Controlling Variables: Integrated Science Process Skills
Controlling Variables: Integrated Science Process Skills
Uploaded by
pally_charmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Controlling Variables: Integrated Science Process Skills
Controlling Variables: Integrated Science Process Skills
Uploaded by
pally_charmedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Controlling Variables: Integrated Science Process Skills
Controlling Variables: Integrated Science Process Skills
Uploaded by
pally_charmedCopyright:
Available Formats
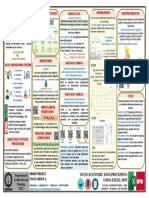
INTEGRATED SCIENCE PROCESS SKILLS
Manipulated
One deliberately change to
CONTROLLING test it
VARIABLES
Definition :
Keep all the
variables which can
effect the Purpose :
experiment the Types Of Variables
same. Make fair test of
hypothesis
Make sure not affect the
results
Responding
Change because of
manipulated variable
Controlled/ constant
Those which must be the
same
Make a prediction about variables
based on past experiences
Statement which explains the
Must be clear worded relationship between variables
Collecting
Observations
HOW
DEFINITION
Evaluating the
Observations
FORMULATING HYPOTHESIS
Imagining Possible
Explanations
USES
Judging Which Explanations
are Hypotheses e.x :
‘that dark coloured object heat up To predict the answer
faster than light coloured object problem
EXPERIMENTING
Steps
Stating hypothesis Purpose :
To find the solutions to a problem
or some facts yet unknown
Manipulated
Stating variables Responding
Constant Demonstrates understanding and
application of scientific method
though inquiry, research and self-
Designing method to Stating early the steps in an design of experiment to test a
collect data experiments hypothesis
Conduct experiments to test hypothesis by
Collecting data
changing variables that are manipulated.
Interpreting data Presenting data in diagram, tables,
charts and graphs.
Explaining findings of experiments and stating conclusions
Defining operationally
Explain relationships Understanding Cause and
between variables in an Effect Relationships
experiment
- what caused what
e.x : to happen and why
Describing Relationships Between Variables
between the independent
and dependant variables
plus the standard of Definition :
comparison
Sub process of communicating
Operationally : an action (operation)
e.x :
very soft
Definitions are in context of students' experiences - not
from the glossary, not to be memorized
Explaining how to measure a variable in an experiment
INTERPRETING Definition :
DATA Data – information scientist
collect by observation and
measurement
Interpreting data – find some
pattern in the data which give
them an answer to the problem
Types of data
Picture Table Writing
Try to indicate about Identify relationship
the hypothesis between variables to
Graphs make conclusion
Colour Line Bar Pie
You might also like
- Three Domains of LearningDocument7 pagesThree Domains of LearningLoiweza AbagaNo ratings yet
- DLL 12 Social Relationships in Middle and Late AdolescentsDocument3 pagesDLL 12 Social Relationships in Middle and Late Adolescentsanon_298904132100% (10)
- Intervention Program For Students With Learning Difficulties in English S.Y. 2020-2021 I. RationaleDocument3 pagesIntervention Program For Students With Learning Difficulties in English S.Y. 2020-2021 I. RationaleJaquelyn Montales100% (6)
- Integrated Science Process SkillDocument7 pagesIntegrated Science Process Skillcikgu gio80% (15)
- Activate 1 BiologyDocument120 pagesActivate 1 BiologyMarina Belloni100% (1)
- Science Process Skills PDFDocument28 pagesScience Process Skills PDFNantha Kumar Sivaperumal100% (1)
- Pertemuan 6 Bab V Variabel Dan Desain Riset AkuntansiDocument15 pagesPertemuan 6 Bab V Variabel Dan Desain Riset AkuntansiSusanto ChNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Aims, Goals and ObjectivesDocument24 pagesTopic 3: Aims, Goals and ObjectivesramoneseNo ratings yet
- Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor DomainsDocument3 pagesCognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor DomainsISEELAHKNo ratings yet
- Expe Chap 7 G3Document11 pagesExpe Chap 7 G3Nadine Chanelle QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Handouts Sa ExpiDocument7 pagesHandouts Sa ExpiNorhaine GadinNo ratings yet
- Exp Psych Midterm RevDocument4 pagesExp Psych Midterm RevNathalie ReyesNo ratings yet
- W1 Intro StatisticsDocument18 pagesW1 Intro StatisticsIli RaihanaNo ratings yet
- 1 Doe TerminologiesDocument3 pages1 Doe TerminologiesSethu Malaravan K ENo ratings yet
- III ReviewerDocument8 pagesIII ReviewereuanjosephgNo ratings yet
- CognitiveDocument4 pagesCognitiveECE CAPILINo ratings yet
- Level Description Action Verbs Describing Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesLevel Description Action Verbs Describing Learning OutcomesjameelaNo ratings yet
- Verbs Reflecting Learning in 3 DomainsDocument3 pagesVerbs Reflecting Learning in 3 DomainsDzois DzoisNo ratings yet
- Qm457-Chapter8Document7 pagesQm457-Chapter8fatialqaffas31No ratings yet
- Community Precepting Teaching Tips: Using Questioning As A Tool For Effective PreceptingDocument2 pagesCommunity Precepting Teaching Tips: Using Questioning As A Tool For Effective PreceptingDaphne DunneNo ratings yet
- HYPO - LanaDocument81 pagesHYPO - Lanalana El-TawilNo ratings yet
- PR2-Q2-Notes-2023-2024-2Document7 pagesPR2-Q2-Notes-2023-2024-2karylleporras2No ratings yet
- Competencies and Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesCompetencies and Learning ObjectivesnicutmihaelaNo ratings yet
- LM1M Main PPT For Module 1Document17 pagesLM1M Main PPT For Module 1matthewisaac624No ratings yet
- Thinking Like A Researcher: Lanang PrayogoDocument16 pagesThinking Like A Researcher: Lanang PrayogoAndrianNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument30 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentma_tabora6283No ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 ReviewerMaria Christine OgenaNo ratings yet
- Science Year 4, Unit 1, Scientific SkillsDocument15 pagesScience Year 4, Unit 1, Scientific SkillsSiti Fadilah Juhan100% (1)
- Learning Domains and Effective Delivery of Instruction by Cindy Vinson Ed.DDocument11 pagesLearning Domains and Effective Delivery of Instruction by Cindy Vinson Ed.DAngelo Garret V. LaherNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document6 pagesPractical Research 2Marco Antonio SurioNo ratings yet
- Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingDocument4 pagesCognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingYoleen SirkNo ratings yet
- Domains Adjectives For LPDocument4 pagesDomains Adjectives For LPnove quimpoNo ratings yet
- Verb Use in Different Domains: Cognitive Domain Level Description Action Verbs Describing Learning OutcomesDocument3 pagesVerb Use in Different Domains: Cognitive Domain Level Description Action Verbs Describing Learning OutcomesEric Doroja MabesaNo ratings yet
- Experimental ResearchDocument25 pagesExperimental ResearchKinjal ShahNo ratings yet
- CONCEPT MAP Science Process SkillsDocument1 pageCONCEPT MAP Science Process Skillsjerungbiru0% (1)
- consumer behavior cheat sheetDocument4 pagesconsumer behavior cheat sheetheckel.ameliaNo ratings yet
- Correlational & Quasi Experimental DesignsDocument52 pagesCorrelational & Quasi Experimental DesignsFerdinand Pagaran100% (1)
- Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingDocument3 pagesCognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains GradingErwin Labayog MedinaNo ratings yet
- Summar Quant Designs ChartDocument1 pageSummar Quant Designs ChartYoni MacNo ratings yet
- Science Process SkillDocument2 pagesScience Process SkillNur Atiqah Mohd MansorNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy Action Verbs Level DefinDocument2 pagesBlooms Taxonomy Action Verbs Level DefinThoa BùiNo ratings yet
- Dementia306 - Practical Research 2.bwDocument4 pagesDementia306 - Practical Research 2.bwAndrei Tan CaonesNo ratings yet
- Research Design: Pragmatic Constructivism Post-PositivismDocument2 pagesResearch Design: Pragmatic Constructivism Post-PositivismMas KudinNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Diagnostic UnitDocument6 pagesMathematics Diagnostic UnitScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- PR2 - Quantitative Research DesignDocument14 pagesPR2 - Quantitative Research DesignSammi ArguelesNo ratings yet
- Research Approaches and Data Collection MethodsDocument25 pagesResearch Approaches and Data Collection Methodsjumanhamdan4No ratings yet
- Correlation and Regression - Interview Questions in Business AnalyticsDocument5 pagesCorrelation and Regression - Interview Questions in Business AnalyticsrohitNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review ResearchDocument2 pagesPointers To Review Researchangel.pinawinNo ratings yet
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument37 pagesTheoretical FrameworkArvie Shayne Tarrago GiananNo ratings yet
- Formulation of The Research TitleDocument14 pagesFormulation of The Research TitleSeizashino AkiyamaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Lesson 1Document2 pagesPractical Research Lesson 1Reinn DionisioNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy BloomDocument5 pagesTaxonomy BloomKhusnul HidayatNo ratings yet
- Document - Ced - Assessment Office - Blooms Taxonomy Action VerbsDocument4 pagesDocument - Ced - Assessment Office - Blooms Taxonomy Action Verbscaa05 caaNo ratings yet
- Cluster Analysis Anova Test Correlation Descriptive StatisticsDocument1 pageCluster Analysis Anova Test Correlation Descriptive StatisticsnimasatheeshNo ratings yet
- 3.1.6 Types of Quantitative Research True Experimental ResearchDocument21 pages3.1.6 Types of Quantitative Research True Experimental Researchcali beeNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed10 Lesson3 CompressedDocument36 pagesProf Ed10 Lesson3 CompressedFerdinand LiquiganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantitative Research: Adonis P. David, PHD Philippine Normal UniversityDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Quantitative Research: Adonis P. David, PHD Philippine Normal Universityabegail solimanNo ratings yet
- App 2 Finals - Quanti MethodsDocument3 pagesApp 2 Finals - Quanti MethodsBryle GarayNo ratings yet
- Guide in Writing LO Under Cognitive DomainDocument4 pagesGuide in Writing LO Under Cognitive DomainveeannejoseNo ratings yet
- Life Orientation Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2021 Final-1Document10 pagesLife Orientation Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2021 Final-1kameshanmarimuthuNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lesson Plan Outline: Shaving Cream Writing ActivityDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Outline: Shaving Cream Writing Activityapi-299102530No ratings yet
- Artifact Reflection SheetDocument3 pagesArtifact Reflection Sheetapi-256081978No ratings yet
- Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary (6Document7 pagesOxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary (6Multahada SiregarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Bearitz paleroNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning Unit IV Learning Theories and Characteristics of Adult LearnersDocument34 pagesTeaching and Learning Unit IV Learning Theories and Characteristics of Adult LearnersSyed MaazNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ARTDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ARTAngela QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Shape of A Lesson of Language Skills: Presentation, Practice, Production, Pre-Stage, While-Stage, Post-StageDocument2 pagesModule 3: Shape of A Lesson of Language Skills: Presentation, Practice, Production, Pre-Stage, While-Stage, Post-StageLuan TranNo ratings yet
- FS 2 Activity 3Document7 pagesFS 2 Activity 3Yang NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Ellis, R. 2012 - Current Issues in The Teaching of Grammar An SLA Perspective PDFDocument25 pagesEllis, R. 2012 - Current Issues in The Teaching of Grammar An SLA Perspective PDFNgocPhamNo ratings yet
- Learning Style InventoryDocument3 pagesLearning Style InventorytituspermadiNo ratings yet
- ngôn ngữ học tri nhận thuyết trìnhDocument4 pagesngôn ngữ học tri nhận thuyết trìnhNgânNo ratings yet
- Lajada LDM 2 PortfolioDocument21 pagesLajada LDM 2 Portfoliojohnedel lajadaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Module 2 Learner PoE GuideDocument53 pages5 - Module 2 Learner PoE GuideDorah TsoseNo ratings yet
- Background of Chitta: Pancha Kosha: Man Has at Least Five Bodies, Pancha KoshaDocument2 pagesBackground of Chitta: Pancha Kosha: Man Has at Least Five Bodies, Pancha KoshaChandra kant PrakashNo ratings yet
- P e LesonDocument3 pagesP e Lesonapi-312383304No ratings yet
- Material Selection & AdaptationDocument6 pagesMaterial Selection & AdaptationJerome Law100% (2)
- Lesson Plan 1Document5 pagesLesson Plan 1api-314438484No ratings yet
- British Council IELTS Online ApplicationDocument2 pagesBritish Council IELTS Online ApplicationRachid MenserNo ratings yet
- Serena Longman Lesson Plan ps1 Snowflake Art Activity Nov 19Document5 pagesSerena Longman Lesson Plan ps1 Snowflake Art Activity Nov 19api-448711351No ratings yet
- Kaintal School PPT 01Document10 pagesKaintal School PPT 01Kaintal Senior SchoolNo ratings yet
- Stroke MistakesDocument10 pagesStroke Mistakeschitra selviNo ratings yet
- Essay On RealityDocument2 pagesEssay On RealityJam Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter A2 How Professionals Learn Through WorkDocument28 pagesChapter A2 How Professionals Learn Through WorkBushra AliNo ratings yet
- Teacher Sheet: TOPIC: Observation and LogicDocument10 pagesTeacher Sheet: TOPIC: Observation and LogicSylvie CatalanNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance: Quarter1 - Module 1: ThesuperheroinmeDocument9 pagesHomeroom Guidance: Quarter1 - Module 1: ThesuperheroinmeRonalyn DejanNo ratings yet
- Clarity of Learning TargetsDocument23 pagesClarity of Learning TargetsClarina Jane DosdosNo ratings yet
- Skills of A Successful TrainerDocument16 pagesSkills of A Successful TrainerShivani BansalNo ratings yet
- Intelligence Assessments For Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic ReviewDocument8 pagesIntelligence Assessments For Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic ReviewZahra SativaniNo ratings yet