Lesson 1 Correction
Uploaded by
Alyanna AngelesLesson 1 Correction
Uploaded by
Alyanna AngelesLESSON 1
Lesson 1- contains a compilation of topics which addresses this learning outcome.
L. O.1- Describe the types of gas turbines, its features and functions
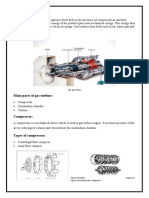
GAS TURBINE DEFINATION
A gas turbine maybe defined as a form of heat engine in which the potential energy of the
working gas is charge into mechanical work in two distinct steps. First, the available energy is
converted into energy of motion, called kinetic energy, by expansion in a nozzle or suitable
passage, from which the gas emerges as a jet at high velocity. Secondly, this kinetic energy is
converted into mechanical energy or useful work by directing the jet against blades mounted on
a revolving rotor, or by the reaction of the jet itself in the expanding passage if the passage
revolves.
Two types of gas turbine in terms of operating principle
(a) Open cycle gas turbine
(b) Closed cycle gas turbine
(a) Open cycle gas turbine:
Working on Joule cycle or Brayton cycle
Air is compressed in a rotary compressor and passed into a combustion chamber where fuel is
burnt, the products of combustion are made to impinge over rings of turbine blades with high
velocity and work is produced. After the work done by the combustion products, rest are given
to the atmosphere.
60% of work produced is used to drive the compressor and rest is available as useful power
For starting purpose, it is first motored to minimum speed, called coming in speed, before
the fuel is turned on
About 5% power output by the motor is used to start the turbine
To improve the turbine performance intercooler, heat exchanger and reheat cycles are used
with simple gas turbine cycle.
(b) Closed cycle gas turbine:
Working fluid air or other gas is circulated continuously inside the machine
Working fluid does not come in contact with the atmospheric air or fuel
Heat to working fluid is given externally by the burning of the fuel that is why it is external
combustion engine
Turbine exhaust rejects heat in a cooler
Advantage of closed cycle gas turbine:
Due to externally fired, cheaper fuel such as coal can be used
Products of combustion is not in directly contact with turbine blades, hence fouling and heat
transfer from the surface of the blade can be avoided
Part load efficiency is improved by changing the pressure ratio and varying the quantity of
working fluid keeping as cycle temperature constant and at constant speed
High operating pressure causes low specific volume for the working fluid reducing the size of
machines, heat exchangers and piping
Heat transfer coefficients are higher which reduces the heat exchanger size
Disadvantage of closed cycle gas turbine:
more complicated and costly system
Air heaters alone represent over 30% of total mass and cost
system is not sufficiently strong to resist high pressure
*Simple Gas turbine:
Following assumptions are made in analysis of ideal gas turbine,
Compression and expansion process are reversible adiabatic
Kinetic energy does not change at the inlet and exit
No pressure loss
Same chemical composition of working fluid
Heat exchanger is counter flow type with 100% efficiency
Fig. 1. Simple gas turbine
T-S diagram P-V diagram
ENGINE TYPES: In terms of construction
SINGLE SHAFT ENGINE
The single-shaft engine - have one shaft which extends throughout the engine. All rotating
parts of the engine are mounted on this shaft. An extension of this same shaft, the power take-
off assembly, drives the load.
The primary use of this type of engine is where constant speed is required such as electrical
power generation.
Block diagram of single shaft engine
In the engine illustrated, the power output shaft is connected directly to the same turbine rotor
that drives the compressor. In most cases, there is a speed decreases or reduction gear
between the rotor and the power output shaft; however, there is still a mechanical connection
throughout the entire engine.
SPLIT-SHAFT ENGINE
The engine is split into two major section, the gas generator and the power turbine section.
The primary use of this type of engine is where variable speed and load is required such as a
main ship propulsion.
In this cycle the turbine is divided into two units, not for the purpose of reheat, but so that
the compressor can be driven by one turbine and the useful output produced by another. The
two shaft machines are more widely applied where there is considerable operation at reduced
speed and load or where high starting torques are required. It is for these reasons that the two-
shaft units are the most suitable for marine propulsion.
Block diagram of a split-shaft engine
The split-shaft engine consist of two main parts: Gas generator and a power turbine, each parts
has its own shaft.
GAS GENERATOR SECTION
The gas generator section consist of a compressor, combustor and gas generator turbine
called the high pressure turbine. The gas generator purpose is to produce a hot expanding gas
for use in the power turbine. The Power turbine is aerodynamically coupled to the gas generator
but the two shaft are not mechanically connected. The power turbine converts the thermal
energy from the gas generator to mechanical energy to drive the load. The main advantage of a
split-shaft engine is the fact that the gas generator is more responsive to load demands
because the compressor is not restricted in operation by the load on the power.
Also, under certain conditions the gas generator can run at a reduced rpm and still provide
maximum power turbine rpm which greatly improves fuel economy and also extends the life of
the gas is lowered appreciably due to the fact that the power turbine, reduction gears, and
output shaft remain stationary until the gas generator reaches approximate idle speed. Another
feature is that in a multi shaft marine propulsion plant where one design (clockwise rotation or
counterclockwise rotation) of gas generator can be used on either shaft, the gas generator
rotates only one way; however, the power turbine can be made to rotate either way by changing
the power turbine wheel and nozzles.
TWIN SPOOL ENGINE
Block diagram of twin spool engine
Another type of turbine is the twin spool, sometimes referred to as a multistage gas turbine.
In the twin spool engine there are two separate compressors and two separate turbine rotors.
They are referred to as L.P. compressor and turbine rotor and H.P. compressor and turbine
rotor. The L.P. compressor and turbine are connected by a shaft which runs through the hollow
shaft that connects the H.P. turbine to the P compressor. The starter drives the H.P. assembly
during light off. The power turbine function the same as in the split shaft engine. A volume of air
can be handled as compared to single or split shaft engine; however, the engine has more
moving parts, and the increase overall dimensions and complexity make engine less desirable
for ship's propulsion compare to the split shaft engine.
You might also like
- Gas Turbine Operation & Maintenance Course89% (9)Gas Turbine Operation & Maintenance Course100 pages
- Massey Ferguson MF 3680 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637189)No ratings yetMassey Ferguson MF 3680 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637189)16 pages
- Gas Turbine Operation & Maintenance Course100% (5)Gas Turbine Operation & Maintenance Course100 pages
- 1nz-Fe Engine Mechanical Timing Chain Installation (2007 Yaris)100% (2)1nz-Fe Engine Mechanical Timing Chain Installation (2007 Yaris)3 pages
- Chapter One Introduction of Gas TurbineNo ratings yetChapter One Introduction of Gas Turbine22 pages
- Gas Turbines Definition Applications Working Components Types Design Advantages PDFNo ratings yetGas Turbines Definition Applications Working Components Types Design Advantages PDF13 pages
- C-1 Energy Efficiency Improvement in Gas Turbine FinalNo ratings yetC-1 Energy Efficiency Improvement in Gas Turbine Final219 pages
- Gas Turbine Working Principles: Bahman ZohuriNo ratings yetGas Turbine Working Principles: Bahman Zohuri27 pages
- Gas Turbine Working Principles: Bahman ZohuriNo ratings yetGas Turbine Working Principles: Bahman Zohuri27 pages
- By: Satyendra Nath Dwivedi: Triune Energy Services, New Delhi100% (1)By: Satyendra Nath Dwivedi: Triune Energy Services, New Delhi46 pages
- Design and Analysis of Gas Turbine Blade: Mr. M.PrasadNo ratings yetDesign and Analysis of Gas Turbine Blade: Mr. M.Prasad10 pages
- GALGALLA - Working Assignment 3 - Gas TurbineNo ratings yetGALGALLA - Working Assignment 3 - Gas Turbine5 pages
- The Emerging Prime Mover: Authored By: Martin Leduc, March 2001No ratings yetThe Emerging Prime Mover: Authored By: Martin Leduc, March 20018 pages
- Power Plant Engineering Unit:Iv Gas Turbine PlantNo ratings yetPower Plant Engineering Unit:Iv Gas Turbine Plant30 pages
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- Types of Starting Motor Drives: LT Devansh Chaturvedi LT Ananthapadmanabhan PG LT Avinash Kumar JhaNo ratings yetTypes of Starting Motor Drives: LT Devansh Chaturvedi LT Ananthapadmanabhan PG LT Avinash Kumar Jha10 pages
- Pi N Connection Pin Connection: 1995-1999 Mitsubishi Eclipse and Eagle Talon Turbo DSM ECU Pinouts100% (1)Pi N Connection Pin Connection: 1995-1999 Mitsubishi Eclipse and Eagle Talon Turbo DSM ECU Pinouts2 pages
- 21-19700-120 Reintjes Product Guide 2021 - Final - LowNo ratings yet21-19700-120 Reintjes Product Guide 2021 - Final - Low186 pages
- Massey Ferguson MF 3680 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637189)Massey Ferguson MF 3680 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637189)
- 1nz-Fe Engine Mechanical Timing Chain Installation (2007 Yaris)1nz-Fe Engine Mechanical Timing Chain Installation (2007 Yaris)
- Gas Turbines Definition Applications Working Components Types Design Advantages PDFGas Turbines Definition Applications Working Components Types Design Advantages PDF
- C-1 Energy Efficiency Improvement in Gas Turbine FinalC-1 Energy Efficiency Improvement in Gas Turbine Final
- By: Satyendra Nath Dwivedi: Triune Energy Services, New DelhiBy: Satyendra Nath Dwivedi: Triune Energy Services, New Delhi
- Design and Analysis of Gas Turbine Blade: Mr. M.PrasadDesign and Analysis of Gas Turbine Blade: Mr. M.Prasad
- The Emerging Prime Mover: Authored By: Martin Leduc, March 2001The Emerging Prime Mover: Authored By: Martin Leduc, March 2001
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet S
- Types of Starting Motor Drives: LT Devansh Chaturvedi LT Ananthapadmanabhan PG LT Avinash Kumar JhaTypes of Starting Motor Drives: LT Devansh Chaturvedi LT Ananthapadmanabhan PG LT Avinash Kumar Jha
- Pi N Connection Pin Connection: 1995-1999 Mitsubishi Eclipse and Eagle Talon Turbo DSM ECU PinoutsPi N Connection Pin Connection: 1995-1999 Mitsubishi Eclipse and Eagle Talon Turbo DSM ECU Pinouts
- 21-19700-120 Reintjes Product Guide 2021 - Final - Low21-19700-120 Reintjes Product Guide 2021 - Final - Low