Foam Systems For Storage Tanks: Scope
Foam Systems For Storage Tanks: Scope
Uploaded by
frgonzalezcOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Foam Systems For Storage Tanks: Scope
Foam Systems For Storage Tanks: Scope
Uploaded by
frgonzalezcCopyright:
Available Formats
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
Foam Systems for Storage Tanks
GP 03-02-02
Scope
1) [I] This Global Practice (GP) covers the design and installation of firefighting foam systems using
high or low back pressure foam makers, for use with fixed roof tanks operating at approximately
atmospheric pressure (not exceeding 21/2 psig [17 kPag]) or with annular pontoon or double deck
open-top floating roof tanks. The systems also are applicable to tanks furnished with internal floating
roofs or covers.
2) [I] An asterisk (*) indicates that additional information is required. If a job is contracted, this
additional information is furnished in the Job Specification.
Refining/Chemicals For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 1 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
Table of Contents
Table of Figures ..............................................................................................................3
1. Required References..............................................................................................4
1.1. Global Practices–ExxonMobil Engineering Practices ....................................4
1.2. NFPA–National Fire Protection Association ..................................................4
2. Materials ..................................................................................................................4
3. Design......................................................................................................................4
4. Additional Design and Installation Requirements for Fixed Roof Tanks ..........6
5. Additional Design and Installation Requirements for Open-Top Floating Roof
Tanks .......................................................................................................................9
6. Inspection and Testing.........................................................................................12
Record of Change .........................................................................................................14
Attachment: Purpose Codes Definitions ...................................................................16
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 2 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
Table of Figures
Figure 1: Design and Installation of Foam Chambers Mounted on Tank Shell ........7
Figure 2: Design and Installation of Foam Chambers Mounted on Shell Extension
for Use with Internal Floating Roofs or Covers..........................................8
Figure 3: Single Foam Outlet Station Layout of Foam Outlet Assembly and
Solution Piping (Schematic and Detailed) ................................................10
Figure 4: Multiple Foam Outlet Locations Tanks over 75 Ft Diameter Typical
Layout of Foam Outlets and Solution Piping (Schematic) ......................11
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 3 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
1. Required References
This Section lists Practices and Standards that are generically referenced and assumed to be a part of this
document. Unless otherwise specified herein, use the latest edition.
1.1. Global Practices–ExxonMobil Engineering Practices
GP 09-07-01 Accessories for Atmospheric Storage Tanks
1.2. NFPA–National Fire Protection Association
NFPA 11 Standard for Low-, Medium-, and High Expansion Foam
NFPA 30 Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code (National Fire Codes, vol. 1)
2. Materials
1) * [S] Piping for risers, laterals, and distribution systems shall be carbon steel, Sch. 40 minimum wall
thickness, galvanized or lined with a heat-cured epoxy or phenolic-epoxy system with a minimum dry
film thickness of 8 mils (200 m). The Owner's Engineer shall approve use of unlined pipe.
2) [S] Foam chambers, outlet assemblies, and deflectors shall be carbon steel, galvanized or epoxy lined.
Foam dams shall be fabricated from carbon steel. Pipe carrying foam concentrate shall not be
galvanized.
3) [S] Foam backboards shall be the same material specification and grade as the shell plate to which
they are attached.
4) [S] Frangible diaphragms, incorporated in the seal chamber of foam chambers, shall be 14 oz (0.061
in. [1.5 mm]) thick common soda lime glass, scored to facilitate breakage under foam pressure.
5) [S] Screening, installed at the foam deflector or air entry ports of foam makers, shall be 2 x 2 mesh
with 0.459-in. (12-mm) nominal opening.
3. Design
1) [S] Lateral terminal connection:
a) Laterals shall terminate on the roadside of all pipelines and drainage ditches.
b) The terminal connections shall be located in relation to fire hydrants so that the total length of
hose from the hydrant to fire truck does not exceed 25 ft (7.5 m) and from fire truck to foam
lateral terminals does not exceed 50 ft (15 m). Connections should be located at least a distance
of one tank diameter from the tank but in no case less than 50 ft (15 m).
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 4 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
c) Terminal connections shall be from 2 ft to 4 ft (600 mm to 1200 mm) above grade and shall be
suitably protected against collision.
d) A sign shall be installed at each lateral termination point identifying the tank served.
2) * [S] Fire hose coupling type to be used at terminal connections and at foam outlet stations will be
specified. In some locations, the plant fire departments will provide the actual fire hose couplings.
* [S] Coupling thread type shall be suitable for use with Owner's firefighting equipment. Couplings
shall be provided with dust caps or plugs.
3) [S] For tanks requiring multiple laterals, up to two laterals can be brought to a single location 4 ft
(1200 mm) apart. However, not more than two laterals from any one tank shall be brought to the
same location.
4) * [S] Locate the lateral terminals on the side of the tank lot that most directly faces the prevailing
wind, if any, consistent with good access.
5) [S] The terminal connections on foam makers shall be as follows:
a) Laterals to single foam outlets up to 250 gpm (0.93 m3/min) capacity shall terminate in one NPS
2 1/2 (65 mm) size mating hose coupling.
b) Laterals to single foam outlets greater than 250 gpm (0.93 m3/min) capacity or to multiple foam
outlets shall terminate in one NPS 2 1/2 inch (65 mm) size mating hose coupling for every 250
gpm (0.93 m3/min) of lateral capacity or part thereof.
6) [S] The riser pipe size from the foam maker to the foam chamber shall be determined by hydraulic
calculation, but shall not be smaller than the foam chamber inlet flange size.
7) [S] Riser supports shall be 1/2 in. (12 mm) thick plate, 12 in. (300 mm) length, with the width
depending on riser dimension, but selected to maintain the riser a minimum of 4 in. (100 mm) clear
from the tank shell. Installation shall be as follows:
a) Each support shall be located on about 8-ft (2.4 m) centers and placed perpendicular to the tank
shell and centered on the riser pipe.
b) The edges of the plate shall be continuously welded on all sides to both tank shell and pipe with
1
/4 in. (6 mm) fillet welds to support the shell in event of a fire.
8) [S] Foam lateral size shall be determined by hydraulic calculation, but shall not be less than NPS 21/2
(65 mm) size. Laterals shall be installed as follows
a) Slope continuously toward the termination point outside the dike. If this is impractical, a
(normally closed) NPS 3/4 (20 mm) drain valve shall be provided at the low point.
b) Not run through the dike area of any other tank, group of tanks, or paired tanks. However, piping
within a group of tanks may cross intermediate toe walls within that group.
c) Extend outside the dike to a safe location (taking into consideration the plant prevailing wind) at
least one tank diameter or 50 ft (15 m), whichever is greater, from the tank.
d) Maintain a minimum elevation of 1 ft (300 mm) above finished grade.
9) [S] The ratio of the strainer's open basket area to its pipe area shall be at least 10:1. The net open area
of the strainer shall be at least four times the area of the suction piping.
10) [S] Underground carbon steel piping and portions of above ground carbon steel piping that pass
through a dike or pipe sleeve shall be protected against external corrosion using a Single Coat-Single
Wrap or Double Coat-Double Wrap protective coating system.
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 5 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
11) [S] Permanent connections between the fire water system and any process system shall be prohibited.
4. Additional Design and Installation Requirements for
Fixed Roof Tanks
1) [S] The provision of fixed fire protection for tanks containing non water-soluble flammable liquids,
meeting the following conditions:
a) Closed cup flash point under 100F (38C), or
b) Closed cup flash point of 100F (38C) and above if such stocks are heated to a temperature
above or within 15F (8C) of their flash point
shall be as follows:
A surface application type firefighting foam system using fixed foam discharge outlets in accordance
with NFPA 11:
The number of foam chambers (and deflectors) installed shall be as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Foam Chambers Required
Nominal Tank Diameter Number of Foam
Chambers per Tank
Ft M
< 20 <6 0
20 to 80 6 to 24 1
> 80 to 110 > 24 to 33 2
> 110 to 130 > 33 to 40 3
> 130 to 150 > 40 to 46 4
Tanks with a fixed roof and no internal floating cover or roof shall be designed such that the foam
chambers shall be shell mounted per Figure 1.
Tanks with a fixed roof and an internal floating cover or roof shall be designed such that the foam
chamber shall be tank-shell mounted per Figure 1, provided the deflector does not interfere with the
specified upper travel limit of the internal floating cover or roof. Shell extension mounted per
Figure 2 is permitted for retrofits.
Exception 1:
* [S] Fixed roof tanks need only meet the requirements for open-top floating roof tanks, per
Section 5, when the construction meets both the following conditions:
a) Provided with an internal floating roof that is either a pontoon-type floating roof or double deck
design floating roof.
b) The fixed roof is aluminum, fiberglass or other lightweight geodesic dome or external cone roof.
Exception 2:
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 6 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
[S] The tank is provided with a SHE Critical nitrogen blanketing system.
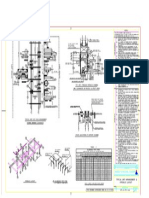
Figure 1: Design and Installation of Foam Chambers Mounted on Tank Shell
Tank Shell
PLAN
D
(Note 1)
A A
18-1/2 in.
Foam chamber and deflector
welded or bolted to tank shell with
vapor tight connections
Vapor Tight 1/2D + 4-1/2 in.
Inspection Hatch
Gasket
Seal
Frangible Glass
Weld
Diaphragm
(Installed per
recommendation of
the manufacturer) 2-1/2 in.
Roof Angle
11 in. max.
13 in.
8 in. Pipe
Foam Chamber
12 in. Pipe
1-1/2 in.
6 in. Class 150
RF, threaded for
welded flange for
6 in. riser 40i
4 in.
Minimum Deflector
SECTION A-A ELEVATION
Acceptable Metric Equivalent
in. 1-1/2 2-1/2 4 4-1/2 8 11 13 14 16 18-1/2 4 NPS 6 NPS 8 NPS 12 NPS
mm 38 63 100 115 200 275 325 350 400 463 100 150 200 300
Notes:
(1) Diameter D =16 in. for tanks with 30 in. shell manhole.
D =14 in. for tanks with 24 in. shell manhole.
(2) All foam chamber welds shall be 2-pass welded.
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 7 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
Figure 2: Design and Installation of Foam Chambers Mounted on Shell
Extension for Use with Internal Floating Roofs or Covers
Weak Roof
Seam
1/8
PLAN
16 in.
1/4
A A
18-1/2 in.
20 in.
22 in.
7 in.
1/4
Vapor Tight
Inspection Hatch 1/8
Gasket 26 in.
Frangible Glass Seal
Diaphragm Weld
(Installed per
recommendation of
the manufacturer) 2-1/2 in.
1/8
1/4
3/8 in. thick,
carbon steel 1/8
13 in.
8 in. Pipe
8 in.
1/8 in. thick
carbon steel
Foam Chamber
12 in. Pipe Weak Roof
Seam
1-1/2 in.
6 in. Class 150
RF, threaded for Roof plate
welded flange for cut
6 in. riser 4 in. 40i
Minimum
1/4 Bottom of deflector to be
located above upper
Roof
most position of floating
Angle
cover (under overflow
SECTION A-A ELEVATION
condition)
Acceptable Metric Equivalent Dimensions
in. 1/8 1/4 3/8 1-1/2 2-1/2 4 8 13 16 18-1/2 22 26 4 NPS 6 NPS 8 NPS 12 NPS
mm 3 6 10 38 63 100 200 325 400 463 550 650 100 150 200 300
Note:
(1) Combination bevel plus fillet welds may be used where double fillet welds are shown.
2) * [S] Water-soluble flammable liquids: the Owner's Engineer and the plant Fire Chief shall specify
the need for foam chambers and the applicable details of design and installation.
3) [S] When multiple foam chambers are required, they shall be equally spaced around the tank.
4) [S] Foam makers shall be provided and installed as follows:
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 8 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
a) * Unless otherwise specified, foam makers with a capacity of 500 gpm at 150 psig (1.89 m3/min
at 1034 kPag) inlet pressure, equal to National Foam Type PHB 50 SS shall be used. The foam
maker shall be located in the riser piping so that the aspirator opening is 5 ft (1500 mm) above
finished grade.
b) * For locations requiring low backpressure foam systems, National Foam Type MCS-33 or MCS-
55 or equivalent shall be used unless otherwise specified. These foam makers shall be located
under the foam chamber at the top of the tank.
c) The foam maker air entry ports shall be provided with screens per Section 2, Item (5). Screens
can be obtained from: National Foam Systems, Inc., 150 Gordon Drive, Lionville, PA 19353
5) [S] Piping layout: Each foam chamber shall be equipped with its own riser, foam maker, and lateral.
Pipe risers and foam makers shall be installed directly below the foam chambers. A flanged spool
piece shall be installed upstream of the foam maker (near finished grade) to permit periodic flushing
of the lateral.
6) [S] Lateral pipe size: Laterals shall be sized so that the maximum pressure drop between the end of
the lateral and foam maker does not exceed 35 psi (240 kPag).
7) [S] Foam chambers on internal floating roof tanks shall not be located above ventilation openings on
the shell.
8) * [C] Non water-soluble combustible liquids: When approved by the Owner’s Engineer and the plant
Fire Chief, a semi-fixed subsurface foam injection system designed per NFPA 11 may be considered
to satisfy local regulatory requirements for tanks that do not require a surface application system (per
Section 4, Item (1), provided both of the following conditions are satisfied:
a) The tank is a fixed roof tank without an internal floating cover.
b) The tank stores a non-polar liquid having a closed-cup flash point of 100F (38C) or higher at a
temperature lower than its closed-cup flash point minus 15F (8C).
5. Additional Design and Installation Requirements for
Open-Top Floating Roof Tanks
1) [S] Foam dams shall be installed on all floating roof tanks.
A firefighting foam system using fixed foam discharge outlets in accordance with NFPA 11 shall be
provided in all open-top floating roof tanks that store crude oils, or that store low-flash stocks with:
a) Closed cup flash point under 100F (38C), or
b) Closed cup flash point of 100F (38C) and above if such stocks are heated to a temperature
above or within 15F (8C) of their flash point.
2) [S] For open-top floating roof tanks up to 75-ft (22.5 m) diameter, a single foam outlet station shall be
located by the top platform per Figure 3.
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 9 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
Figure 3: Single Foam Outlet Station Layout of Foam Outlet Assembly and
Solution Piping (Schematic and Detailed)
10 ft. Min. D Deflector
Foam C 1/8 in. Thick
Fabricated Deflector:
12 in.
Foam Backboard
From 4 in. Mounted To Clear
Extension Sheet
Std Wall Uppermost
Mounted Minimum Height Piping Position Of Roof
Above Of Backboard
Shell. Depends On Top Screen
Note (1) Position Of Roof 24 in. C
Foam
Bracing
Maker Weather Shield Pad
(Fire Hose Or Secondary B 1/4 in. Thick
Connections Seal
VIEW C-C
Not Shown In
Top Of Shell
24 in.
This View) Note (3)
Foam Dam
3/16 in.
Drain Slots:
Platform Floating 1 in. Wide x 1/2 in. High,
Platform Foam
Solution Piping: Roof Dam On 10 ft Centers
Braced To Tank Shell D B (Approximate Dimensions)
1-1/2 in. Fire Hose Connections Seal
Windgirder (Toroidal type shown)
Note (2) Continuous Fillet Weld
VIEW D-D Tank Shell VIEW B-B
DETAIL A
ACCEPTABLE METRIC EQUIVALENTS
Piping And Fire Hose
Connections, NPS
See Detail A
in. mm
1-1/2 40
2-1/2 65
4 100
Other Linear Dimensions
2-1/2 in. NPS Mating
in. mm in. mm Fire Hose Connections
Grade
1/8 3 1 25 Slope
3/16 5 12 300
1/4 6 24 600
1/2 13 10 ft 3000
Notes:
(1) FOAM BACKBOARD shall be offset from PLATFORM to avoid blocking entrance to FLOATING ROOF.
(2) NPS 1-1/2 fire hose connections and block valve to FOAM MAKER to be accessible from top PLATFORM.
(3) The FOAM DAM shall be increased in height to be 6 in. (150 mm) higher than the weather shield or secondary seal
if these are constructed entirely from non-combustible material. If the weather shield or secondary seal is
constructed of both combustible and non-combustible materials it shall be treated as constructed entirely of
non-combustible material.
3) [S] For open-top floating roof tanks larger than 75-ft (22.5 m) diameter, one foam station shall be
installed for each 80 ft (24 m), and fraction thereof, of tank circumference, equally spaced around the
circumference per Figure 4.
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 10 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
Figure 4: Multiple Foam Outlet Locations Tanks over 75 Ft Diameter Typical
Layout of Foam Outlets and Solution Piping (Schematic)
Blind Flanges For Flushing
Foam
Backboard
Foam Outlet
80 Ft. Assembly
Foam
Deflector
Solution Supply Piping
(To Hose Connections And
Dike Wall Foam Outlet Assemblies)
General Note:
Two NPS 1-1/2 fire hose connections, per Figure 3, required at only one foam station at top
of tank stairs by the platform. (Other foam outlets around the tank do not require these fire
hose connections or valves.)
Acceptable Metric Equivalents
in. NPS 1-1/2 80 ft
mm 40 24 m
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 11 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
4) * [S] Unless otherwise specified, the foam outlet assembly, consisting of a foam maker, foam
deflector, and mounting assembly, shall be National Foam Systems, Inc., Type MBS-9SA/MCS-9FR
or equivalent. Unless otherwise specified, the foam maker shall be furnished with an orifice diameter
of 0.65 in. (16.5-mm). The foam maker air entry ports and the foam deflector shall be provided with
a bird screen per Section 2, Item (5). See Section 4, Item 4 (c) for address of National Foam Systems.
5) [S] A single foam riser may be used to deliver foam solution to the foam outlets. When multiple
foam outlets are installed, the distribution piping to individual outlets shall be located on top of the
wind girder to be accessible for inspection.
6) [S] The foam system including the lateral, riser, and distribution piping shall be sized to deliver 60
gpm (0.23 m3/ min) foam solution to each foam maker inlet at a pressure of 60 psig (420 kPag), based
on a foam proportioning truck discharge pressure of 100 psig (700 kPag).
7) * [S] Foam backboards and foam dams shall be designed for wind pressure (design wind velocity
shall be specified by the Owner's Engineer). Foam dam bracing shall be on the outside of the dam,
away from the foam, so as not to impede the flow of foam. The foam dam shall extend completely
around the roof, and, except for drain slots per Figure 3, shall be continuously seal welded to the roof
for the full length of the dam.
8) [S] Foam backboards mounting and minimum dimensions shall comply with the following:
a) Foam backboards shall be mounted flush with the ID of the shell.
b) The backboard shall be minimum height, but sufficient to have the foam deflector clear the
maximum travel of the roof seal weather shield and other protruding parts at the uppermost
position of the roof.
c) * The width of the backboard shall be 10 ft (3000 mm) minimum, unless otherwise dictated by
unusual wind conditions or experience at the plant location. The Owner's Engineer shall approve
deviation from this minimum width.
9) [S] Guard railings as per GP 09-07-01 shall be installed on wind girders of open-top floating roof
tanks, completely around the tank, when one or more foam outlet stations are installed.
6. Inspection and Testing
1) * [S] Acceptance tests: Foam systems covered by this GP shall be tested in accordance with NFPA
11 requirements and in the presence and to the satisfaction of the Owner's Representative and the
plant Fire Chief, by generating foam into the storage tank prior to the tank being placed in service.
The following are minimum requirements:
a) During the test, the foam proportioning truck discharge pressure shall be sufficient to obtain the
desired pressure at each foam maker inlet.
b) The test shall demonstrate that the installed system is capable of covering the area to be protected,
as specified below:
i) Fixed roof tanks: Complete coverage of the bottom of the tank shall be achieved in not
more than 15 minutes of foam application.
ii) Open-top floating roof tanks with single foam outlet system: Coverage shall extend over
approximately 40 linear ft (12 m) of seal area on both sides of the foam station within 10
minutes of application time.
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 12 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
iii) Open-top floating roof tanks with multiple foam outlet system: Coverage of the complete
seal area shall be achieved within 10 minutes of application time.
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 13 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
Record of Change
Version 1.0.0 Date: 01/02
Location Action Description
Initial Publish.
Version 2.0.0 Date: 08/03
General General technical and editorial revisions.
Section 3 Addition Rationale for fire hose couplings to reflect plant consistency.
Section 3 Addition Rationale to reflect that terminals for laterals do not have to be exactly
upwind.
Section 4, Item Modification Clarified that this applies to all internal floating roof tanks except those
1 provided with a double or pontoon roof and the roof is a geodesic dome.
Sections 4 and Modification Rationale for firefighting practice for internal floating roof tanks.
5
Version 2.0.0 Date: 11/03
Global Practice version number and format updated to comply with new
process; however, original publish date remains, and no content was
modified.
Version 3.0.0 Date: 12/04
Section 1.1 Addition Added reference to GP 09-07-01.
Section 1.2 Modification Changed National Fire Prevention Association to National Fire
Protection Association. Added NFPA 30.
Section 2, Item Modification Added "Pipe carrying foam concentrate shall not be galvanized."
(2)
Section 2, Item Modification Modified Rationale to include debris accumulation as a reason for
(5) installing screening.
Section 3, Item Modification Added "Connections should be located at least a distance of one tank
(1b) diameter from the tank but in no case less than 50 ft (15 m)
Section 3, Item Modification Modified Rationale to state "The maximum distance for hose connections
(1b) from the hydrants and foam system to the fire trucks are established to"
be consistent with fire truck hoses.
Section 3, Item Modification Modified Rationale to add "Collision protection may be provided by
(1c) installing guards where systems are located within 3 ft (1 m) of roadways
or accessways in areas of high vehicular traffic. Guards shall be NPS 4
(100 mm) Sch. 40 pipe, filled with concrete and set in a concrete
foundation"
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 14 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
Section 3, Item Modification Modified Rationale to include preventing a spill fire "at one tank" from
(8b) damaging the foam laterals of other tanks.
Section 3, Item Modification Modified Rationale to specify "safely" hooking up hoses to laterals.
(8c)
Section 3, Item Addition Added requirement that "The ratio of the strainer's open basket area to its
9 pipe area shall be at least 10:1. The net open area of the strainer shall be
at least four times the area of the suction piping."
Section 3, Item Modification Changed from 3.9. Modified to read "Underground carbon steel piping
(10) and portions of above ground carbon steel piping that pass through a dike
or pipe sleeve shall be protected against external corrosion using a Single
Coat Single Wrap or Double Coat Double Wrap protective coating
system."
Section 3, Item Modification Changed from 3.9. Modified Rationale to include "These portions can
(10) experience severe corrosion if not protected as described."
Section 3, Item Addition Added, "Permanent connections between the fire water system and any
(11) process system shall be prohibited" to prevent contamination of fire
water with process fluids.
Section 4, Item Modification Consolidated criteria for specifying fixed fire protection by incorporating
(1) information from former 5.10 and added provision to exclude internal
floating roof tanks with nitrogen blanketing from requiring foam systems
unless required by local codes. The nitrogen system should be "safety
critical."
Section 4, Item Modification Modified Rationale to note that foam concentrates for alcohol type fires
(2) "are often alcohol type specific."
Section 4, Item Modification Modified Rationale to include use of screens to prevent debris from
(4c) plugging the system.
Section 5, Item Modification Relocated the Note in Section 5, Item (2) to the Section 5, Item (2)
(2) Rationale.
Section 5, Item Modification Added a reference to GP 09-07-01 for guard railings.
(9)
Section 5, Item Deleted Deleted Section 5, Item (10). See Section 4, Item (1).
(10)
Section 6, Item Modification Added the plant Fire Chief's approval to acceptance testing.
(1)1
Section 6, Item Modification Clarified the test requirements for foam systems.
(1a)
Section 6, Item Modification Modified Rationale to specify that these are the minimum requirements.
(1b)
General Modification Added references to NFPA 11 and NFPA 30 in Rationale. Removed
Pipelines from GP.
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 15 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
GP 03-02-02 Foam Systems for Storage Tanks December 2004
Attachment: Purpose Codes Definitions
Code Description
C Assigned to paragraphs containing specifications whose primary purpose is reduced costs.
Reduced cost in this context refers to initial investment cost and does not include Life-Cycle
cost considerations. Life-Cycle cost considerations are captured under reliability,
maintainability, or operability purpose codes.
E Assigned to paragraphs containing specifications whose primary purpose is driven by
environmental considerations. Environmental considerations typically include specifications
intended to protect against emissions/leakage to the air, water, and/or soil. Deviations from the
specifications contained in such paragraphs require formal review and approval according to
local environmental policy.
I Assigned to paragraphs that provide only clarifying information such as Scope statements,
definitions of terms, etc.
M Assigned to paragraphs containing specifications whose primary purpose is to provide for
maintainability of equipment or systems. Maintainability provisions are those that facilitate the
performance of maintenance on equipment/systems either during downtimes or during on-
stream operations.
O Assigned to paragraphs containing specifications whose primary purpose is to assure
operability of equipment or systems. Operability is the ability of the equipment/system to
perform satisfactorily even though conditions are off-design, such as during startups, process
swings, subcomponent malfunction, etc.
R Assigned to paragraphs containing specifications whose primary purpose is to improve or
assure the reliability of equipment or systems. Reliability is a measure of the ability of
equipment/systems to operate without malfunction or failure between planned maintenance
interventions.
S Assigned to paragraphs containing specifications whose primary purpose is avoidance of
personnel or operational safety incidents. Any deviation from the specifications contained in
such designated paragraphs requires formal review and approval according to local safety
policy.
Personnel Safety: Refers to the avoidance of recordable personnel injuries; i.e., burns, cuts,
abrasions, inhalation, or exposure to dangerous substances, etc., that
could result in medical treatment, restricted work, lost-time incidents, or
fatalities.
Operational Refers to the prevention and control of process releases, fires, explosions,
Safety: etc.
RFCH For ExxonMobil Use Only Version 3.0.0
Page 16 of 16 ExxonMobil Development Company
You might also like
- Control System Engineering Reference ManualDocument144 pagesControl System Engineering Reference ManualKaleem Ullah96% (26)
- Dry Gas Seal and Wet Oil SealDocument13 pagesDry Gas Seal and Wet Oil SealAhmad Riaz Khan100% (1)
- GP 03 19 01Document12 pagesGP 03 19 01Anonymous fvO1W3100% (2)
- Philippine HR Policy Manual Sept 8 2004Document43 pagesPhilippine HR Policy Manual Sept 8 2004Jm Noval75% (12)
- Pressure Testing of Unfired Pressure Vessels: ScopeDocument9 pagesPressure Testing of Unfired Pressure Vessels: Scopebenedicto soto mestanzaNo ratings yet
- Positive Material Identification: ScopeDocument15 pagesPositive Material Identification: Scopebenedicto soto mestanzaNo ratings yet
- Separation Design and Operation Tools For Transfering Best PracticesDocument7 pagesSeparation Design and Operation Tools For Transfering Best PracticesGabriela UrdanetaNo ratings yet
- GP-03!12!01 Valve SelectionDocument11 pagesGP-03!12!01 Valve Selectionabenitech100% (1)
- IPS Standards ListDocument77 pagesIPS Standards ListMudassir Khalil100% (1)
- Propane Storage TankDocument1 pagePropane Storage TankMarakanaMahesh100% (1)
- Pressure Relieving Systems: ScopeDocument54 pagesPressure Relieving Systems: Scopefrgonzalezc100% (1)
- UL 1709 Ed 2017Document43 pagesUL 1709 Ed 2017frgonzalezc100% (2)
- IEEE Guide For The Protection of Communication Installations From Lightning EffectsDocument39 pagesIEEE Guide For The Protection of Communication Installations From Lightning EffectsfrgonzalezcNo ratings yet
- Naval Architecture II Theory Detailed NotesDocument96 pagesNaval Architecture II Theory Detailed NotesAnkit Maurya100% (1)
- Link Configuration Guide For XMC-5DDocument7 pagesLink Configuration Guide For XMC-5DHamid Raza100% (3)
- Flushing and Drain Piping For Centrifugal and Rotary Gas CompressorsDocument11 pagesFlushing and Drain Piping For Centrifugal and Rotary Gas CompressorsfrgonzalezcNo ratings yet
- Control Narrative TAR 13 09 Rev2Document17 pagesControl Narrative TAR 13 09 Rev2Anonymous t12LV5No ratings yet
- GP-03!06!01 Piping For InstrumentsDocument18 pagesGP-03!06!01 Piping For Instrumentsabenitech100% (1)
- Flare Radiation 1.3: User ManualDocument10 pagesFlare Radiation 1.3: User ManualLazaro Hernandez GallegosNo ratings yet
- Fail Safe PhilosophyDocument3 pagesFail Safe PhilosophyjojonNo ratings yet
- Datasheet For ESD Push ButtonsDocument5 pagesDatasheet For ESD Push ButtonsEvren GürbüzNo ratings yet
- GP161901 ComDocument29 pagesGP161901 Comsalic2013100% (1)
- Process Design Basis Unit 107: NGL FractionationDocument17 pagesProcess Design Basis Unit 107: NGL Fractionationmohsen ranjbarNo ratings yet
- GP 02 01 01Document23 pagesGP 02 01 01Anonymous fvO1W3No ratings yet
- GP170501 Human Factors in Plant Design PDFDocument27 pagesGP170501 Human Factors in Plant Design PDFegfernandez21100% (1)
- Conventional Type Pressure Relief Valve NumbersDocument18 pagesConventional Type Pressure Relief Valve NumbersswatkoolNo ratings yet
- Pub021 001 00 - 0116Document20 pagesPub021 001 00 - 0116arefNo ratings yet
- PP Aaa PP1 148Document14 pagesPP Aaa PP1 148Rabah Amidi100% (1)
- Liquid Monopropellant CombustionDocument4 pagesLiquid Monopropellant Combustionherdi sutanto adigunaNo ratings yet
- Control Valve MR Tender Specifications 79649aDocument20 pagesControl Valve MR Tender Specifications 79649asyamsulNo ratings yet
- Webinar FAQ - Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersDocument8 pagesWebinar FAQ - Shell and Tube Heat Exchangersrameshkarthik810No ratings yet
- Additional Requirements For Special Criteria Pressure VesselsDocument15 pagesAdditional Requirements For Special Criteria Pressure Vesselsbenedicto soto mestanza100% (1)
- Process Isolation Guidelines - Refining, Hydrocarbons, Oil, and Gas - CheresourcesDocument5 pagesProcess Isolation Guidelines - Refining, Hydrocarbons, Oil, and Gas - Cheresourcesjayrolling dollaz100% (1)
- Kolmetz Handbook of Process Equipment Design Flare Systems Safety, Selection, Sizing and Troubleshooting (Engineering Design Guidelines)Document24 pagesKolmetz Handbook of Process Equipment Design Flare Systems Safety, Selection, Sizing and Troubleshooting (Engineering Design Guidelines)ramadan rashadNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers: The Effectiveness - NTU Method: Sections 11.4 Through 11.7Document15 pagesHeat Exchangers: The Effectiveness - NTU Method: Sections 11.4 Through 11.7Joli SmithNo ratings yet
- Temperature Cross in Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger - How and WhyDocument8 pagesTemperature Cross in Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger - How and Whyjesus_manrique2753No ratings yet
- High Fidelity Dynamic Simulation of Compressor SystemsDocument9 pagesHigh Fidelity Dynamic Simulation of Compressor SystemsTrần Quang ThắngNo ratings yet
- Datasheet For Pressure Safety Valve - IfbDocument66 pagesDatasheet For Pressure Safety Valve - Ifbfathan fathullahNo ratings yet
- Edr-Hysys Oh Cond Sim Rev1Document6 pagesEdr-Hysys Oh Cond Sim Rev1Wali AhsanNo ratings yet
- EGE15B5Document56 pagesEGE15B5Jhonny Rafael Blanco CauraNo ratings yet
- Symmetry 2023 Installation GuideDocument14 pagesSymmetry 2023 Installation GuideIan MannNo ratings yet
- Iranian Petroleum Standards: Typical Unit Arrangement & Piperack Layout IPS-D-PI-102Document1 pageIranian Petroleum Standards: Typical Unit Arrangement & Piperack Layout IPS-D-PI-102reza329329No ratings yet
- TASC Evaluation of A Heat ExchangerDocument6 pagesTASC Evaluation of A Heat ExchangerJesus Andres SuarezNo ratings yet
- Overpressure StudyDocument25 pagesOverpressure StudyBudiman -No ratings yet
- Aspen Flare System Analyzer: Getting Started GuideDocument57 pagesAspen Flare System Analyzer: Getting Started GuideHaris ShahidNo ratings yet
- Design BasisDocument11 pagesDesign BasisvasudhaNo ratings yet
- PP Aaa PP1 145Document13 pagesPP Aaa PP1 145Rabah AmidiNo ratings yet
- 2) Selection of Lift ModeDocument21 pages2) Selection of Lift ModeHet PatelNo ratings yet
- FlareDocument39 pagesFlareMuhammad Tahir RazaNo ratings yet
- Oil Spill From Floating Roof TankDocument2 pagesOil Spill From Floating Roof TankShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Flare Calc Sheet API RP 521Document9 pagesFlare Calc Sheet API RP 521Miftahul HudaNo ratings yet
- Anyone Can Suggest The Criteria of Velocity in Downcomer For Valve TrayDocument4 pagesAnyone Can Suggest The Criteria of Velocity in Downcomer For Valve Trayonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Saes L 140 PDFDocument13 pagesSaes L 140 PDFsamsurendran_mech4020No ratings yet
- Minimum DistanceDocument2 pagesMinimum DistancehmdhojjatNo ratings yet
- Coral FLNG SA Is The Special Purpose Entity Responsible To Develop and Operate Coral South Floating Platform (FLNG)Document4 pagesCoral FLNG SA Is The Special Purpose Entity Responsible To Develop and Operate Coral South Floating Platform (FLNG)MateusPauloNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Checklist As Per TEMADocument6 pagesHeat Exchanger Checklist As Per TEMAMONANo ratings yet
- Aspen Plus Tutorial SeparationsDocument15 pagesAspen Plus Tutorial SeparationsLi ChNo ratings yet
- Gas Sweetening Systems-Engineering-Design-Guide PDFDocument24 pagesGas Sweetening Systems-Engineering-Design-Guide PDFJerry GumpNo ratings yet
- Flaresim Getting StartedDocument116 pagesFlaresim Getting Startedfiqry DarwansyahNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Control of Heat ExchangerDocument29 pagesInstrumentation and Control of Heat Exchangerpra578No ratings yet
- Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger DesignDocument87 pagesShell & Tube Heat Exchanger DesignankitmundharaNo ratings yet
- Depressuring Systems PDFDocument32 pagesDepressuring Systems PDFkumar_chemicalNo ratings yet
- USe of Higher PSV Set PressureDocument12 pagesUSe of Higher PSV Set Pressurezubair195No ratings yet
- 015-FH-1002 (Rev.1) PDFDocument8 pages015-FH-1002 (Rev.1) PDFarjun PV RaoNo ratings yet
- PRG.E1-27.2020.07.10.Automatic Sprinkler SystemsDocument10 pagesPRG.E1-27.2020.07.10.Automatic Sprinkler Systemshassanqr89No ratings yet
- Chevron Specification TAM-MU-6: Cone Roof ReplacementDocument8 pagesChevron Specification TAM-MU-6: Cone Roof ReplacementBurak GülenNo ratings yet
- Underground Fuel TanksDocument24 pagesUnderground Fuel TanksAlupole_AlbertLim100% (2)
- Industrial Flow MeasurementDocument464 pagesIndustrial Flow Measurementfrgonzalezc100% (1)
- Gan Dissection Visualizing and Understanding Generative Adversarial NetworksDocument19 pagesGan Dissection Visualizing and Understanding Generative Adversarial NetworksfrgonzalezcNo ratings yet
- Absorptive Silencer Design Criteria: ScopeDocument16 pagesAbsorptive Silencer Design Criteria: ScopefrgonzalezcNo ratings yet
- Hcdslk1i DVD Receiver PDFDocument88 pagesHcdslk1i DVD Receiver PDFfrgonzalezcNo ratings yet
- Effect of Using Texting On Vocabulary Instruction For English LearnersDocument22 pagesEffect of Using Texting On Vocabulary Instruction For English LearnersfrgonzalezcNo ratings yet
- Book Series Hydropowerdevelopment WebDocument28 pagesBook Series Hydropowerdevelopment WebfrgonzalezcNo ratings yet
- Get 8034Document456 pagesGet 8034frgonzalezcNo ratings yet
- Using NSD - A Practical Guide Hands On Track Session HND107 Lotusphere 2008 Presented By: Elliott Harden and Joe WallaceDocument48 pagesUsing NSD - A Practical Guide Hands On Track Session HND107 Lotusphere 2008 Presented By: Elliott Harden and Joe Wallaceporpatham0% (1)
- Appendix E Checklist - Review Performance Audits Performed by OIG September 2014Document16 pagesAppendix E Checklist - Review Performance Audits Performed by OIG September 2014hotwarezNo ratings yet
- Science 10 2nd Quarter ExamDocument2 pagesScience 10 2nd Quarter ExamKenneth Rose BajeNo ratings yet
- Serial Number Range: From SN 3084-101 To 3090-2213Document118 pagesSerial Number Range: From SN 3084-101 To 3090-2213Святослав ВороновNo ratings yet
- 5SL Miniature Circuit Breakers: BETA Low-Voltage Circuit ProtectionDocument8 pages5SL Miniature Circuit Breakers: BETA Low-Voltage Circuit Protectionashish sahaNo ratings yet
- Free - Multiple - Intelligences - Test (Indo) SipDocument3 pagesFree - Multiple - Intelligences - Test (Indo) SiprendraNo ratings yet
- Taxonomic Study and Identification Key To The Species of The Shrimps, Particularly The Family Penaeidae in Kakkaithivu Coastal Waters, Jaffna, Sri LankaDocument9 pagesTaxonomic Study and Identification Key To The Species of The Shrimps, Particularly The Family Penaeidae in Kakkaithivu Coastal Waters, Jaffna, Sri LankaJASH MATHEWNo ratings yet
- Topic 14.0: Haloalkanes (Alkyl Halides)Document12 pagesTopic 14.0: Haloalkanes (Alkyl Halides)Supia NazmaNo ratings yet
- Moha Soft DrinkDocument11 pagesMoha Soft DrinkBizuayehu GeroNo ratings yet
- A Review of General Introduction To Political Communication (Brian McNair)Document12 pagesA Review of General Introduction To Political Communication (Brian McNair)Tenz BhutiNo ratings yet
- William 0061076156 MKT1002 Assignment1Document16 pagesWilliam 0061076156 MKT1002 Assignment1anita5695No ratings yet
- Useful Links & Resources - Radical RedDocument9 pagesUseful Links & Resources - Radical Redjay cdjNo ratings yet
- Watu Waingapu D Umbu Mehang Kunda 3Document7 pagesWatu Waingapu D Umbu Mehang Kunda 3agusNo ratings yet
- CET ECE 412 Lec Robin EditedDocument17 pagesCET ECE 412 Lec Robin EditedlornfateNo ratings yet
- Ovm PrestressingDocument68 pagesOvm Prestressingnadeesha100% (1)
- Jagadeesh Kumar FresherDocument2 pagesJagadeesh Kumar FresherJ SR Raghavendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document48 pagesSession 1Gilbert AggreyNo ratings yet
- QITP 002 Part 1Document12 pagesQITP 002 Part 1ivanbfNo ratings yet
- C5 ProbDocument4 pagesC5 ProbMihir Kumar MechNo ratings yet
- 23 - Braga Filofteia, Diaconescu FlorinDocument6 pages23 - Braga Filofteia, Diaconescu FlorinAda KuprowskaNo ratings yet
- AMA Multimedia v. Spankbang - Com - Complaint PDFDocument29 pagesAMA Multimedia v. Spankbang - Com - Complaint PDFMark JaffeNo ratings yet
- 12f508 PDFDocument100 pages12f508 PDFZdravko RusevNo ratings yet
- Written Report ForDocument3 pagesWritten Report ForMark Angelo Manuel ElduayanNo ratings yet
- Cruz, Mico Adam D. - Bsentrep 1-1 - Midterm PortfolioDocument5 pagesCruz, Mico Adam D. - Bsentrep 1-1 - Midterm PortfolioPete CruzNo ratings yet
- 03.E. Airworthiness RequirementsDocument6 pages03.E. Airworthiness RequirementsUDAYAPRAKASH RANGASAMYNo ratings yet
- Determination of CaCO3 in The EggshellDocument33 pagesDetermination of CaCO3 in The EggshellbushlalaNo ratings yet
- CS401 - Short Notes Chapter 17Document4 pagesCS401 - Short Notes Chapter 17malikNo ratings yet