0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsPHY3 AJune 2006
This document contains a physics exam question with multiple parts about astrophysics topics:
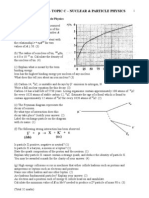
1) A Hertzsprung-Russell diagram showing different stars is provided, and students are asked to label the axes, identify stars as red giants or low mass main sequence stars, and calculate the luminosity of star ζ Tau.
2) Nuclear fusion is discussed, where students calculate the mass change and energy released in the fusion of hydrogen to helium.
3) Pulsars are introduced, with students identifying pulsar characteristics and explaining how double pulsars could be detected. It is suggested the two pulsars in the discovered double pulsar system will coalesce after 85 million years.
4) The density
Uploaded by
api-3726022Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsPHY3 AJune 2006
This document contains a physics exam question with multiple parts about astrophysics topics:
1) A Hertzsprung-Russell diagram showing different stars is provided, and students are asked to label the axes, identify stars as red giants or low mass main sequence stars, and calculate the luminosity of star ζ Tau.
2) Nuclear fusion is discussed, where students calculate the mass change and energy released in the fusion of hydrogen to helium.
3) Pulsars are introduced, with students identifying pulsar characteristics and explaining how double pulsars could be detected. It is suggested the two pulsars in the discovered double pulsar system will coalesce after 85 million years.
4) The density
Uploaded by
api-3726022Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 1
PHY3 JUNE 2006 - TOPIC A - ASTROPHYSICS 30 minutes 1
1. (a) On the Hertzspmng-Russell diagram shown
opposite X indicates the position of the Sun.
(i) On a copy of this diagram, add labels
and units to each axis. (2)
(ii) Complete the scale on the y-axis by
adding three further values where indicated. (2)
(iii) Complete the scale on the x-axis by adding
two further values where indicated. (1)
(iv) Letters A, B, C, D and E represent different
stars. Identify all stars which could be:
(a) a red giant;
(b) a low mass star on the main sequence (2)
(v) Use the data given show that the luminosity of the star ζ Tau (Zeta Tauri) is approximately
4 x 1030 W. DATA: Intensity = 1.9 x 10 -8 Wm-2 ; Distance from Earth = 4.0 x 1018 m. (3)
(vi) One of the labelled stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is ζ Tau. Calculate the luminosity
of ζ Tau in terms of solar luminosities and thus deduce which letter must represent this star.
Luminosity of the Sun L۞ == 3.9 x 1026 W. (3)
(b) When stars undergo nuclear fusion, hydrogen
is fused to form helium. As part of this process
two 32He nuclei react to form 42He.
(i) Calculate the change in mass in one such fusion reaction. (2)
(ii) Hence calculate the energy released by this
fusion reaction. (2)
(c) In 2004 astronomers discovered a double pulsar: a system
of two pulsars orbiting each other.
(i) Identify the four options that can be used to correctly
describe pulsars.
A pulsar is a {neutron star / red giant / white dwarf/ core remnant}.
A pulsar was previously a {white dwarf/ black hole / supernova}.
A pulsar has a mass of at least {0.4 /1.4 / 2.5 / 8} solar masses. (4)
(ii) Explain how astronomers detect pulsars and suggest how a double pulsar might be recognised.
You may be awarded a mark for the clarity of your answer. (4)
(iii) It is suggested that these two stars will spiral in towards each other and coalesce into a single
mass after 85 million years. Suggest what might be formed by such an event. (1)
(d) (i) Write an equation for the density
of a star in terms of its mass and radius. (1)
(ii) The graph shows the mass-radius
relationship for white dwarf stars.
The mass of the Sun M۞ = 2.0 x 1030 kg.
Using the graph, calculate the density of two
white dwarf stars and hence show that the density
of a white dwarf increases as its mass increases. (3)
(iii) Describe what eventually happens to a
white dwarf star. (2)
Total 32 marks
You might also like
- Astronomy Notes - Year 10 Victorian Curriculum 2022No ratings yetAstronomy Notes - Year 10 Victorian Curriculum 20224 pages
- Physics Resources - Astrophysics HSC Questions PDFNo ratings yetPhysics Resources - Astrophysics HSC Questions PDF22 pages
- MadXAbhi - World Geography - by MadXAbhi - RobotNo ratings yetMadXAbhi - World Geography - by MadXAbhi - Robot49 pages
- University of Colombo, Sri Lanka Faculty of Science: Level Iii Examination in Science - Semester I - 2013No ratings yetUniversity of Colombo, Sri Lanka Faculty of Science: Level Iii Examination in Science - Semester I - 20133 pages
- AST-103L Spring 2001: Hubble Redshift-Distance Relation: Page 1 of 9No ratings yetAST-103L Spring 2001: Hubble Redshift-Distance Relation: Page 1 of 99 pages
- Unit-5 Topic-7 Astrophysics and Cosmology Answers (End-Of-Chapter & Examzone)100% (3)Unit-5 Topic-7 Astrophysics and Cosmology Answers (End-Of-Chapter & Examzone)8 pages
- E5 Stellar Evolution Q From Old SyllabusNo ratings yetE5 Stellar Evolution Q From Old Syllabus23 pages
- Francois Legrand Et Al - On The Metallicity of Star-Forming Dwarf GalaxiesNo ratings yetFrancois Legrand Et Al - On The Metallicity of Star-Forming Dwarf Galaxies11 pages
- The Orbital Periods of AA Dor and NY VirNo ratings yetThe Orbital Periods of AA Dor and NY Vir5 pages
- Gravitational Lensing - A Short Treatise: April 2016No ratings yetGravitational Lensing - A Short Treatise: April 20167 pages
- Math-Assignment-Part-3 - 1 - (7585779 - 1 - 1942-1-1634011863s00287752)No ratings yetMath-Assignment-Part-3 - 1 - (7585779 - 1 - 1942-1-1634011863s00287752)2 pages
- Mid-sem_question_paper_172690876192381853766ee8959be3be (1)No ratings yetMid-sem_question_paper_172690876192381853766ee8959be3be (1)2 pages
- You May Not Start To Read The Questions Printed On The Subsequent Pages of This Question Paper Until Instructed That You May Do So by The InvigilatorNo ratings yetYou May Not Start To Read The Questions Printed On The Subsequent Pages of This Question Paper Until Instructed That You May Do So by The Invigilator5 pages
- Solution - Astrophysics - D - Test - IB 2016, 2017 2018, 2019 and 2023No ratings yetSolution - Astrophysics - D - Test - IB 2016, 2017 2018, 2019 and 202317 pages
- Alcyone (star) : Alcyone /æl Tauri, abbreviated Eta Tau, η Tau), is a multiple starNo ratings yetAlcyone (star) : Alcyone /æl Tauri, abbreviated Eta Tau, η Tau), is a multiple star4 pages
- Gecaa - Theory Final Question Sheet: (Total 150 Points)No ratings yetGecaa - Theory Final Question Sheet: (Total 150 Points)11 pages
- H. G. White and E. W. Davis - The AlcubierreWarp Drive in Higher Dimensional SpacetimeNo ratings yetH. G. White and E. W. Davis - The AlcubierreWarp Drive in Higher Dimensional Spacetime22 pages
- 1B23 Modern Physics, Astronomy, and Cosmology: Partial Notes, Astronomy Set 2 - Galaxies Normal GalaxiesNo ratings yet1B23 Modern Physics, Astronomy, and Cosmology: Partial Notes, Astronomy Set 2 - Galaxies Normal Galaxies6 pages
- Characteristics of Stars - Introduction on Stars - Ignacio, Kaya MargarethNo ratings yetCharacteristics of Stars - Introduction on Stars - Ignacio, Kaya Margareth62 pages
- Aperture Photometry Obtaining and Analysing A H-R Diagram of M38 v2.0No ratings yetAperture Photometry Obtaining and Analysing A H-R Diagram of M38 v2.014 pages
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-2. Structure of Atom Q & ANo ratings yetHsslive-Xi-Chem-2. Structure of Atom Q & A14 pages