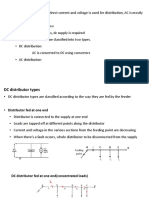
Theory:: Experiment 4 Boost Converter
Uploaded by
RAVI DUTTTheory:: Experiment 4 Boost Converter
Uploaded by
RAVI DUTTExperiment 4
Boost Converter
Objective
To study the closed loop response of a boost converter load regulation
Software/ Hardware Required: Multisim 12.0, DC Power supply(0-30V),
L=250uH,NMOS:2N7000,Schottky Diode 1B0Q015,C=1000uF,R=1kohm,CRO, Function
generator.
Theory:
Boost Converter
A boost converter (step-up converter) is a DC to DC that steps up voltage (while stepping
down current) from its input (supply) to its output (load). It is a class of switched-mode
power supply(SMPS) containing at least two semiconductors (a diode and a transistor) and
at least one energy storage element: a capacitor, inductor, or the two in combination. To
reduce voltage ripple, filters made of capacitors (sometimes in combination with inductors)
are normally added to such a converter's output (load-side filter) and input (supply-side
filter)
Circuit Diagram:
Circuit diagram of boost converter is shown in Figure
Figure 1 Boost DC-DC converter
Working Principle:
The function of boost converter can be divided into two modes, Mode 1 and Mode 2. Mode 1
begins when transistor M1 is switched on at time t=0. The input current rises and flows
through inductor L and transistor M1.
Mode 2 begins when transistor M1 is switched off at time t=t1. The input current now flows
through L, C, load, and diode Dm. The inductor current falls until the next cycle. The energy
stored in inductor L flows through the load.
Observation Table:
Measure and tabulate the following readings.
SET Input voltage = 30V
Set pulse voltage: 10V (Buck operation )
Load Regulation:
S.no Input TON TOFF D= Load Output Output
Voltage TON/T Resistor Voltage calculated
Vin (R Ω) Measured(Vo) Vo=
I*R(volts)
1
Model Calculation:
T = TON +TOFF
= …….𝜇s +…… 𝜇s = ……. 𝜇s
D = TON / T
= …………..
Vo (calculated)= I*R(volts)
Expected Waveforms For Load Regulation
Results: The open loop response for boost converter for load regulation has been examined.
Output voltage is boosted to………V DC voltage.
Precautions:1. Use only isolated power sources (either isolated power supplies or AC power
through isolation power transformers). This helps using a grounded oscilloscope and reduces the
possibility of risk of completing a circuit through your body or destroying the test equipment.
2. Check for all the connections of the circuit and scope connections before powering the circuit, to
avoid shorting or any ground looping that may lead to electrical shocks or damage of equipment.
3. Double-check your wiring and circuit connections. It is a good idea to use a point-to-point wiring
diagram to review when making these checks.
4.After switching off Let the load be connected at the output for some time, so that it helps to
discharge capacitor or inductor if any, completely.
You might also like
- Hourglass Workout Program by Luisagiuliet 276% (21)Hourglass Workout Program by Luisagiuliet 251 pages
- The Hold Me Tight Workbook - Dr. Sue Johnson100% (16)The Hold Me Tight Workbook - Dr. Sue Johnson187 pages
- Read People Like A Book by Patrick King-Edited62% (65)Read People Like A Book by Patrick King-Edited12 pages
- Livingood, Blake - Livingood Daily Your 21-Day Guide To Experience Real Health77% (13)Livingood, Blake - Livingood Daily Your 21-Day Guide To Experience Real Health260 pages
- COSMIC CONSCIOUSNESS OF HUMANITY - PROBLEMS OF NEW COSMOGONY (V.P.Kaznacheev,. Л. V. Trofimov.)94% (212)COSMIC CONSCIOUSNESS OF HUMANITY - PROBLEMS OF NEW COSMOGONY (V.P.Kaznacheev,. Л. V. Trofimov.)212 pages
- Donald Trump & Jeffrey Epstein Rape Lawsuit and Affidavits83% (1016)Donald Trump & Jeffrey Epstein Rape Lawsuit and Affidavits13 pages
- The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times94% (34)The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times3 pages
- The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times95% (21)The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times3 pages
- Jeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDF75% (12)Jeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDF95 pages
- The 4 Hour Workweek, Expanded and Updated by Timothy Ferriss - Excerpt23% (954)The 4 Hour Workweek, Expanded and Updated by Timothy Ferriss - Excerpt38 pages
- Basic Electrical Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yetBasic Electrical Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical Engineering42 pages
- Observation of Polarity Test of A Single Phase Transformer100% (2)Observation of Polarity Test of A Single Phase Transformer3 pages
- Cha:3 Special Instruments: Power Factor Meter Frequency Meter Synchroscope Phase Sequence IndicatorNo ratings yetCha:3 Special Instruments: Power Factor Meter Frequency Meter Synchroscope Phase Sequence Indicator25 pages
- Interpretation of Data and Result and Conclusion. Exp.6 - Resonance FrequencyNo ratings yetInterpretation of Data and Result and Conclusion. Exp.6 - Resonance Frequency1 page
- "Bridge B2HZ" For The Control of A DC MotorNo ratings yet"Bridge B2HZ" For The Control of A DC Motor16 pages
- Ell100 Lab Report: Single Phase Transformer B-H LoopNo ratings yetEll100 Lab Report: Single Phase Transformer B-H Loop10 pages
- Non-Linear Wave Shaping Circuits Clippers AIMNo ratings yetNon-Linear Wave Shaping Circuits Clippers AIM5 pages
- What Is Swinburne's Test - Advantages, Disadvantages & Limitations - Circuit GlobeNo ratings yetWhat Is Swinburne's Test - Advantages, Disadvantages & Limitations - Circuit Globe17 pages
- Magnetic Amplifier in Series: Operation ManualNo ratings yetMagnetic Amplifier in Series: Operation Manual6 pages
- Electrical Machines Lab Manual (DC Machines and Transformer)No ratings yetElectrical Machines Lab Manual (DC Machines and Transformer)34 pages
- Experimental Verification of Thevenin's TheoremNo ratings yetExperimental Verification of Thevenin's Theorem6 pages
- Single Phase Transformer Construction and WorkingNo ratings yetSingle Phase Transformer Construction and Working11 pages
- Lecture 1-Electrical Elements - Series & Parallel Circuits.No ratings yetLecture 1-Electrical Elements - Series & Parallel Circuits.49 pages
- Aim: To Test Differentiator and Integrator Circuits Using Ua741op-Amp100% (2)Aim: To Test Differentiator and Integrator Circuits Using Ua741op-Amp8 pages
- Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and EfficiencyNo ratings yetSteady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency20 pages
- Determination of Transformer Equivalent Circuit Parameters of A SingleNo ratings yetDetermination of Transformer Equivalent Circuit Parameters of A Single18 pages
- Open Circuit & Short Circuit Test On A Single Phase TransformerNo ratings yetOpen Circuit & Short Circuit Test On A Single Phase Transformer7 pages
- Experiment No. 13: Objective: To Investigate The Use of JFET As A Constant Current Source & As Chopper ApparatusNo ratings yetExperiment No. 13: Objective: To Investigate The Use of JFET As A Constant Current Source & As Chopper Apparatus3 pages
- Single-Phase Transformer Lab Report: Load TestNo ratings yetSingle-Phase Transformer Lab Report: Load Test3 pages
- Difference Between Power and Small Signal DiodeNo ratings yetDifference Between Power and Small Signal Diode4 pages
- Slides - 17 - CH 18 - Network Theorems (Ac) - Updated - 2No ratings yetSlides - 17 - CH 18 - Network Theorems (Ac) - Updated - 259 pages
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Study and Evaluation of Performances of The Digital MultimeterNo ratings yetStudy and Evaluation of Performances of The Digital Multimeter10 pages
- 2010 Suzuki Swift OBD2 Code U0100 Lost Communication With ECMNo ratings yet2010 Suzuki Swift OBD2 Code U0100 Lost Communication With ECM2 pages
- Overload Monitoring System in Public Transportation100% (4)Overload Monitoring System in Public Transportation41 pages
- Characteristics of Instruments and Measurement SystemsNo ratings yetCharacteristics of Instruments and Measurement Systems23 pages
- Transformer Protection - Abstract From NEC - EEP100% (1)Transformer Protection - Abstract From NEC - EEP7 pages
- 2N3724 2N3725 2N3725A NPN Silicon Transistor DescriptionNo ratings yet2N3724 2N3725 2N3725A NPN Silicon Transistor Description4 pages
- Prefunctional Test Checklist - Cooling Tower - AirportNo ratings yetPrefunctional Test Checklist - Cooling Tower - Airport9 pages
- 2...... - Light Emitting Diodes' Applications PDFNo ratings yet2...... - Light Emitting Diodes' Applications PDF2 pages
- Microcontroller Based Voltage Stabilizer 5No ratings yetMicrocontroller Based Voltage Stabilizer 515 pages
- Realistic HTX-100 Mobile Transceiver: Care and Maintenance Features Installation Operation Specifications TroubleshootingNo ratings yetRealistic HTX-100 Mobile Transceiver: Care and Maintenance Features Installation Operation Specifications Troubleshooting21 pages
- Multiple Battery Set-Up For Hilux Surf: FeaturesNo ratings yetMultiple Battery Set-Up For Hilux Surf: Features4 pages
- IoT Modules For LPWA, 4G, 3G, and 2G Networks - Sierra WirelessNo ratings yetIoT Modules For LPWA, 4G, 3G, and 2G Networks - Sierra Wireless8 pages
- Skanti KDU 2000: Keyboard Display Unit For Automatic Identification SystemNo ratings yetSkanti KDU 2000: Keyboard Display Unit For Automatic Identification System56 pages
- Solidworks: Srikanth Kyatoor Applications Engineer Logical Solutions LTDNo ratings yetSolidworks: Srikanth Kyatoor Applications Engineer Logical Solutions LTD25 pages