Spring Boot is a powerful framework that makes it easy to create RESTful APIs. In this article, we will go through a step-by-step guide on how to create a RESTful API in Spring Boot with MySQL and JPA. We will start by creating a new Spring Boot project and configuring it for our needs.
Step-by-Step Implementation to Create REST API using Spring Boot
Below are the steps to implement REST API in Spring Boot with MySQL and JPA.
Step 1: Setup Development Environment
Before we begin, we need to set up our development environment. We will need to install the following software:
- Java Development Kit (JDK)
- Intellij (or any other preferred IDE like Eclipse)
- MySQL Server
Step 2: Create a Spring Boot Project
The first step is to create a new Spring Boot project using the Spring Boot Initializer . Open any web browser and go to Spring Initializer.
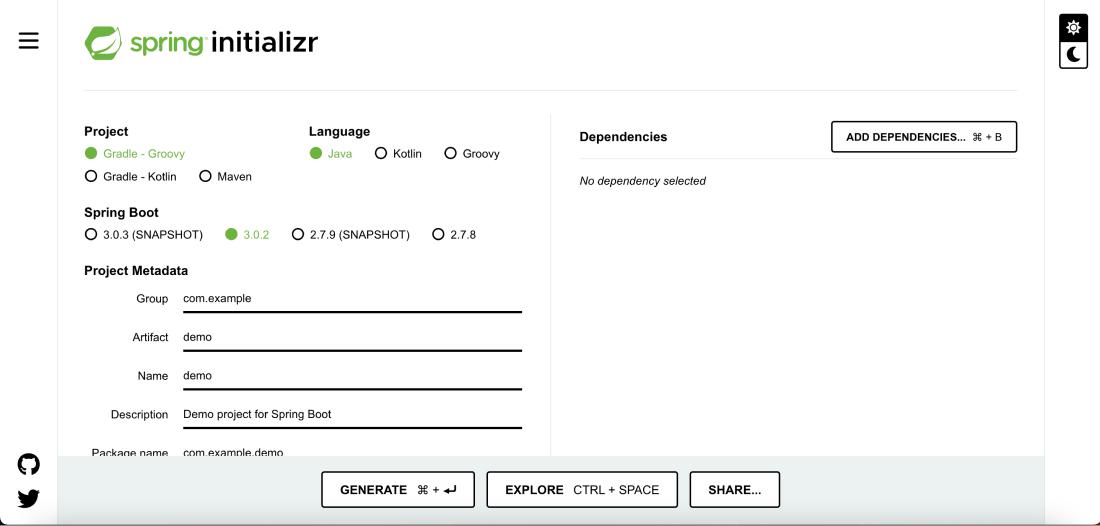
Set the following options:
- Project: Maven Project/Gradle according to your need
- Language : Java
- Spring Boot: 3.0.2 (or the latest version)
- Group : com.example
- Artifact : spring boot API/any desired info of your own choice
- Description : Demo Project for Spring Boot API/ any information you like about the project
- Packaging : Jar
- Java : 11
Click on the “Add Dependencies” button and add the following dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Data JPA
- MySQL Driver
Select these dependencies and click on the Generate button. Extract the downloaded project ZIP file to your preferred location.
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Data JPA -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL Driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
pom.xml File:
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-api</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-boot-api</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
The above XML file contains all the Maven dependencies needed for our application.
Step 3: Create Entity Class
Next, we need to create an entity class to represent our data model. In this example, we will create a “Product” entity class.
- Right-click on the “com.example” package and create a package called entity inside it.
- Enter “Product” as the class name in the “entity” package and click on the “Finish” button.
- In the “Product” class, add the following code:
Java
package com.example.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "product")
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false)
private double price;
@Column(nullable = false)
private int quantity;
// Constructors, getters and setters, and other methods...
// Getters
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public int getQuantity() {
return quantity;
}
// Setters
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public void setQuantity(int quantity) {
this.quantity = quantity;
}
}
The @Entity annotation specifies that this class is an entity and should be mapped to a database table. The @Table annotation specifies the name of the database table that will store instances of this entity. The @Id annotation specifies the primary key of the entity, while the @GeneratedValue annotation specifies that the primary key should be generated automatically.
Step 4: Create Repository Interface
Now, we need to create a repository interface to handle database operations for the “Product” entity.
- In the “ProductRepository” interface, add the following code:
Java
package com.example.springbootapi.repository;
import com.example.springbootapi.entity.Product;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* Repository interface for Product entity.
*/
@Repository
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Long> {
}
The @Repository annotation specifies that this interface is a repository, and Spring will create an instance of it automatically. The JpaRepository interface provides a set of methods for performing CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on the “Product” entity.
Step 5: Create A Service Class
Next, we need to create a service class to handle the business logic for our REST API.
- In the “ProductService” class, add the following code:
Java
package com.example.springbootapi.service;
import com.example.springbootapi.entity.Product;
import com.example.springbootapi.repository.ProductRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
/**
* Service class for managing Product entities.
*/
@Service
public class ProductService {
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
@Autowired
public ProductService(ProductRepository productRepository) {
this.productRepository = productRepository;
}
/**
* Save a product.
*
* @param product the entity to save
* @return the persisted entity
*/
public Product saveProduct(Product product) {
return productRepository.save(product);
}
/**
* Get all the products.
*
* @return the list of entities
*/
public List<Product> getAllProducts() {
return productRepository.findAll();
}
/**
* Get one product by ID.
*
* @param id the ID of the entity
* @return the entity
*/
public Optional<Product> getProductById(Long id) {
return productRepository.findById(id);
}
/**
* Update a product.
*
* @param id the ID of the entity
* @param updatedProduct the updated entity
* @return the updated entity
*/
public Product updateProduct(Long id, Product updatedProduct) {
Optional<Product> existingProduct = productRepository.findById(id);
if (existingProduct.isPresent()) {
Product product = existingProduct.get();
product.setName(updatedProduct.getName());
product.setPrice(updatedProduct.getPrice());
product.setQuantity(updatedProduct.getQuantity());
return productRepository.save(product);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Product not found");
}
}
/**
* Delete the product by ID.
*
* @param id the ID of the entity
*/
public void deleteProduct(Long id) {
productRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
For saving a product in the database we will use the following code:
// Save Product
public ResponseEntity<Product> saveProduct(@RequestBody Product product)
{
Product newProduct = productRepository.save(product);
return ResponseEntity.ok(newProduct);
}
For getting all products from the database we will use the following code:
// Get all products
public ResponseEntity<List<Product> > fetchAllProducts()
{
return ResponseEntity.ok(productRepository.findAll());
}
For getting a single product from the database we will use the following code:
// Get a product by ID
public ResponseEntity<Optional<Product> >
fetchProductById(Long id)
{
Optional<Product> product
= productRepository.findById(id);
if (product.isPresent()) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(product);
}
else {
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
}
For updating a single product from the database, we will use the following code:
public ResponseEntity<Product> updateProduct(Long id, Product updatedProduct)
{
if (id == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"ID cannot be null");
}
Product Existingproduct
= productRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(
()
-> new EntityNotFoundException(
String.valueOf(id)));
Existingproduct.setName(updatedProduct.getName());
Existingproduct.setPrice(updatedProduct.getPrice());
Existingproduct.setQuantity(
updatedProduct.getQuantity());
Product savedEntity
= productRepository.save(Existingproduct);
return ResponseEntity.ok(savedEntity);
}
For deleting a single product from the database, we will use the following code:
public ResponseEntity<String> deleteProduct(Long id)
{
productRepository.deleteById(id);
return ResponseEntity.ok(
"Product Deleted Successfully");
}
Step 6: Create Controller Class
Next, we need to create a controller class to handle HTTP requests for our REST API.
- In the “ProductController” class, add the following code:
Java
package com.example.springbootapi.controller;
import com.example.springbootapi.entity.Product;
import com.example.springbootapi.service.ProductService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class ProductController {
private final ProductService productService;
@Autowired
public ProductController(ProductService productService) {
this.productService = productService;
}
/**
* Create a new product.
*
* @param product the product to create
* @return the ResponseEntity with status 200 (OK) and with body of the new product
*/
@PostMapping("/product")
public ResponseEntity<Product> saveProduct(@RequestBody Product product) {
Product newProduct = productService.saveProduct(product);
return ResponseEntity.ok(newProduct);
}
/**
* Get all products.
*
* @return the ResponseEntity with status 200 (OK) and with body of the list of products
*/
@GetMapping("/products")
public List<Product> getAllProducts() {
return productService.getAllProducts();
}
/**
* Get a product by ID.
*
* @param id the ID of the product to get
* @return the ResponseEntity with status 200 (OK) and with body of the product, or with status 404 (Not Found) if the product does not exist
*/
@GetMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Product> getProductById(@PathVariable Long id) {
Optional<Product> product = productService.getProductById(id);
return product.map(ResponseEntity::ok).orElseGet(() -> ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
/**
* Update a product by ID.
*
* @param id the ID of the product to update
* @param product the updated product
* @return the ResponseEntity with status 200 (OK) and with body of the updated product, or with status 404 (Not Found) if the product does not exist
*/
@PutMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Product> updateProduct(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Product product) {
Product updatedProduct = productService.updateProduct(id, product);
return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedProduct);
}
/**
* Delete a product by ID.
*
* @param id the ID of the product to delete
* @return the ResponseEntity with status 200 (OK) and with body of the message "Product deleted successfully"
*/
@DeleteMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<String> deleteProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
productService.deleteProduct(id);
return ResponseEntity.ok("Product deleted successfully");
}
}
The @RestController annotation specifies that this class is a controller for RESTful API requests. The @RequestMapping annotation specifies the base URL for all requests handled by this controller.
Next, we need to add methods to handle HTTP requests. In this example, we will add methods to handle GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE requests.
For Post Request, we will be using the following code:
// Create a new Product
@PostMapping("/product")
public ResponseEntity<Product> saveProduct(@RequestBody Product product) {
Product newProduct = productService.saveProduct(product);
return ResponseEntity.ok(newProduct);
}
The @PostMapping annotation is used to indicate that this class will handle HTTP Post requests and return the response as JSON. It is used to map the /api/v1/products path to this class. @RequestBody is an annotation in Spring Framework used to bind the HTTP request body to a parameter in a controller method. When a client sends an HTTP POST or PUT request, it may include data in the request body. This data is typically in JSON or XML format and contains information about the resource being created or updated.
For Get Request all the products, we will be using the following code:
// Get all Products
@GetMapping("/products")
public List<Product> getAllProducts() {
return productService.getAllProducts();
}
The @GetMapping annotation is used to indicate that this class will handle HTTP Get requests and return the response as JSON. It is used to map the /api/v1/products path to this class. Here the getAllProducts() method fetches all the products and has a path/products.
For Get Request of a single product, we will be using the following code:
// Get a single product
@GetMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Product> getProductById(@PathVariable Long id) {
Optional<Product> product = productService.getProductById(id);
return product.map(ResponseEntity::ok).orElseGet(() -> ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
The @PathVariable annotation is used to extract data from the URL path of an HTTP request. It is used to capture dynamic segments of a URL and map them to a method parameter in a Spring Boot controller. getProductById() method is used to get a product by id and has a path /products/{id}.
For Update Requests, we will be using the following code:
// Update Product
@PutMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Product> updateProduct(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Product product) {
Product updatedProduct = productService.updateProduct(id, product);
return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedProduct);
}
In this example, we’ve added a @PutMapping annotation for the updateProduct() method. The @PutMapping annotation is used to map HTTP PUT requests to the /product/{id} endpoint, where {id} is a path variable for the product ID. The @RequestBody annotation is used to bind the request body to the product parameter in the method. When a PUT request is made to /api/v1/product/{id}, the updateProduct() method will be executed with the id parameter set to the product ID from the URL path and the product.
For Delete Requests, we will be using the following code:
// Delete a Product
@DeleteMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<String> deleteProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
productService.deleteProduct(id);
return ResponseEntity.ok("Product deleted successfully");
}
Now, we are completed with the programming side and just remain with the database and then test the endpoints and then we are done. First of all, we will have to configure MySql in our application.properties files. We will add the following code in the application.properties file.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/name of your database
spring.datasource.username=your username for mysql
spring.datasource.password=your password for mysql
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop
Now, after this, we will test our API endpoints in postman. The default port for Spring Boot is 8080. You can change the port by using the command inside the application.properties file:
server.port=any port of your choice
In this case, the port is 8080. In this case, for our Post Request, the endpoint will be like “ http://localhost:8080/api/v1/product ” and the output is:
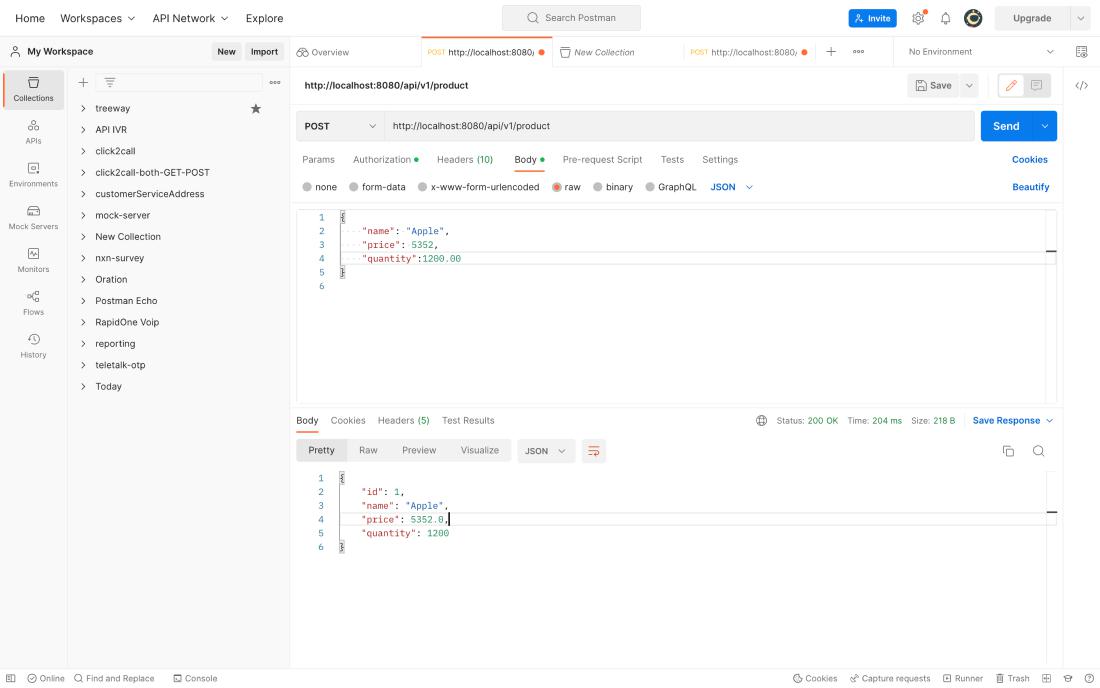
For our Get Request, the endpoint will be like “ http://localhost:8080/api/v1/products ” and the output is:
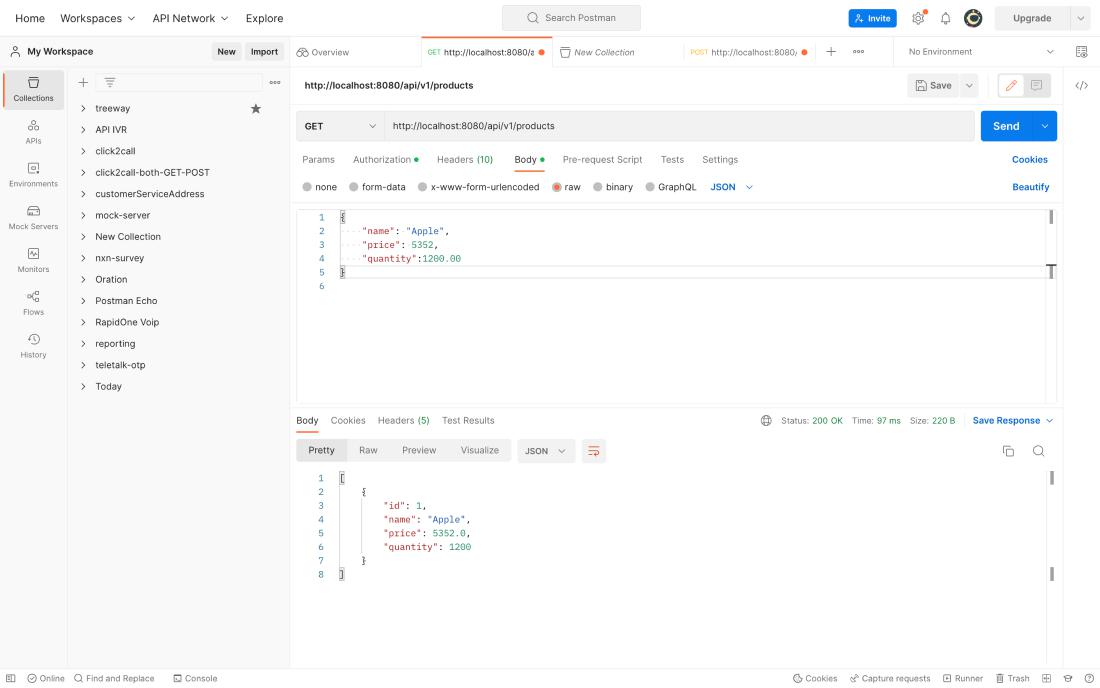
For our Get by Id Request, the endpoint will be like “ http://localhost:8080/api/v1/products/{id} ” and the output is:

For our Update Request, the endpoint will be like “ http://localhost:8080/api/v1/products/{id} ” and the output is:

And finally, for our Delete Request, the endpoint will be like “ http://localhost:8080/api/v1/products/{id}” and the output is:
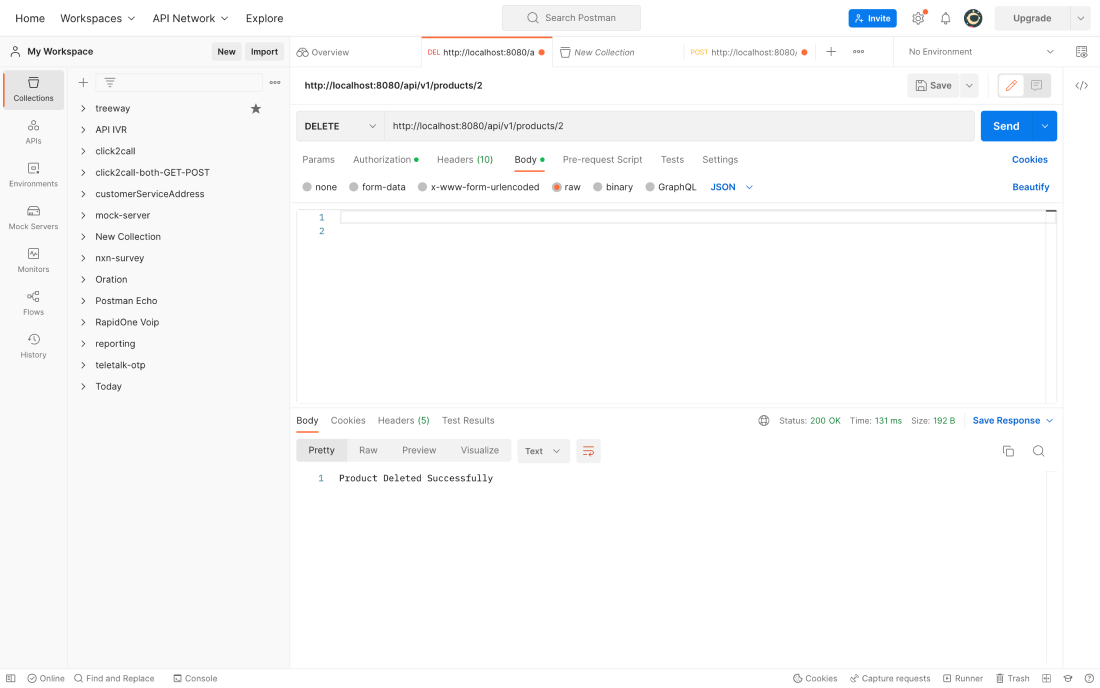
We made our Rest API in Spring Boot.
Please Login to comment...