0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 viewsCompetitive Strategy
Competitive Strategy
Uploaded by
Harsh KathotiaA competitive strategy outlines how a company will attract customers, withstand competition, and strengthen its market position. There are five main competitive strategies: overall low-cost leadership, best cost provider, broad differentiation, focused low-cost, and focused differentiation. The strategies involve reducing costs, differentiating products, or focusing on a niche market to generate competitive advantages over rivals. The choice of strategy depends on factors like customer needs, price sensitivity, and barriers to entry in the industry.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Competitive Strategy
Competitive Strategy
Uploaded by
Harsh Kathotia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views13 pagesA competitive strategy outlines how a company will attract customers, withstand competition, and strengthen its market position. There are five main competitive strategies: overall low-cost leadership, best cost provider, broad differentiation, focused low-cost, and focused differentiation. The strategies involve reducing costs, differentiating products, or focusing on a niche market to generate competitive advantages over rivals. The choice of strategy depends on factors like customer needs, price sensitivity, and barriers to entry in the industry.
Original Title
CompetitiveStrategy
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
A competitive strategy outlines how a company will attract customers, withstand competition, and strengthen its market position. There are five main competitive strategies: overall low-cost leadership, best cost provider, broad differentiation, focused low-cost, and focused differentiation. The strategies involve reducing costs, differentiating products, or focusing on a niche market to generate competitive advantages over rivals. The choice of strategy depends on factors like customer needs, price sensitivity, and barriers to entry in the industry.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views13 pagesCompetitive Strategy
Competitive Strategy
Uploaded by
Harsh KathotiaA competitive strategy outlines how a company will attract customers, withstand competition, and strengthen its market position. There are five main competitive strategies: overall low-cost leadership, best cost provider, broad differentiation, focused low-cost, and focused differentiation. The strategies involve reducing costs, differentiating products, or focusing on a niche market to generate competitive advantages over rivals. The choice of strategy depends on factors like customer needs, price sensitivity, and barriers to entry in the industry.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Competitive Strategy
Competitive Strategy
A competitive strategy consists of moves to
Attract customers
Withstand competitive pressures
Strengthen an organization’s market position
The objective of a competitive strategy is to generate a competitive
advantage, increase the loyalty of customers and beat competitors
A competitive strategy is narrower in scope than a business strategy
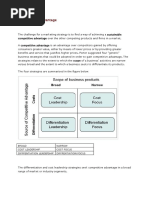
Five competitive strategies are
Overall low-cost leadership strategy
Best cost provider strategy
Broad differentiation strategy
Focused low-cost strategy
Focused differentiation strategy
Overall Low-Cost Leadership Strategy
Strive to be the overall low-cost provider in an industry
How to achieve overall low-cost leadership
Scrutinize each cost activity
Manage each cost lower year after year
Reengineer cost activities to reduce overall costs
Cut some cost activities out of the value chain
Competitive strengths of a overall low-cost strategy
Organization in a better position to compete offensively on price
Organization is better able to negotiate with large customers
Organization is able to use price as a defense against substitutes
Low cost is a significant barrier to entry
Organization is more insulated from the power of suppliers
When Does an Overall Low-Cost Strategy Work
the Best
When price competition is a dominant competitive force
The product is a “commodity”
There are few ways to differentiate the product
Most customers have similar needs/requirements
Customers incur low switching costs changing sellers
Customers are large and have significant bargaining power
When Doesn’t a Overall Low-Cost Strategy Work
When technological breakthroughs open cost reductions for
competitors, negating a low-cost provider’s efficiency advantage
Competitors find it relatively easy and inexpensive to imitate the
leader’s low cost methods
Low-cost leader focuses so much on cost reduction that the
organization fails to respond to
Changes in customer requirements for quality and service
New product developments
Reduced customer sensitivity to price
Broad Differentiation Strategies
Striving to build customer loyalty by differentiating an organization’s
products from competitors’ products
Keys to success include
Finding ways to differentiate to create value for customers that are not easily
copied
Not spending more to differentiate than the price premium that can be charged
A successful differential strategy allows an organization to
Set a premium price
Increase unit sales
Build brand loyalty
Broad Differentiation Strategies
Where to look for differentiation opportunities
Supply chain
Research and development
Production activities
Marketing, sales and service activities
Strengths of a Differentiation Strategy
Customers develop loyalty to the brand
Brand loyalty acts as an entry barrier
Organization is better able to fend off threats of substitute products because of
brand loyalty
Reduces bargaining power of large customers since other brands are less
attractive
Seller may be in a better position to resist efforts of suppliers to raise prices
Pitfalls of a Broad Differentiation Strategy
Trying to differentiate on an unimportant product feature that doesn’t result
in providing more value to the customer
Over differentiating the product such that the product features exceed the
customers’ needs
Charging a price premium that buyers perceive as too high
Ignoring need to signal value
Not identifying what customers consider valuable
Best-Cost Provider Strategy
Striving to give customers more value for the money by combining an
emphasis on low cost with an emphasis on upscale differentiation
Combines low-cost and differentiation
The objective is to create superior value by meeting or beating customer
expectation on product attributes and beating their price expectations
Keys to success
Match close competitors on key product attributes and beat them on cost
Expertise at incorporating upscale product attributes at a lower cost than
competitors
Contain costs by providing customers a better product
Advantages of Best-Cost Provider Strategy
Competitive advantage comes from matching close competitors on key
product attributes and beating them on price
Most successful best-cost providers have skills to simultaneously manage
costs down and product quality up
Best-cost provider can often beat an overall low-cost strategy and a broad
differentiation strategy where
Customer diversity makes product differentiation the norm
Many customers are price and value sensitive
Focus Strategies
Focus strategy based on low-cost
Concentrate on a narrow customer segment beating the competition on lower
cost
Focus strategy based on differentiation
Offering niche customers a product customized to their needs
Overall objective of both focus strategies is to do a better job of serving a
niche target market than competitors
Keys to success
Choose a niche were customers have a distinctive preference, unique needs or
special requirements
Develop a unique ability to serve the needs of a niche target market
What Makes a Niche Attractive?
Large enough to be profitable
Good growth potential
Not critical to the success of major competitors
Organization has the resources to effectively serve the niche
Organization can defend itself against challengers through a superior ability
to serve the niche
No competitors are focusing on the niche
Strengths and Risks of Focus Strategies
Strengths
Competitors don’t have the motivation to meet specialized needs of the niche
Organization’s competitive advantage could be seen as a barrier to entry
Organization’s competitive advantage provides an obstacle for substitutes
Organization’s ability to meet the needs of customers in the niche can reduce the
bargaining power of large niche buyers
Risks
Broad differentiated competitors may find effective ways to enter the niche
Niche customers’ preferences may move toward the product attributes desired by
a larger market segment
Profitability may be limited if too many competitors enter the niche
You might also like
- Scott Cunningham - Causal Inference (2020) PDFDocument591 pagesScott Cunningham - Causal Inference (2020) PDFRoger Mario Lopez0% (1)
- Business Management 3B Exam NotesDocument39 pagesBusiness Management 3B Exam NotesTashaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMarketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Competitive Strategy: Presented byDocument13 pagesCompetitive Strategy: Presented byARsal_8No ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competing StrategiesDocument30 pagesThe Five Generic Competing StrategiesFarhana MituNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Presentation by Omkar, Vijay and DilleshwarDocument20 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Presentation by Omkar, Vijay and DilleshwarEverton Snow MuberekwaNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Competitive Advantage Chapter 6Document7 pagesStrategy and Competitive Advantage Chapter 6Drishtee DevianeeNo ratings yet
- Strategy Management Chp. 4-Business Level StrategyDocument8 pagesStrategy Management Chp. 4-Business Level StrategyNabilah UsmanNo ratings yet
- Competitive StrategyDocument16 pagesCompetitive Strategyaerogem100% (2)
- On Competitive StrategiesDocument33 pagesOn Competitive Strategiesmmjmmj100% (1)
- The Five Generic Competitive StrategiesDocument11 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive StrategiesMonoar HossainNo ratings yet
- 6Document26 pages6vikas mauryaNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?Document21 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?RajatNo ratings yet
- Five Generic Competitive StrategiesDocument11 pagesFive Generic Competitive StrategiesJianelli MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To All Five Strategies Competitive Advantages How To Achieve? Key Success Advantages and Pitfalls ExamplesDocument35 pagesIntroduction To All Five Strategies Competitive Advantages How To Achieve? Key Success Advantages and Pitfalls ExamplesSaurabh ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Assignment 3Document14 pagesStrategic Management Assignment 3Djimajor Robert TettehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document6 pagesChapter 5rakibulislammbstu01No ratings yet
- GRP5 GCSDocument42 pagesGRP5 GCSThilak AlvaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management: Accounting & ControlDocument25 pagesStrategic Cost Management: Accounting & ControlEricka BendongNo ratings yet
- Building Competitive Advantage Through Business-Level StrategyDocument33 pagesBuilding Competitive Advantage Through Business-Level StrategyRizwan Sait100% (2)
- V. Five Generic Competitive Strategies Cost Efficient Management and Revamping of The Value ChainDocument5 pagesV. Five Generic Competitive Strategies Cost Efficient Management and Revamping of The Value Chaingwyneth aquino100% (1)
- Competitive Strategy and Customer Satisfaction Market SegmentationDocument43 pagesCompetitive Strategy and Customer Satisfaction Market Segmentationjacobseraphine88No ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?Document30 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?amitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5ERICKA MAE NATONo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive StrategiesDocument36 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive StrategiesPratyush JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Generic Strategies: Presented by R.Antlin Jenifer MBA 905Document13 pagesGeneric Strategies: Presented by R.Antlin Jenifer MBA 905augastinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Global Business-Level Strategies - Choosing Competitive Strategies in A Single IndustryDocument27 pagesChapter 4 - Global Business-Level Strategies - Choosing Competitive Strategies in A Single IndustryBảo ChâuuNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Presented By: Group12Document14 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Presented By: Group12oopsrishiNo ratings yet
- SM 6Document22 pagesSM 6Ayesha TariqNo ratings yet
- Business Level StrategyDocument41 pagesBusiness Level Strategyrohitp628No ratings yet
- generic startegies(porter)Document6 pagesgeneric startegies(porter)Mandhlaenkosi MugaraNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Chapter TitleDocument25 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Chapter TitleMd.Islam ShajibNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 MCQDocument8 pagesChap 5 MCQethanvampireNo ratings yet
- Business Level Strategies UnitDocument23 pagesBusiness Level Strategies Unitwruttika jadhavNo ratings yet
- Corporate Policy & Strategy: Dr. Nguyễn Gia NinhDocument44 pagesCorporate Policy & Strategy: Dr. Nguyễn Gia NinhSơn VũNo ratings yet
- S1 - 2 Business StrategiesDocument33 pagesS1 - 2 Business Strategiespravit08No ratings yet
- EMB 690 SM Lecture 6 NSU FinalDocument21 pagesEMB 690 SM Lecture 6 NSU FinalmarufNo ratings yet
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocument4 pagesPorter's Generic StrategiesJayanta RakshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Resumen y CasoDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Resumen y CasoPolly GarcíaNo ratings yet
- BLSDocument21 pagesBLSArvind MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?Document22 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?ThuyDuongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Strat Formulation Long Term Goals PP Slides 2024Document22 pagesChapter 6 Strat Formulation Long Term Goals PP Slides 2024gailastrid16No ratings yet
- STRM 05Document44 pagesSTRM 05Professor Dr. Md. Atiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?Document24 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?MahiraNo ratings yet
- Generic StrategiesDocument7 pagesGeneric StrategiesMagnus ColacoNo ratings yet
- SM Mod 05Document60 pagesSM Mod 05Kavi_3788No ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?Document15 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?Ramana Reddy NarapureddyNo ratings yet
- 11 1204 Porter StrategyDocument13 pages11 1204 Porter Strategyanna rambuNo ratings yet
- Module VDocument17 pagesModule Vaksharmohta17No ratings yet
- Competitive AdvantageDocument3 pagesCompetitive AdvantageAnonymous X8hNvFAyzNo ratings yet
- Business Policy & StrategyDocument25 pagesBusiness Policy & StrategyRohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Business-Level StrategyDocument40 pagesChapter 5: Business-Level StrategyNadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Chapter TitleDocument25 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Chapter TitlemadanmohansinghNo ratings yet
- 05 02102015 Lima Strategi GenerikDocument12 pages05 02102015 Lima Strategi Generiktaiyo_hoshiNo ratings yet
- Business Level Strategy: Ijaz AhmedDocument51 pagesBusiness Level Strategy: Ijaz AhmedNaeem Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- PorterDocument31 pagesPorterKashif Niaz Meo100% (1)
- The Five Generic StrategiesDocument29 pagesThe Five Generic StrategiesmahiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Business-Level Strategy: OverviewDocument22 pagesChapter 4: Business-Level Strategy: OverviewTeerraNo ratings yet
- Value-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1From EverandValue-based Intelligent Pricing: Marketing and Business, #1No ratings yet
- Competition Demystified (Review and Analysis of Greenwald and Kahn's Book)From EverandCompetition Demystified (Review and Analysis of Greenwald and Kahn's Book)No ratings yet
- Profitable Promotions : A Blueprint for Entrepreneurial Advertising SuccessFrom EverandProfitable Promotions : A Blueprint for Entrepreneurial Advertising SuccessNo ratings yet
- Lud. Jego Zwyczaje, Sposób Życia, Mowa, Podania, Przysłowia, Obrzędy, Gusła, Zabawy, Pieśni, Muzyka I Tańce - Kujawy - Oskar Kolberg - Warszawa 1867 R.Document336 pagesLud. Jego Zwyczaje, Sposób Życia, Mowa, Podania, Przysłowia, Obrzędy, Gusła, Zabawy, Pieśni, Muzyka I Tańce - Kujawy - Oskar Kolberg - Warszawa 1867 R.Ewa Mitura PNo ratings yet
- 2334 96381202057M PDFDocument7 pages2334 96381202057M PDFMuhammad NajeebNo ratings yet
- Buffer ATLDocument10 pagesBuffer ATLIkke Astrid DewiNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Catch Your FIDICDocument5 pagesProject Management: Catch Your FIDICboomiNo ratings yet
- Linear Programing and Types of MatrixDocument5 pagesLinear Programing and Types of MatrixAbdu Mohammed86% (7)
- CIVE1144 - Structural Analysis Lec 3 (2019)Document35 pagesCIVE1144 - Structural Analysis Lec 3 (2019)Leon TltNo ratings yet
- Legal Opinion SampleDocument2 pagesLegal Opinion SampleMikhail RamosNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1Document59 pagesLecture Notes 1Prabal RawatNo ratings yet
- Cpe 561Document19 pagesCpe 561Akpan Anthonia AthanasiusNo ratings yet
- Job Evaluation MethodsDocument5 pagesJob Evaluation MethodsSai KumarNo ratings yet
- ABRY Scheme Guidelines Amended On 02 07 2021Document12 pagesABRY Scheme Guidelines Amended On 02 07 2021Mohit KhatriNo ratings yet
- 2011 Costume Jewellery in FranceDocument6 pages2011 Costume Jewellery in Francesavior1989No ratings yet
- Hard HandoffDocument2 pagesHard HandoffSiddharth JainNo ratings yet
- Plutus Smart ContractsDocument126 pagesPlutus Smart Contractscaminante992997100% (1)
- Chaotic Pulsing and Quasi-Periodic Route To Chaos in A Semiconductor Laser With Delayed Opto-Electronic FeedbackDocument8 pagesChaotic Pulsing and Quasi-Periodic Route To Chaos in A Semiconductor Laser With Delayed Opto-Electronic Feedback侯博文No ratings yet
- DZ BANK Corporate PresentationDocument64 pagesDZ BANK Corporate PresentationDiego BrandeauNo ratings yet
- Exposé AnglaisDocument5 pagesExposé AnglaisEFRAIM BouadjeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Batch - Processing (Avidemux) PDFDocument4 pagesTutorial Batch - Processing (Avidemux) PDFSasa MiljkovicNo ratings yet
- Eee2001 NT Module 6 l1Document7 pagesEee2001 NT Module 6 l1akshata bhatNo ratings yet
- Community and public health nursing promoting the public s health Allender All Chapters Instant DownloadDocument55 pagesCommunity and public health nursing promoting the public s health Allender All Chapters Instant Downloadmaalabelda6m100% (2)
- Stock Statement FormatDocument4 pagesStock Statement FormatshreefillingstationddnNo ratings yet
- Xpress LanguageDocument600 pagesXpress Languageghitza123456No ratings yet
- RP2-1 Action Request Response - QMSDocument2 pagesRP2-1 Action Request Response - QMSwindel dimaandalNo ratings yet
- 02 - F - LexisNexis JurisClasseurDocument4 pages02 - F - LexisNexis JurisClasseurkyanlee0721No ratings yet
- 2 ADVIA 360 560 Presentation 2016-06-09Document30 pages2 ADVIA 360 560 Presentation 2016-06-09April WoodsNo ratings yet
- TD2Document3 pagesTD2Elias KhouryNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory (Waiting Line Theory) : Queueing Theory Study Notes - Emma Charles 0753-236-367/0787-080-333 - Win 10 ProDocument10 pagesQueuing Theory (Waiting Line Theory) : Queueing Theory Study Notes - Emma Charles 0753-236-367/0787-080-333 - Win 10 ProemmaNo ratings yet
- Dip Ipm App NoteDocument43 pagesDip Ipm App Noteamateur123456No ratings yet
- 2016 2020 Succession Case DigestsDocument27 pages2016 2020 Succession Case Digestsdennis buclanNo ratings yet