Physical Science: Sources of Energy
Physical Science: Sources of Energy
Uploaded by
James Ryan AlzonaCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Science: Sources of Energy
Physical Science: Sources of Energy
Uploaded by
James Ryan AlzonaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Physical Science: Sources of Energy
Physical Science: Sources of Energy
Uploaded by
James Ryan AlzonaCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Science o Emissions from fossil fuel power plants also
cause acid rain and global scale pollution by
Sources of Energy elements such as mercury
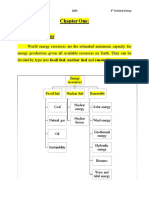
Two Types of Sources of Energy o Fossil fuel is not a sustainable energy source
Battery
1. Renewable o Gives electricity via an electrochemical
2. Non-Renewable- fossil fuels, electrochemical, reaction
nuclear energy o Parts
Anode- negative end
Renewable Energy- energy sources which are not Cathode- positive end
based on the burning of fossil fuels or the splitting of Electrolyte- medium between
atoms anode and cathode
Energy o Invented by Alessandro Volta
o Ability to do work o Commonly used because of portability and
o Takes form to: efficiency
Mechanical
Chemical Electrochemical Usage
Thermal
Types of Battery
Electrical
Converting energy into electricity 1. Disposable- alkaline, Mercury, silver oxide, zinc
1.) Energy from bond breaking/formation in fuels is carbon
converted to heat energy (not necessary if power 2. Rechargeable- lead- acid and lithium-ion
generation does not require burning of fuels)
2.) Heat energy is used to convert water to steam Downsides
which has kinetic energy
Toxic metal pollution
3.) Steam’s kinetic energy becomes mechanical
Involves hazardous chemical
energy which makes turbines turn
Contributes to electronic waste
4.) Mechanical energy creates electricity via
electromagnetism Recycling batteries are an expensive and labor-
intensive process
Non- Renewable Energy o Presents dangerous elements from entering
the environment
Fossil fuels Example: Lead, Mercury,
o Formed from hydrocarbon chain (coal, oil Cadmium
and natural gas) Nuclear Energy
o Comes from the sun through photosynthesis o No CO2 emission
o Formation of these fuels is due to a series of o Splitting of atoms or combination of atoms
geologic processes at the nuclear level releases large amounts of
o Remains of organic life accumulates at the heat energy
bottom of the ocean o Done in specialized unclear power plants
o Remains are buried into the crust and
become part of the geosphere Downsides
o Buried to depths to high temperatures
1. Limited supply
o In the Philippines, 69% of electricity is
2. Environmental hazard
derived from fossil fuels
3. Possibility of meltdown in the case of nuclear power
o In the entire world, around 75% of our
energy is generated by the combustion of Renewable Resources
fossil fuels
o Power plants burn fossil fuels and the heat Geothermal Energy
o Heat energy from Earth’s crust
generated turns water into steam which
moves turbines to create electricity o Heat raises the temperature of rocks which
o Hydrocarbon+ Oxygen ------ CO2 + H2O in turn increase the temperature of nearby
o Combustion is an exothermic process groundwater
o Some groundwater turns into underground
o CH4+ 2 O2 ----- CO2+ 2 H2 O + Heat energy
steam which is then trapped to turn turbines
o Combustion creates carbon dioxide that is
to create electricity
harmful to the environment in large amounts
o Main source of energy in the Visayas Minimal emission
Region (38% of electricity) o Disadvantages
o Less of an environmental hazard compared Expensive installation
to fossil fuels but still emits Oxygen gas, Requires rare metals
nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide Requires a large amount of space
Biomass
Geothermal Energy Examples o Organic matter from plants and animals
Geysers, boiling mud pots, volcanoes and hot spring o Used t create alcohol and methane
Direct uses: o Involves the action of microorganisms
o Hot spring spas, water heating at fish farms, o Advantages
provide buildings with natural heating, Renewable fuel source
raising plants in greenhouses. Drying crops Minimal impact
Indirect uses: electricity generation Employment generation
Alcohol fuels and efficient and
Advantage Disadvantage clean burning
Available year-round Not widespread (limited to Universal availability
locations near geothermal
reservoirs)
Not involve combustion of High installment costs
fuel
Independent of weather Can run out of steam
Clean resource- small May release harmful gases
overall environmental
impact
Economically sound Possible high transportation
costs
Fuel is free, rate/KwH likely Susceptible to earthquakes
to be competitive
Hydroelectric energy
o Moving water to turn turbines
o Dams
o Advantages
Clean and safe
Self-sustaining
Create habits for more types of
marine life
Flood controllers
Very efficient (90-95%)
o Disadvantage
Dam construction
May displace marine life and
change the ecosystem around the
dam
Wind energy
o More ships and pump water
o Wind turbines installed in strategic location
o Mechanical energy to electrical energy
Solar energy
o Accessible as long as the sun exists
o Solar panels: photovoltaic cells that convert
light into electricity
o Advantages
Abundant
Low maintenance
Environment friendly
You might also like
- BUSINESS PLAN - PotatoDocument8 pagesBUSINESS PLAN - PotatoJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- GP5 - Energy, Work & Power 1Document8 pagesGP5 - Energy, Work & Power 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Special Topics in P2CDocument2 pagesSpecial Topics in P2CErrol SalutaNo ratings yet
- Energy Resourses Worksheet AnswersDocument6 pagesEnergy Resourses Worksheet Answersapi-292550476No ratings yet
- GP5 Energy, Work & PowerDocument6 pagesGP5 Energy, Work & PowerDays NyambeNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology and EnergyDocument2 pagesScience, Technology and EnergySuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Ees Ii 2.4Document46 pagesEes Ii 2.4Amrit SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Physics 9 - Energy ResourcesDocument33 pagesPhysics 9 - Energy ResourcesAngeline AngelNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources ProjectDocument19 pagesEnergy Resources ProjectAFAN NOMANINo ratings yet
- Physics 9 - Energy ResourcesDocument32 pagesPhysics 9 - Energy Resourcesccbpxprwd2No ratings yet
- تأشيرات الشرحيات المطلوبة1Document6 pagesتأشيرات الشرحيات المطلوبة1احمد كريم خلفNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Module 1Document22 pagesMechanical Module 1aymanNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument111 pagesIlovepdf Mergedvarshabijapur7No ratings yet
- Module 1Document19 pagesModule 1Ganesh T NaikNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument20 pagesEnergy Resourcesanju clNo ratings yet
- 4.5 - 4.8 Renewable and Non Renewable EnergyDocument55 pages4.5 - 4.8 Renewable and Non Renewable EnergyShereena FaisalNo ratings yet
- Worsheet EnglishDocument19 pagesWorsheet EnglishJefferson BarriosNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: - A Renewable Energy Source For Electricity GenerationDocument22 pagesGeothermal Energy: - A Renewable Energy Source For Electricity GenerationSuraj SunnyNo ratings yet
- 4.17 Energy Resources and Electricity GenerationDocument5 pages4.17 Energy Resources and Electricity Generationp68y6bph5tNo ratings yet
- Technology and ComputingDocument16 pagesTechnology and ComputingAntwan MeloNo ratings yet
- Energy: Franziska Palme, Vincent Kalnin and Hamza OuerfelliDocument26 pagesEnergy: Franziska Palme, Vincent Kalnin and Hamza OuerfelliHamza OuerfelliNo ratings yet
- 04 Activity 1Document5 pages04 Activity 1Czedrick LuzonNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument26 pagesEnergy ResourcesAnum ObaidNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1-Introduction To Renewable and Non Renewable EnergyDocument45 pagesCHAPTER 1-Introduction To Renewable and Non Renewable Energyyahyaxx10176No ratings yet
- Hydropower Engineering I (HWRE 3141) Ch-1 & Ch-2Document55 pagesHydropower Engineering I (HWRE 3141) Ch-1 & Ch-2kader ArefeNo ratings yet
- NuclearEnergy 1Document5 pagesNuclearEnergy 1athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Revision NotesDocument6 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 14 Revision NotesMuzafar ahmadNo ratings yet
- Concentrated Solar Heat - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument8 pagesConcentrated Solar Heat - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsRudolph ScheepersNo ratings yet
- H.E.P, Biomas and NuclearDocument3 pagesH.E.P, Biomas and NuclearRoman SionisNo ratings yet
- Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierDocument12 pagesPlease Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierEzra OrtilanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document6 pagesUnit 6Ernie CoachNo ratings yet
- Physics 9 - Energy ResourcesDocument36 pagesPhysics 9 - Energy ResourcesHakim Abbas100% (1)
- Sources of EnergyDocument19 pagesSources of EnergyARNAV DEYNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument19 pagesElectricityAdie Alie PumpNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Energy and The EnvironmentDocument20 pagesCH 2 Energy and The Environmentmhussainarabi@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- U6 Physics Cala B AnswersDocument4 pagesU6 Physics Cala B Answershmatara8No ratings yet
- Element of Mechanical Engineering (2) NITPDocument24 pagesElement of Mechanical Engineering (2) NITPmayankraj.2415No ratings yet
- E and W SourceDocument6 pagesE and W SourcegwynethredondoNo ratings yet
- Conventional and Non Conventional Sources of Energy: Submitted By-Reetika AgarwalDocument29 pagesConventional and Non Conventional Sources of Energy: Submitted By-Reetika AgarwalhemantNo ratings yet
- Diosdado Macapagal BLVD, Pasay, Philippines College of NursingDocument8 pagesDiosdado Macapagal BLVD, Pasay, Philippines College of NursingSkyeNo ratings yet
- 1 Energy Placemat 2 ANSDocument1 page1 Energy Placemat 2 ANS10daimuviyi2No ratings yet
- (Renewable Energy) - Chapter-1Document24 pages(Renewable Energy) - Chapter-1Mahmoud TarekNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Hydrogen and Fuel CellDocument7 pages1.3 Hydrogen and Fuel CellPrince DuraNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources PDFDocument3 pagesEnergy Resources PDFTahmeed AzizNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument3 pagesEnergy ResourcesQuazi Rafquat HossainNo ratings yet
- Renewable: Energy ResourcesDocument6 pagesRenewable: Energy Resourceshfitzwater29No ratings yet
- Technology and Computing: Grade NinthDocument18 pagesTechnology and Computing: Grade NinthAntwan MeloNo ratings yet
- Class X Physics Chapter 12 - Sources of Energy: A. B. C. D. eDocument5 pagesClass X Physics Chapter 12 - Sources of Energy: A. B. C. D. eAnand YendrembamNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Quarter 1 Week 7 1Document16 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 1 Week 7 1CrimstonNo ratings yet
- Energy SourcesDocument16 pagesEnergy SourcesdivyavjosephNo ratings yet
- Physical Scienc1Document3 pagesPhysical Scienc1JULLIE CARMELLE H. CHATTONo ratings yet
- MCN 201 Module 4Document98 pagesMCN 201 Module 4Alvin Saji JohnNo ratings yet
- Non Conventional Sources of EnergyDocument7 pagesNon Conventional Sources of EnergytanishqahumbeNo ratings yet
- Energy1 (1) بيترولDocument20 pagesEnergy1 (1) بيترولkhaledalgashat80No ratings yet
- Non Renewable Info SheetsDocument4 pagesNon Renewable Info SheetsShaikhAbdullaXecNo ratings yet
- Non Renewable and Renewable EnergyDocument1 pageNon Renewable and Renewable EnergyJoseph Peter CabanganganNo ratings yet
- Wa0011.Document16 pagesWa0011.PRANAMI BORAHNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering (Midterm)Document8 pagesPower Plant Engineering (Midterm)Manash PaulNo ratings yet
- Renewable Power Generation NoteDocument182 pagesRenewable Power Generation NoteMohammed AbadiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear EnergyDocument11 pagesNuclear EnergySteven NgNo ratings yet
- PEH3 Lesson 2Document2 pagesPEH3 Lesson 2James Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Alzona Resume - Used in Work ImmersionDocument2 pagesAlzona Resume - Used in Work ImmersionJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary ArtsDocument5 pagesContemporary ArtsJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion at Creotech Philippines IncorporatedDocument3 pagesWork Immersion at Creotech Philippines IncorporatedJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Theater: Paghihintay Kay Godot That Was Translated To Waiting For Godot by Samuel BeckettDocument3 pagesTheater: Paghihintay Kay Godot That Was Translated To Waiting For Godot by Samuel BeckettJames Ryan Alzona0% (1)
- Chapter 4 EthicsDocument2 pagesChapter 4 EthicsJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Arts Chapter 2Document2 pagesContemporary Arts Chapter 2James Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EthicsDocument2 pagesChapter 4 EthicsJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Feasib 2Document10 pagesFeasib 2James Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Puto Has Emerged As A Popular Snack For Filipinos Across The Country For Its Savory Taste, SoftDocument3 pagesPuto Has Emerged As A Popular Snack For Filipinos Across The Country For Its Savory Taste, SoftJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Philosophical Foundations of EthicsDocument4 pagesChapter 5: Philosophical Foundations of EthicsJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Virtue EthicsDocument3 pagesVirtue EthicsJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Name Tag Senior HighDocument2 pagesName Tag Senior HighJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Sit PlanDocument3 pagesSit PlanJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature (AutoRecovered)Document3 pagesReview of Related Literature (AutoRecovered)James Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting University Choices Among Grade 12-ABM Students of Binan and Santa Rosa S.Y. 2018-2019Document26 pagesFactors Affecting University Choices Among Grade 12-ABM Students of Binan and Santa Rosa S.Y. 2018-2019James Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Energy Piles and Other Thermo-Active Ground-Source Systems: Heinz BrandlDocument22 pagesEnergy Piles and Other Thermo-Active Ground-Source Systems: Heinz BrandlwongtianhuiNo ratings yet
- Appreciate The Positive Side of A Volcano: A. Readings/Discussions How Energy From Volcanoes May Be Tapped For Human Use?Document8 pagesAppreciate The Positive Side of A Volcano: A. Readings/Discussions How Energy From Volcanoes May Be Tapped For Human Use?Kadita Mage100% (1)
- Electric Generation by Spinning Exercise: Bachelor of Engineering in Electrical EngineeringDocument40 pagesElectric Generation by Spinning Exercise: Bachelor of Engineering in Electrical EngineeringSHAIKH MOHAMMAD UMAR MERAJUDDIN100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Plan For Ste 9 Week 4Document6 pagesDaily Lesson Plan For Ste 9 Week 4Jhea-May Calipay JimenezNo ratings yet
- Review of Renewable Energy Technologies Utilized in The Oil and Gas IndustryDocument8 pagesReview of Renewable Energy Technologies Utilized in The Oil and Gas Industryhoss mosafaNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy PowerpointDocument19 pagesGeothermal Energy PowerpointgilangNo ratings yet
- ES21 Q1 Mod5 Earths Energy and Water ResourcesDocument17 pagesES21 Q1 Mod5 Earths Energy and Water ResourcesFrancine CañasNo ratings yet
- Alamos: Scientific LaboratoryDocument67 pagesAlamos: Scientific Laboratorythomas williansNo ratings yet
- 2019-2020 Chuyên Thái BìnhDocument6 pages2019-2020 Chuyên Thái BìnhNgoc Mai HongNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Materials Used in Geothermal Power Generation - Review of Materials and Treatment TechnologiesDocument72 pagesCorrosion of Materials Used in Geothermal Power Generation - Review of Materials and Treatment Technologiesu477669No ratings yet
- GeothermalDocument7 pagesGeothermalRizky Esa RespatiNo ratings yet
- Jha 2017Document21 pagesJha 2017bepol88No ratings yet
- Distributed GenerationDocument21 pagesDistributed Generationlipika008No ratings yet
- Obnovljivi Izvori Energije StefanDocument20 pagesObnovljivi Izvori Energije StefanStefanNo ratings yet
- Ee1252 - Power Plant Engineering: Question Bank Unit I - Thermal Power Plants PART A (2 Marks)Document4 pagesEe1252 - Power Plant Engineering: Question Bank Unit I - Thermal Power Plants PART A (2 Marks)Vivek BendreNo ratings yet
- Physics Project - Sources of EnergyDocument16 pagesPhysics Project - Sources of Energyyasiero75% (4)
- Page 49 PDFDocument1 pagePage 49 PDFJuan Ponce ManríquezNo ratings yet
- CH 212 Energy EngineeringDocument35 pagesCH 212 Energy EngineeringMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy 4743Document8 pagesGeothermal Energy 4743eceLebiNo ratings yet
- Different Forms of Energy and How Each Is Produced and HarnessedDocument39 pagesDifferent Forms of Energy and How Each Is Produced and HarnessedTara SantosNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: - A Renewable Energy Source For Electricity GenerationDocument25 pagesGeothermal Energy: - A Renewable Energy Source For Electricity GenerationGregson GucelaNo ratings yet
- GTZ, Renewable Energy Policy in The Caribbean, September 2007Document34 pagesGTZ, Renewable Energy Policy in The Caribbean, September 2007Detlef Loy100% (2)
- Geothermal Energy Use, Country Update For Turkey: June 2019Document11 pagesGeothermal Energy Use, Country Update For Turkey: June 2019Rivan TYNo ratings yet
- Ch18 GeothermalDocument17 pagesCh18 GeothermalHenok gebrehiwotNo ratings yet
- Unu-Gtp-Sc-02-06 Environmental and Social Issues in Geothermal in El SalvadorDocument10 pagesUnu-Gtp-Sc-02-06 Environmental and Social Issues in Geothermal in El SalvadorPrince MubaiwaNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power GenerationDocument36 pagesGeothermal Power GenerationdlebreromNo ratings yet
- Omdal Kjetil PDFDocument110 pagesOmdal Kjetil PDFMehdi SoltaniNo ratings yet
- The Application of Na-K-Mg, Na-K/Mg-Ca and K-Mg/Quartz Diagrams To Evaluate Water Geochemistry in West Java Geothermal Prospects, IndonesiaDocument8 pagesThe Application of Na-K-Mg, Na-K/Mg-Ca and K-Mg/Quartz Diagrams To Evaluate Water Geochemistry in West Java Geothermal Prospects, IndonesiaReinhard DanangNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity StudyDocument118 pagesBiodiversity StudyAndrea Lizares Si100% (1)
- The Effect of Well Elevation On Production in Lumut Balai FieldDocument3 pagesThe Effect of Well Elevation On Production in Lumut Balai FieldTalang AkarNo ratings yet