0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
307 viewsStatistical Method
Statistical methods involve the mathematical analysis of raw research data to extract useful information. Descriptive statistics describe the basic features of data like averages and distributions. Inferential statistics allow statisticians to draw conclusions about entire populations based on samples, such as estimating consumer demand from a survey sample or predicting future events based on past data. Common inferential methods include regression analysis, which determines the relationship between dependent and independent variables and can assess the statistical significance of results.
Uploaded by
Alia buttCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
307 viewsStatistical Method
Statistical methods involve the mathematical analysis of raw research data to extract useful information. Descriptive statistics describe the basic features of data like averages and distributions. Inferential statistics allow statisticians to draw conclusions about entire populations based on samples, such as estimating consumer demand from a survey sample or predicting future events based on past data. Common inferential methods include regression analysis, which determines the relationship between dependent and independent variables and can assess the statistical significance of results.
Uploaded by
Alia buttCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 3
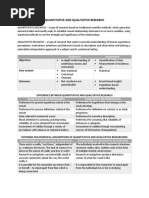
Statistical methods
Statistical methods are mathematical formulas, models,
and techniques that are used in statistical analysis of raw research data.
The application of statistical methods extracts information from research
data and provides different ways to assess the robustness of research
outputs.
Statistics is a branch of applied mathematics that involves the collection,
description, analysis, and inference of conclusions from quantitative data.
The mathematical theories behind statistics rely heavily on differential and
integral calculus, linear algebra, and probability theory. Statisticians, people
who do statistics, are particularly concerned with determining how to draw
reliable conclusions about large groups and general phenomena from the
observable characteristics of small samples that represent only a small
portion of the large group or a limited number of instances of a general
phenomenon.
Two types of statistical methods are used in analyzing data:
descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. Statisticians measure and
gather data about the individuals or elements of a sample, then analyze
this data to generate descriptive statistics.
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics mostly focus on the central tendency, variability, and
distribution of sample data. Central tendency means the estimate of the
characteristics, a typical element of a sample or population, and includes
descriptive statistics such as mean, median, and mode. Variability refers to
a set of statistics that show how much difference there is among the
elements of a sample or population along the characteristics measured,
and includes metrics such as range, variance, and standard deviation.
The distribution refers to the overall "shape" of the data, which can be
depicted on a chart such as a histogram or dot plot, and includes properties
such as the probability distribution function, skewness, and kurtosis.
Descriptive statistics can also describe differences between observed
characteristics of the elements of a data set. Descriptive statistics help us
understand the collective properties of the elements of a data sample and
form the basis for testing hypotheses and making predictions using
inferential statistics.
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics are tools that statisticians use to draw conclusions
about the characteristics of a population from the characteristics of a
sample and to decide how certain they can be of the reliability of those
conclusions. Based on the sample size and distribution of the sample data
statisticians can calculate the probability that statistics, which measure the
central tendency, variability, distribution, and relationships between
characteristics within a data sample, provide an accurate picture of the
corresponding parameters of the whole population from which the sample
is drawn.
Inferential statistics are used to make generalizations about large groups,
such as estimating average demand for a product by surveying a sample of
consumers' buying habits, or to attempt to predict future events, such as
projecting the future return of a security or asset class based on returns in
a sample period.
Regression analysis is a common method of statistical inference that
attempts to determine the strength and character of the relationship
(or correlation) between one dependent variable (usually denoted by Y)
and a series of other variables (known as independent variables). The
output of a regression model can be analyzed for statistical significance,
which refers to the claim that a result from findings generated by testing or
experimentation is not likely to have occurred randomly or by chance but
are instead likely to be attributable to a specific cause elucidated by the
data. Having statistical significance is important for academic disciplines or
practitioners that rely heavily on analyzing data and research.
You might also like
- Comparing and Contrasting Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchNo ratings yetComparing and Contrasting Quantitative and Qualitative Research4 pages
- Selection of A Non-Experimental Research Method For Proposed ResearchNo ratings yetSelection of A Non-Experimental Research Method For Proposed Research5 pages
- Data Collection Is An Important Aspect of Any Type of Research StudyNo ratings yetData Collection Is An Important Aspect of Any Type of Research Study20 pages
- Organizational Research Methods: (Pick The Date)No ratings yetOrganizational Research Methods: (Pick The Date)15 pages
- Chapter One Introduction To Research MethodologyNo ratings yetChapter One Introduction To Research Methodology27 pages
- Association Rule Generation For Student Performance Analysis Using Apriori AlgorithmNo ratings yetAssociation Rule Generation For Student Performance Analysis Using Apriori Algorithm5 pages
- Qualitative and Quantitative Data Analysis ApproachesNo ratings yetQualitative and Quantitative Data Analysis Approaches2 pages
- A Review of Research Methodologies in International Business100% (2)A Review of Research Methodologies in International Business17 pages
- Husmann Et Al-2019-Anatomical Sciences Education100% (1)Husmann Et Al-2019-Anatomical Sciences Education14 pages
- IKM - Sample Size Calculation in Epid Study PDFNo ratings yetIKM - Sample Size Calculation in Epid Study PDF7 pages
- Collecting of Secondary Data: Selection Appropriate Method For Data Collection Case Study MethodNo ratings yetCollecting of Secondary Data: Selection Appropriate Method For Data Collection Case Study Method10 pages
- Difference Between Correlation and Regression in StatisticsNo ratings yetDifference Between Correlation and Regression in Statistics1 page
- Social Research Methods Class IV: Dr. Shubhasree Bhadra University of Calcutta May 6, 2021100% (2)Social Research Methods Class IV: Dr. Shubhasree Bhadra University of Calcutta May 6, 202122 pages
- Chapter 3: Research Methodology: 1.2.1 Type of StudyNo ratings yetChapter 3: Research Methodology: 1.2.1 Type of Study8 pages
- All About Statistical Significance and TestingNo ratings yetAll About Statistical Significance and Testing15 pages
- Prof Identity Formation Stony Brook Med DevelopingAWayOfBeingNo ratings yetProf Identity Formation Stony Brook Med DevelopingAWayOfBeing7 pages
- Prospectus Discussion Notes 33 Ppgs Upload100% (1)Prospectus Discussion Notes 33 Ppgs Upload33 pages
- Theresa Hughes Data Analysis and Surveying 101No ratings yetTheresa Hughes Data Analysis and Surveying 10137 pages
- Sample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignFrom EverandSample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignNo ratings yet
- MAN5004: Statistics For Business Decision: Problem Set 1 Answer KeyNo ratings yetMAN5004: Statistics For Business Decision: Problem Set 1 Answer Key7 pages
- Chapter 5 Testbank Topic Grid: Garrison/Noreen/Brewer, Managerial Accounting, Twelfth Edition 5-1No ratings yetChapter 5 Testbank Topic Grid: Garrison/Noreen/Brewer, Managerial Accounting, Twelfth Edition 5-14 pages
- Daf1212 Business Statistics II Virt MainNo ratings yetDaf1212 Business Statistics II Virt Main3 pages
- Test Bank For Interactive Statistics 3 e 3rd Edition 0131497561No ratings yetTest Bank For Interactive Statistics 3 e 3rd Edition 01314975614 pages
- Statistical Quality Control of EngineereNo ratings yetStatistical Quality Control of Engineere175 pages
- Customer Month Age Region Product Sales RevenueNo ratings yetCustomer Month Age Region Product Sales Revenue11 pages
- Robust Covariance Estimation Campbell1980No ratings yetRobust Covariance Estimation Campbell19808 pages
- Segunda Asignación de Estadística Aplicada A La IngenieríaNo ratings yetSegunda Asignación de Estadística Aplicada A La Ingeniería5 pages
- Expected Values, Covariance, Correlation and Expected ValuesNo ratings yetExpected Values, Covariance, Correlation and Expected Values25 pages