100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
182 viewsAnatomy of Skin
Anatomy of Skin
Uploaded by
aimi BatrisyiaThe skin is the largest organ of the body, weighing approximately 5 kg in adults. It has three layers - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous keratinized epithelium made of keratinocytes. The dermis is made of connective tissue and contains structures like hair follicles and sweat glands. The hypodermis contains adipose tissue. Skin has important protective, sensory and regulatory functions. Thick skin on palms and soles differs from thin skin covering most of the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Anatomy of Skin
Anatomy of Skin
Uploaded by
aimi Batrisyia100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
182 views25 pagesThe skin is the largest organ of the body, weighing approximately 5 kg in adults. It has three layers - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous keratinized epithelium made of keratinocytes. The dermis is made of connective tissue and contains structures like hair follicles and sweat glands. The hypodermis contains adipose tissue. Skin has important protective, sensory and regulatory functions. Thick skin on palms and soles differs from thin skin covering most of the body.
Original Title
7. Anatomy of Skin
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The skin is the largest organ of the body, weighing approximately 5 kg in adults. It has three layers - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous keratinized epithelium made of keratinocytes. The dermis is made of connective tissue and contains structures like hair follicles and sweat glands. The hypodermis contains adipose tissue. Skin has important protective, sensory and regulatory functions. Thick skin on palms and soles differs from thin skin covering most of the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
182 views25 pagesAnatomy of Skin
Anatomy of Skin
Uploaded by
aimi BatrisyiaThe skin is the largest organ of the body, weighing approximately 5 kg in adults. It has three layers - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is stratified squamous keratinized epithelium made of keratinocytes. The dermis is made of connective tissue and contains structures like hair follicles and sweat glands. The hypodermis contains adipose tissue. Skin has important protective, sensory and regulatory functions. Thick skin on palms and soles differs from thin skin covering most of the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 25
At a glance
Powered by AI
The key takeaways are that skin is the largest organ of the body, it has multiple layers and functions such as protection, temperature regulation and sensation.
The main layers of the skin are the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis.
The main functions of the skin are protection, vitamin D synthesis, temperature regulation, sensation and psychosexual communication.
Prepared by
Dr. Belqees A. Allaw
2021
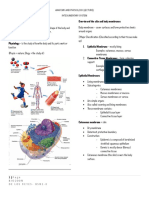
Introduction
• Skin covers the outer surface of the body
and is the largest organ in the human body,
and comprises approximately 8% of total
body mass.
• Skin and it's accessory structures (hair, sweat
glands, sebaceous glands, and nails) make up
the integumentary system.
• in adults weighs about 5 kilograms.
• The thickness of skin varies from 0.5mm
thick on the eyelids to 4.0mm thick on the
heels of feet.
Function of the skin
• It provides protection from mechanical
impacts and pressure, variations in
temperature, micro-organisms, radiation and
chemicals.
• A role in the synthesis of vitamin D.
• Regulation of body temperature.
• Psychosexual communication.
• A major sensory organ for touch,
temperature, pain, and other stimuli.
Gross structure
Skin is classified into two types:
1. Thick skin (glabrous) - covers the palms of the
hands and the soles of the feet
2. Thin skin - covers the rest of the body
vSkin consists of 3 layers:
• Epidermis - outer layer of stratified squamous
keratinized epithelium
• Dermis - dense, irregular connective tissue that
contains other structures (such as hair follicles
and sweat glands)
• hypodermis is deep to the dermis a layer of
varying thickness of loose connective tissue and
adipose tissue.
Epidermis
• the most superficial layer of the
skin.
• It is stratified squamous
keratinized epithelium.
• It is largely formed by layers
of keratinocytes that responsible
for increasing keratin production
and migration toward the external
surface, a process
termed cornification.
Layers of epidermis
From deepest to most superficial, these
layers are:
• Stratum basale – mitosis of keratinocytes
occurs in this layer.
• Stratum spinosum – keratinocytes are
joined by tight intercellular junctions
called desmosomes.
• Stratum granulosum – cells secrete lipids
and other waterproofing molecules in this
layer.
Layers of epidermis
• Stratum lucidum – cells lose nuclei and
drastically increase keratin production.
• Stratum corneum – cells lose all
organelles, continue to produce keratin.
A keratinocyte typically takes between 30
– 40 days to travel from the stratum
basale to the stratum corneum.
Keratin
• Keratin is one of a family of fibrous
structural proteins known as
scleroproteins.
• α-Keratin is a type of keratin found in
vertebrates.
It is the key structural material making up
scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws,
hooves, calluses, and the outer layer of
skin among vertebrates.
Types of skin
Thin skin Thick skin
4 layers 5 layers
Stratum corneum less prominent Stratum corneum prominent
Less developed stratum granulosum Well developed stratum granulosum
Lines most of the body surface Palms of the hands & soles of the feet
Thicker dermis Thinner dermis
Contain hair & sebaceous glands No hair and sebaceous glands
Epidermis
Other cells that houses the epidermis:
1- Langerhans cells
dendritic cells (antigen-presenting
immune cells) of the skin.
They are present in all layers of the
epidermis and are most prominent in
the stratum spinosum.
• Have branched shape & central
nuclei.
• Represent 3-8% of epidermal cells.
Epidermis
2- Melanocytes – branched cells with
central nuclei; contains organelles for
protein synthesizes. responsible for melanin
production and pigment formation.
3- Merkel cells – modified epidermal cells;
sensory mechanoreceptors (touch receptor)
found in basal cell layer.
Dermis
It is dense irregular connective tissue that
supports the epidermis.
The dermis has only two layers, which are less
clearly defined than the layers of the
epidermis.
1- superficial papillary layer:
Contains vascular networks that play role in:
• Supply the avascular epidermis with messiners corpuscles
nutrients.
• thermoregulation.
• light touch via meissners corpuscles which
are free sensory nerve endings.
Dermis
2- deeper reticular layer (features thicker
bundles of collagen fibres that provide more
durability).
Important of this layer:
• Giving the skin it overall strength and
elasticity.
• Housed other epithelial derived structures
such as glands and hair follicles.
Dermis
This layer contain the following cells:
• Fibroblasts –synthesise the extracellular
matrix
• Mast cells –histamine granule-containing
cells (response to allergy).
• Skin appendages :
hair follicles, nails, sebaceous and sweat
glands.
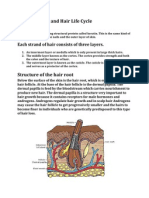
Hair follicles
A hair follicle is dermal & epidermal sheath
surrounds hair root which grows a hair by
packing old cells together.
• Attached inside the top of the follicle are
sebaceous glands, which are tiny sebum
(lubrication & bactericidal) -producing
glands in almost all skin EXCEPT on the
palms, lips and soles of the feet.
• The hair follicle itself is associated with
an arrector pili muscle (smooth muscle)
which contracts to cause the follicle to
stand upright.
Root of the hair
• Root Sheaths -comprised of two parts:
• Internal root sheath - extends from the
hair bulb to the level of sebaceous
glands. It is divided into Huxley's layer
(inner layer of flattened cells) and Henle's
layer (outer single layer of cuboidal cells).
• External root sheath- layers of cells
continuous with the epidermis
• Glassy membrane - thick basement
membrane that separates the hair follicle
from the dermis
Hair
Hair is made of hard keratinized epithelial
cells.
• Melanocytes provide pigment for hair color.
• Hair- shafts (which are absent in most
follicles) are found at the center of hair
follicles.
• Hair shaft contain:
1- central medulla
2- cortex surrounds medulla
3- thin cuticle outer layer of cortex (keratin).
Sweat glands
There are two main types of sweat glands:
• Eccrine glands
• the major sweat glands of the human body.
• coiled tubular glands (lightly stained) and
ducts (dark stained) with simple or stratified
cuboidal epithelium.
• They release a clear, odourless substance,
comprised mostly of sodium chloride and
water (involved in thermoregulation).
Sweat glands
• Apocrine glands
• simple cuboidal epithelium and
widely dilated lumen that stores the
secretory product.
• larger sweat glands located in the
axillary and genital regions.
• These apocrine glandular products
can be broken down by cutaneous
microbes, producing body odour.
Eccrine glands Apocrine glands
cells excrete their substances by a portion of the cell membrane that
exocytosis. contains the excretion buds off.
Location: most all over body Armpites, groin, nipples.
especially on palms & soles
Clear, watery secretion (99%H2O; Viscous cloudy secretions which is
rest NaCl+ some waste products) good nutrient source for bacteria
(odor)
Involved in thermoregulation involved in emotional sweating in
humans (induced by anxiety, stress,
fear, sexual stimulation, and pain)
Nail
• General features of nail:
1- Nail : scale- like modifications of the
epidermis, heavily keratinized.
2- Stratum basale extends beneath the
nail bed responsible for growth.
3- Lack of pigment make them
colorless.
Nail
vNail anatomy:
• Free edge
• Body is visible attached portion.
• The lunula is the visible part of the
root of the nail. Rest root of nail
embedded in skin.
• the eponychium (cuticle) is the
thickened layer of skin surrounding
fingernails and toenails. It can also
be called the medial or proximal nail
fold. Its function is to protect the
area between the nail and epidermis
from exposure to bacteria.
hypodermis
• It is loose connective tissue with
adipose tissue. located immediately
deep to the dermis.
• It is a major body store of adipose
tissue, and as such can vary in size
between individuals depending on the
amount of fatty tissue present.
YO U
ANK
T H
Anatomy- Dr. Belqees A. Allaw
You might also like
- Grim Hollow Valikan Clans Path of The Carrion RavenDocument4 pagesGrim Hollow Valikan Clans Path of The Carrion Ravendanieldots100% (1)
- The Skin NotesDocument7 pagesThe Skin NotesSafeer SefiNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells in The EpidermisDocument13 pagesTypes of Cells in The EpidermisSairelle Sordilla Obang88% (8)
- Hematology FormulasDocument2 pagesHematology FormulasJoan ClaveNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesLymphatic Systempriya garciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Skinay254No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - The VitaminsDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - The VitaminsYcell Latido100% (2)
- Body CavitiesDocument10 pagesBody CavitiesGoutam ChandraNo ratings yet
- Culture MethodsDocument26 pagesCulture Methodsdrunken monkey100% (1)
- Homonymous Visual Field Defects PDFDocument186 pagesHomonymous Visual Field Defects PDFNooramad Abbas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument25 pagesAnatomy of The SkinJanak KcNo ratings yet
- LG2 Histology of The SkinDocument26 pagesLG2 Histology of The SkinRawa AyubNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesIntegumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD0% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument52 pagesIntegumentary Systemyasin oumer0% (1)
- 7 Integumentary SystemDocument38 pages7 Integumentary Systemvanderphys100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Integumentary SystemSmol PadernalNo ratings yet
- Physiology of SkinDocument29 pagesPhysiology of SkinIlham KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of SkinDocument26 pagesAnatomy of SkinArvinth Guna SegaranNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of SkinDocument60 pagesAnatomy of SkinYashdeepMalik75% (4)
- The Skin: - Structure and ClassificationDocument25 pagesThe Skin: - Structure and Classificationmzbaig04No ratings yet
- SKINDocument52 pagesSKINFrances Rose Luna-Alcaraz100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of SkinDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Skinjose abadNo ratings yet
- Tissues Glands and Membranes PDFDocument59 pagesTissues Glands and Membranes PDFJE ED100% (1)
- Histology of SkinDocument33 pagesHistology of SkinH R A K Kulathilaka75% (4)
- Ch04 Anatomy SkinDocument50 pagesCh04 Anatomy Skinاحمد مازن العدم100% (1)
- Human Skin 1Document9 pagesHuman Skin 1Baciu DianaNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument38 pagesSkinrodelagapito100% (1)
- Integumentary System (Skin & It'S Appendages)Document29 pagesIntegumentary System (Skin & It'S Appendages)explorerNo ratings yet
- The Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDocument72 pagesThe Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDeborahMcCloudNo ratings yet
- Skin - HistologyDocument30 pagesSkin - Histologydaw022100% (11)
- Skin AssessmentDocument39 pagesSkin Assessmentjhommmmm100% (2)
- Skin Functions and LayersDocument23 pagesSkin Functions and LayersAnis Samrotul Lathifah100% (2)
- The Skin Structure: Presentation ofDocument35 pagesThe Skin Structure: Presentation ofdimple bachkaniwalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SkinDocument30 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SkinNancy VargasNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument39 pagesIntegumentary SystemJam Knows Right100% (5)
- Integumentary SystemDocument28 pagesIntegumentary SystemChoukung Fuboi2No ratings yet
- Hair Growth CycleDocument3 pagesHair Growth CycleReynan Cabatbat100% (1)
- Skin DisordersDocument11 pagesSkin DisordersCheyenne LayNo ratings yet
- Smooth and Cardiac MusclesDocument55 pagesSmooth and Cardiac MusclesIni UsenNo ratings yet
- Skin Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesSkin Anatomy and PhysiologyKhan KamaalNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument22 pagesIntegumentary Systemnimfa t. plazaNo ratings yet
- Skin AnatomyDocument17 pagesSkin AnatomyAnonymous 1gH7ra9ANo ratings yet
- ANP 1105 The Lymphatic SystemDocument23 pagesANP 1105 The Lymphatic SystemMathios Tigeros100% (1)
- Skin and Its AppendagesDocument7 pagesSkin and Its AppendagesSheena PasionNo ratings yet
- Skin, Hair, and Nails AssessmentDocument44 pagesSkin, Hair, and Nails Assessmentعمر حليم omar haleem100% (1)
- HairDocument4 pagesHairRena Carissa100% (2)
- Skin Structure and DevelopmentDocument45 pagesSkin Structure and DevelopmentNikhileshReddyNo ratings yet
- Nails and HairDocument3 pagesNails and HairJhon de ToledoNo ratings yet
- Pragyan College of Nusing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Integumentary System/The SkinDocument4 pagesPragyan College of Nusing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Integumentary System/The SkinNeelofur Ibran AliNo ratings yet
- Histology Skin & AppendagesDocument44 pagesHistology Skin & AppendagesMathew JosephNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument26 pagesSkinMario Baemamenteng100% (1)
- The SkinDocument10 pagesThe SkinThamaraiNo ratings yet
- SDL IntegumentaryDocument4 pagesSDL IntegumentaryMonique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lymphatic SystemDocument46 pagesAnatomy Lymphatic SystemJenise MuLatto Franklin100% (2)
- Structure of SkinDocument19 pagesStructure of SkinFiqi Lampard100% (1)
- Telogen Effluvium PDFDocument18 pagesTelogen Effluvium PDFVidinikusuma100% (1)
- Anatomy&Physiology of SkinDocument45 pagesAnatomy&Physiology of Skinpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent - Chemical Skin Peels and Treatments 2016Document10 pagesInformed Consent - Chemical Skin Peels and Treatments 2016Ashraf AboNo ratings yet
- Telogen EffluviumDocument13 pagesTelogen EffluviumYunita Salaka100% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary SystemDelosreyes Joy Ann ANo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesIntegumentary SystemMaddie BulauNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lymphatic SystemDocument27 pagesAnatomy of The Lymphatic SystemAntonio Lima Filho100% (2)
- Lecture 9 Integumentary SystemDocument64 pagesLecture 9 Integumentary Systemhafiz patahNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument22 pagesUntitledclaireNo ratings yet
- Types of Sentences in Writing (AIMI BATRISYIA BT ALI-MBBS0321299)Document2 pagesTypes of Sentences in Writing (AIMI BATRISYIA BT ALI-MBBS0321299)aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Ospe ParasitologyDocument19 pagesOspe Parasitologyaimi Batrisyia100% (2)
- (Challenges of Online Learning) AIMI BATRISYIA BT ALI-MBBS0321299Document2 pages(Challenges of Online Learning) AIMI BATRISYIA BT ALI-MBBS0321299aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Histology Nervous TissueDocument27 pagesHistology Nervous Tissueaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- OSPE AnatomyDocument16 pagesOSPE Anatomyaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Single Verb Agreement Exercise (Aimi Batrisyia Ali - MBBS0321299)Document7 pagesSingle Verb Agreement Exercise (Aimi Batrisyia Ali - MBBS0321299)aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument26 pagesEpithelial Tissueaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument31 pagesMuscle Tissueaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Ospe HistologyDocument17 pagesOspe Histologyaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 4-Bacteria-Nutrition-Growth and CultureDocument40 pages4-Bacteria-Nutrition-Growth and Cultureaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To MicrobologyDocument17 pages1-Introduction To Microbologyaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period 4-8weekDocument25 pagesEmbryonic Period 4-8weekaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 2-Bacterial Classification and Normal FloraDocument26 pages2-Bacterial Classification and Normal Floraaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week DevelopmentDocument26 pages3rd Week Developmentaimi Batrisyia100% (1)
- Exercise (One Sentence Each Rule) Aimi Batrisyia-MBBS0321299Document1 pageExercise (One Sentence Each Rule) Aimi Batrisyia-MBBS0321299aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 4 PharmacodynamicsDocument21 pages4 Pharmacodynamicsaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Routes of Administration of DrugsDocument20 pages3 Routes of Administration of Drugsaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of 2nd WeekDocument25 pagesEmbryology of 2nd Weekaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Pharmacology An OverviewDocument17 pages1 Pharmacology An Overviewaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Healing & Repair2Document36 pages2 - Healing & Repair2aimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Hemodynamic EdemaDocument57 pages3 - Hemodynamic Edemaaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- ME4253 Biomat Eng 0 - Overview-2Document7 pagesME4253 Biomat Eng 0 - Overview-2shellyp4No ratings yet
- UNP-CN Do Not Reproduce: Learning Pocket DescriptionDocument14 pagesUNP-CN Do Not Reproduce: Learning Pocket DescriptionKathleen Joy PingenNo ratings yet
- CS-2000i ASTM - Host - Interface For - SiemensDocument2 pagesCS-2000i ASTM - Host - Interface For - SiemensJavier Andres leon HigueraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1.3Document3 pagesExperiment 1.3izdiyad2501izdyNo ratings yet
- 8th Science Chap 1Document7 pages8th Science Chap 1joelthomas112007No ratings yet
- Disappearing Human MicrobiotaDocument8 pagesDisappearing Human MicrobiotaWilson PalacioNo ratings yet
- Protein MarkersDocument1 pageProtein MarkersMónika Whiltierna SzenykivNo ratings yet
- Whole System ThinkingDocument21 pagesWhole System ThinkingazkkrNo ratings yet
- Designing, Prototyping and Manufacturing Medical Devices: An OverviewDocument20 pagesDesigning, Prototyping and Manufacturing Medical Devices: An OverviewFaisalNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Lab 8: Population Genetics Report ConclusionDocument1 pageAP Biology Lab 8: Population Genetics Report Conclusionjchaps11224432100% (2)
- Oxynex ST LIQUID - Inf TécnicaDocument12 pagesOxynex ST LIQUID - Inf TécnicaAnonymous vqv5q1B100% (1)
- Assay For Uronic Acid Carbazole Reaction PDFDocument3 pagesAssay For Uronic Acid Carbazole Reaction PDFph_swordman0% (1)
- Author Information IndjstDocument3 pagesAuthor Information IndjstFiqa SuccessNo ratings yet
- History of The BiopondDocument5 pagesHistory of The BiopondEric ChenNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Wise NCERT - Exemplar - Bio - Disha ExpertsDocument287 pagesChapter-Wise NCERT - Exemplar - Bio - Disha ExpertsDEBJITA MAITY XI CNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument1 pageMuscle TissueJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- New Orbital Single Use BioreactorDocument1 pageNew Orbital Single Use BioreactorCharles LeeNo ratings yet
- TestcaminalculesDocument2 pagesTestcaminalculesdavidbioigeoNo ratings yet
- U World Notes IIDocument54 pagesU World Notes IIFeroz RaZa SoomrOoNo ratings yet
- Science of Bone CementDocument12 pagesScience of Bone CementajinkyaNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing at 40 - Past Present and FutureDocument10 pagesDNA Sequencing at 40 - Past Present and FutureSamuel Morales NavarroNo ratings yet
- TS1068Document2 pagesTS1068fathan jefriansyahNo ratings yet
- BCM 3521 L5Document26 pagesBCM 3521 L5khekhyNo ratings yet
- Sapiens A Brief History of Humankind PDFDocument2 pagesSapiens A Brief History of Humankind PDFSitaram Padhy100% (1)
- Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceDocument20 pagesWater, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balancevarsha CRNo ratings yet
- Lieberman (2012)Document5 pagesLieberman (2012)Renzo LanfrancoNo ratings yet
- Acid Sulphate SoilsDocument79 pagesAcid Sulphate SoilsThisul MethsiluNo ratings yet