Form 3 Chapter 2
Form 3 Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Mariana AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
Form 3 Chapter 2
Form 3 Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Mariana AhmadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Form 3 Chapter 2
Form 3 Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Mariana AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
MODUL RELIEF BERFOKUS
PANITIA SAINS
Form 3 Scienc
Chapter 2
FORM 3 CHAPTER 2
TRANSPORT SYSTEM
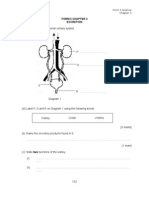
1. Diagram 1 shows two types of blood vessels, P and Q.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan dua jenis salur darah, P dan Q
P: .
Q: .
Diagram 1
(a) Name blood vessels P and Q on Diagram 1.
Namakan salur darah P dan Q di Rajah 1
[2 marks]
(b) What is the function of P and Q?
Apakah fungsi P dan Q
(i) P: .
(ii) Q:
..
[2 marks]
(c) Name the blood vessel that connects blood vessel P and Q?
Namakan salur darah yang menghubungkan salur darah P dan Q
[1 mark]
(d) Explain why there is a difference in the thickness of the wall in blood vessels P and Q.
Terangkan mengapa ketebalan dinding salur darah P dan Q berbeza
[1 mark]
(e) What is the function of R?
Apakah fungsi R?
143
MODUL RELIEF BERFOKUS
PANITIA SAINS
Form 3 Scienc
Chapter 2
[1 mark]
2. Diagram 2.1 shows the transverse section of the stem of a balsam plant.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan keratan rentas batang pokok keembong
_
Q
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
Diagram 2.1
_
_
_
_
(a) Based on Diagram 2.1, label structure P and Q and
_ state their functions.
Berdasarkan rajah 2.1 labelkan struktur P dan Q_
_dan nyatakan fungsinya
Structure
Name
Function _
_
_
P
_
_
_
Q
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
[4 marks]
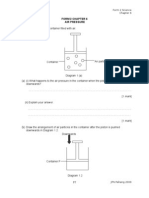
(b) The outer part of the stem of a plant is removed as
_ shown in Diagram 2.2.
Bahagian luar batang pokok tersebut dikeluarkan seperti ditunjukkan dalam rajah 2.2
Diagram 2.2
(i) What can be observed about the condition of the plant after 8 weeks? Draw your
observation in the box provided.
Apakah pemerhatian terhadap keadaan tumbuhan tersebut selepas 8 minggu. Lukis
pemerhatian anda dalam kotak yang disediakan
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain your observation in (b)(i).
Terangkan pemerhatian anda di (b)(i)
144
MODUL RELIEF BERFOKUS
PANITIA SAINS
Form 3 Scienc
Chapter 2
..
..
[1 mark]
3. Diagram 3 illustrates the circulation of blood in the human body.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan aliran darah dalam badan
Lungs
Body
Diagram 3
(a) Label the following on Diagram 3.
Labelkan rajah 3
Aorta
Right ventricle
Pulmonary artery
[3 marks]
(b) Mark using arrow,
, to show the flow of oxygenated blood in the circulatory system.
Dengan menggunakan
tunjukkan darah beroksigen dalam sistem
[1 mark]
(c) The systemic circulation is the circulation of blood from the heart to the body cells and back
to the heart again. Label the systemic circulation on Diagram 3.
Peredaran sistemik adalah peredaran darah dari jantung ke sel badan dan kembali semula
ke jantung. Labelkan peredaran sistemik
[1 mark]
(d) State one difference between blood vessel P and blood vessel Q.
nyatakan satu perbezaan salur darah P dan salur darah Q
..
145
MODUL RELIEF BERFOKUS
PANITIA SAINS
Form 3 Scienc
Chapter 2
..
[1 mark]
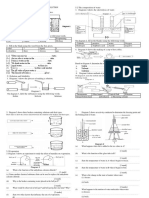
4. (a) A pupil observed that the condition of a plant is different in the morning compared to the
afternoon.
11 12
11 12
1
10
1
2
10
9
8
Morning
3
7
Afternoon
Diagram 4.1
(i) Based on the observations in Diagram 4.1, state the difference in the condition of
the plant.
[1 mark]
(ii) What inference can be made based on Diagram 4.1.?
..
..
[1 mark]
(iii) State your hypothesis based on your observations in Diagram 4.1.
..
..
[1 mark]
146
MODUL RELIEF BERFOKUS
PANITIA SAINS
Form 3 Scienc
Chapter 2
(b) The pupil then carries out an experiment to investigate the situation in Diagram 4.1.
Diagram 4.2 shows the arrangement of apparatus for the experiment.
Thermometer
Thermometer
Heat source
30 oC
40 oC
Cotton wool
Cotton wool
Layer of oil
Layer of oil
Water
Water
Electronic balance
Electronic balance
Plant X
Plant Y
Diagram 4.2
The pupil takes the following steps:
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
Two similar green plants X and Y are set up as shown in Figure 4.2.
Initial mass of X and Y are taken.
Plant X is left at room temperature that is 30 oC
Plant Y is put under a heat source that is 40 oC
The final mass of X and Y are taken after 2 hours.
The results are tabulated in table 4.3
Results:
Plants
X
Y
Initial mass
280.60 g
280.60 g
Table 4.3
(i) Using the formula,
Rate of transpiration = Mass lost (g)
Time (hour)
147
Final mass
280.00 g
278.80 g
MODUL RELIEF BERFOKUS
PANITIA SAINS
Form 3 Scienc
Chapter 2
calculate the rate of transpiration for plant X and Y and complete Table 4.4.
Plant
P
Rate of transpiration (g/hour)
Q
Table 4.4
[2 marks]
Rate of transpiration (g/hour)
(ii) Using Table 4.4, draw a bar chart to show the rate of transpiration in plant P and plant Q.
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
[2 marks]
Plant
(iii) Based on the bar chart in (b)(ii), what can be said about the rate of transpiration in the
plants?
148
MODUL RELIEF BERFOKUS
PANITIA SAINS
Form 3 Scienc
Chapter 2
[1 mark]
(c) State the variables involved in this experiment.
Manipulated variable
Responding variable
Constant variable
[3 marks]
(d) Based on the experiment, state the relationship between temperature and the rate of
transpiration.
[1 mark]
149
MODUL RELIEF BERFOKUS
PANITIA SAINS
Form 3 Scienc
Chapter 2
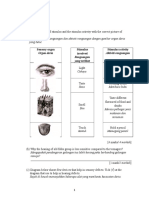
5. Diagram 5 shows the components of blood.
Diagram 5.1
(a) Using the following words, label P, Q and R on Diagram 5.1.
Red blood cell
White blood cell
Platelet
[3 marks]
(b) State the function P.
[1 mark]
(c) Name the component of blood which contains haemoglobin.
..
[1 mark]
(d) What is the importance of R?
.
[1 mark]
150
MODUL RELIEF BERFOKUS
PANITIA SAINS
Form 3 Scienc
Chapter 2
(e) Diagram 5.2 shows three bags of blood from three different donors.
A
AB
Diagram 5.2
(i) If a patient with blood group B needs a blood transfusion, which bag of blood will be
compatible?
Mark ( ) in the box provided in Diagram 5.2.
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain what will happen if incompatible blood group is used for the transfusion.
.
.
[1 mark]
151
You might also like
- Kuiz Kimia Kebangsaan 2015Document29 pagesKuiz Kimia Kebangsaan 2015Mariana Ahmad84% (19)
- Form 3 Chapter 3Document7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 3naza977582% (11)
- F3 Chapter 7 Energy and PowerDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 7 Energy and PowerJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Chapter 1Document9 pagesForm 3 Science Chapter 1Mohamad Harith100% (2)
- Science Answer Scheme Paper 1 and 2 Form1 09Document6 pagesScience Answer Scheme Paper 1 and 2 Form1 09azmijaaffarNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE FORM 3 Chapter 4 ExerciseDocument7 pagesSCIENCE FORM 3 Chapter 4 ExerciseWan Shuhaimi Wan Ali100% (1)
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 12 Solution of TrianglesDocument5 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 12 Solution of TrianglesManisha Sekaran MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Sce Form 2Document22 pagesSce Form 2williamkong123No ratings yet
- Form 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 8Document8 pagesForm 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 8Kelvin0% (1)
- Form 2 Chapter 3Document3 pagesForm 2 Chapter 3Ng Imm Khuan100% (1)
- F2 CHP 2 Ecosystem (Chinese)Document12 pagesF2 CHP 2 Ecosystem (Chinese)ChuahSiewHoonNo ratings yet
- M012-Consumer Mathematics (Taxation)Document5 pagesM012-Consumer Mathematics (Taxation)Tan Jun YouNo ratings yet
- Ahilvani's Book Review - RatburgerDocument2 pagesAhilvani's Book Review - RatburgerMariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Science-Form 3-Chapter 3 Excretion by KelvinDocument10 pagesScience-Form 3-Chapter 3 Excretion by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 pagesForm 3 Chapter 2naza9775100% (17)
- F3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 2 RespirationJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science, Chapter 1Document47 pagesForm 3 Science, Chapter 1qq23586% (57)
- Form 3 Module Chapter 6 Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesForm 3 Module Chapter 6 Electricity and MagnetismJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 3 TestDocument7 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 3 TestShatviga Visvalingam100% (1)
- Science Form 3 CHAPTER 1Document8 pagesScience Form 3 CHAPTER 1loga yuthrashreeNo ratings yet
- Nexus PMR Science Form 1 - 2 - 3 Page 131 (Questions)Document3 pagesNexus PMR Science Form 1 - 2 - 3 Page 131 (Questions)Ms_SyazanaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 PPTnewDocument9 pagesScience Form 3 PPTnewRedzuan Sulaiman100% (1)
- Exercise On Chapter 8 Science Form 3Document3 pagesExercise On Chapter 8 Science Form 3Sasi RekaNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 9Document3 pagesForm 3 Chapter 9naza9775100% (5)
- Science-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinDocument14 pagesScience-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- PMR 2012 Science 108 MantraDocument16 pagesPMR 2012 Science 108 MantraJun MingNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 3: Name: Class: DateDocument6 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 3: Name: Class: DateTeng Pei ErNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 6Document9 pagesForm 2 Chapter 6naza9775100% (7)
- Mid Year Exam Science Form 2 2011 - LatestDocument22 pagesMid Year Exam Science Form 2 2011 - LatestTan Phei Ling75% (4)
- Form 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5Document4 pagesForm 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5KelvinNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of MetalsDocument11 pagesForm 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of Metalsgrace_lo_1100% (1)
- Form 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Document6 pagesForm 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Kelvin50% (2)
- Form 3 Chapter 6Document7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 6naza9775100% (6)
- Exercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Document2 pagesExercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Nor Adila100% (1)
- Form 3 - Chapter 9Document9 pagesForm 3 - Chapter 9MARHAINI33% (3)
- Form 2 Chapter 9Document10 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9naza9775100% (3)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument18 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionAutumn JJ100% (3)
- Sci F1 T1 (E)Document7 pagesSci F1 T1 (E)Sylvia ChinNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 6Document9 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 6Syazwani Radzi100% (1)
- 1 Form 2 Chapter 2 Nutrition Paper 1 Answer All Questions. Each ...Document9 pages1 Form 2 Chapter 2 Nutrition Paper 1 Answer All Questions. Each ...Amira Jasmin JayaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 3 Trial Paper 1Document22 pagesMathematics Form 3 Trial Paper 1Kenny Cheah Soon LeeNo ratings yet
- POEM Questions A Poison Tree SPMDocument3 pagesPOEM Questions A Poison Tree SPMenesus100% (1)
- 40 Chemistry Question For RevisionDocument5 pages40 Chemistry Question For RevisionSathish Sarma SathianarayananNo ratings yet
- PT3 Science Form 3 SEMINARDocument28 pagesPT3 Science Form 3 SEMINARSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 RevisionDocument7 pagesScience Form 3 Revisionstanleylee100% (1)
- Form 4 Science Chapter 2Document13 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 2Cheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- Science-Form 3-Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and Transport by KelvinDocument10 pagesScience-Form 3-Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and Transport by KelvinKelvin100% (1)
- SCALE DRAWING FORM 3 - Print - QuizizzDocument6 pagesSCALE DRAWING FORM 3 - Print - QuizizzMATHANA SOORIA A/P ADEYAH MoeNo ratings yet
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsDocument9 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsAimi Nadia Yusof100% (1)
- Science Form 4 Chapter 1 KSSMDocument6 pagesScience Form 4 Chapter 1 KSSMAFIQAH BINTI MARZUKHI MoeNo ratings yet
- F3 - CP3 - Consumer MathematicsDocument8 pagesF3 - CP3 - Consumer MathematicsAdelryeNo ratings yet
- F2 Chap 3 MCQDocument5 pagesF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanNo ratings yet
- Quick Notes Form 2 (Science)Document11 pagesQuick Notes Form 2 (Science)FishGlob50% (2)
- Chemistry f4 Mid-Year ExamDocument13 pagesChemistry f4 Mid-Year ExamWindy SanNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Science Form 3Document5 pagesMarking Scheme Science Form 3YusNo ratings yet
- STF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Document12 pagesSTF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Syahrul67% (3)
- Latihan Cuti Sekolah PMR t3Document7 pagesLatihan Cuti Sekolah PMR t3sheh8758No ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 1Document6 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1naza977590% (29)
- Form 3 Chapter 3 ExcretionDocument7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 3 ExcretionJimmy NelsonNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 1 Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1 Respiratory SystemZacky Zack AsfanuddinNo ratings yet
- Science Form-3-Chapter-3Document6 pagesScience Form-3-Chapter-3Jy KooNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Document9 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Wan NazrinaNo ratings yet
- Aktiviti 1 (Azwanisa)Document4 pagesAktiviti 1 (Azwanisa)Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan Kelantan Percubaan Kimia 2019, K1, K2, K3..Document9 pagesSkema Jawapan Kelantan Percubaan Kimia 2019, K1, K2, K3..Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Katalog BukuDocument20 pagesKatalog BukuMariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Kelantan Percubaan Kimia 2019, K2Document15 pagesKelantan Percubaan Kimia 2019, K2Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Jadual Bertugas Guru KRS 2020Document1 pageJadual Bertugas Guru KRS 2020Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 2 (2015)Document17 pagesSains Tingkatan 2 (2015)Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- O Tema Contoh Gambar Dan Link 1 Kesihatan Kesedaran Tentang DenggiDocument4 pagesO Tema Contoh Gambar Dan Link 1 Kesihatan Kesedaran Tentang DenggiMariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Five People You Meet in Heaven: FictionDocument4 pagesThe Five People You Meet in Heaven: FictionMariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- TTH Handbook2015 RevisedDocument41 pagesTTH Handbook2015 RevisedMariana Ahmad100% (1)
- Skema Jawapan Pt3 PPT 2018Document4 pagesSkema Jawapan Pt3 PPT 2018Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Skema Trial MRSM PT3 PDFDocument16 pagesSkema Trial MRSM PT3 PDFMariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Midyear Exam English Year 3 2012 2Document10 pagesMidyear Exam English Year 3 2012 2Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept - Exercise With AnswerDocument1 pageMole Concept - Exercise With AnswerMariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ceramah 2QDocument45 pagesCeramah 2QMariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- History 1Document14 pagesHistory 1Yash JoshiNo ratings yet
- Greenwich in The Mean TimeDocument41 pagesGreenwich in The Mean TimePsy0psAgent100% (3)
- Kumpulan Irreguler VerbsDocument7 pagesKumpulan Irreguler VerbsHealth CareNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology IBN SinaDocument33 pagesMedical Terminology IBN SinaIbeanys CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For PresentationDocument1 pageRubrics For PresentationEllaNo ratings yet
- OB HX and PEDocument37 pagesOB HX and PEdenekeNo ratings yet
- ATPL Inst 7.3 PDFDocument12 pagesATPL Inst 7.3 PDFKoustubh VadalkarNo ratings yet
- Coca ColaDocument97 pagesCoca Colaaccord123No ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument36 pagesPHARMACOLOGYjanr123456100% (1)
- IplDocument12 pagesIplAlyssa Clarizze MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Socy101: Sociology: Lecture-24 Topic: Crime and DevianceDocument19 pagesSocy101: Sociology: Lecture-24 Topic: Crime and DevianceSaad Nadeem 090No ratings yet
- Program 13th International ConferenceDocument3 pagesProgram 13th International ConferenceΟδυσσεας ΚοψιδαςNo ratings yet
- Research Report: The Leisure Time Activities of International University Students Are Different From The Activities They Did As School StudentDocument18 pagesResearch Report: The Leisure Time Activities of International University Students Are Different From The Activities They Did As School StudentgrayNo ratings yet
- English A Literature - Teacher Support MaterialDocument56 pagesEnglish A Literature - Teacher Support MaterialJai Khanna100% (3)
- Huawei HCNA-HNTD (H12-211) Chinese Test BankDocument114 pagesHuawei HCNA-HNTD (H12-211) Chinese Test BankDamisaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Improving Reading ComprehensionDocument7 pagesThesis Improving Reading Comprehensionsamanthacaldwellphoenix100% (1)
- Shangri-La vs. Developers Group of CompanyDocument18 pagesShangri-La vs. Developers Group of CompanyKrister Vallente100% (1)
- V STD SCIENCE ln-4 - 3&4 WORKSHEETDocument8 pagesV STD SCIENCE ln-4 - 3&4 WORKSHEETMR SMILYNo ratings yet
- Heart of Darkness by Joseph Conrad: Themes, Characters, Symbols, StyleDocument16 pagesHeart of Darkness by Joseph Conrad: Themes, Characters, Symbols, StyleDaniela Matei Şora100% (1)
- Are You Afraid?Document2 pagesAre You Afraid?coultershaneNo ratings yet
- Whats IncludedDocument2 pagesWhats IncludedCrudes CrudesNo ratings yet
- Lperrotti ResumeDocument4 pagesLperrotti Resumeapi-276489492No ratings yet
- Tle 6Document2 pagesTle 6Daisy PascuaNo ratings yet
- b1 Lines Written in Early SpringDocument8 pagesb1 Lines Written in Early Springsahej48007No ratings yet
- Tumors2 MCQs PRIMEsDocument23 pagesTumors2 MCQs PRIMEsskNo ratings yet
- Social and Religious Influences On The Form of Turkish CitiesDocument13 pagesSocial and Religious Influences On The Form of Turkish CitiessaranasharrNo ratings yet
- Hoda Hassan CVDocument2 pagesHoda Hassan CVhoda_hassan8838No ratings yet
- Ingles 4 Modulo 1 PDFDocument32 pagesIngles 4 Modulo 1 PDFGonzalo Talledo100% (1)
- Taqleed K Khofnak Nataij RDocument41 pagesTaqleed K Khofnak Nataij RIslamic Reserch Center (IRC)No ratings yet
- Cinemas V National Pension Scheme Authority - Jan-2016 PDFDocument9 pagesCinemas V National Pension Scheme Authority - Jan-2016 PDFSteward KabasoNo ratings yet