0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 viewsAsm 3789
Asm 3789
Uploaded by
Mohammad Farhan KhanThis document provides answers to review questions about the respiratory system from Class IX Biology. It includes multiple choice, very short answer, short answer, and structured questions. The multiple choice questions cover topics like the function of the diaphragm during inspiration and the parts of the respiratory system where gas exchange occurs. The short answer questions require labeling diagrams and parts of the respiratory system, explaining processes like respiration and how breathing rate increases, and differentiating between key terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Asm 3789
Asm 3789
Uploaded by
Mohammad Farhan Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views6 pagesThis document provides answers to review questions about the respiratory system from Class IX Biology. It includes multiple choice, very short answer, short answer, and structured questions. The multiple choice questions cover topics like the function of the diaphragm during inspiration and the parts of the respiratory system where gas exchange occurs. The short answer questions require labeling diagrams and parts of the respiratory system, explaining processes like respiration and how breathing rate increases, and differentiating between key terms.
Original Title
ASM_3789
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document provides answers to review questions about the respiratory system from Class IX Biology. It includes multiple choice, very short answer, short answer, and structured questions. The multiple choice questions cover topics like the function of the diaphragm during inspiration and the parts of the respiratory system where gas exchange occurs. The short answer questions require labeling diagrams and parts of the respiratory system, explaining processes like respiration and how breathing rate increases, and differentiating between key terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views6 pagesAsm 3789
Asm 3789
Uploaded by
Mohammad Farhan KhanThis document provides answers to review questions about the respiratory system from Class IX Biology. It includes multiple choice, very short answer, short answer, and structured questions. The multiple choice questions cover topics like the function of the diaphragm during inspiration and the parts of the respiratory system where gas exchange occurs. The short answer questions require labeling diagrams and parts of the respiratory system, explaining processes like respiration and how breathing rate increases, and differentiating between key terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Class IX Biology , Chapter – Respiratory System
Answers of the Review Questions
A. Multiple Choice Type
1. During inspiration, the diaphragm – contracts
2. The ultimate end parts of the respiratory system in humans are known as
– alveoli
3. During respiration there is – loss in dry weight ( this is because respiration
is a catabolic process in which complex substances are broken down into
simple compounds)
B. Very Short Answer Type
1. Choose the odd one out in each of the following groups of four items
each:
a. Odd :- Diaphragm , Category of others :- Parts of respiratory tract.
b. Odd:- Starch, Category of other three:- anaerobic respiration in plants.
c. Odd:- Diffusion, Category of other three:- structures and substances
involved in respiration.
d. Odd:- Diffusion, Category of other three:- structures of respiratory tract.
e. Odd:- Hypoxia, Category of other three:- Compounds formed of
haemoglobin
f. Odd:- Vocal cord, Category of other three:- Parts or structures in nose.
2. Name the body structures concerned with the given functional activity:-
a. Epiglottis
b. RBC/Erythrocytes
c. Diaphragm
d. Haemoglobin
e. Pleural fluid
f. Alveoli
3. What is the normal percentage composition of gases in spired air and
expired air respectively?
Component Inspired air % Expired air %
Oxygen 20.96 16.40
Carbon dioxide 0.04 4.00
Nitrogen 79.00 79.60
Water vapour low high
4. Which chemical compound inside a cell can be termed “Currency of
Energy”
ATP – Adenosine triphosphate
5. Match the items in column I with Column II
Column I Column II
Alveoli Diffusion of gases
Bronchioles small air tubes
Nasal chamber lined with hairs
bronchi An inverted Y – shaped tube
C. Short Answer Type
1. Fill in the balnks
a. Alveoli and exchanges of gases
b. Mitochondria and cellular respiration
c. Epiglottis and prevent the entry of food into the trachea
d. Pleura and protection of lungs
e. Diaphragm and increase or decrease the volume of thoracic cavity
lengthwise during breathing movements.
f. “C” shaped cartilage rings and distention of the trachea and bronchi/
prevent the trachea and bronchi from collapsing.
2. State one function each of the following.
a. Ciliated epithelium and lash out the solid particle entering into the
trachea.
b. Mitochondria and cellular respiration
c. Diaphragm and increase or decrease the volume of thoracic cavity
lengthwise during breathing movements.
d. Intercostal muscles and increases or decreases the volume of thoracic
cavity breadthwise during breathing movements.
e. Pleural fluid and protects the lungs from mechanical shock.
3. Match the items in column I with Column II
Column I Column II
Cartilaginous Bronchi
Large surface area Alveoli
Breathing movements Diaphragm
Voice Larynx
Complemental air Extra inhalation
swallowing epiglottis
4. Under what condition would the breathing rate increases?
When we do physical exercise, laborious jobs, when we perform athletic
activities, while going to higher altitude and in psychic conditions.
5. How would you prove that air you breathe out is warmer?
When we breath out the air on palm by keeping it closely to the mouth.
6. How is the respiratory passage kept free of dust particles?
The hairs present in the nostrils, the constant motion of cilia in the
respiratory tract and the mucus secreted in the respiratory tract help to
prevent the dust particles.
7. What is wrong in the statement “We breath in oxygen and breath out
carbon dioxide”?
We breath in air rich of oxygen and breath out air rich of carbon dioxide.
D. Long Answer Type.
1. Differentiate between the following pairs.
a. Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration
Carbon dioxide and water vapour Ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide in
plants and lactic acid in animals
b. Respiration photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide and water vapour oxygen
c. Photosynthesis Respiration
Water and carbon dioxide Glucose and oxygen
d. Inspired air Alveolar air
0.04% 4.00%
e. Respiration breathing
Cells and tissues lungs
f. Tidal volume Residual volume
500 ml 1500 ml
2. Give suitable explanation
a. Because nose has hairs which can filter the air, nose has mucus which has
lysozyme which can kill the germs and it also helps to warm and
moisturize the air which helps in the active exchange of gases in the lungs.
b. This is due to the residual air that is left in the lungs even after forcible
inhalation.
c. The air is thin in the higher altitude therefore the air we breath in will
have comparatively less amount of oxygen, but the oxygen demand of the
body remains same. Therefore, we feel breathlessness at higher altitude.
3. With regards to the respiratory system ……….
a. Intercostal muscle and diaphragm
b. The external intercostal muscle contracts as a result the rib cage is pushed
outward and upward. This will help in increasing the volume of thoracic
cavity lengthwise. At the same time the diaphragm contracts and become
flat, this will help to increase the volume inside the thoracic cavity
lengthwise. As a result of these actions the pressure inside the thoracic
cavity decreases and the air rushes in from outside.
c. C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ 6H₂O + 6CO₂
d. What is meant by
1. residual air :- The volume of air left in the lungs after forcible
exhalation.
2. Dead air space:- The volume of air left in the respiratory tracts like
trachea and bronchi which do not participate in the exchange of gases.
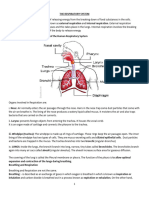
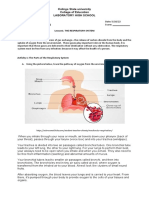
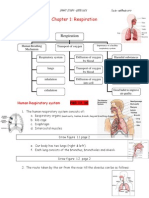
4 Starting from nostrils………
Nostrils pharynx trachea bronchi bronchiole alveoli.
5 What are the functions …..
a. Ribs:- helps in protection of the lungs and breathing movements to
regulates the volume of thoracic cavity breadthwise.
b. Diaphragm:- Regulate the volume of thoracic cavity lengthwise and helps
in breathing movements.
c. Abdominal muscle:- Helps in forcible inhalation and exhalation.
E. Structured/ Application/Skill Type.
1. Given alongside …..
i. 1- blood capillary, 2 – RBC, 3 – blood plasma, 4 – alveoli.
ii. 5 represents diffusion of carbon dioxide from RBC to alveoli.
6 represents diffusion of oxygen from alveoli to RBC of blood capillary.
2. Given below is an overall ……
a. Anaerobic respiration
b. Only to animals
c. Biceps and triceps muscles/ skeletal muscles of the body.
3. Given below are ………
a. Write reaction number ………
i. Reaction number 5/E
ii. Reaction number 4/D
iii. Reaction number 3/C
iv. Reaction number 1/A
v. Reaction number 3/C
b. Which reactions ……..
i. Reaction number 4/D
ii. Reaction number 3/C
iii. Reaction number 5/E
iv. Reaction number 2/B
v. Reaction number 1/A
4. The volume of air in the lungs ……..
a. Tidal volume :- It is the volume of air used in normal quite breathing
which is equal to 500 ml.
b. Inspiratory reserve volume:- It is the volume of air inhaled forcibly after
the normal quite breathing which is equal to 3000 ml.
c. It is the volume of air exhaled forcibly after the normal breathing out
which is equal to 1000 ml.
d. Vital capacity:- It is the volume of air breath in and out by maximum
inspiration and expiration which is equal to 4500 ml.
e. It is the volume of air left in the lungs after forcible exhalation which is
equal to 1500 ml.
You might also like
- Foundations of Neural Development. 1st Edition. ISBN 1605355798, 978-1605355795Document23 pagesFoundations of Neural Development. 1st Edition. ISBN 1605355798, 978-1605355795clarinesybillarl100% (10)
- Rwa Complete Geography Notes by Ankit Chaudhary SirDocument342 pagesRwa Complete Geography Notes by Ankit Chaudhary Siranurag4534591% (11)
- 3 Protein Structure-S PDFDocument10 pages3 Protein Structure-S PDFNathan Pittman0% (1)
- Bruce McCune-James B. GraceDocument307 pagesBruce McCune-James B. GraceAndrea Mendoza100% (1)
- The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Respiratory Systemefe shanNo ratings yet
- 2024 Note On The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pages2024 Note On The Respiratory SystemtrinitytricolchapelNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1m1Document26 pagesScience 9 q1m1jessa diezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - THE RESPIRATORY SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 14 - THE RESPIRATORY SystemNaveen Kumar PokalaNo ratings yet
- 556Document3 pages556Nokutenda KachereNo ratings yet
- Class 7, Science, Chapter 11 (Answer Key)Document6 pagesClass 7, Science, Chapter 11 (Answer Key)kashishgupta3011No ratings yet
- Respiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerDocument6 pagesRespiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerRatna PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- RTP Q1 G9 Science Module 1Document20 pagesRTP Q1 G9 Science Module 1Julie Ann Pineda BalichaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1st Quiz 1 The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesScience 9 1st Quiz 1 The Respiratory SystemRyan BersaminNo ratings yet
- Human RespirationDocument4 pagesHuman RespirationRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Respiratory System (2 Hours Lecture/3 Hours Lab) : at The End of This Unit, Students Will Be Able ToDocument4 pagesUnit 7: Respiratory System (2 Hours Lecture/3 Hours Lab) : at The End of This Unit, Students Will Be Able ToRUSSEL AQUINONo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Respiration Revision Worksheet Chapter 1Document4 pagesGrade 7 Respiration Revision Worksheet Chapter 1chiminhvas2012No ratings yet
- Class 7 Lesson 6Document3 pagesClass 7 Lesson 6gunjanrichaNo ratings yet
- 5959522-Class-7 Science Respiration in Organisms Ws NeenaDocument6 pages5959522-Class-7 Science Respiration in Organisms Ws NeenaMyra kohliNo ratings yet
- Ans 2 Bio Grade 9 SelinaDocument5 pagesAns 2 Bio Grade 9 SelinaAyaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Respiratory System OUTLINEDocument3 pagesAnatomy Physiology Respiratory System OUTLINENursing NotesNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasDocument7 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasParasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Document5 pagesChapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Precious Aiverose EspinaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10Document6 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10Ratnesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesActivity 1 - Respiratory SystemZian TallongonNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1st Quiz 1 The Respiratory System With EvalbeeDocument3 pagesScience 9 1st Quiz 1 The Respiratory System With EvalbeeRyan BersaminNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument3 pagesRespiration Noteseshoukat353No ratings yet
- Course Module Course Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing Outcome Based Clinical Learning 1Document11 pagesCourse Module Course Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing Outcome Based Clinical Learning 1Michelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Biology Matric Class NotesDocument38 pagesBiology Matric Class NotesNaveed Haroon BhachoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Q1-WK 1-2.a FOR STUDENTDocument14 pagesSCIENCE 9 Q1-WK 1-2.a FOR STUDENTErra PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Respiratory SysDocument3 pagesTest 1 Respiratory SysJaskirat SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson PlanBryanAngelo Laguilles100% (1)
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument5 pagesGaseous Exchangehafsa.r.yasirNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document9 pagesLab 6InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageSummative Test in Respiratory SystemMelvin Cabonegro100% (8)
- What I Know: Pre - TestDocument8 pagesWhat I Know: Pre - TestPamela Jane GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Respiration Doc1Document6 pagesChapter 1 Respiration Doc1api-248021925No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Respiratory SystemHazel Jane Ambrona VillegasNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exchange of GasesDocument9 pagesBreathing Exchange of Gasesravinderinst2No ratings yet
- Week 11 Anph 111Document6 pagesWeek 11 Anph 111itsmearonsupanNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument9 pagesRespirationpriya.kesharwani0557No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Gas Exchange Notes 1 PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 11 Gas Exchange Notes 1 PDFKai TongNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesUnit 5. Respiratory SystemRaquelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - 2 - WsDocument5 pagesRespiratory - 2 - WsRatna PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- NOTES (2024-2025) Subject: Science (Biology) Class: Vii Chapter: 10. Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesNOTES (2024-2025) Subject: Science (Biology) Class: Vii Chapter: 10. Respiration in OrganismscrowemojoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 BIOLOGY Life Processes Respiration Ref NotesDocument5 pagesGrade 10 BIOLOGY Life Processes Respiration Ref NotesjmisamflbozoNo ratings yet
- Class X Bio NotesDocument55 pagesClass X Bio Notesguneshraja2k20No ratings yet
- Science 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDDocument7 pagesScience 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ReviewerDocument8 pagesRespiratory ReviewerBLAIRY ZYNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFDocument7 pagesChapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFben martin100% (1)
- Biology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabanDocument3 pagesBiology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabannoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsDocument5 pagesRespiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Parts of The Respiratory System - (Catalyst Group)Document4 pagesLesson Plan On Parts of The Respiratory System - (Catalyst Group)Rovelyne A De LunaNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasesakshitarao4960No ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1-Module 1Document27 pagesScience: Quarter 1-Module 1Kent TayoneNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms ExerciseDocument2 pagesRespiration in Organisms Exerciseaanjalisharma017No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesLesson 3 - Respiratory SystemPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- RespiratorysystemexamDocument4 pagesRespiratorysystemexamapi-301967158No ratings yet
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationDocument5 pagesCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (Chart)Document4 pagesRespiratory System (Chart)Rommel Urbano YabisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The Respiratory System: Things You Should Know (Questions and Answers)From EverandAnatomy and Physiology: The Respiratory System: Things You Should Know (Questions and Answers)No ratings yet
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Neilletal2009-Diseases, Pathogens and ParasitesOfUndariaInNZDocument108 pagesNeilletal2009-Diseases, Pathogens and ParasitesOfUndariaInNZFacu UrsinoNo ratings yet
- Panik Productions - Modern Dungeon5Document142 pagesPanik Productions - Modern Dungeon5Rony Do Carmo100% (3)
- Biology of Tooth MovementDocument120 pagesBiology of Tooth Movementheena malikNo ratings yet
- F4 Chapter 5 KSSM SCIENCE DLP EditedDocument138 pagesF4 Chapter 5 KSSM SCIENCE DLP Editedsalizamatisa100% (1)
- Answer Key NAFS Science Worksheet 1Document9 pagesAnswer Key NAFS Science Worksheet 1ManaalNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Document24 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Mysterio OfficiallyNo ratings yet
- Pmls Midterms ReviewerDocument10 pagesPmls Midterms ReviewerCute ni LeynesNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Phytoalexin Metabolism and AcDocument632 pagesHandbook of Phytoalexin Metabolism and Accporto_silvaNo ratings yet
- Test Series 1 Marking Scheme (Strictly With Reference To NCERT) Class 11 BiologyDocument5 pagesTest Series 1 Marking Scheme (Strictly With Reference To NCERT) Class 11 BiologyRajeev TiwariNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan: Department of EducationDocument19 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan: Department of EducationMaya CondeNo ratings yet
- Histology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureDocument7 pagesHistology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureAli HayderNo ratings yet
- Dominate 3Document25 pagesDominate 3BonnyNo ratings yet
- Science ArticleDocument4 pagesScience ArticleSamNo ratings yet
- Postbiotics - What's New - Gabriel VinderolaDocument24 pagesPostbiotics - What's New - Gabriel VinderolaNguyen Minh ChauNo ratings yet
- The Varroa MiteDocument17 pagesThe Varroa Mites_barriosNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Plant Growth and Water ConsumptionDocument16 pagesThe Relationship Between Plant Growth and Water ConsumptionShannen SaycoNo ratings yet
- Stress PhysiologyDocument4 pagesStress PhysiologyCynthia Adeline SNo ratings yet
- 3 (Movement of Substances Across Plasma Membrane)Document16 pages3 (Movement of Substances Across Plasma Membrane)Jia YueNo ratings yet
- Classification by Depth Distribution of Phytoplankton and ZooplanktonDocument31 pagesClassification by Depth Distribution of Phytoplankton and ZooplanktonKeanu Denzel BolitoNo ratings yet
- Taking Play SeriouslyDocument2 pagesTaking Play SeriouslyMargarita HualmeNo ratings yet
- Learning Competency Directory in Science 7 First Quarter: Region III Guzmanville, Sto. Cristo, City of San Jose Del MonteDocument5 pagesLearning Competency Directory in Science 7 First Quarter: Region III Guzmanville, Sto. Cristo, City of San Jose Del MonteBerith Grace Magcalas-Gallardo100% (1)
- De Thi Chon DT Olympic 1819Document9 pagesDe Thi Chon DT Olympic 1819Thai ThuyNo ratings yet
- Antibody Structure and Functions: ImmunologyDocument40 pagesAntibody Structure and Functions: ImmunologyMoody Maxi KhanNo ratings yet
- 9. (TIÊU CHUẨN) Đề soạn theo cấu trúc minh họa 2021 - Tiếng Anh - Đề 9Document16 pages9. (TIÊU CHUẨN) Đề soạn theo cấu trúc minh họa 2021 - Tiếng Anh - Đề 9Thanh TrânNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Anatomi Dan Histologi Oesofagus Dan Proventrikulus Pada Ayam Hutan Merah (Gallus Gallus) Asal Pulau TimorDocument19 pagesGambaran Anatomi Dan Histologi Oesofagus Dan Proventrikulus Pada Ayam Hutan Merah (Gallus Gallus) Asal Pulau TimorMuhammad Gaidar AliNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument75 pagesFlashcards - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSERinen ParacadNo ratings yet