Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations Paracetamol
Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations Paracetamol
Uploaded by
Anne Monique Moran OngjocoCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations Paracetamol
Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations Paracetamol
Uploaded by
Anne Monique Moran OngjocoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations Paracetamol
Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations Paracetamol
Uploaded by
Anne Monique Moran OngjocoCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Paracetamol
Action Antipyretic-Reduces fever by acting directly on the hypothalamic heat-regulating center to cause vasodilation and sweating, which helps dissipate heat. Analgesic: Site and mechanism of action unclear
Indications Analgesic-antipyretic in patients with aspirin allergy, hemostatic disturbances, bleeding diatheses, upper GI disease, gouty arthritis Arthritis and rheumatic disorders involving musculoskeletal pain (but lacks clinically significant antirheumatic and antiinflammatory effects) Common cold, flu, other viral and bacterial infections with pain and fever Unlabeled use: Prophylactic for children receiving DPT vaccination to reduce incidence of fever and pain
Side Effect CNS: Headache CV: Chest pain, dyspnea, myocardial damage when doses of 58 g/day are ingested daily for several weeks or when doses of 4 g/day are ingested for 1 yr GI: Hepatic toxicity and failure, jaundice GU: Acute kidney failure, renal tubular necrosis Hematologic: Methemoglobinemia cyanosis; hemolytic anemia hematuria, anuria; neutropenia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypoglycemia Hypersensitivity: Rash, fever
Nursing Considerations Assessment History: Allergy to acetaminophen, impaired hepatic function, chronic alcoholism, pregnancy, lactation Physical: Skin color, lesions; T; liver evaluation; CBC, LFTs, renal function tests Interventions Do not exceed the recommended dosage. Consult physician if needed for children < 3 yr; if needed for longer than 10 days; if continued fever, severe or recurrent pain occurs (possible serious illness). Avoid using multiple preparations containing acetaminophen. Carefully check all OTC products. Give drug with food if GI upset occurs. Discontinue drug if hypersensitivity reactions occur. Treatment of overdose: Monitor serum levels regularly, Nacetylcysteine should be
Antipyretic Analgesic
available as a specific antidote; basic life support measures may be necessary. Teaching points Do not exceed recommended dose; do not take for longer than 10 days. Take the drug only for complaints indicated; it is not an antiinflammatory agent. Avoid the use of other over-the-counter preparations. They may contain acetaminophen, and serious overdosage can occur. If you need an over-the-counter preparation, consult your health care provider. Report rash, unusual bleeding or bruising, yellowing of skin or eyes, changes in voiding patterns. Review dosing schedule and prescribed length of therapy with patient. Instruct patient or caregiver to shake well before measuring dose, and to measure and administer prescribed
Ceftriaxone Antibiotic Cephalosporin
Inhibits mucopeptide synthesis in bacterial cell wall.
Treatment of uncomplicated UTIs, otitis media, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, acute bronchitis, acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, and uncomplicated gonorrhea caused by susceptible strains of specific
CNS Dizziness, headache, seizure (less than 2%).
Dermatologic Erythema multiforme, facial edema, pruritus, skin rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome,
organisms.
toxic epidermal necrolysis, urticaria (less than 2%). GI Diarrhea (16%); nausea (7%); loose or frequent stools (6%); flatulence (4%); abdominal pain, dyspepsia (3%); vomiting (less than 2%); pseudomembranous colitis. Genitourinary Acute renal failure, candidiasis, genital pruritus, transient elevations in BUN or creatinine, vaginitis (less than 2%). Hematologic-Lymphatic Eosinophilia, leukopenia, neutropenia, prolongation in PT, transient thrombocytopenia (less than 2%); agranulocytosis, pancytopenia. Hepatic Hepatitis, jaundice, transient elevations in alkaline phosphatase, ALT, and AST (less than 2%). Hypersensitivity Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions (including shock
dose using dosing spoon, dosing syringe, or medicine cup. Advise patient to take without regard to meals but to take with food if GI upset occurs. Instruct patient to complete entire course of therapy even if symptoms of infection have disappeared. Advise patient to discontinue therapy and contact health care provider immediately if skin rash, hives, itching, or shortness of breath occur. Advise patient to report the following signs of superinfection to health care provider: black furry tongue, foul-smelling stools, vaginal itching or discharge, white patches in mouth. Instruct patient to notify health care provider if infection does not appear to improve or worsens. Instruct patient to
and death), angioedema, drug fever, serum sicknesslike reactions (less than 2%). Monitor Monitor PT and patient's response to therapy Adverse reactions Monitor patient for GI, CNS, general body adverse reactions, and signs of superinfection.
immediately report severe diarrhea, diarrhea containing blood or pus, or severe abdominal cramping.
Pregnancy Category B .
Lactation Undetermined.
Children Safety and efficacy not established in children younger than 6 mo of age.
Hypersensitivity If administered to penicillinallergic patients, use with caution because crosssensitivity has been documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with penicillin allergy.
Renal Function Use with caution in patients
with renal function impairment. Dosage adjustment based on renal function may be required. Ensure that reduced dose is administered to patient with renal function impairment (CrCl less than 60 mL/min) following manufacturer's guidelines. Superinfection May result in bacterial or fungal overgrowth of nonsusceptible microorganisms. GI disease Use with caution, especially for colitis. Prothrombin activity A fall in prothrombin activity may occur; patients at risk include patients with renal or hepatic function impairment, poor nutritional status, patients receiving protracted antimicrobial therapy, and patients previously stabilized on anticoagulant therapy. CNS: Transient, mild drowsiness initially; sedation, depression, lethargy, apathy, fatigue, light-headedness, disorientation, restlessness, confusion,crying, delirium, headache, slurred speech,
Diazepam
Benzodiazepine Anxiolytic Antiepileptic
Exact mechanisms of action not understood; acts mainly at the limbic system and reticular formation; may act in spinal cord and at supraspinal sites to produce skeletal muscle
Management of anxiety disorders or for short-term relief of symptoms of anxiety Acute alcohol withdrawal; may be useful in symptomatic relief of acute
Take this drug exactly as prescribed. Do not stop taking this drug (longterm therapy, antiepileptic therapy) without consulting your health care provider.
Skeletal muscle relaxant (centrally acting)
relaxation; potentiates the effects of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter; anxiolytic effects occur at doses well below those necessary to cause sedation, ataxia; has little effect on cortical function.
agitation, tremor, delirium tremens, hallucinosis Muscle relaxant: Adjunct for relief of reflex skeletal muscle spasm due to local pathology (inflammation of muscles or joints) or secondary to trauma;spasticity caused by upper motoneuron disorders (cerebral palsy and paraplegia); athetosis, stiff-man syndrome Parenteral: Treatment of tetanus Antiepileptic: Adjunct in status epilepticus and severe recurrent convulsive seizures (parenteral); adjunct in seizure disorders (oral) Preoperative (parenteral): Relief of anxiety and tension and to lessen recall in patients prior to surgical procedures, cardioversion, and endoscopic procedures Rectal: Management of selected, refractory patients with epilepsy who require intermittent use to control bouts of increased seizure activity Unlabeled use: Treatment of panic attacks
dysarthria, stupor, rigidity, tremor, dystonia, vertigo, euphoria, nervousness, difficulty in concentration, vivid dreams, psychomotor retardation, extrapyramidal symptoms; mild paradoxical excitatory reactions, during first 2 wk of treatment, visual and auditory disturbances, diplopia, nystagmus, depressed hearing, nasal congestion CV: Bradycardia, tachycardia, CV collapse, hypertension and hypotension, palpitations, edema Dependence: Drug dependence with withdrawal syndrome when drug is discontinued (common with abrupt discontinuation of higher dosage used for longer than 4 mo); IV diazepam: 1.7% incidence of fatalities; oral benzodiazepines ingested alone; no well-documented fatal overdoses Dermatologic: Urticaria, pruritus, skin rash, dermatitis GI: Constipation; diarrhea, dry mouth; salivation; nausea; anorexia; vomiting; difficulty in swallowing; gastric disorders; elevations of blood enzymesLDH, alkaline phosphatase, AST, ALT; hepatic impairment; jaundice GU: Incontinence, urinary
Caregiver should learn to assess seizures, administer rectal form, and monitor patient. Use of barrier contraceptives is advised while using this drug; if you become or wish to become pregnant, consult with your health care provider. It is advisable to wear a medical alert ID indicating your diagnosis and treatment (as antiepileptic). You may experience these side effects: Drowsiness, dizziness (may lessen; avoid driving or engaging in other dangerous activities); GI upset (take drug with food); dreams, difficulty concentrating, fatigue, nervousness, crying (reversible).
Clonidine Anti-hypertensive
Stimulates central alpha-adrenergic receptors to inhibit sympathetic cardioaccelerator and vasoconstrictor centers.
Management of all grades of hypertension (HPN) with the exception of HPN due to phaeochromocytoma. Prophylactic treatment of migraine or recurrent vascular treatment of migraine. For relief of cancer of pain , in combination with opiates for epidural use.
retention, changes in libido, menstrual irregularities Hematologic: Decreased hematocrit, blood dyscrasias Other: Phlebitis and thrombosis at IV injection sites, hiccups, fever, diaphoresis, paresthesias, muscular disturbances, gynecomastia; pain, burning, and redness after IM injection Local skin irritation Drowsiness Dry mouth Dizziness Headache Constipation Depression Fatigue Nausea Urinary retention
Assess BP and apical pulse before initial dose. If systolic BP is less than 90 mm Hg or pulse is less than 60 bpm, withhold drug and notify physician. Check for edema in feet, legs daily; monitor inputoutput ratio: check for decreasing output. Assess for symptoms of CHF: edema, dyspnea, wet rales, B/P, weight gain, report significant changes. Inform patient that drug may impair ability to drive or operate machinery, thus should be avoided in tasks that require mental alertness. Drug may cause dizziness, fainting; light headedness.Teach patient to administer 1 hour before meals.
You might also like
- Vindicate For LBPDocument10 pagesVindicate For LBPShaun TylerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument14 pagesDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Ncp&drugstudDocument12 pagesNcp&drugstudSarah Mae Billano BermudezNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Last DutyDocument5 pagesDrugstudy Last DutyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis (RN) - 3Document9 pagesDrug Analysis (RN) - 3Joannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocument12 pagesC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNo ratings yet
- 1.) Generic Name: Gabapentin Brand Name Classification Dosage Route and Frequency Mechanism of ActionDocument15 pages1.) Generic Name: Gabapentin Brand Name Classification Dosage Route and Frequency Mechanism of ActionTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyYrban GuyuranNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study For PneumoniaDocument5 pagesDrugs Study For PneumoniaLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Medication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Document43 pagesMedication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Kath Rubio0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Drugstudy and SoapieDocument17 pagesDrugstudy and SoapieYasi EcheniqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDocument6 pagesDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉No ratings yet
- Drug Cards BarryDocument6 pagesDrug Cards BarryJessica Lynn DyeNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument2 pagesKetorolacJacqueline LimNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NRMFDocument11 pagesDrug Study NRMFKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pharma Sheet1Document7 pagesPharma Sheet1Lyssa ShannenNo ratings yet
- DADocument8 pagesDAErditha MirandaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study Meropenem Trihydrate (Mepenem) - Carbapenem AntibioticDocument5 pagesDrugs Study Meropenem Trihydrate (Mepenem) - Carbapenem AntibioticLourdes MercadoNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- All Kinds of DrugsDocument11 pagesAll Kinds of DrugsRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Drug Study FORTDocument3 pagesDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicDocument37 pagesTherapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRye IbarraNo ratings yet
- Pharma Cards.Document19 pagesPharma Cards.Brent NicholsNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument12 pagesOB Drug StudyCj AttoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyLovely EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case Study PebsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Case Study PebsMichael John Gambong SalaNo ratings yet
- DTRDocument63 pagesDTRAlex SilvanoNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument27 pagesDrugspeterjongNo ratings yet
- Brand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilDocument3 pagesBrand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilPoinsithia OrlandaNo ratings yet
- Ix. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDocument21 pagesIx. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril PDFDocument3 pagesLisinopril PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug General Actio N Specific Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsib IlitiesDocument8 pagesName of Drug General Actio N Specific Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsib IlitiesJade ParkNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyCzarinah Ela MesiasNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsmidskiescreamzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Vasotec EnalaprilDocument1 pageVasotec EnalaprilCassie100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Drug Analysis AdultDocument4 pagesDrug Analysis AdultXian AlbsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyMaye HerbitoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)From EverandTop 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- 9700 m18 QP 22 PDFDocument16 pages9700 m18 QP 22 PDFIG UnionNo ratings yet
- 7285 NMMSDocument52 pages7285 NMMSShanilDayalanNo ratings yet
- Variant Lymphocyte: @colezekielDocument4 pagesVariant Lymphocyte: @colezekielMicole NatividadNo ratings yet
- INFECTION CONTROL TRENDS OF CHANGE by Dr.T.V.Rao MDDocument25 pagesINFECTION CONTROL TRENDS OF CHANGE by Dr.T.V.Rao MDtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Safe SexDocument2 pagesSafe Sexapi-318300545No ratings yet
- Trichiasis Surgery: Rapid AssessmentDocument2 pagesTrichiasis Surgery: Rapid AssessmentShella JamilahNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Loa LoaDocument28 pagesDokumen - Tips Loa LoaSababil AliNo ratings yet
- Unang YakapDocument57 pagesUnang YakapHelen Grace Avila100% (3)
- New Biophilia FeaturesDocument14 pagesNew Biophilia Featuresdues babao100% (2)
- Sesi 08 One HealthDocument47 pagesSesi 08 One HealthFika FebrianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MicroorganismsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 MicroorganismsNIKHILPATNINo ratings yet
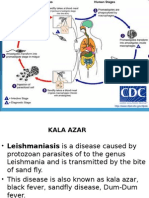
- Kala Azar AutosavedDocument12 pagesKala Azar AutosavedSubbarao ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Classification PDFDocument8 pagesBacterial Classification PDFdenportillo12No ratings yet
- Accuracy of A Commercial Igm Elisa For The Diagnosis of Human Leptospirosis in ThailandDocument4 pagesAccuracy of A Commercial Igm Elisa For The Diagnosis of Human Leptospirosis in Thailandrestu anindityaNo ratings yet
- Bells PalsyDocument2 pagesBells PalsyJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- PNEUMONIA Pathophysiology PDFDocument5 pagesPNEUMONIA Pathophysiology PDFMariaNo ratings yet
- Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus (Mers-Cov) : Group# 4 MembersDocument11 pagesMiddle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus (Mers-Cov) : Group# 4 MembersIbrahimAslamNo ratings yet
- D3780 GML May 2017Document14 pagesD3780 GML May 2017rc_holyspiritNo ratings yet
- MSSA Information FactsheetDocument2 pagesMSSA Information FactsheetAlinaNo ratings yet
- National Immunization ProgramDocument9 pagesNational Immunization ProgramCriselda PabuaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Dispenser Course: Duration - One Year Paper - A Section - IDocument4 pagesSyllabus For Dispenser Course: Duration - One Year Paper - A Section - IFarhan AliNo ratings yet
- MICP LAB (WEEK - 5) Antimicrobial Agents in TherapydocDocument8 pagesMICP LAB (WEEK - 5) Antimicrobial Agents in Therapydoccaitie miracleNo ratings yet
- Bee Propolis PresentationDocument23 pagesBee Propolis PresentationPERRYAMNo ratings yet
- TonsillitisDocument3 pagesTonsillitisVina MuspitaNo ratings yet
- HIV LeafletDocument4 pagesHIV Leafletkbl27No ratings yet
- Food Borne Disease: Prepared by Sharjil MahmoodDocument72 pagesFood Borne Disease: Prepared by Sharjil Mahmoodjayand_net100% (1)
- Basic Principles of Diagnostic of Infectious DiseasesDocument38 pagesBasic Principles of Diagnostic of Infectious DiseasesBombomNo ratings yet
- AFP Tumor Markers: The TestDocument20 pagesAFP Tumor Markers: The TestMuhammad Umar SaleemNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Laboratory Diagnosis of The NovelDocument27 pagesChallenges in Laboratory Diagnosis of The NovelRidho Al Fiqri100% (1)