Drug Study Hydralazine
Drug Study Hydralazine
Uploaded by
Luige AvilaCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Hydralazine
Drug Study Hydralazine
Uploaded by
Luige AvilaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Hydralazine
Drug Study Hydralazine
Uploaded by
Luige AvilaCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Name
Dosage & Route
Action
Indication
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
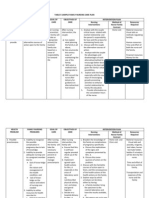
ampicillin (am pi sill' in) ampicillin sodium Oral: Ampicin (CAN), Apo -Ampi (CAN), NovoAmpicillin (CAN), Nu-Ampi (CAN), Penbritin (CAN), Pri ncipen Pregnancy Category B Drug classes Antibiotic Penicillin
Capsules250, 500 mg; powder for oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL, 250 mg/5 mL; powder for injection250, 500 mg, 1, 2 g Dosages Maximum recommended dosage: 8 14 mg/day (14 g should be reserved for serious infections, such as meningitis, septicemia); may be given IV, IM, or PO. Use parenteral ro utes for severe infections, and switch to oral route as soon as possible.
Bactericidal action against sensitive organisms; inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing cell death.
Treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of Shigella, Salmonella, E. coli, H. influenzae, P. mirabilis, N. gonorrhoeae,entero cocci, gram-positive organisms (penicillin G sensitive staphylococci, streptococci, pneum ococci) Meningitis caused by Neisseria meningiti dis Unlabeled use: Prophylaxis in cesarean section in certain high-risk patients
CNS: Lethargy, hallucinations, seizures CV: CHF GI: Glossitis, stomatitis, gastritis, sore mouth, furry tongue, black "hairy" tongue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, enterocolitis, pseu domembranous colitis, nonspecific hepatitis GU: Nephritis Hematologic: Anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukope nia, neutropenia, prolonged bleeding time Hypersensitivity: Rash, fever, wheezing, anaphylaxis Local: Pain, phlebitis, thrombosis at injection site (parenteral) Other: Superinfectionsoral and rectal moniliasis, vaginitis
Contraindicated with allergies to penicillins, cephal osporins, or other allergens. Use cautiously with renal disorders.
Culture infected area before treatment; reculture area if response is not as expected. Check IV site carefully for signs of thrombosis or drug reaction. Do not give IM injections in the same site; atrophy can occur. Monitor injection sites. Administer oral drug on an empty stomach, 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals with a full glass of water; do not give with fruit juice or soft drinks.
Drug Name
Dosage & Route
Action
Indication
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
Oxytocin (Pictopin, Syntocinon)
For stimulation of labor: 10 units (1ml) of drug infused in 1L D5LRS before deliver For Reduction of Postpartum bleeding: 1 amp after delivery of placenta
Oxytocin Causes potent and selective stimulation of uterine and mammary gland smooth muscles producing sustained contractions Induces labor and milk ejection and reduces post partum bleeding
Induction of labor at term; control of postpartum bleeding; adjunctive therapy in management of abortion
Cardiovascular: hypertension; increased heart rate, systemic venous return, and cardiac output, and arrhytmias CNS: seizures, coma from water intoxication Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, GU: titanic uterine contractions, abruption placentae, impaired uterine blood flow, pelvic hematoma Hematologic: afibrinogenemia Respiratory: anoxia, asphyxia
> Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to the drug or any of its component. > Also contraindicated in cephalopelvic disproportion or delivery that requires conversion, as in tranverse lie; in fetal distress when delivery isnt imminent; in prematurity and in severe toxemia, hypertonic uterine patterns, total placenta previa or vasa previa. > Also contraindicated in fetal distress.
> Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to the drug or any of its component. > Also contraindicated in cephalopelvic disproportion or delivery that requires conversion, as in tranverse lie; in fetal distress when delivery isnt imminent; in prematurity and in severe toxemia, hypertonic uterine patterns, total placenta previa or vasa previa. > Also contraindicated in fetal distress.
Drug Name
Dosage & Route
Action
Indication
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
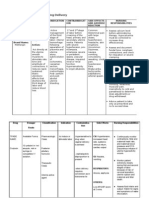
Hydralazine (Apresoline)
5 mg/dose then 5-10 mg every 20-30 minutes as needed.
Hydralazine Directly relaxes arteriolar smooth muscle Vasodilaion Lowers Blood Pressure
CNS: peripheral neuritis, headache, dizziness Pre-eclampsia / eclampsia CV: orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, arrythmias, angina, palpitations. GI: n/v, diarrhea, anorexia Hematologic: neutropenia, leukopenia, agranulocytopenia Metabolic: weight gain, sodium retention Skin: rash
Contraindicated to patients hypersensitive to the drug and any of its component and in those with coronary artery disease or mitral valvular rheumatic heart disease. Use cautiously in patients with suspected cardiac disease, CVA, or severe renal impairment, and in those taking other antihytensives.
>Assess blood pressure before starting therapy and regularly thereafter. >Instruct client to take oral form with meals. >Inform client that orthostatic hypotension can be minimized by rising slowly and not changing position suddenly. >Tell pt. not to abruptly stop taking drug, but to call prescriber if adverse reaction occurs. >Tell client to limit sodium intake.
Drug Name
Dosage & Route Dosage: 1.8 mg IV q6
Action
Indication
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
Dexamethasone Classification: Anti inflammatory Glucocorticoid
The patient was given dexamtehasone 1.8 mg through IV every 6 hours to decreases inflammation, mainly by stabilizing leukocyte lysosomal membranes; suppresses immune response; stimulates bone marrow; and influences protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism.
Specific Adjunctive treatment in bacterial meningitis. General Cerebral edema Allergic and inflammatory conditions Shock Tuberculosis meningitis
CNS: euphoria, insomnia, psychotic behavior, pseudotumor cerebri, vertigo, headache, paresthesia, seizures, depression. CV: hypertension, edema, arrythmias, thromboembolism. EENT: cataracts, glaucoma.
1.
2.
3.
4. GI: peptic ulceration, GI irritation, increased appetite, pancreatitis, nausea, vomiting. 5. GU: increase urine glucose, and calcium levels Metabolic: hypokalemia, hyperglycemia Musculoskeletal: muscle weakness Skin: Delayed wound healing Other: Susceptibility to infections.
6. 7.
8.
Determine whether patient is sensitive to other corticosteroids Most adverse reactions to corticosteroids are dose-or durationdependent. For better results and less toxicity, give once daily dose in morning. Give oral dose with food when possible. Patient may need drugs to prevent GI irritation. Give I.M injection deeply into gluteal muscle. Rotate injection sites to prevent muscle atrophy. Avoid subcutaneous injection because atrophy and sterile abscesses may occur. Alwats adjust to lowest effective dose Monitor patient weight, blood pressure, and electrolyte levels. Monitor patient for cushingoid effects, including moon face, buffalo hump, thinning of hair.
Drug Name
Dosage & Route IV 50mg q6
Action
Indication
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
Cefuroxime Classification: ANTIINFECTIVE; ANTIBIOTIC; SECONDGENERATION CEPHALOSPORIN
It is effective for the treatment of penicillinaseproducing Neisseria gonorrhoea (PPNG). Effectively treats bone and joint infections, bronchitis, meningitis, gonorrhea, otitis media, pharyngitis/tonsillitis, sinusitis, lower respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and is used for surgical prophylaxis, reducing or eliminating infection.
Body as a Whole: Thrombophlebitis (IV site); pain, burning, cellulitis (IM site); superinfections, positive Coombs' test. GI: Diarrhea, nausea, antibioticassociated colitis. Skin: Rash, pruritus, urticaria. Urogenital: Increased serum creatinine and BUN, decreased creatinine clearance.
Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins and related antibiotics; pregnancy (category B), lactation.
Determine history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins, and history of allergies, particularly to drugs, before therapy is initiated. Inspect IM and IV injection sites frequently for signs of phlebitis. Report onset of loose stools or diarrhea. Although pseudomembranous colitis. Monitor I&O rates and pattern: Especially important in severely ill patients receiving high doses. Report any significant changes.
Drug Name
Dosage & Route
Action
Indication
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
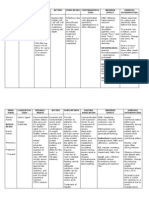
Generic name: Isoxsuprine
Brand Name: Duvadilan
Chemically similar to sympathomimetic amines and often described as beta adrenergic agonist. However, the drug appears to be a musculotropic vasodilator and its effects are not blocked by propanolol.
Peripheral and cerebral vascular insufficiency with spastic component showing symptoms: Dizziness Forgetfulness Confusion Visual, auditory and speech abnormalities Coldness and numbness of limbs Color changes and ischemic ulcers Raynaud disease
Transient flushing Hypotension Rashes
recent arterial hemorrhage, heart disease, severe anemia should not be administered immediately post partum and premature labor. Avoid parenteral administration to patients with hypotension, tachycardia, premature detachment of placenta or immediate post partum.
Assess patients condition before therapy. Assess potential benefits from drug therapy. Monitor for possible drug induced adverse reactions: Hypotension Tachycardia Nausea Vomiting Dizziness Severe rash Inform the patient about possible side effects , adverse symptoms to report.
Gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances Maternal pulmonary edema Fetal tachycardia Transient palpitations Dizziness
Uterine hypermotility disorders Threatened abortion Premature labor Dysmenorrheal
Drug Name
Dosage & Route
Action
Indication
Adverse Effects CNS: Weakness, drowsiness, dizziness, fainting, sweating Respiratory: Decreased respiratory rate CV: Palpitations GI: Excessive bowel activity, perianal irritation Metabolic: Magnesium intoxication, hypocalcemia with tetany
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
Generic Name Magnesium Sulfate Trade Name Martham Pharmacologic Class Mineral, Electrolyte Therapeutic Class Antiepileptic, Laxative; Mineral, electrolyte replacement Pregnancy Risk Factor A B (Laxative)
Minimum Dose 1-2 g qH by IV infusion Maximum Dose 4-6 g qH by IV infusion Contents Magnesium sulfate Availability and color - Granules- 40 mEq/5 g - Injection- 0.325, 0.65, 1, 4 mEq/mL Routes of administration Oral Intramuscular Intravenous
Cofactor of many enzyme systems involved in neurochemical transmission and muscular excitability; prevents or controls seizures by locking the neuromuscular transmission; attracts and retains the water in the intestinal lumen and distends the bowel to promote mass movement and relieve constipation.
General Indications - Constipation - Torsades de pointes - Muscle stimulating effects of barium poisoning - Reduction of cerebral oedema. Hypomagnesaemia - Seizures associated with epilepsy, glomerulonephritis or hypothyroidism. - Toxemias of pregnancy - Boils and carbuncles
Concentrations - Allergy to magnesium products - Abdominal pain - Nausea - Vomiting - Acute surgical abdomen - Fecal impaction - Intestinal and biliary tract obstruction - Hepatitis - Myocardial damage - Heart blocks - 2 hr preceding delivery Precaution - Renal insufficiency Drug interaction Drug to drug - Potentiation of neuromuscular blockade produced by nondepolarizing neuromuscular relaxants Drug to food - none reported
Before - Assess for contraindicated conditions. - Monitor knee-jerk reflex before repeated parenteral administration. - Give as laxative as temporary measure. - Reserve IV use in eclampsia for lifethreatening situations. - Observe the 15 rights in drug administration. During - Give IM route by deep IM injection. - Monitor serum magnesium levels. - Do not give oral MgSO4 with abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting. - Do not administer if knee-jerk reflexes are suppressed - Monitor bowel function. After - Arrange to discontinue administration as soon as levels are within normal limits and desired clinical response is obtained. - Discontinue if diarrhea or cramping occurs. - Arrange for dietary measures, exercise and environmental control to return to normal bowel activity. - Report sweating, flushing, muscle tremors or twitching, inability to move extremities. - Maintain urine output at a level of 100 mL every 4 hr during parenteral administration.
Drug Name
Dosage & Route
Action
Indication
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
Drug Name
Dosage & Route
Action
Indication
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
You might also like
- The Paper Doctor A Vibrational Medicine CabinetDocument385 pagesThe Paper Doctor A Vibrational Medicine CabinetCEF041941100% (30)
- Nursing Care Plan AMLDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan AMLAllan Macacapagal67% (9)
- Table 5 Sample Family Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesTable 5 Sample Family Nursing Care Plandave_castañeda86% (78)
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyGi Ey ElNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMaan Molinyawe82% (17)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Case StudyDocument21 pagesCase StudyLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- NCP LeukemiaDocument3 pagesNCP LeukemiaLuige Avila100% (5)
- The Calling of The Health Care ProviderDocument4 pagesThe Calling of The Health Care ProviderLuige Avila75% (4)
- Oet - Support Speaking Sub-Test (Medicine) : Warm Up (5 Minutes)Document30 pagesOet - Support Speaking Sub-Test (Medicine) : Warm Up (5 Minutes)Tahseen Talib100% (4)
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Class: Ergot Alkaloid Therapeutic Class: Oxytocic Pregnancy Risk Category CDocument6 pagesPharmacologic Class: Ergot Alkaloid Therapeutic Class: Oxytocic Pregnancy Risk Category CayotanNo ratings yet
- Spring 2023 DrugsDocument3 pagesSpring 2023 Drugshqqbx9dy65No ratings yet
- Drug Cards BarryDocument6 pagesDrug Cards BarryJessica Lynn DyeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoy Jarin100% (1)
- Drug Analysis (RN) - 3Document9 pagesDrug Analysis (RN) - 3Joannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeDocument9 pagesDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument16 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsJosepNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugsjheverly123100% (1)
- Drug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study JrodDocument8 pagesDrug Study JrodGaez ﭢ UlpindoNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument15 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsDennise Juayang100% (2)
- VIII. Drug StudyDocument11 pagesVIII. Drug StudyCharlayne AnneNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyChristine PunsalanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study Meropenem Trihydrate (Mepenem) - Carbapenem AntibioticDocument5 pagesDrugs Study Meropenem Trihydrate (Mepenem) - Carbapenem AntibioticLourdes MercadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ShenDocument12 pagesDrug Study ShenLass KazeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolDocument7 pagesName of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Drug StudyDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugs Drug StudyCathrine Sandile Tangwara100% (1)
- ECLAMPSIA Drug StudyDocument10 pagesECLAMPSIA Drug Studyjessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument19 pagesOB Drug StudyKismet Summons100% (8)
- Drug Study DMDocument8 pagesDrug Study DMJana Ross Serranilla100% (2)
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 pagesMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMonica Lyka BancaleNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Blockers AtenololDocument3 pagesAdrenergic Blockers AtenololPoinsithia OrlandaNo ratings yet
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- DADocument8 pagesDAErditha MirandaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesAmoxicillindheng05No ratings yet
- Pentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GanDocument34 pagesPentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GankotonashiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyKynaWeeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Chief Complaint: Body WeaknessDocument13 pagesChief Complaint: Body WeaknessJohn MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Common MedicationsDocument12 pagesCommon MedicationsJasmeen KaurNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsVal Ian Palmes SumampongNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study-Po (1) EwesdfdsfdsfsddsfdsfdsDocument14 pagesDrug-Study-Po (1) EwesdfdsfdsfsddsfdsfdsIbrahim RegachoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study For PneumoniaDocument5 pagesDrugs Study For PneumoniaLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)From EverandTop 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Drug Study NubainDocument2 pagesDrug Study NubainLuige Avila100% (11)
- Drug Study ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study ParacetamolLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HNBBDocument2 pagesDrug Study HNBBLuige Avila0% (1)
- Drug Study CytotecDocument2 pagesDrug Study CytotecLuige Avila60% (10)
- Or Instruments: 3. Deep Gelpi RetractorDocument2 pagesOr Instruments: 3. Deep Gelpi RetractorLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DulcolaxDocument1 pageDrug Study DulcolaxLuige Avila100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors Precipatating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Predisposing Factors Precipatating FactorsLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Roosevelt College System Institute of Nursing and Health Education Sumulong Highway, Cainta, Rizal Leadership and Management Head NursingDocument1 pageRoosevelt College System Institute of Nursing and Health Education Sumulong Highway, Cainta, Rizal Leadership and Management Head NursingLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LeukemiaDocument7 pagesDrug Study LeukemiaLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework - ResearchDocument1 pageTheoretical Framework - ResearchLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Lyks - Part 7 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesLyks - Part 7 Drug StudyLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease: Management of Inpatients (Including Those With Swallowing Difficulty)Document7 pagesParkinson's Disease: Management of Inpatients (Including Those With Swallowing Difficulty)Dan SoundararajahNo ratings yet
- Product Development Pipeline - FebruaryDocument4 pagesProduct Development Pipeline - FebruaryCebin VargheseNo ratings yet
- GastritisDocument16 pagesGastritisAngie Mandeoya50% (2)
- Tugas Percakapan Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesTugas Percakapan Bahasa InggrisSri HalipahNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Paediatric Abdominal PainDocument32 pagesAn Approach To Paediatric Abdominal PaindrsaleemNo ratings yet
- Morning SicknessDocument7 pagesMorning SicknessNovadilah Arifia ShintadewiNo ratings yet
- Garcia, Nehemiah B. BSN 2Y2-2A: Ncma 219 Lec Course Task # 5Document2 pagesGarcia, Nehemiah B. BSN 2Y2-2A: Ncma 219 Lec Course Task # 5Mushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- Paralytic Ileus: Prepared By: Laurence A. Adena, ManDocument43 pagesParalytic Ileus: Prepared By: Laurence A. Adena, ManJanah Beado PagayNo ratings yet
- GingerfmçmDocument5 pagesGingerfmçmElisa BarcelosNo ratings yet
- b1b2 Taking Patient History Vocab Questions Worksheet Teachers NotesDocument5 pagesb1b2 Taking Patient History Vocab Questions Worksheet Teachers NotesHakan GünayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studygracebel reyesNo ratings yet
- Transform Your BodyDocument93 pagesTransform Your BodyNaresh Muttavarapu0% (1)
- Food PoisoningDocument26 pagesFood PoisoningYağmur ÇakmakNo ratings yet
- Deep Blue StickDocument2 pagesDeep Blue StickMarianNo ratings yet
- Fish Poisoning (Print)Document65 pagesFish Poisoning (Print)Cristina SarinoNo ratings yet
- M Digestion" Absorption" EliminationDocument104 pagesM Digestion" Absorption" EliminationChristine Carol FilipinasNo ratings yet
- 029 Medication TrayDocument3 pages029 Medication TrayS BindhiyaNo ratings yet
- A. Any ST-segment Elevation Greater Than or Equal To 1 MMDocument35 pagesA. Any ST-segment Elevation Greater Than or Equal To 1 MMmashe1No ratings yet
- Giving Advice DialogueDocument2 pagesGiving Advice DialogueEuis JuwitaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Clinical ExemplarDocument6 pagesPortfolio Clinical Exemplarapi-365196865No ratings yet
- Optimization and Scale Up Process For Su-1Document20 pagesOptimization and Scale Up Process For Su-1Roxana AlinNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Project of Zingiber Officinale (Ginger)Document2 pagesA Proposed Project of Zingiber Officinale (Ginger)Karen Padilla100% (1)
- Magnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMagnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug Studyprog.ecleo.swuNo ratings yet
- Epitome of HomeopathyDocument57 pagesEpitome of Homeopathyed_corcoranNo ratings yet
- Cot 2012 English Canada v02.02 1 0Document410 pagesCot 2012 English Canada v02.02 1 0MDBNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis and CholecystitisDocument10 pagesCholelithiasis and CholecystitisMaria Theresa BuscasNo ratings yet
- Vomiting in ChildrenDocument44 pagesVomiting in ChildrenAstri Faluna SheylavontiaNo ratings yet
- Pain Assessment FormDocument1 pagePain Assessment FormPipit100% (1)