Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 5
Lesson 5
Uploaded by
Angelica May ClaritoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 5
Lesson 5
Uploaded by
Angelica May ClaritoCopyright:
Available Formats
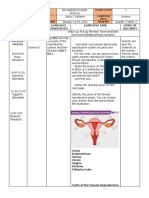
Summary LESSON 5 THE PROCESS OF REPRODUCTION
Humans experience various physical changes from childhood to adulth behavioral traits,
Despite differences in physical appearance, the sexual organs of men and women a rise from Lesson Objectives:
the same structures and fulfill similar functions. Each person has a pair of gonads ; ovaries are When you finish reading this chapter, you should be able to:
female gonads; testes are the male gonads. The gonads produce germ cells and sex
hormones. The female germ cells are ova (egg) and the male germ cells are sperm. Ov a and t. define fertilization, conception and pregnancy;
sperm are the basic units of reproduction; their union can lead to the creation of a new life. 2. explain how pregnancy occurs and its prevention;
and
Assessment 3. identify the complications of early pregnancy in the
I. Compare and contrast the male and the female genitalia
2. Draw a mind map showing the progression oldie male and female from birth, puberty, Definition of Terms:
and adulthood. Ovulation - the process when a mature ovum is released from the
ovary and travels to the fallopian tube for possible fertilization.
References
Fertilization - union of the sperm and the ovum.
Farrell, K. et al. (t995). Life Planning Education: A Youth Development Program. Washington DC: Pregnancy - the process when an offspring develops within the
Advocates for the youth. mother's womb.
German Foundation for World Population DSW (2006). Sexual and Reproductive Health
Training for Manual for Young People. Introduction
Jones, J. (2ott). Human Sexuality.
Although human beings are fully sexually differentiated at birth, the differences
between males and females are accentuated at puberty. This is when the reproductive system
Photo/Image Attributions matures, secondary sexual characteristics develop, and the bodies of males and females
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wild/File:ut6_Muscle_ of the_ Female_ Perineum.png, p22 appear more distinctive.
lut s://en.wiki edia.or /w
p p g ild/Tubal_factor_infertilityx/media/File:Biausen_o732_PID-Sit es. png, p23 Female puberty usually begins at about 8—t3 years of age; the reproduction maturation
of boys lags about two years behind that of girls. The physical changes of female puberty
lsometrik and Kaldari [CC BY 3.o (htt s:
p //creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)J, p25 include breast development, rounding of the hips and buttocks, growth of the hair in the
h
pubic region and the underarm, and the start of menstruation.
ttpsillsc_wilcipedia_org/wikilFile:Uierine_anatomy_jp g, p25
Don Bliss (Illustrator) [P ublt.c domain), p27 How does one ovulate?
Male_anatorny.png: alt. sex FAQderivative work Tsaitgaist (CC BY-SA 3.0 (http:// The major landmark of puberty among females is the onset of the menstrual cycle,
creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0), p28 the monthly ovulation cycle that leads to menstruation (loss of blood and tissues lining the
uterus) in the absence of pregnancy. The menstrual cycle is from the first day of a period
until the day before the next period starts.
Normally, it lasts around 28 days, on the average, but can be as short as 2t or as long as
40. Whatever the length, ovulation will happen about to-t6 days before the start of the next
Ex A Course Module for Gender and Society: A Human Ecological
period.
Unit II: Biomedical Perspective in Gerultriand Sexuality
Approach
You might also like
- Ovarian Cyst - CSDocument42 pagesOvarian Cyst - CSMASII88% (26)
- The First Six Weeks by Midwife Cath (Extract)Document24 pagesThe First Six Weeks by Midwife Cath (Extract)Allen & Unwin14% (7)
- General Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekDocument141 pagesGeneral Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third Weekmutumamiguel15No ratings yet
- (Get Through) Chu, Justin - Clark, T. Justin - Coomarasamy, Arri - Smith, Paul Philip - Get Through MRCOG Part 3 - Clinical Assessment (2019, CRC Press) PDFDocument217 pages(Get Through) Chu, Justin - Clark, T. Justin - Coomarasamy, Arri - Smith, Paul Philip - Get Through MRCOG Part 3 - Clinical Assessment (2019, CRC Press) PDFwai lynn100% (1)
- ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN EMBRYOLOGY by Prof NGASSAPADocument315 pagesESSENTIALS OF HUMAN EMBRYOLOGY by Prof NGASSAPAJumbe Mohamed100% (3)
- Life's Greatest MiracleDocument2 pagesLife's Greatest MiracleJessa Mae Cuenco50% (4)
- Introduction To EmbryologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To EmbryologyDr Md Abedur Rahman100% (3)
- INFERTILITYDocument10 pagesINFERTILITYSakshi SangleNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Sex, Gender, and CultureDocument58 pagesBasic Concepts of Sex, Gender, and CultureKipi Waruku BinisutiNo ratings yet
- Ullang - NCM 107a Module1-2Document16 pagesUllang - NCM 107a Module1-2Rahima UllangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 To 7Document35 pagesLesson 4 To 7Macario estarjerasNo ratings yet
- Prenatalpdf PDFDocument27 pagesPrenatalpdf PDFKeesha YbanezNo ratings yet
- Hce - Module 2 - MidDocument8 pagesHce - Module 2 - MidLorraine CayamandaNo ratings yet
- Gender and Society: Lanie N. E. Avelino, LPT, Ma Eimee D. Potato, EddDocument13 pagesGender and Society: Lanie N. E. Avelino, LPT, Ma Eimee D. Potato, EddFranz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gender Society 1Document32 pagesModule 2 Gender Society 1John Syvel QuintroNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationDocument13 pagesUnit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationAntonio PrietoNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Lesson-1 BSME 1ADocument23 pagesChapter2 Lesson-1 BSME 1AFate GraphiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gas NgaunDocument27 pagesChapter 2 Gas NgaunGary NavarroNo ratings yet
- The Process of ReproductionDocument4 pagesThe Process of ReproductionIvan BixenmanNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1Document18 pagesMidterm 1Jenelyn AbayatoNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIVEDocument12 pagesREPRODUCTIVEBalolot RalphNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gender SocietyDocument28 pagesModule 2 Gender SocietyMariza GiraoNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 (13) Lifespan Psychology ModDocument10 pagesUnit-2 (13) Lifespan Psychology Modashish1981No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans CLASS 10Document5 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans CLASS 10shallowNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument10 pagesUnit 2 PDFRajeshNo ratings yet
- Gender and Society - Modules 2 & 3Document17 pagesGender and Society - Modules 2 & 3Lexter JonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 by SuryaDocument29 pagesUnit 2 by SuryayashiranjNo ratings yet
- NCM107 Prelim Lecture 3Document17 pagesNCM107 Prelim Lecture 3Sachi Reuel BernateNo ratings yet
- BookDocument33 pagesBookObiogwu MichaelNo ratings yet
- R&S Health Presentation1Document24 pagesR&S Health Presentation1Nidhi KaushikNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Module 2 Lesson 1Document18 pagesUnderstanding The Self Module 2 Lesson 1Marites MancerasNo ratings yet
- Sarong, MyrelDocument2 pagesSarong, MyrelMyrel Kay SarongNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Exercises Reproduction SolutionDocument10 pagesUnit 5 Exercises Reproduction SolutionxdryzzyNo ratings yet
- Educ 101 (Sim-Sdl) - 49-77Document29 pagesEduc 101 (Sim-Sdl) - 49-77Joselle VillarbaNo ratings yet
- Lesson+6 +the+Sexual+Self+Part+ADocument37 pagesLesson+6 +the+Sexual+Self+Part+AMA. CARLYN GLAYZEL MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Population Control: Module - 3Document26 pagesReproduction and Population Control: Module - 3Jessa Ariño MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lecture Guide: Introduction To EmbryologyDocument23 pagesLecture Guide: Introduction To EmbryologyAldrin Hardy PabloNo ratings yet
- An Infomation Guide Sheet Sex EducationDocument18 pagesAn Infomation Guide Sheet Sex EducationMahmoud ArtNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesHuman Reproductive System - Britannica Online Encyclopediatie chieng szeNo ratings yet
- Embryology: Department of Anatomy & Histology, Khulna Agricultural UniversityDocument42 pagesEmbryology: Department of Anatomy & Histology, Khulna Agricultural Universityআহানাফ তাহমিদ শব্দNo ratings yet
- MISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Document27 pagesMISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Di VianNo ratings yet
- Educ 101 ReviewerDocument27 pagesEduc 101 ReviewerRolando AmadNo ratings yet
- HiiDocument19 pagesHiiTruptimayiGiriNo ratings yet
- When Does Human Life BeginDocument5 pagesWhen Does Human Life BeginAna Cláudia Rocheto100% (1)
- Human Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFAubrey EuropeNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument42 pagesReproductionValentina Bermudez CadavidNo ratings yet
- 1.1 DefinitonDocument14 pages1.1 DefinitonLayne R.No ratings yet
- Human Physiology-25 (DR Sachin Kapur)Document42 pagesHuman Physiology-25 (DR Sachin Kapur)AmitNo ratings yet
- Q3-DLL Week 4Document4 pagesQ3-DLL Week 4Jun Dadiahon AlindayoNo ratings yet
- Concept of Pregnancy and Childbirth in Yoga and Spiritual LoreDocument21 pagesConcept of Pregnancy and Childbirth in Yoga and Spiritual LoreanuNo ratings yet
- Caadlawon-Prenatal - Dev.and Infancy Nov.7Document36 pagesCaadlawon-Prenatal - Dev.and Infancy Nov.7Joan Rosanne CaadlawonNo ratings yet
- General Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekDocument142 pagesGeneral Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekSalma LyambilaNo ratings yet
- XII-Bio - Last Minute Revision Study MaterialDocument18 pagesXII-Bio - Last Minute Revision Study MaterialghjNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 2Document5 pagesGrade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 2Balram HaroldNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SDocument15 pagesHuman Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SSrajanNo ratings yet
- Developing Through The Life Span: Learning ObjectivesDocument18 pagesDeveloping Through The Life Span: Learning ObjectivesHayaton IRNo ratings yet
- Developing Through The Life SpanDocument11 pagesDeveloping Through The Life SpanMa. Nenita L. MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesReproductive SystemnbcNo ratings yet
- General Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekDocument143 pagesGeneral Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekSam MumoNo ratings yet
- Daily Task #3Document2 pagesDaily Task #3LEAHN MAE LAMANNo ratings yet
- Fertilitas Dan Infertilitas: BY Tettisolehati, S.KP., M.KepDocument32 pagesFertilitas Dan Infertilitas: BY Tettisolehati, S.KP., M.KepAny AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Sexual Self (Understanding The Self)Document25 pagesSexual Self (Understanding The Self)StephRecato100% (1)
- Letter For Cibi - SurveyDocument8 pagesLetter For Cibi - SurveyAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Pair Up: What Can Be Done To Prevent Teenage Pregnancy?Document1 pagePair Up: What Can Be Done To Prevent Teenage Pregnancy?Angelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Development and Change - 2020 - Ramos - Change Without Transformation Social Policy Reforms in The Philippines UnderDocument21 pagesDevelopment and Change - 2020 - Ramos - Change Without Transformation Social Policy Reforms in The Philippines UnderAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Report - Lecture5 - CLARITODocument3 pagesPlagiarism Report - Lecture5 - CLARITOAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER Environmental ManagementDocument10 pagesREVIEWER Environmental ManagementAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Religion Blessing or CurseDocument1 pageReligion Blessing or CurseAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Chart For Contraception:: PreventsDocument1 pageChart For Contraception:: PreventsAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Fin Math ModuleDocument10 pagesFin Math ModuleAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- 1 SequencesbackgrounderDocument10 pages1 SequencesbackgrounderAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Febie Rovinne G. Mancion Ab Sociology - 1A Activity For MMW (Speaking Matimatically)Document1 pageFebie Rovinne G. Mancion Ab Sociology - 1A Activity For MMW (Speaking Matimatically)Angelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- MMW Activity Problem SolvingDocument3 pagesMMW Activity Problem SolvingAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- CLARITO - BPA-1B - Math Languange and SymbolsDocument3 pagesCLARITO - BPA-1B - Math Languange and SymbolsAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Speaking MathematicallyDocument7 pagesLesson 3 Speaking MathematicallyAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- JALucilo Problem SolvingDocument7 pagesJALucilo Problem SolvingAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- JALucilo Problem SolvingDocument7 pagesJALucilo Problem SolvingAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Presentation by SlidesgoDocument48 pagesE-Learning Presentation by SlidesgoLavinia NicolaeNo ratings yet
- MS Obstetrics & Gynaecology - Plan of Thesis (Year 2015)Document4 pagesMS Obstetrics & Gynaecology - Plan of Thesis (Year 2015)RachnaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Birth After Previous Caesarean SectionDocument26 pagesVaginal Birth After Previous Caesarean SectionWonyenghitari George100% (1)
- Sediaan KBDocument9 pagesSediaan KBREZUANTO PUALILLINNo ratings yet
- 04 STS - Stem CellsDocument44 pages04 STS - Stem CellsAlyza Ashley Tan GallardoNo ratings yet
- Thousand AutumnsDocument8 pagesThousand Autumnschristelle zhengNo ratings yet
- 21 Reasons Why You Should Have Sex and The Advantages To Our HealthDocument12 pages21 Reasons Why You Should Have Sex and The Advantages To Our HealthnelsonNo ratings yet
- Asian Institute of Computer Studies-Montalban Monte Brissa Subdivision, San Jose, Rodriguez RizalDocument7 pagesAsian Institute of Computer Studies-Montalban Monte Brissa Subdivision, San Jose, Rodriguez RizalCABAGSANG KYLA T.No ratings yet
- Promotif Dan Preventif Kesehatan Reproduksi Pekerja Terhadap Risiko Bahaya Di Tempat KerjaDocument29 pagesPromotif Dan Preventif Kesehatan Reproduksi Pekerja Terhadap Risiko Bahaya Di Tempat KerjaSugi YantiNo ratings yet
- OB Mod 4 Review QuestionsDocument26 pagesOB Mod 4 Review QuestionsMohit AnjanaNo ratings yet
- Hard Cock Pictures From Horny Guys Taking Dick Pics 2Document1 pageHard Cock Pictures From Horny Guys Taking Dick Pics 2Johnsonjr RodriguezNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument22 pagesAbstractnayayathNo ratings yet
- Lapjag Poli Obgyn 27-29 April 2021 (KLMPK Syifa)Document13 pagesLapjag Poli Obgyn 27-29 April 2021 (KLMPK Syifa)Adi Joyo NegoroNo ratings yet
- The Role of Sexual Reproductive Health Education in Adolescents: Sexual Behaviours in Secondary Schools in Morogoro Municipality, TanzaniaDocument15 pagesThe Role of Sexual Reproductive Health Education in Adolescents: Sexual Behaviours in Secondary Schools in Morogoro Municipality, TanzaniaMusa EnockNo ratings yet
- General Science TuesdayDocument11 pagesGeneral Science TuesdayAljoy Bascos Bernardo - NeriNo ratings yet
- 72 Surrogacy CanDocument10 pages72 Surrogacy CanTamara MoralesNo ratings yet
- Surrogacy (Third Party Parenting, Gestational Carrier)Document17 pagesSurrogacy (Third Party Parenting, Gestational Carrier)Dwi WulandariNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument40 pagesCombinepdfShaira UntalanNo ratings yet
- What Is in Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and Its ProcessDocument4 pagesWhat Is in Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and Its ProcessPlanet womenNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory FileDocument13 pagesBiology Investigatory FileSidra khan100% (2)
- EpisiotomyDocument18 pagesEpisiotomyAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2Ruiz Von LaguneroNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Emergency and Anesthetic ManagementDocument11 pagesObstetric Emergency and Anesthetic ManagementmichaelNo ratings yet
- Report On Family Planning (4400)Document27 pagesReport On Family Planning (4400)Bikram KushaalNo ratings yet
- Articulo 4Document6 pagesArticulo 4Eduardo GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Seksualitas ManusiaDocument46 pagesSeksualitas ManusiaSepti RahayuNo ratings yet
- Endometrium in Surgical PathologyDocument129 pagesEndometrium in Surgical PathologyleartaNo ratings yet
- Milk Princess Vol 2Document212 pagesMilk Princess Vol 2Frank Soo50% (4)