0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 viewsZigbee Vs Bluetoorh
Zigbee Vs Bluetoorh
Uploaded by
MehulLathiyaZigBee and Bluetooth are wireless network technologies, but they have key differences. ZigBee is intended for low-power applications like sensor networks and home automation that require battery-powered devices to last for years. It supports mesh networks of up to 65,000 devices with very low latency. In contrast, Bluetooth is aimed at cable replacement between devices like phones, laptops, and headsets within 10 meters of each other, with higher power consumption and latency. The technologies also differ in operating frequencies, security methods, and typical applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Zigbee Vs Bluetoorh
Zigbee Vs Bluetoorh
Uploaded by
MehulLathiya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views7 pagesZigBee and Bluetooth are wireless network technologies, but they have key differences. ZigBee is intended for low-power applications like sensor networks and home automation that require battery-powered devices to last for years. It supports mesh networks of up to 65,000 devices with very low latency. In contrast, Bluetooth is aimed at cable replacement between devices like phones, laptops, and headsets within 10 meters of each other, with higher power consumption and latency. The technologies also differ in operating frequencies, security methods, and typical applications.
Original Description:
difference in both technology
Original Title
zigbee vs bluetoorh
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
ZigBee and Bluetooth are wireless network technologies, but they have key differences. ZigBee is intended for low-power applications like sensor networks and home automation that require battery-powered devices to last for years. It supports mesh networks of up to 65,000 devices with very low latency. In contrast, Bluetooth is aimed at cable replacement between devices like phones, laptops, and headsets within 10 meters of each other, with higher power consumption and latency. The technologies also differ in operating frequencies, security methods, and typical applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views7 pagesZigbee Vs Bluetoorh
Zigbee Vs Bluetoorh
Uploaded by
MehulLathiyaZigBee and Bluetooth are wireless network technologies, but they have key differences. ZigBee is intended for low-power applications like sensor networks and home automation that require battery-powered devices to last for years. It supports mesh networks of up to 65,000 devices with very low latency. In contrast, Bluetooth is aimed at cable replacement between devices like phones, laptops, and headsets within 10 meters of each other, with higher power consumption and latency. The technologies also differ in operating frequencies, security methods, and typical applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
The Differences of between
ZigBee and Bluetooth technologies
Can Kaya
201171221
CENG 502 Computer Networks - Cankaya University
Ankara, TURKEY
November 15, 2012
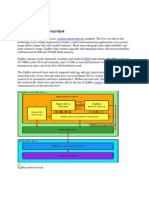
What is a ZigBee Wireless Network?
ZigBee networks can be cluster, star or mesh networks as shown in the diagram.
Each ZigBee network has one device that is setup as a coordinator that controls and
initializes the network. Other devices can either be setup as routers that can pass data or as
End Points, that can only have one connection. End points or Reduced Function Devices
can be set to sleep mode so they use very little power and so can be battery operated.
Because of this very low power requirement, ZigBee is ideal for sensor networks or other control applications, which
require:
Low to medium data rates
Lots of nodes (up to 65,565)
Easy addition or removal of nodes from network
robust mesh network that doesn't fall over if one node fails
very low power, battery operated equipment
ZigBee protocols are intended for use in embedded applications requiring low data rates and low power
consumption. ZigBees current focus is to define a general-purpose, inexpensive, self-organizing mesh
network that can be used for industrial control, embedded sensing, medical data collection, smoke and
intruder warning, building automation, home automation, etc. The resulting network will use very small
amounts of power individual devices must have a battery life of at least two years to pass ZigBee
certification.
ZigBee is a low-cost, low-power, wireless mesh networking proprietary standard. The low cost allows the
technology to be widely deployed in wireless control and monitoring applications, the low power-usage
allows longer life with smaller batteries, and the mesh networking provides high reliability and larger
range.
ZigBee can activate (go from sleep to active mode) in 15 msec or less, the latency can be very low and
devices can be very responsive particularly compared to Bluetooth wake-up delays, which are
typically around three seconds. Because ZigBees can sleep most of the time, average power
consumption can be very low, resulting in long battery life.
Where to use ZigBee?
Building Automation
Remote Control
Home energy savings
Health and fitness monitoring
Smart homes
Easy-to-use touchpads
mice, keyboards, wands
LED lighting control etc
What can ZigBee do for you?
ZigBee protocols are intended for embedded applications requiring low data rates and low power
consumption. The resulting network will use very small amounts of power individual devices must have
a battery life of at least two years to pass ZigBee certification
Home Entertainment and Control Home automation, smart lighting, advanced temperature
control, safety and security, movies and music
Wireless sensor networks Starting with individual sensors like Telosb/Tmote and Iris from
Memsic
Industrial control
Embedded sensing
Medical data collection
Smoke and intruder warning
Building automation
What is a Bluetooth Wireless Network?
Bluetooth technology was invented in 1994 by engineers at Ericsson.
Bluetooth is a standard and a communications protocol primarily designed for
low power consumption, with a short range (power-class-dependent: 100m,
10m and 1m, but ranges vary in practice) based on low-cost transceiver
microchips in each device. Bluetooth makes it possible for these devices to
communicate with each other when they are in range.
Where to use Bluetooth?
Specifically, Bluetooth connects devices such as;
Mobile phones, PDA, laptops, Pcs together
Modems, headsets, computer mouse, keyboards
Digital Camera
Personal digital assistants
Printers, Fax machines
Car Kits etc.
Bluetooth exists in many products, such as telephones, modems and headsets.. I you are specific users
to file transfer or synchronization something, multi-functional cell phone and so on.
What can Bluetooth do for you?
The technology is useful when transferring information between two or more devices that are
near each other in low-bandwidth situations. Bluetooth is commonly used to transfer sound data with
telephones (i.e., with a Bluetooth headset) or byte data with hand-held computers (transferring files).
For instance, you can use your phone or PDA to consult databases located in your laptop, or even to
print documents. You can use your MP3 player around the house to listen to music stored on your PC.
Recently, car manufacturers such as BMW, Lexus and Toyota have equipped some of their models with
Bluetooth car kits. This allows you to use the features of your cell phone through the car's audio system
while the phone itself is stored away in the trunk, for instance.
What are differences between ZigBee and Bluetooth wireless
networks?
There is a table about difference between ZigBee and Bluetooth wireless network technologies. We
listed major difference between the two technologies.
ZigBee Bluetooth
Range 10-100 meters 10 meters
Networking Topology Ad-hoc, peer to peer, star, or mesh Ad-hoc, very small networks
Operating Frequency 868 MHz (Europe)
900-928 MHz (NA), 2.4 GHz
(worldwide)
2.4 GHz
Complexity (Device
and application
impact)
Low High
Power Consumption
(Battery option and
life)
Very low (low power is a design
goal)
Medium
Security 128 AES plus application layer
security
64 and 128 bit encryption
Typical Applications Industrial control and monitoring,
sensor networks, building
automation, home control and
automation, toys, games
Wireless connectivity between devices
such as phones, PDA, laptops, headsets
Modulation technique
Spreading
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
(DSSS)
Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum
(FHSS)
Protocol stack size 28 Kbyte 250 Kbyte
Battery Not rechargeable (one reason
batteries will last for up to 10
years)
Intended for frequent recharging
Data Rate 250 Kbit/s 1 Mbit/s
Typical network join
time
30 milliseconds 3 seconds
Application Monitoring and Control Cable replacement
Number of devices for
Network
64K 7
Typical Applications
Industrial control and monitoring,
sensor networks, building
automation, home control and
automation, toys, games
Wireless connectivity between devices
such as phones, PDA, laptops, headsets
Physical/ MAC layers IEEE 802.15.4 IEEE 802.15.1
Basic Cell star Piconet
Bluetooth is more oriented toward user mobility and eliminating short-distance cabling; ZigBee aims
more for grand-scale automation and remote control.
REFERENCES
http://docs.zigbee.org/zigbee-docs/dcn/07-5482.pdf
http://www.askmen.com/money/how_to_200/221_how_to.html#ixzz2CIeHy0DS
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ZigBee
http://www.differencebetween.net/technology/difference-between-zigbee-and-bluetooth/
http://www.sena.com/blog/?p=359
http://news.techworld.com/mobile-wireless/2406/zigbee-is-the-future-dead-in-the-water-delete-as-
appropriate/
http://www.zigbee.org/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bluetooth
http://www.bluetooth.com/
You might also like
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)From EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- ZigbeeDocument9 pagesZigbeelikithavonamalaNo ratings yet
- Zigbee Vs BluetoothDocument2 pagesZigbee Vs Bluetoothለዛ ፍቅርNo ratings yet
- Zigbee TutorialDocument9 pagesZigbee TutorialrahulNo ratings yet
- Is A Specification For A Suite of High Level Communication Protocols Using Small, LowDocument3 pagesIs A Specification For A Suite of High Level Communication Protocols Using Small, LowTejas TailorNo ratings yet
- Project On Bluetooth Technology: Presented ByDocument9 pagesProject On Bluetooth Technology: Presented BySanjeev Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Technical Overview: Zigbee Is ADocument12 pagesTechnical Overview: Zigbee Is AyouaredeadNo ratings yet
- Zigbee TechnologyDocument20 pagesZigbee TechnologyChikkapriyankaNo ratings yet
- Zigbee: Origin of WordDocument9 pagesZigbee: Origin of WordRajan VermaNo ratings yet
- Bluetoothtechnology: Seminor OnDocument9 pagesBluetoothtechnology: Seminor OnNitturi VinodkumarNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Vs ZigbeeDocument20 pagesBluetooth Vs ZigbeeZarnigar AltafNo ratings yet
- WN Assignment 1Document10 pagesWN Assignment 1mhafiza038No ratings yet
- Zigbee - An Emerging Technology For FutureDocument4 pagesZigbee - An Emerging Technology For FutureLuis Filipe SilvaNo ratings yet
- Zigbee Technology Seminar PresentationDocument10 pagesZigbee Technology Seminar PresentationmithNo ratings yet
- Zigebee: Arvind KumarDocument41 pagesZigebee: Arvind KumarARVINDNo ratings yet
- ZigBee NewDocument15 pagesZigBee Newlakshmi anusha achantaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Zigbee Technology in Future Data Communication SystemDocument7 pagesThe Role of Zigbee Technology in Future Data Communication SystemsandeepmahankaliNo ratings yet
- Seminar TopicsDocument15 pagesSeminar TopicsUsha MarigoudarNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems FinalDocument16 pagesDistributed Systems FinalAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- M.tech Project PaperDocument10 pagesM.tech Project PaperRakshithaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: Wireless Device Controlling With ZigbeeDocument6 pagesSynopsis: Wireless Device Controlling With ZigbeeJaiparkash SaveliaNo ratings yet
- 1 Coin: Zigbee Is ADocument17 pages1 Coin: Zigbee Is AShrikant JagtapNo ratings yet
- Application of Zigbee Technology in Telecommunication SystemDocument7 pagesApplication of Zigbee Technology in Telecommunication SystemPraveen D JadhavNo ratings yet
- BluetoothDocument13 pagesBluetoothManikandan MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Indoor non-WIFI - Learning GuideDocument6 pagesIndoor non-WIFI - Learning Guiderayhane.gouissemNo ratings yet
- Seminar On-Seminar OnDocument41 pagesSeminar On-Seminar OnAnshula GuptaNo ratings yet
- How Does ZigBee Compare With Other Wireless StandardsDocument6 pagesHow Does ZigBee Compare With Other Wireless StandardsChirag MistryNo ratings yet
- Zigbee Wireless Control That Simply WorksDocument11 pagesZigbee Wireless Control That Simply WorksTb ShilpaNo ratings yet
- Technical Overview: Wireless Mesh NetworkDocument13 pagesTechnical Overview: Wireless Mesh NetworkNaveen Telugudesam0% (1)
- Ebook Connectivity Options QDN 04 FinalDocument10 pagesEbook Connectivity Options QDN 04 FinalVarun SainiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-I M - CombineDocument36 pagesUnit 3-I M - Combinenitin kachhiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-I MDocument11 pagesUnit 3-I Mnitin kachhiNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument21 pagesSeminar ReportKunjesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Zigbee TechnologyDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Zigbee Technologyveere_arunNo ratings yet
- The Networking Technology Within Smart Home System - Zigbee TechnologyDocument5 pagesThe Networking Technology Within Smart Home System - Zigbee Technologyhyj890417No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document26 pagesChapter 3الحسيني خطابNo ratings yet
- Zigbee-A New Generation Technology: For Why I Am Choosing This TopicDocument6 pagesZigbee-A New Generation Technology: For Why I Am Choosing This TopicSellam PannerNo ratings yet
- IoT Wireless TechnologiesDocument4 pagesIoT Wireless TechnologiesBahi AliNo ratings yet
- Zigbee Protocol: A Seminar Report OnDocument31 pagesZigbee Protocol: A Seminar Report OnKranthi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Wireless Network ProtocolsDocument6 pagesWireless Network ProtocolsDanish mughalNo ratings yet
- XbeeeDocument4 pagesXbeeeHarish PandamaneniNo ratings yet
- Zigbee Literature ReviewDocument22 pagesZigbee Literature ReviewBhaskar Rao PNo ratings yet
- IOT Notes Unit-3 Part-BDocument22 pagesIOT Notes Unit-3 Part-BECE N.V.Satyanarayana MurthyNo ratings yet
- Zigbee TechnologyDocument20 pagesZigbee TechnologyVigneshInfotechNo ratings yet
- IoT Technologies and ProtocolsDocument13 pagesIoT Technologies and Protocolsshalivahana naveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Switch On IoT Connected Lighting - Element14Document6 pagesSwitch On IoT Connected Lighting - Element14Sree SagarNo ratings yet
- Zigbee SlidesDocument15 pagesZigbee SlidesArun RajNo ratings yet
- Zigbee Transmitter For Iot Wireless DevicesDocument13 pagesZigbee Transmitter For Iot Wireless DevicesAnonymous e4UpOQEPNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocument13 pagesBluetooth TechnologyParthasarathi AnbalaganNo ratings yet
- Users Make A Beeline For Zigbee Sensor Technology: Industry TrendsDocument4 pagesUsers Make A Beeline For Zigbee Sensor Technology: Industry TrendsdabrevipulNo ratings yet
- Zigbee: Presented byDocument9 pagesZigbee: Presented bySwathi YennamNo ratings yet
- BLUETOOTH BasedDocument3 pagesBLUETOOTH BasedShilpa ChavareNo ratings yet
- Zigbee Technology: Mekapati Rajamohan Reddy Institute of Technology ScienceDocument15 pagesZigbee Technology: Mekapati Rajamohan Reddy Institute of Technology ScienceHarshaneela KonakalaNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Medium Access Control (MAC), Physical Layer (PHY), Wireless Personal Area NetworkingDocument9 pagesKeywords: Medium Access Control (MAC), Physical Layer (PHY), Wireless Personal Area Networkingmnry414No ratings yet
- "Auto Monitoring of Appliances by Internet": Vivek N. Katare, Pradeep B. Dahikar, S.J. DhobleDocument4 pages"Auto Monitoring of Appliances by Internet": Vivek N. Katare, Pradeep B. Dahikar, S.J. DhobleIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- Network Communication ProtocolDocument12 pagesNetwork Communication ProtocolKohinoor BegumNo ratings yet
- Building the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsFrom EverandBuilding the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- The 5G Revolution: How the Next Generation of Wireless Will Change EverythingFrom EverandThe 5G Revolution: How the Next Generation of Wireless Will Change EverythingNo ratings yet
- Using LearningDocument134 pagesUsing Learning67890d65d46eb7No ratings yet
- Power Over Ethernet: The IEEE 802.3af StandardDocument12 pagesPower Over Ethernet: The IEEE 802.3af StandardLaxman KiranNo ratings yet
- Radiomuseum Philips Do Brasil S BR 416 Z 1673066Document2 pagesRadiomuseum Philips Do Brasil S BR 416 Z 1673066Claudinei Lopes0% (1)
- Course Name: Gap and Flushness in Automotive Body Design Instructor: Ali HosseiniDocument5 pagesCourse Name: Gap and Flushness in Automotive Body Design Instructor: Ali Hosseiniyasar jawaidNo ratings yet
- Password Manager Pro - Security SpecificationsDocument15 pagesPassword Manager Pro - Security Specificationsunicycle1234No ratings yet
- Mean Time Between FailuresDocument3 pagesMean Time Between Failuresocchitya0% (1)
- Flysimware's LEAR 35A Manual - V1.7Document41 pagesFlysimware's LEAR 35A Manual - V1.7Joao Vitor RojasNo ratings yet
- HP Laser Jet Common ErrorsDocument32 pagesHP Laser Jet Common ErrorsTame PcAddictNo ratings yet
- S 20 EEE SyllabusDocument186 pagesS 20 EEE SyllabusSampathNo ratings yet
- TABLE of CONTENTS Artificial IntelligenceDocument3 pagesTABLE of CONTENTS Artificial IntelligenceXtremeInfosoftAlwarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Decision Support and Business Intelligence Systems 9th Edition Efraim TurbanDocument12 pagesTest Bank For Decision Support and Business Intelligence Systems 9th Edition Efraim TurbanCatherine SmithNo ratings yet
- DDR SDRAM PresentationDocument21 pagesDDR SDRAM Presentationsantanu_sinha87No ratings yet
- Est200 Module 2 Part 1Document18 pagesEst200 Module 2 Part 1VYSAGH OFFICIAL CSENo ratings yet
- Workshop Cost EstimatingDocument22 pagesWorkshop Cost EstimatinghasanNo ratings yet
- Powerschool Report Card Guide For ParentsDocument7 pagesPowerschool Report Card Guide For Parentsapi-237234753No ratings yet
- DS K1T342MFX Face Recognition Terminal - Datasheet - V1.0 - 20220825Document4 pagesDS K1T342MFX Face Recognition Terminal - Datasheet - V1.0 - 20220825RoshaanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RoboticsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To RoboticsBharath ThatipamulaNo ratings yet
- TmlogDocument10 pagesTmlogShushang PankajNo ratings yet
- 2.atlassian Quote AT-152621027Document3 pages2.atlassian Quote AT-152621027Raheel KaziNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Re-Engineering Abia State Polytechnic Aba Towards Attaining Sustainable Academic and MoDocument16 pagesStrategies For Re-Engineering Abia State Polytechnic Aba Towards Attaining Sustainable Academic and MoMichaelNo ratings yet
- Paper Presentation TopicsDocument3 pagesPaper Presentation TopicsRitu KadyanNo ratings yet
- Media Release: Varley Electric Vehicles Plugs Into Electric Vehicle Market With Introduction of The Evr-450 SupercarDocument2 pagesMedia Release: Varley Electric Vehicles Plugs Into Electric Vehicle Market With Introduction of The Evr-450 SupercarDavid HerronNo ratings yet
- Multiple Vacancies With MENAISCO in Jazan - Saudi ArabiaDocument5 pagesMultiple Vacancies With MENAISCO in Jazan - Saudi ArabiaViiq Corpse GrinderNo ratings yet
- Total Obsolete Plant & Machinery List Ready For Disposal Qty: 211 No'sDocument9 pagesTotal Obsolete Plant & Machinery List Ready For Disposal Qty: 211 No'sAccounts Inmartech100% (1)
- 138-TartarSauce HTB Official Writeup TamariskDocument10 pages138-TartarSauce HTB Official Writeup TamariskLeonardo SaputraNo ratings yet
- Waveform Design TSDSI-IITP 28thjulyDocument12 pagesWaveform Design TSDSI-IITP 28thjulyMuhannad AydiNo ratings yet
- TVL - Ict (Computer System Servicing) Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - LO 1.2 Set Up User AccessDocument11 pagesTVL - Ict (Computer System Servicing) Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - LO 1.2 Set Up User AccessRica Jean BlasurcaNo ratings yet
- Fund Transfer 27112021Document18 pagesFund Transfer 27112021Avinash ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- IATEX2012 03 B PN IntroductionDocument61 pagesIATEX2012 03 B PN Introductionnice hossainNo ratings yet
- Hacking Win2k Through Ipc$Document3 pagesHacking Win2k Through Ipc$Kell Valdyr LerydNo ratings yet