S4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of Chemistry
S4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of Chemistry
Uploaded by
羅絲雷朵Copyright:
Available Formats
S4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of Chemistry
S4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of Chemistry
Uploaded by
羅絲雷朵Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
S4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of Chemistry
S4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of Chemistry
Uploaded by
羅絲雷朵Copyright:
Available Formats
S.4 Chemistry Chapter 1 Fundamentals of chemistry 1.1 What is Chemistry?
Chemistry is the study of matter. The chemist makes observations and takes measurements. finds patterns in the observations. finds explanations. The observations and measurements are called facts or data. In science, a good guess is called a hypothesis. Laws are statements of important patterns.
1.2 Matter
What is matter? Matter is anything, which occupies space and has mass. There are three states of matter: solid, liquid and gas.
The evidence of the particle in the matter Diffusion (E.g., Blue ink spreads out through water.) The properties of matter - kinetic theory 1. All matter is made up of very small particles. 2. There are spaces between the particles. 3. Particles are in constant motion and have kinetic energy. 4. Temperature average kinetic energy .
1.3 Inter-conversion of states
1.4 Classification of Matter
A. Element An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical methods. e.g. Oxygen, hydrogen 118 elements (92 occur naturally)
Abundance of elements in nature: Elements Oxygen Silicon Aluminium % by mass 46.6% 27.7% 8.1% Oxygen is the most abundant element in nature as 1) free element o2 (in atmosphere,) Iron 5.0% Others 12.6%
2) combined forms (e.g. in water (h2o), sand (Si02), etc.)
B. Compound
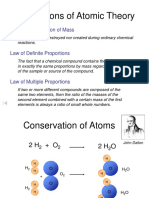
A compound is a pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined together. e.g. Water (h2o), glucose (C6H12O6) Carbon + Oxygen Carbon dioxide
(Reactants) Water
(Product) Hydrogen + Calcium oxide (by electrolysis)
Compound can be decomposed into simple substance by heating or electrolysis.
Calcium carbonate Calcium oxide + Carbon dioxide (by heating) C. Mixture A mixture consists of two or more pure substance (elements or compounds) which have not chemically combined together. e.g. Sea Water (h2o + NaCl), Alloy (Coin: Cu + Ni ; Steal: Fe + C), Air
The differences between mixtures and compounds: Mixture
Composition by mass Changes in formation variable no chemical reaction takes place; usually no heat change in making mixture each constituent substance retains its own properties constituents can be separated by differences in physical properties Does not have a sharp m.p. or b.p.
Compound
fixed chemical reaction takes place; heat is usually given out or absorbed when compound is made. properties are entirely different from those of its constituent elements constituent elements can only be separated by chemical reaction, not by differences in physical properties | Has a sharp m.p. and b.p.
General properties Separation of constituents
Melting point / boiling point
1.5 The separation of mixtures
Mixtures are separated by physical methods. The method used depends on the physical properties of the substances. Filtration Filtration separates an insoluble solid from a liquid. The solid that remains in the filter paper is called the residue. The liquid that passes through is called the filtrate.
Crystallization Crystallization separates a solid from a solution.
Simple distillation Simple distillation separates a pure liquid from a solution.
Fractional distillation Fractional distillation separates mixtures of miscible liquids. The mixture can be separated by fractional distillation if the boiling points of the liquids are different. The important uses of fractional distillation in industry are: To separate crude oil into different fractions To increase the concentration of ethanol in alcohol drinks. The test for a pure substance If the substance is a solid, we check its melting point. If the substance is a liquid, we check its boiling point.
1.6 Properties of substances
Physical properties of a substance are properties that can be measured without changing the chemical composition of the substance. e.g. colour, odour, solubility, electrical conductivity, heat conductivity Chemical properties of a substance are properties that describe its ability to form new substances, e.g. Iron rusts in water, town gas bums in air.
1.7 Changes of substances
A physical change is a change in which on new substance are formed, e.g. Change of states, A chemical change is a change in which one or more new substances are formed, e.g. a piece of paper bums and change to carbon, carbon dioxide and some other gases. Chemical change & Physical change: Chemical change Physical Change Difference New substance(s) is/ are formed No new substance is formed Usually No or Small energy change Large energy change: exothermic or endothermic e.g. Dissolving salt in water Burning carbon in air to give carbon dioxide 4
1.8 Laboratory safety
Laboratory safety is of first importance in any experimental work.
You might also like
- Topic 2 Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument19 pagesTopic 2 Kinetic Particle TheoryKaixin HuangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Practice Test Chem Gas LawsDocument14 pagesChapter 10 Practice Test Chem Gas LawscabbiemartinezNo ratings yet
- Matter & Its CompositionDocument16 pagesMatter & Its CompositionVenkat100% (1)
- Average Atomic Mass Worksheet 2Document1 pageAverage Atomic Mass Worksheet 2api-320485715No ratings yet
- MAR224 Lab Properties of Seawater Complete V3-LaboratorDocument14 pagesMAR224 Lab Properties of Seawater Complete V3-LaboratorpiticmicNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Curriculum UnitDocument37 pagesChemical Reactions Curriculum Unitapi-354615171100% (1)
- Chapter 2 PowerPointDocument38 pagesChapter 2 PowerPointpopadora100% (1)
- Adam Lesson Plan 1Document7 pagesAdam Lesson Plan 1api-257142724No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSneh PatelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Physical and Chemical Change Law of Conservation of Mass and Balancing Equations PDFDocument44 pagesLesson 1 Physical and Chemical Change Law of Conservation of Mass and Balancing Equations PDFJellyNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1050 - General Chemistry II: Introduction To THERMODYNAMICSDocument64 pagesCHEM 1050 - General Chemistry II: Introduction To THERMODYNAMICSMarikNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas: General Chemistry 1Document9 pagesIdeal Gas: General Chemistry 1Daniel Corcino100% (1)
- Chemical-EquilibriumDocument31 pagesChemical-EquilibriumAngelo PunzalanNo ratings yet
- ChemicalReactions PDFDocument27 pagesChemicalReactions PDFJeff Manalo SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - 'Stoichiometry'Document28 pagesTopic 5 - 'Stoichiometry'Nayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Mini Unit Lesson PlansDocument10 pagesMini Unit Lesson Plansapi-207258443100% (1)
- JCE Online - Conceptual Questions and Challenge Problems - Chemical Concepts Inventory PDFDocument6 pagesJCE Online - Conceptual Questions and Challenge Problems - Chemical Concepts Inventory PDFMenna GalalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesChemistry 2 Answer KeyMarielle BuesingNo ratings yet
- Avogadros Law 10Document1 pageAvogadros Law 10ROXAN ANGGOT100% (1)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Chemistry 2015 Form 4Document15 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Chemistry 2015 Form 4suzi0108No ratings yet
- Mole Concept Notes 2Document43 pagesMole Concept Notes 2Gupta's StudioNo ratings yet
- Practice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sDocument10 pagesPractice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sjeffrey XiaoNo ratings yet
- Molar Mass 2Document5 pagesMolar Mass 2FlyEngineer100% (1)
- I. Choose The Correct Answer For Each of The Following Questions From The Given Optional AnswersDocument5 pagesI. Choose The Correct Answer For Each of The Following Questions From The Given Optional AnswersJUNIED MIFTAHNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Chemistry 2Document77 pagesReviewer in General Chemistry 2Ana Marie100% (1)
- Classifying MatterDocument4 pagesClassifying MatterJovanie EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Balancing of Redox Reactions - 1Document2 pagesBalancing of Redox Reactions - 1Anonymous vRpzQ2BL0% (1)
- Lesson 20Document4 pagesLesson 20MarcTnnNo ratings yet
- CY6151 Engineering Chemistry - I - 2 Marks With AnswersDocument4 pagesCY6151 Engineering Chemistry - I - 2 Marks With AnswersalagarsamyveerarajNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Neutralization 2ndDocument14 pagesAcid-Base Neutralization 2ndnabila nur fidiyahNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws GenChemDocument3 pagesGas Laws GenChemNarutoNo ratings yet
- Steps To Predicting The Products of Chemical ReactionsDocument15 pagesSteps To Predicting The Products of Chemical ReactionsAldi JonataNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Document6 pagesChemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Anisah MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding1Document26 pagesCovalent Bonding1BaselNo ratings yet
- The Mole Concept PDFDocument12 pagesThe Mole Concept PDFIftikhar Ahmed0% (2)
- 01 The Study of Chemistry and MeasurementsDocument6 pages01 The Study of Chemistry and MeasurementsJoshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Chemical Reactions and EquationsgustafNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes Lab Pre-Lab DiscussionDocument4 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes Lab Pre-Lab DiscussionDenver Monico MoscosoNo ratings yet
- Intro To Gases and Gas LawsDocument61 pagesIntro To Gases and Gas LawsLuigie100% (1)
- Rates of ReactionDocument10 pagesRates of ReactionAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- 7 Elements in The Human BodyDocument2 pages7 Elements in The Human BodyCris CorsinoNo ratings yet
- Test 1 SolutionsDocument7 pagesTest 1 Solutionsgreg brownNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Document41 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Abcd Reyes100% (1)
- DP Chem Unit 12 Option C - EnergyDocument8 pagesDP Chem Unit 12 Option C - EnergyPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Hess Law QuestionsDocument2 pagesHess Law Questionsronnie schwiersNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument30 pagesChemical ReactionAnna Liza GomezNo ratings yet
- Dalton Model of The AtomDocument10 pagesDalton Model of The AtomLilo TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Naming Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesNaming Covalent Compoundsapi-296446442No ratings yet
- Teacher Name: Shobana Reddy Unit Name Grade: 7 Lesson Name: Exothermic Reactions Subject: ScienceDocument7 pagesTeacher Name: Shobana Reddy Unit Name Grade: 7 Lesson Name: Exothermic Reactions Subject: Scienceapi-531387818No ratings yet
- Equilibrium Worksheet Solutions Final-1Document12 pagesEquilibrium Worksheet Solutions Final-1duderpurrfektNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Properties of Solutions Dr. DDocument36 pagesChapter 12 Properties of Solutions Dr. DRoseman TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Final ReviewDocument3 pages11 Chemistry Final Reviewapi-307565882No ratings yet
- Unit Practice Test: Gas Laws: Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesUnit Practice Test: Gas Laws: Multiple Choiceanj pianoNo ratings yet
- Ionic Covalent LABDocument3 pagesIonic Covalent LABPriyasree KarunanethiNo ratings yet
- Chm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument34 pagesChm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsOluwabusolami Akinola100% (1)
- COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES OF SOLUTION WorksheetDocument11 pagesCOLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES OF SOLUTION Worksheetdefitra131No ratings yet
- First Grading G8 Summative 3 and 4Document3 pagesFirst Grading G8 Summative 3 and 4Ederzon IlustricimoNo ratings yet
- Qca 1bDocument48 pagesQca 1bAlfredo Salamanca :No ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction: Matter and Measurements: OutlineDocument70 pagesChapter 1. Introduction: Matter and Measurements: Outlinelawchung93No ratings yet
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet