
Furthermore, communication between the nucleus and cytoplasm is important for cellular homeostasis and response to external stimuli. Signaling molecules generated in the cytoplasm can influence gene expression in the nucleus, altering cellular responses to changes in the environment or physiological conditions.
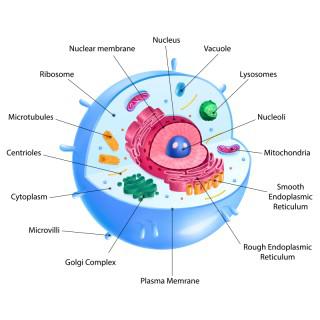
Cytoplasm and Nucleus
Nucleus
The nucleus is a large, centrally located spherical cellular component. It represents the whole eukaryotic complex that contains genetic information. It is bounded by two nuclear membranes, both forming a nuclear envelope. A nuclear envelope encloses the space between two nuclear membranes and is connected to the system of membranes called ER (endoplasmic reticulum).
The nuclear envelope separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. The nuclear envelope contains many pores (the nuclear pores) and encloses the liquid ground substance, the nucleoplasm. Nucleopores allow the materials to transfer between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm
Two types of nuclear structures are embedded within nucleoplasm – the nucleolus and chromatin material. The nucleolus may be one or more in number and is not limited by any membrane. It is rich in protein and RNA(ribonucleic acid) molecules and acts as the site for ribosome formation. the nucleolus is known as the factory of ribosomes. ribosomes are known as the factory of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm.
The chromatin material is a thin,thread-like mass of chromosome material and consists of the genetic substance DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and proteins (i.e., histones). The nucleosome is a part of DNA that is coiled around a core of proteins.
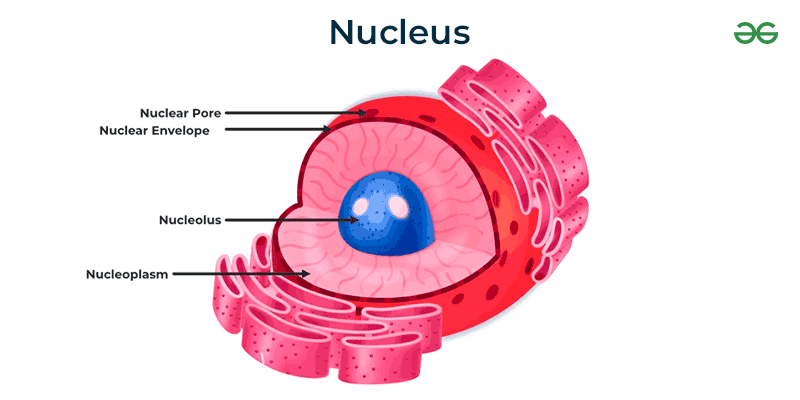
Nucleus Diagram
Function of Nucleus
- The nucleus is known as the controller of a cell and its metabolic activities. If the nucleus is removed from a cell, the protoplasm will dry up and dies ultimately.
- The nucleus is responsible for the cell cycle, it regulates it.
- The nucleus plays an important role in transmitting the hereditary traits from parent to offspring.
- The nucleus controls the protein and enzyme synthesis.
- The nucleus is the storehouse of DNA, RNA, and ribosomes.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the part of the cell which comes between the cell membrane and nuclear envelope. The inner granular mass of the cytoplasm is called endoplasm, while the outer, clearer layer is called ectoplasm. The cytoplasm consists of gel-like fluid or thick solution inside the cell which contains a variety of cell organelles. It is mainly composed of salts, water, and proteins. moreover, it is the medium for chemical reaction and thus, is an essential component of the cell.
Cell organelles such as ER (endoplasmic reticulum), ribosomes, Golgi apparatus (Golgi body or Golgi complex), Lysosomes, Mitochondria, plastids, chloroplasts, vacuoles, peroxisomes, and centrosomes are embedded in the cytoplasm and perform different functions in the cell.
The largest cell organelle is ribosome while the largest cell structure is Nucleus. Furthermore, the largest cellular organelle in plants is plastids and in animals is mitochondria.
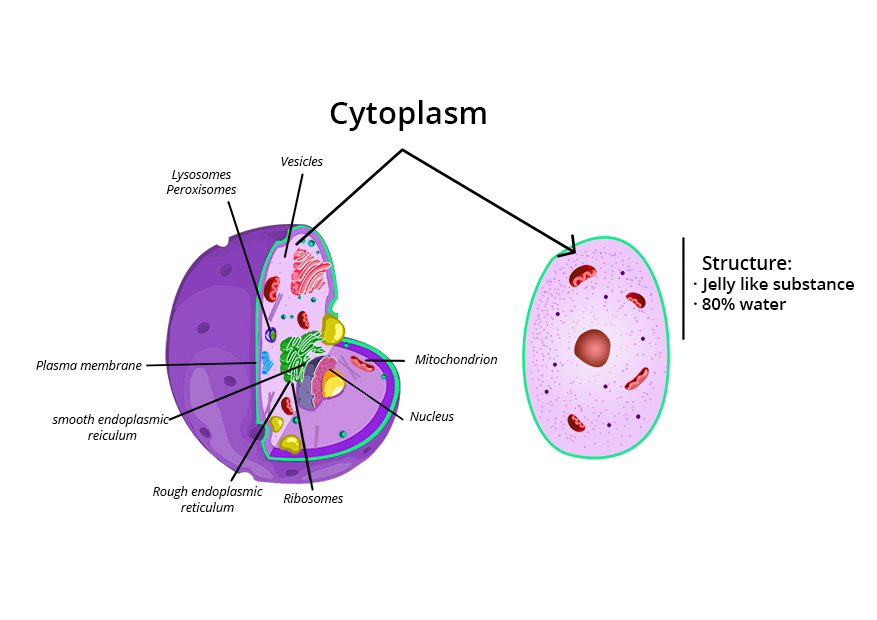
Cytoplasm
Function of Cytoplasm
The functions of cytoplasm are:
- Living cytoplasm is always at the site of movement.
- The cytoplasm is the site of many metabolic reactions to take place such as glycolysis.
- The synthesis of fatty acids, nucleotides, and some amino acids also takes place in the cytosol.
- Cytosol (cytoplasm) acts as the storehouse of vital chemicals such as amino acids, glucose, vitamins, ions, etc.
- Cytoplasm enables other organelles to perform their functions in the cell of organisms.
Cytoplasm and Nucleus Make
Cytoplasm and Nucleus together make protoplasm, the basic substance found in living cells. Together, they form the building blocks of cellular life, with the cytoplasm containing various cell parts and the nucleus containing genetic material. Protoplasm is essential for cellular function, as it encompasses the core processes necessary for life.
Cytoplasm and Nucleus Difference
The difference between cytoplasm and nucleus are given below:
| Aspect |
Cytoplasm |
Nucleus |
| Location |
Found throughout the cell, surrounding the nucleus. |
Typically located centrally within the cell. |
| Composition |
Contains organelles, cytosol, and cytoskeleton. |
Contains chromatin, nucleolus, and nuclear envelope. |
| Function |
Site of various cellular processes, including metabolism and protein synthesis. |
Controls cellular activities and contains genetic material (DNA). |
| Size |
Generally larger in volume compared to the nucleus. |
Relatively smaller in volume compared to the cytoplasm. |
| Structure |
Less organized structure with a fluid consistency. |
Well-defined structure with distinct components. |
Conclusion – Cytoplasm and Nucleus
In conclusion, the cytoplasm and nucleus play fundamental roles in the functioning of eukaryotic cells, each with distinct characteristics and functions. The cytoplasm, comprising organelles, cytosol, and cytoskeleton, serves as the site for various cellular processes, while the nucleus, housing chromatin, nucleolus, and nuclear envelope, governs cellular activities and contains genetic material. Despite their differences in size and structure, both entities are integral to cellular homeostasis and are interconnected in orchestrating the intricate dance of life within the cell.
Also Read:
FAQs on Cytoplasm and Nucleus
What is the Connection Between Cytoplasm and Nucleus?
The cytoplasm surrounds the nucleus, providing a medium for cellular processes.
What is the Difference Between Cytoplasm and Nucleolus?
Cytoplasm consists of organelles and cytosol, while the nucleolus is a substructure within the nucleus.
What is the Cytoplasm and its Function?
Cytoplasm serves as the site for various cellular activities, including metabolism and protein synthesis.
What is Found in the Nucleus and the Cytoplasm?
The nucleus contains genetic material (DNA) and regulates cellular activities, while the cytoplasm contains organelles, cytosol, and the cytoskeleton.
Please Login to comment...