Cryogenic Engineering
Cryogenic Engineering
Uploaded by
ArjunCopyright:
Available Formats
Cryogenic Engineering
Cryogenic Engineering
Uploaded by
ArjunOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Cryogenic Engineering
Cryogenic Engineering
Uploaded by
ArjunCopyright:
Available Formats
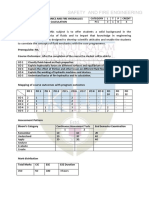
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
CODE COURSE NAME CATEGORY L T P CREDIT
MET476 CRYOGENIC ENGINEERING PEC 2 1 0 3
Preamble: This course provides fundamental knowledge of types of cryogenic fluids,
behavior of materials and properties at temperatures, liquefaction systems, cryogenic
refrigeration, gas separation, purification, insulators, cryogenic storage, transfer and
measuring instruments
Prerequisite: MET202-Engineering Thermodynamics, MET303-Thermal Engineering
Course Outcomes :After completion of the course the student will be able to
Explain the properties of cryogenic liquids and properties of material at
CO1
cryogenic temperatures
CO2 Describe and analyze cryogenic liquefaction systems using first principles of
thermodynamics
CO3 Describe and analyze cryogenics refrigeration using first principles of
thermodynamics
CO4 Identify insulation system for cryogenic application and explain cryogenic storage
vessels.
CO5 Understand gas separation and purification methods
CO6 Understand instrumentation for various measurements in cryogenic engineering.
Mapping of course outcomes with program outcomes
PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
CO 1 3 2 1
CO 2 3 2
CO 3 3 2 1
CO 4 3 1
CO 5 3 1
Assessment Pattern
Continuous Assessment
End Semester Examination
Bloom’s Category Tests
(in %)
1 (in %) 2 (in %)
Remember 10 10 10
Understand 20 20 20
Apply 20 20 70
Analyse
Evaluate
Create
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Mark distribution
Total CIE ESE ESE
Marks Marks Marks Duration
150 50 100 3 hours
Continuous Internal Evaluation Pattern:
Attendance : 10 marks
Continuous Assessment Test (2 numbers) : 25 marks
Assignment/Quiz/Course project : 15 marks
End Semester Examination Pattern: There will be two parts; Part A and Part B. Part A
contain 10 questions with 2 questions from each module, having 3 marks for each question.
Students should answer all questions. Part B contains 2 questions from each module of which
student should answer any one. Each question can have maximum 2 sub-divisions and carry
14 marks.
Course Level Assessment Questions:
Course Outcome 1 (CO1):
1. Describe in detail the variation of mechanical properties of various materials at
cryogenic temperatures
2. Explain the terms i) Transition temperature and ii) Critical current of
superconductors.
3. Explain the application of cryogenics in space technology.
Course Outcome 2 (CO2):
1. Explain the production of low temperatures using Joule-Thomson effect.
2. How the cryo coolers are classified? Explain the working of strilling cycle cryo
cooler.
3. Explain about the working of a precooled Linde-Hampson system with suitable
diagram for neon and hydrogen.
Course Outcome 3 (CO3):
1. Explain the working of Vuilleumier refrigerator with neat sketch.
2. Explain briefly the importance of refrigerator effectiveness.
3. Explain refrigerators using solids as working media.
Course Outcome 4 (CO4):
1. Explain about the basic design parameters of cryogenic fluid storage vessels.
2. Explain the different types and use of insulations in cryogenic applications.
3. Explain about the cryogenic fluid transfer system.
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Course Outcome 5 (CO5):
1. Explain the pressure measurement system used in cryogenic applications.
2. Explain the working principle of different types of cryogenic liquid level
indicators.
3. Explain different temperature measuring techniques used in cryogenic
applications.
Model Question Paper
APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
VIII SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION
MET476: CRYOGENIC ENGINEERING
Maximum: 100 Marks Duration: 3 hours
PART A
Answer all questions, each question carries 3 marks
1. Explain the historical development of cryogenics?
2. Distinguish between Ortho Hydrogen and Para Hydrogen.
3. Explain Meissner effect?
4. Explain Joule Thomson coefficient.
5. What are the performance parameters to be considered in gas liquefaction systems?
6. Define FOM for the refrigerator.
7. What is vapour shielding in cryogenic vessels?
8. What are super insulations?
9. Write a short note on hydrostatic liquid level gauge.
10. List few heat exchangers used in cryogenic systems.
(10 X 3 = 30 marks)
PART B
Answer one full question from each module
Module 1
11. a) What is cryogenics? Mention the few areas involving cryogenic engineering
(7 marks)
b) Determine the thermal conductivity of air at 250 K and 101.3 kPa if the mean free
path of air at this condition is 49 nm, the gas constant for air is 287 J/kg K, the
specific heat ratio is 1.4 and the specific heat at constant volume is 716.5 J/kg K.
(7 marks)
12. a) With sketches, explain the different critical components present in gas liquefaction
systems. (7 marks)
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
b) With the help of a T-s diagram explain working of a Simon Helium liquefier.
(7 marks)
Module 2
13. a) Compare Claude Liquefaction system and Linde Hampson Liquefaction systems.
(4 marks)
b) Explain the Joule Thomson effect. Show the inversion curve of a real gas on a T-p
diagram.
Prove that an ideal gas will not experience a temperature change upon isenthalpic
expansion. (10 marks)
14. a) With sketches, explain the different critical components present in gas liquefaction
systems. (7 marks)
b) With the help of a T-s diagram explain working of a Simon Helium liquefier.
(7 marks)
Module 3
15. a) Explain the working of a dilution refrigerator with neat schematic. (7 marks)
b) With the help of schematic and T-S diagram, explain Philips Refrigerator. Also
explain briefly the importance of refrigerator effectiveness. (7 marks)
16. a) What are the gas purification methods? With sketches, explain adsorption purifier
along with refrigerator purifier. (7 marks)
b) With sketches, explain Linde single column gas separation system. (7 marks)
Module 4
17. a) With sketches, explain the cryogenic fluid storage vessels. (7 marks)
b) Write about vacuum insulation and opacified powder insulation used in cryogenics.
(7 marks)
18. a) Explain about cryogenic fluid transfer systems. (7 marks)
b) With Sketch, explain the functions of different components in a Dewar vessel.
(7 marks)
Module 5
19. a) Explain the working of a turbine flow meter. (7 marks)
b) Write short notes on the various heat exchanger configurations used in cryogenic
systems. (7 marks)
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
20. a) Explain the different temperature measurement techniques used in cryogenic
application (7 marks)
b) Explain different safety devices used in cryogenic liquid storage systems.
(7 marks)
Syllabus
Module 1
Introduction to cryogenic engineering, Historical background - Major events in the
development of cryogenic engineering, Low Temperature properties of Engineering
Materials - Mechanical properties- Thermal properties- Electric and magnetic properties,
Cryogenic fluids and their properties.
Applications of cryogenics: Applications in space, food processing, super conductivity,
electrical power, biology, medicine, electronics and cutting tool industry.
Module 2
Liquefaction systems – System performance parameters, ideal liquefaction system,
Joule-Thomson expansion, Adiabatic expansion, Liquefaction systems for gases other
than Neon. Hydrogen and Helium. Simple Linde - Hampson system, Claude &
Cascaded System.
Liquefaction systems for Neon. Hydrogen and Helium – LN2 precooled Linde
Hampson and Claude systems, Ortho to Para conversion arrangement in hydrogen
liquefaction system, Simon Helium liquefaction system, Collins Helium liquefaction
system. Critical components of Liquefaction systems – critical components and their
effect on system performance.
Module 3
Cryogenic Refrigeration systems: Ideal isothermal and isobaric refrigeration systems-
Refrigeration using liquids as refrigerant- Linde-Hampson refrigerator, Claude refrigerator.
Refrigeration using gases as refrigerant- Stirling cycle cryocoolers, Philips refrigerator,
Effect of regenerator effectiveness on performance of Philips refrigerator, Gifford
McMahon refrigerators. Refrigerators using solids as working media-Magnetic refrigerators
– Thermodynamics of magnetic refrigerators, dilution refrigerators.
Module 4
Gas separation and purification: - Thermodynamic ideal separation system, mixture
characteristics, principle of gas separation, separation of air, hydrogen and helium, gas
purification methods
Cryogenic fluid storage and transfer systems:, Cryogenic fluid storage vessel, Thermal
insulation and their performance at cryogenic temperatures, Super Insulations, Vacuum
insulation, Powder insulation, Cryogenic fluid transfer systems, Cryo pumping.
Module 5
Cryogenic instrumentation, Pressure measurement – Mc Leod gauge, Pirani gauge and
Penning gauge, Flow measurement – Orifice meter, Venturi meter and Turbine flow
meter. Liquid level gauges- hydrostatic, resistance gauge,, capacitance gauge anf
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
thermodynamic gauge, Temperature measurements- ITS-90, Thermocouple, RTD,
magnetic thermometers and vapor pressure thermometers, Types of heat exchangers
used in cryogenic systems, Safety in cryogenic fluid handling, storage and use.
Text Books:
1. Randal F. Barron, Cryogenic systems, McGraw Hill, 1986
2. M Mukhopadhyay, Fundamentals of Cryogenic Engineering, PHI Learning , 2010
3. K. D. Timmerhaus and T. M. Flynn, Cryogenic Process Engineering, Springer, 2013
4. S.S Thipse, Cryogenics, Narrosa, 2012
Reference Books:
1. A. R. Jha, Cryogenic Technology and applications, Elsevier Science, 2011
2. R. B. Scott, Cryogenic Engineering, Van Nostrand Co., 1989
3. M. D. Atrey (Ed.) Cryocoolers: Theory and Applications, 1st ed., International Cryogenics
Monograph Series, Springer International Publishing, 2020
Course Contents and Lecture Schedule
No. Topic No. of Lectures
1 Module 1
Introduction to Cryogenic Systems, Historical
development, Low Temperature properties of
1.1 Engineering Materials, Mechanical properties- Thermal 4
properties- Electric and magnetic properties –Cryogenic
fluids and their properties.
Applications of Cryogenics: Applications in space, Food
Processing, super conductivity, Electrical Power,
1.21.2 Biology, Medicine, Electronics and Cutting Tool 3
Industry. Low temperature properties of engineering
materials
2 Module 2
Liquefaction systems ideal system, Joule Thomson
expansion, Adiabatic expansion, Linde - Hampson
2.1 4
Cycle, Claude & Cascaded System, Magnetic Cooling,
Stirling Cycle Cryo Coolers.
Gas liquefaction systems: Introduction-Production of
1.22.2 low temperatures-General Liquefaction systems-
4
Liquefaction systems for Neon. Hydrogen and Helium –
Critical components of Liquefaction systems
3 Module 3
Cryogenic Refrigeration systems: Ideal Refrigeration
3.1 systems- Refrigeration using liquids and gases as 4
refrigerant- Refrigerators using solids as working media
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Gas separation and purification: Thermodynamic ideal
1.23.2 separation system, mixture characteristics, principle of gas
3
separation, separation of air, hydrogen and helium, gas
purification methods
4 Module 4
Cryogenic fluid storage and transfer systems:
Cryogenic Storage vessels and Transportation, Thermal
insulation and their performance at cryogenic
4.1 7
temperatures, Super Insulations, Vacuum insulation,
Powder insulation, Cryogenic fluid transfer systems,
Cryo pumping.
5 Module 5
Cryogenic instrumentation, Pressure flow-level and
temperature measurements, Types of heat exchangers
5.1 7
used in cryogenic systems, Safety in cryogenic fluid
handling, storage and use.
Downloaded from Ktunotes.in
You might also like
- Control Flownex SimulinkDocument8 pagesControl Flownex SimulinkSrashmiNo ratings yet
- 2019-Design of Helical Coil Heat Exchanger For A Mini Power Plant PDFDocument11 pages2019-Design of Helical Coil Heat Exchanger For A Mini Power Plant PDFAshish AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Sparklet EngineersDocument2 pagesSparklet Engineershappale2002No ratings yet
- Ee470 Final Project 1Document30 pagesEe470 Final Project 1api-271770058No ratings yet
- Multiphase Catalytic Reactors: Theory, Design, Manufacturing, and ApplicationsFrom EverandMultiphase Catalytic Reactors: Theory, Design, Manufacturing, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hydro Testing-Process PipingDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Hydro Testing-Process Pipingsanthosh thomasNo ratings yet
- Design and Thermal Analysis On Cryogenic Pressure VesselDocument6 pagesDesign and Thermal Analysis On Cryogenic Pressure VesselktejankarNo ratings yet
- 2phase Flow and Boiling Heat TransferDocument218 pages2phase Flow and Boiling Heat TransfercmegmhiNo ratings yet
- Jacket Piping NotesDocument2 pagesJacket Piping NotesArindomNo ratings yet
- Manual For Wetted Wall ColumnDocument7 pagesManual For Wetted Wall ColumnBalRam DhimanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ThermalDocument3 pagesLesson Plan ThermalGokulraju RangasamyNo ratings yet
- Universiti Malaysia Pahang: Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDocument13 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Pahang: Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringFirdaus IliasNo ratings yet
- Cold Spring of Restrained Piping SystemDocument5 pagesCold Spring of Restrained Piping Systemsateesh chandNo ratings yet
- MEC551 Assignment - Design September 2015Document7 pagesMEC551 Assignment - Design September 2015SyafiqAsyrafNo ratings yet
- Cryogenics IntroductionDocument26 pagesCryogenics Introductionsenior high100% (1)
- ME467 Cryogenic EngineeringDocument2 pagesME467 Cryogenic Engineeringnandan144No ratings yet
- Hot Tapping Data Sheet-2012 From TDWDocument1 pageHot Tapping Data Sheet-2012 From TDWRachel Flores0% (1)
- Models For Analysis of Water Hammer in Piping With Entrapped Air - Chaiko - 2002 - PPL CorporationDocument11 pagesModels For Analysis of Water Hammer in Piping With Entrapped Air - Chaiko - 2002 - PPL CorporationElias TascaNo ratings yet
- CryogenicDocument23 pagesCryogenicmgskumar100% (1)
- Organic Rankine Cycle As Efficient Alternative To PDFDocument9 pagesOrganic Rankine Cycle As Efficient Alternative To PDFGuilherme SixeNo ratings yet
- Process Industry Practices Piping: PIP PNC00004 Piping Flexibility Analysis Criteria For ASME B31.3 Metallic PipingDocument5 pagesProcess Industry Practices Piping: PIP PNC00004 Piping Flexibility Analysis Criteria For ASME B31.3 Metallic Pipingsunil601No ratings yet
- Boiling Heat TransferDocument26 pagesBoiling Heat TransfercmegmhiNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument6 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchangereafz111No ratings yet
- Estimation of Fracture Toughness KIC From Charpy Impact Test Data in T-Welded Connections Repaired by Grinding and Wet WeldingDocument10 pagesEstimation of Fracture Toughness KIC From Charpy Impact Test Data in T-Welded Connections Repaired by Grinding and Wet WeldingGayan0511No ratings yet
- Temp StrainersDocument12 pagesTemp StrainersRahul Lavand100% (1)
- A Review of Flow and Heat TransferDocument28 pagesA Review of Flow and Heat TransferOssama Bohamd100% (1)
- Critical Heat Flux PDFDocument32 pagesCritical Heat Flux PDFahmadstNo ratings yet
- Blade Number Effect For A Ducted Wind TurbineDocument9 pagesBlade Number Effect For A Ducted Wind TurbineAnonymous LnQ4lBXiPjNo ratings yet
- 2010 - SANDIA - Design Considerations For Concentrated Solar Tower Plants Using Molten Salts PDFDocument51 pages2010 - SANDIA - Design Considerations For Concentrated Solar Tower Plants Using Molten Salts PDFDavide FranziniNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Flownex Software Fired Heater Design PDFDocument11 pagesBrochure - Flownex Software Fired Heater Design PDFdatalogger123456No ratings yet
- Screening Reactor For Water HammerDocument49 pagesScreening Reactor For Water HammerYu GanNo ratings yet
- Process Skid TrainingDocument5 pagesProcess Skid TrainingrutujaNo ratings yet
- Yanbu: Export Refinery ProjectDocument7 pagesYanbu: Export Refinery ProjectJanakiraman MalligaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Safety Valve AnalysisDocument21 pagesPressure Safety Valve AnalysissidNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Enconman 2018 08 042 PDFDocument15 pages10 1016@j Enconman 2018 08 042 PDFteorikdeliNo ratings yet
- For Masela LNG PJ Piping Stress Analysis Review and SupportDocument23 pagesFor Masela LNG PJ Piping Stress Analysis Review and Supportsprashant5No ratings yet
- 12th CRYOGENICS 2012 IIR International Conference Dresden GermanyDocument477 pages12th CRYOGENICS 2012 IIR International Conference Dresden GermanyRavi Kumar Verma100% (1)
- Brosur Lintech LNG ISO Tank & Other Pressure VesselDocument6 pagesBrosur Lintech LNG ISO Tank & Other Pressure VesselAndi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility Study of Implementing An Ammonia EconomyDocument111 pagesA Feasibility Study of Implementing An Ammonia EconomyNisha SundarNo ratings yet
- GST-250 PSI Vertical Storage Tanks: 1500 Gallons Through 20,000 GallonsDocument33 pagesGST-250 PSI Vertical Storage Tanks: 1500 Gallons Through 20,000 GallonsPham LanphuongNo ratings yet
- Technology To Counter Silica Scaling in Binary Power-Generating System Using Geothermal Hot WaterDocument7 pagesTechnology To Counter Silica Scaling in Binary Power-Generating System Using Geothermal Hot WaterRidho Adrianto SitepuNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Systems (For Radioastronomy) : Gianluca Morgante INAF - IASF BolognaDocument67 pagesCryogenic Systems (For Radioastronomy) : Gianluca Morgante INAF - IASF BolognaHimanshuKalbandheNo ratings yet
- 1.7 Evaporative Air Cooling EquipmentDocument8 pages1.7 Evaporative Air Cooling EquipmentRio BananNo ratings yet
- Jacketed Piping Stress Analysis 1681811585Document28 pagesJacketed Piping Stress Analysis 1681811585AliNo ratings yet
- Energy: Ò Ali Ghannadzadeh, Raphaële Thery-Hetreux, Olivier Baudouin, Philippe Baudet, Pascal Floquet, Xavier JouliaDocument22 pagesEnergy: Ò Ali Ghannadzadeh, Raphaële Thery-Hetreux, Olivier Baudouin, Philippe Baudet, Pascal Floquet, Xavier JouliaHarold Valle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Flange & Bolt SelectionDocument5 pagesFlange & Bolt SelectionManzar KhanNo ratings yet
- PROJECT STANDARDS and Specifications Offshore Skid Packages Piping Design Rev01Document7 pagesPROJECT STANDARDS and Specifications Offshore Skid Packages Piping Design Rev01mihahudeaNo ratings yet
- AET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SDocument5 pagesAET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- 11 Heat Transfer To The Riser Wall of A Circulating Fluidised Bed CFBDocument8 pages11 Heat Transfer To The Riser Wall of A Circulating Fluidised Bed CFBMahesh DasarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Exergy Analysis of Renewable Energy Systems 2013 Exergy Second EditionDocument24 pagesChapter 11 Exergy Analysis of Renewable Energy Systems 2013 Exergy Second EditionAnonymous dUXvWL61No ratings yet
- Gas Pipe Line DesignDocument31 pagesGas Pipe Line DesignRajnikant DehariaNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis of FRP PipeDocument3 pagesStress Analysis of FRP Pipebraianvegas12No ratings yet
- Applied MechanicsDocument4 pagesApplied Mechanicszahin_132000% (1)
- CFD Modeling of Ground FlareDocument12 pagesCFD Modeling of Ground Flarehk1680% (1)
- Thermal Design Analysis of A Liquid Hydrogen VesselDocument9 pagesThermal Design Analysis of A Liquid Hydrogen Vessel이경률No ratings yet
- Cryo Module I and II PDFDocument208 pagesCryo Module I and II PDFReby RoyNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 MarksDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 MarksVishvesh T SNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument3 pagesRefrigerationelorannnNo ratings yet
- CHT301 - Ktu QbankDocument10 pagesCHT301 - Ktu QbankYuxin CasioNo ratings yet
- Semester - 3: Chemical EngineeringDocument135 pagesSemester - 3: Chemical EngineeringKevinNo ratings yet
- FST 202 FMFHC SyllabusDocument7 pagesFST 202 FMFHC SyllabusAnnwin Moolamkuzhi shibuNo ratings yet
- BaCO3WITH TiO2AND BaOWITHTiO2 RECN DETAIL AND XRD TEM ETCDocument130 pagesBaCO3WITH TiO2AND BaOWITHTiO2 RECN DETAIL AND XRD TEM ETCrajaram huptaNo ratings yet
- Rohini 34950090004Document11 pagesRohini 34950090004varalakshmiakash2712No ratings yet
- 7th Grade Pretest and KeyDocument8 pages7th Grade Pretest and Keyapi-377802356No ratings yet
- Negros Occidental Geohazard Report Dec 2011Document69 pagesNegros Occidental Geohazard Report Dec 2011Aimee SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Scenario of Global Health Course-Paw-2018Document9 pagesScenario of Global Health Course-Paw-2018Hilmy Bravianto KartonoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics One Word Interview Questions and Answers PDF - Mechanical Engineering Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesThermodynamics One Word Interview Questions and Answers PDF - Mechanical Engineering Questions and AnswersS Sweet SweetNo ratings yet
- Nagaland - State Action Plan On Climate Change 2012Document207 pagesNagaland - State Action Plan On Climate Change 2012Jongpong ChitenNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy: Brian Snyder, Mark J. KaiserDocument12 pagesRenewable Energy: Brian Snyder, Mark J. KaiserAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental Awareness - BSED E2B GROUP 10Document24 pagesEnvironmental Awareness - BSED E2B GROUP 10Ma. Adelfa ApipiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: SettlersDocument16 pagesUnit 2: SettlersRavi BhollahNo ratings yet
- Green: A Seminar Report OnDocument29 pagesGreen: A Seminar Report OnManish kumarNo ratings yet
- Durag High Energy Spark Igniter (D-HG 400)Document2 pagesDurag High Energy Spark Igniter (D-HG 400)senthilrsenthilNo ratings yet
- MAG LEVintroductionDocument3 pagesMAG LEVintroductionlance galorportNo ratings yet
- 02 Purrucker LindeDocument16 pages02 Purrucker Lindehiggsboson83No ratings yet
- Appendix A: Dimensionless Groups: By. Robert B. HeimannDocument2 pagesAppendix A: Dimensionless Groups: By. Robert B. HeimannGusti Ayoe NurjanahNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Total: 60 Marks: Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (15 Marks)Document11 pagesDiagnostic Test Total: 60 Marks: Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (15 Marks)Meenah KumariNo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Ivana Carevic, Ana Baric Evic, Nina Štirmer, Jelena Šantek BajtoDocument14 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Ivana Carevic, Ana Baric Evic, Nina Štirmer, Jelena Šantek BajtoSavaNo ratings yet
- Chronological History of Wind Turbine TechnologyDocument2 pagesChronological History of Wind Turbine TechnologyDeepak AshokanNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Desalinizacion de Agua para Utilizarla en Equipos de Enfriamiento PDFDocument11 pagesAnalisis de Desalinizacion de Agua para Utilizarla en Equipos de Enfriamiento PDFMariuxiNo ratings yet
- Focus Topics On Microplastics in Soil Analytical Methods, Occurrence, Transport, and Ecological RisksDocument37 pagesFocus Topics On Microplastics in Soil Analytical Methods, Occurrence, Transport, and Ecological RisksNur AbsarNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pages7 Types of Electromagnetic Wavesvee propaganda100% (1)
- Module 4 Note Taking SheetDocument2 pagesModule 4 Note Taking Sheet;No ratings yet
- Atlas of Namibia - 03 ClimateDocument36 pagesAtlas of Namibia - 03 ClimateCesar Ricardo Lopez ValerioNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Module 5 Balancing EquationADocument7 pagesChem 1 Module 5 Balancing EquationACharles Andrei OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Document36 pagesChapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Ng Kee NainNo ratings yet
- Ingwehumbe Management Plan Final 2018Document87 pagesIngwehumbe Management Plan Final 2018Natalie BlackmoreNo ratings yet
- Temperature Inversion: MeaningDocument5 pagesTemperature Inversion: MeaningMohAmmAd sAmiNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Images and Technical SpecificationsDocument6 pagesInstrumentation Images and Technical SpecificationsTAN YEE LINGNo ratings yet
- Antárctica IiDocument38 pagesAntárctica Iiapi-3701747No ratings yet