R R R Root Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis
R R R Root Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis
Uploaded by
Anoop RaghuCopyright:
Available Formats
R R R Root Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis
R R R Root Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis
Uploaded by
Anoop RaghuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
R R R Root Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis
R R R Root Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis Oot Cause Analysis
Uploaded by
Anoop RaghuCopyright:
Available Formats
ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS.
Possible cause which we identify after performing root cause analysis for welding during are as follows.
ACTION PLAN IMPLEMENTED TO COUNTER THE WELD JOINTS
Sr. No. 1
Reason which we ear marked after performing RCA Bevel areas not free from contaminant like rust mill scale grease etc, which eventually results in to Porosty.
4M cause effect region Method
Occurrence of cutting kerfs during preparation of bevel edges were not removed which lead to Porosity.
Method
Irregular and excess root gaps which is varying from the WPS stated requirement
Method
Improper techniques used at the time of root welding and weaving of the electrodes of subsequent passes Lack of in process check points ( Internal) by welding inspectors
Men
Men
Lack of 100% Non evasive check points( DPI of the root welding) 100% severity level Lack of customer requirements for utilization of codes like EN/ISO 5817 classes for the visual weld imperfection evaluations
Method
ACTION PLAN IMPLEMENTED AFTER RCA 1.0 Mill scales removed by buffing to about 25mm either side of the weld centre 2.0 Grease removed by thinner, plugged the cause of oil spillage on plate material by tightening the Maintenance of Drilling machines, Cranes ( Source of oil spillage/ Grease) 3.0 Quality check points implemented with QC to monitor the cleanliness of the bevel surface during fit up stage 1.0 All cutting activities done by CNC supported by Nesting software . 2.0 Quality check points implemented with QC to monitor the occurrence cutting kerf on the bevel surface during fit up stage. 3.0 Maintaining correct O2 pressure and cutting speed ( Process parameter) 1.0 Maintenance of correct root gap through stringent check points by the qc inspector during fit up stage. 2.0 By providing root gap gauge to the fitters for checking gap and profile at the time of gap preparation 1.0 Qualification of welders against ISO 9606-1 2.0 Constant orientation to grass root level stage by training 1.0 Qualification of welding inspectors against IIW / ISO 5817 requirement. 2.0 Quality check points and weld process checks through log sheet. 1.0 Checking of root weld coming under wet joints by 100% DPI 1.0 Oriented internal QC personnel to the requirement of ISO 5817 Class
Method
Lack of awareness of the visual weld imperfection standards among the inspectors and supervisors related to standards like ISO 5817 Human error at the time of weld inspection Lack of monitoring of the process parameters like current, voltage and inter pass temperature Non adherence to the repair procedure such as (Through excavations of defective region and not maintaining minimum size of the repair area 25mm length. Use of improper or damaged electrodes
Men
2.0 Check list developed against the requirement of ISO 5817 3.0 Internal training program conducted for ISO 5817 1.0 Hired external party to train internal inspectors and supervisors
Men
1.0 Inspector identified as expert in weld checking is deputed for the inspection. 1.0 Log sheet already implemented daily basis 1.0 Monitored though checklist for welding.
Machine
10
Men
11
Material aterial
1.0 FIFO and IMIR implemented
Cause effect analysis
METHOD MEN MATERIAL MACHINE
You might also like
- Method Statement For Structural Fabrication & ErectionDocument11 pagesMethod Statement For Structural Fabrication & ErectionBinay89% (19)
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideFrom Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Repair and Buttering ProcedureDocument14 pagesRepair and Buttering Proceduremohd as shahiddin jafri100% (4)
- ISO IEC 17020 A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandISO IEC 17020 A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Welding Repair ProcedureDocument6 pagesWelding Repair ProcedureSenthil Kumaran100% (4)
- Welding Repair ProcedureDocument4 pagesWelding Repair Proceduregstketut100% (2)
- Method Statement Pipe WeldingDocument14 pagesMethod Statement Pipe Weldingjayasjb90% (10)
- Komatsu PC160LC 7Document20 pagesKomatsu PC160LC 7Virgil Cenariu100% (3)
- Advantages of Each Type of Separator PDFDocument17 pagesAdvantages of Each Type of Separator PDFAHMED100% (4)
- Technical English For Automotive Engineering - Chapter 1 - Automotive Introduction-Đã G PDocument34 pagesTechnical English For Automotive Engineering - Chapter 1 - Automotive Introduction-Đã G PNguyễn Hoàng MỹNo ratings yet
- WMS JOB Procedure FOR PIPING WORKDocument9 pagesWMS JOB Procedure FOR PIPING WORKsatyamech1_395565923No ratings yet
- Welding Process: Work InstructionDocument6 pagesWelding Process: Work Instructionmkcsekar100% (2)
- Welding Grooving ProcedureDocument19 pagesWelding Grooving ProcedureAzhar Ali67% (3)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Industrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionFrom EverandIndustrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successFrom EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Aw60 40le Zip BookDocument8 pagesAw60 40le Zip BookMohamd Fadel Hassan80% (5)
- Certification To Iso 3834 For Fabrication IndustryDocument9 pagesCertification To Iso 3834 For Fabrication IndustryvilukNo ratings yet
- Advanced Quality Assurance-EDocument3 pagesAdvanced Quality Assurance-EthomasreinerNo ratings yet
- Visual Weld InspectionDocument7 pagesVisual Weld InspectioninsiderrNo ratings yet
- Dutyies of Welding InspectorDocument30 pagesDutyies of Welding InspectorMorg Actus100% (1)
- Welding Inspection ProcedureDocument7 pagesWelding Inspection ProcedureAlexandros KritsotakisNo ratings yet
- Engineering ProceduresDocument23 pagesEngineering ProceduresadammzjinNo ratings yet
- 9 Cswip 3.1 Book 2010 Coloured BookDocument338 pages9 Cswip 3.1 Book 2010 Coloured BookBùi Công LộcNo ratings yet
- VisualProcedure - LouDocument8 pagesVisualProcedure - Loujoshrathburn19800% (1)
- Cswip 3.1 New BookDocument342 pagesCswip 3.1 New BookMohsin Rasul90% (52)
- Inspection and Welding Repairs of Pressure VesselsDocument9 pagesInspection and Welding Repairs of Pressure VesselsClaudia Mms100% (1)
- Stage 1 - Welding Inspection Prior To Welding WorkDocument7 pagesStage 1 - Welding Inspection Prior To Welding WorkIrvansyah RazadinNo ratings yet
- CSWIP 3.1-2010 The Welding Inspection of SteelDocument317 pagesCSWIP 3.1-2010 The Welding Inspection of Steelapply19842371100% (1)
- Inspection and Test ProcedureDocument8 pagesInspection and Test Proceduregaehdd1100% (1)
- The Welding Inspection Services Are Define in Three Stages As BelowDocument9 pagesThe Welding Inspection Services Are Define in Three Stages As BelowdeliNo ratings yet
- Visual Testing ProcedureDocument4 pagesVisual Testing ProcedureAnirban Sen Sharma100% (2)
- Title:: NDT & Corrosion Control ServicesDocument1 pageTitle:: NDT & Corrosion Control Servicesm_armoutiNo ratings yet
- Welding InspectionDocument7 pagesWelding Inspectionzahid_497100% (1)
- General Repair ProcedureDocument3 pagesGeneral Repair ProcedurevenkateshNo ratings yet
- Sop Welding RevisiDocument12 pagesSop Welding RevisifandyNo ratings yet
- Works Instruction For Piping Welding InspectionDocument5 pagesWorks Instruction For Piping Welding InspectionAbg SepulNo ratings yet
- MM 88100 E r3 - ISO 17637 ISO 5817 - Algemeen - VTDocument27 pagesMM 88100 E r3 - ISO 17637 ISO 5817 - Algemeen - VTgueridi100% (2)
- Welding Inspection ProcedureDocument7 pagesWelding Inspection ProcedureVaradaraj CkNo ratings yet
- 1 Typical Duties of Welding InspectorsDocument7 pages1 Typical Duties of Welding InspectorspandimrNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspection ProcedureDocument5 pagesWelding Inspection ProcedurePugalNo ratings yet
- 74.00.02.000 (Stainless Steel)Document8 pages74.00.02.000 (Stainless Steel)Andres Romero PinedaNo ratings yet
- 7-Method Statement For Gypsum PartitionDocument9 pages7-Method Statement For Gypsum Partitionozyoclown83% (6)
- Shop Fabrication Procedure (Supply of Tank Option#3) PDFDocument7 pagesShop Fabrication Procedure (Supply of Tank Option#3) PDFGATOTNo ratings yet
- Document Purpose & Personnel ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDocument Purpose & Personnel ResponsibilityIlkin hasanovNo ratings yet
- Spot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingFrom EverandSpot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Process Control for Injection MoldingFrom EverandTotal Quality Process Control for Injection MoldingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Estimator's Piping Man-hours Tool: Estimating Man-hours for Carbon Steel Process Piping Projects. Manual of Man-hours, ExamplesFrom EverandEstimator's Piping Man-hours Tool: Estimating Man-hours for Carbon Steel Process Piping Projects. Manual of Man-hours, ExamplesNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AFrom EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&ANo ratings yet
- Construction Methodologies & Procedures for Civil Engineers - Part -1From EverandConstruction Methodologies & Procedures for Civil Engineers - Part -1No ratings yet
- Welding Terminology: A Guide to MIG, TIG, Stick, Gas, and Spot Welding TermsFrom EverandWelding Terminology: A Guide to MIG, TIG, Stick, Gas, and Spot Welding TermsNo ratings yet
- Improving Product Reliability and Software Quality: Strategies, Tools, Process and ImplementationFrom EverandImproving Product Reliability and Software Quality: Strategies, Tools, Process and ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Technical Standards and Design Guidelines: Mixed - Use BuildingsFrom EverandTechnical Standards and Design Guidelines: Mixed - Use BuildingsNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Quality to Gain Access to Global Markets: A Reform ToolkitFrom EverandEnsuring Quality to Gain Access to Global Markets: A Reform ToolkitNo ratings yet
- The Laboratory Quality Assurance System: A Manual of Quality Procedures and FormsFrom EverandThe Laboratory Quality Assurance System: A Manual of Quality Procedures and FormsNo ratings yet
- Fine - V TypeDocument1 pageFine - V TypeAnoop RaghuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Anchors, Styrene Free: K-A-L-MDocument2 pagesChemical Anchors, Styrene Free: K-A-L-MAnoop RaghuNo ratings yet
- Test Certificate 01Document1 pageTest Certificate 01Anoop RaghuNo ratings yet
- Foundry CompleteDocument206 pagesFoundry CompleteAnoop RaghuNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document21 pagesModule 1Jyothi SamanthulaNo ratings yet
- Inclined Columns Design - Loads and Bending Moment in Inclined Column PDFDocument9 pagesInclined Columns Design - Loads and Bending Moment in Inclined Column PDFAnonymous gnJDEVEsKVNo ratings yet
- F 714 PDFDocument9 pagesF 714 PDFDanilo Rojas MartinezNo ratings yet
- Dimensiones de Referencia Actuador Neumático Bray S92-93Document6 pagesDimensiones de Referencia Actuador Neumático Bray S92-93davidgarciaarteagaNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics and Mechanics: (English Edition)Document16 pagesApplied Mathematics and Mechanics: (English Edition)Anonymous IqCUJjOINo ratings yet
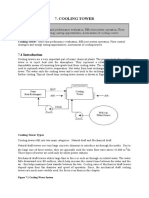
- Chapter 3.7 Cooling TowerDocument16 pagesChapter 3.7 Cooling TowerRaj Kumar ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Robot: Manipulator Maintenance ManualDocument147 pagesHyundai Robot: Manipulator Maintenance ManualNguyenHuuĐucNo ratings yet
- Ansi Valve Catalogue: Contracting & Terminal SolutionsDocument63 pagesAnsi Valve Catalogue: Contracting & Terminal SolutionsFrancisco Andres Rivas SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Warn Service ManualDocument16 pagesWarn Service Manualadrianram1100% (1)
- Tutorial 09 Importing Slide Files + SSRDocument14 pagesTutorial 09 Importing Slide Files + SSRMarcos MaNo ratings yet
- ASTM A312-24aDocument13 pagesASTM A312-24achundongxNo ratings yet
- Bending in Beam: Lab ReportDocument30 pagesBending in Beam: Lab ReportLa'ibah Kamal100% (1)
- 4th - Flow Across Banks of TubesDocument16 pages4th - Flow Across Banks of TubesPrakash AchyuthanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ActivityDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer ActivityMark Angelo UyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Bangladesh Physics Olympiad Category-D: 1. MathematicsDocument5 pagesSyllabus For Bangladesh Physics Olympiad Category-D: 1. Mathematicskutta vallukNo ratings yet
- LG 4.2 Phase ChangeDocument7 pagesLG 4.2 Phase ChangeapngbnNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6Document3 pagesWorksheet 6John Angelo CompetenteNo ratings yet
- Instructions To The CandidatesDocument3 pagesInstructions To The CandidatesNthanzi MuwandiaNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Piping Handbook Part I Engineering: Garth DenisonDocument72 pagesRefrigerant Piping Handbook Part I Engineering: Garth Denisonjm sausaNo ratings yet
- Air University Fire FightingDocument2 pagesAir University Fire FightingCE capital BuildersNo ratings yet
- Aiche-19-008 Ammonia Shift ConverterDocument6 pagesAiche-19-008 Ammonia Shift ConverterHsein WangNo ratings yet
- Chest Heated Ironers - Two Rolls: RangeDocument2 pagesChest Heated Ironers - Two Rolls: Rangemandster1978No ratings yet
- Bulldozer Specifications: MM in MM in MM in M Yd MM in KG LB Deg. MM inDocument2 pagesBulldozer Specifications: MM in MM in MM in M Yd MM in KG LB Deg. MM inRobert HutapeaNo ratings yet
- Products Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)Document31 pagesProducts Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)osama raufNo ratings yet
- D10414410a Fmea MachiningDocument13 pagesD10414410a Fmea MachiningSuraj RawatNo ratings yet
- APCN-S Series: Air Cooled Packaged ChillersDocument52 pagesAPCN-S Series: Air Cooled Packaged Chillersahmed abdohNo ratings yet