Developing and Managing an application are the two most important aspects of the application’s life cycle. It is very crucial to know what’s going on beneath the application. Also when we push the application into production, managing it gradually becomes critically important. Therefore, it is always recommended to monitor the application both while at the development phase and at the production phase.
For the same use case, Spring Boot provides an actuator dependency that can be used to monitor and manage your Spring Boot application, By /actuator and /actuator/health endpoints you can achieve the purpose of monitoring.
- With the help of Spring Boot, we can achieve the above objectives.
- Spring Boot’s ‘Actuator’ dependency is used to monitor and manage the Spring web application.
- We can use it to monitor and manage the application with the help of HTTP endpoints or with the JMX.
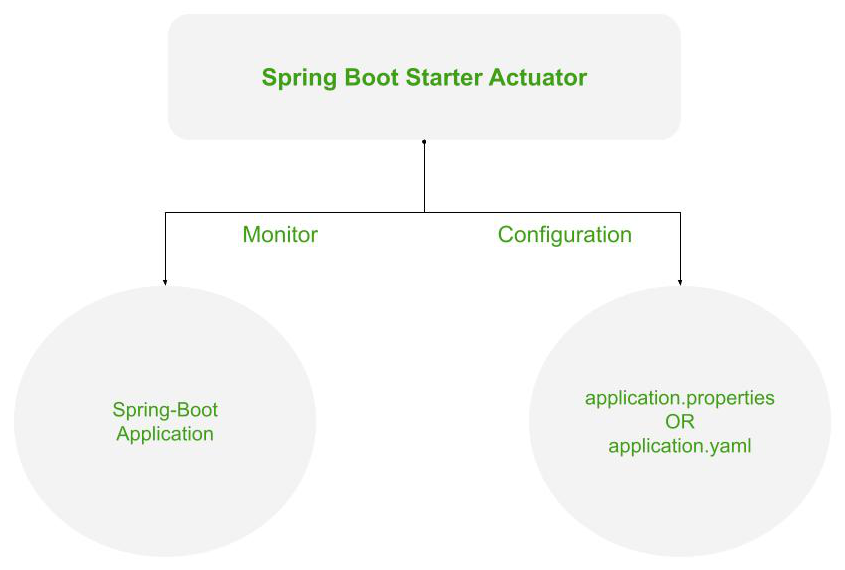
Working of the Spring’s Actuator
Advantages of Actuator the Application
- It increases customer satisfaction.
- It reduces downtime.
- It boosts productivity.
- It improves Cybersecurity Management.
- It increases the conversion rate.
1. Configuration for Actuator
In order to use hibernate validators, these configurations are necessary in your Spring Boot project.
1.1 Dependency for Actuator
To use the ‘Actuator’ add the following dependency in your application’s project settings file.
Dependency configuration for both Maven and Gradle build system.
Maven -> pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Gradle
-> build.gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator'
}
1.2 Application Properties configuration for Actuator
There more configurations available for Actuator, few of them are listed:
- You can also change the default endpoint by adding the following in the application.properties file.
management.endpoints.web.base-path=/details
By default, all IDs are set to false except for ‘health’. To include an ID, use the following property in the application.properties file.
management.endpoint.<id>.enabled
Example -> management.endpoint.metrics.enabled=true
- List down all IDs that you want to include which are separated by a comma.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=metrics,info
- Include only metrics and info IDs and will exclude all others (‘health’ too).
To add/include all ID information about your application, you can do it in the application.properties file by simply adding the following –
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
To exclude an ID or endpoint, use the following property and list out the respective IDs separated by a comma in the application.properties file.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude
Example -> management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude=info
Folder structure for projects
The below image demonstrates the picture of how your project must look

Project Structure – Maven
2. Implementing the project
2.1 Entity
UserEntity.java (Entity class representing the model data) is explained below:
- This class acts as a simple java bean whose properties are returned as JSON response by the REST API’s get() method.
- ‘Lombok’ library is used to generate GETTER/SETTER methods automatically at runtime using ‘@Data‘ annotation.
- ‘@RequiredArgsConstructor‘ annotation is used to generate a zero-argument constructor and if final or ‘@NonNull’ fields are present, then respective arguments constructor is created.
- To add the ‘Lombok‘ library in your application, add the following dependency in your application’s project build.
- ‘@Component‘ annotation is used so that this bean automatically gets registered in Spring’s application context.
Java
package gfg;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Data
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class UserEntity {
String id = "1";
String name = "Darshan.G.Pawar";
String userName = "@drash";
String email = "drash@geek";
String pincode = "422-009";
}
|
2.2 Controller
RESTfulController.java (A REST API controller) for defining APIs and testing the program.
This controller’s get() method uses the UserEntity bean to return JSON response. UserEntiy bean is outsourced through ‘@Autowired‘ annotation which was registered in Spring’s application context.
Java
package gfg;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/get")
public class RESTfulController {
@Autowired
UserEntity entity;
@GetMapping("/data")
public UserEntity getEntity(){
return entity;
}
}
|
3. Testing Actuator APIs
3.1 Controller APIs
Here, the JSON Formatter Chrome extension is used to automatically parse the JSON body. Further, it will be required to work with ‘Actuator’.
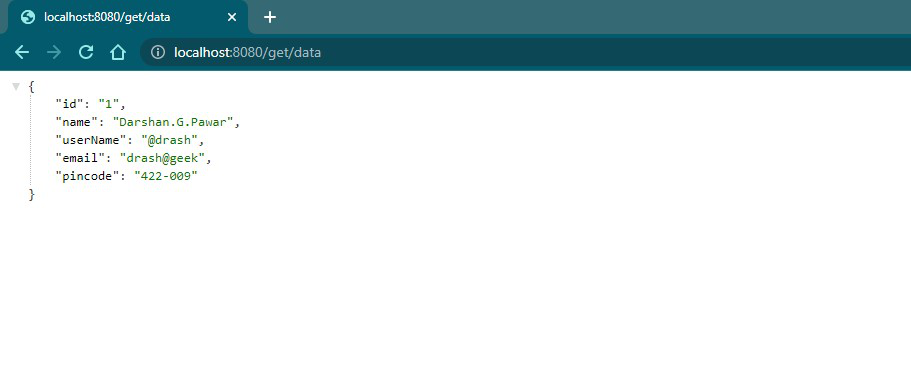
JSON response returned by REST API
3.2 Working with Spring Boot Actuator APIs
To access the ‘Actuator’ services, you will have to use the HTTP endpoint as it becomes reliable to work with.
3.2.1 /actuator
It’s simple just hit the default endpoint ‘/actuator’, ensure that your Application is running.
Example:

You can also change the default endpoint by adding the following in the application.properties file.
management.endpoints.web.base-path=/details

3.2.2 /actuator/health
You can click on these above links and see the respective information. Additionally, you can activate other Actuator IDs and use them after ‘/actuator’ to see more information. For example, ‘health’ ID is activated by default. Therefore you can click the link in the image or directly use ‘http://localhost:8080/actuator/health’.

The health of an application
‘UP’ means the application’s health is good. There are a total of 25 IDs out of which the commonly used are listed out here –
| beans |
Displays a complete list of all the Spring beans in your application. |
| caches |
Exposes available caches. |
| conditions |
Shows the conditions that were evaluated on configuration and auto-configuration classes and the reasons why they did or did not match. |
| health |
Shows application health information. |
| httptrace |
Displays HTTP trace information (by default, the last 100 HTTP request-response exchanges). Requires an HttpTraceRepository bean. |
| loggers |
Shows and modifies the configuration of loggers in the application. |
| mappings |
Displays a collated list of all @RequestMapping paths. |
| sessions |
Allows retrieval and deletion of user sessions from a Spring Session-backed session store. Requires a servlet-based web application that uses Spring Session. |
| threaddump |
Performs a thread dump. |
3.2.3 /actuator/beans
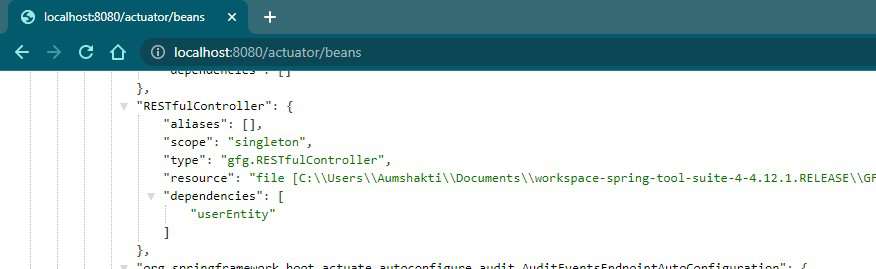
Accessing ‘beans’ ID of the above project
3.2.4 /actuator/mappings
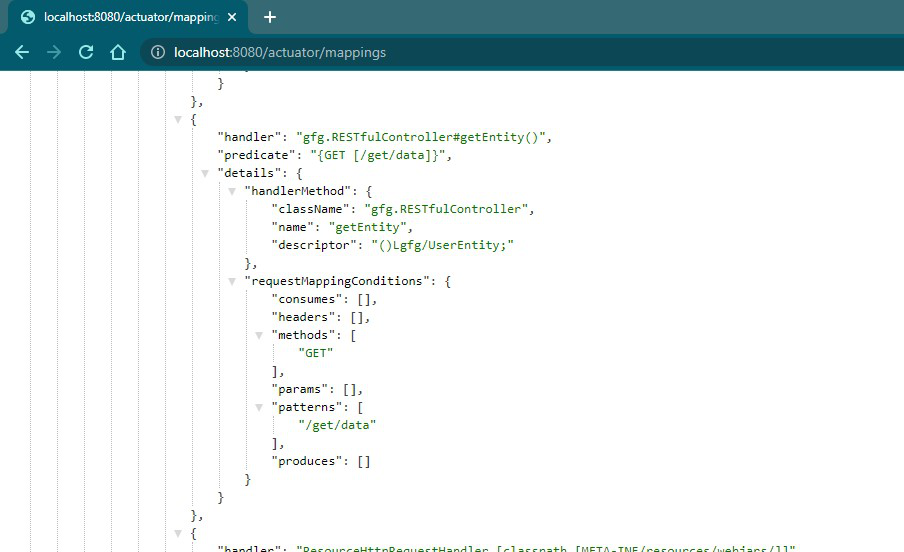
Accessing ‘mappings’ ID of the above project
Including IDs/Endpoints
By default, all IDs are set to false except for ‘health’. To include an ID, use the following property in the application.properties file.
management.endpoint.<id>.enabled
Example -> management.endpoint.metrics.enabled=true
OR, you can just list down all IDs that you want to include which are separated by a comma.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=metrics,info
This will include only metrics and info IDs and will exclude all others (‘health’ too). To add/include all ID information about your application, you can do it in the application.properties file by simply adding the following –
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
Output:
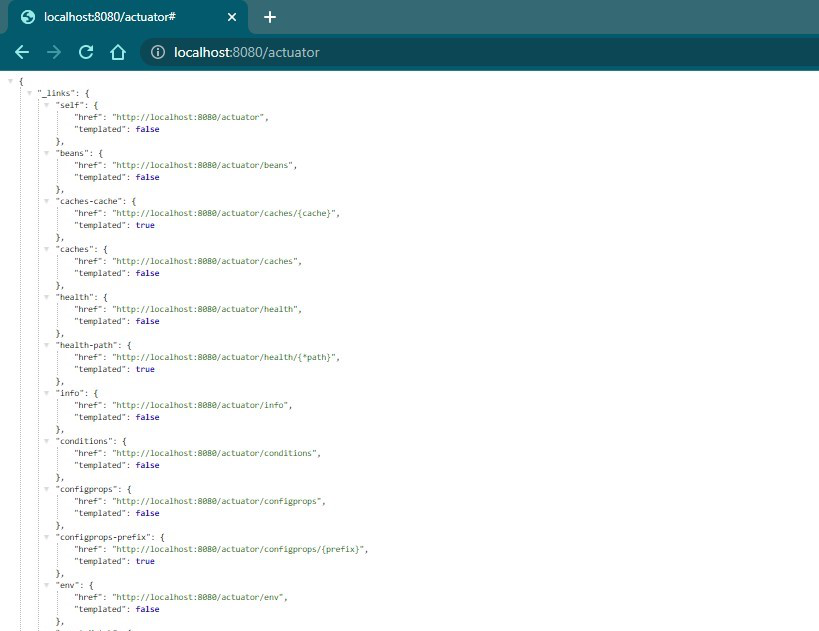
All the IDs or the Endpoint are now enabled
Excluding IDs/Endpoints
To exclude an ID or endpoint, use the following property and list out the respective IDs separated by a comma in the application.properties file.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude
Example -> management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude=info
Use ‘*’ in place of IDs in property to exclude all the IDs or endpoints.
Notes:
- Before setting the management.endpoints.web.exposure.include, ensure that the exposed actuators do not contain sensitive information.
- They should be secured by placing them behind a firewall or are secured by something like Spring Security.
Please Login to comment...