House Drainage Notes
House Drainage Notes
Uploaded by
gsenv20r09Copyright:
Available Formats
House Drainage Notes
House Drainage Notes
Uploaded by
gsenv20r09Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
House Drainage Notes
House Drainage Notes
Uploaded by
gsenv20r09Copyright:
Available Formats
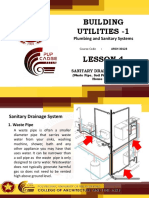
House drainage refers to the system of pipes, fittings, and fixtures within a
house that is designed to carry wastewater and sewage away from the building
to a public sewer or a private septic system. The main components of a house
drainage system include drain pipes, traps, vents, and waste outlets.
1. Drain pipes:
Soil Pipes: These pipes carry wastewater from toilets. They are
usually larger in diameter and made of materials resistant to
corrosion.
Waste Pipes: These pipes carry wastewater from sinks, showers,
bathtubs, and other fixtures. They are typically smaller in diameter
than soil pipes.
2. Traps:
Traps are U-shaped pipe sections designed to hold a small amount
of water. This water forms a seal that prevents sewer gases from
entering the house. Every fixture connected to the drainage system
should have a trap.
3. Vents:
Vent pipes allow air to enter the drainage system, preventing the
creation of a vacuum that could slow down or stop the flow of
wastewater. Proper venting also helps to release sewer gases
outside the house.
4. Waste Outlets:
These are the points where wastewater exits the house and enters
the drainage system. They include outlets for toilets, sinks,
bathtubs, showers, and appliances like washing machines and
dishwashers.
Properly designed and maintained house drainage systems, along with secure
connections to street sewers, are essential for the effective and safe disposal of
wastewater while preventing the spread of sewer gases and contaminants within
and around the house.
The connection of house drains to street sewers is a crucial aspect of a building's
plumbing system, ensuring the proper and safe disposal of wastewater from the
house into the larger municipal or local sewage network. Here is a step-by-step
explanation of the process:
1. House Drainage System:
The house drainage system consists of pipes, fittings, and fixtures
within a building that collect and carry wastewater and sewage
away from toilets, sinks, showers, and other fixtures.
2. House Sewer Line:
The house sewer line is a pipe that runs from the building's
plumbing system to the point where it connects with the public
sewer or a private septic system. This pipe is typically buried
underground and is designed to transport wastewater from the
house to the larger sewer network.
3. Cleanouts:
Cleanouts are access points in the house sewer line that provide a
means for inspection, maintenance, and clearing blockages. They
are usually installed at strategic locations, such as changes in
direction or near the connection to the main sewer.
4. Connection Point:
The connection point is the specific location where the house sewer
line joins the municipal or street sewer system. This connection is
typically made near the property line or at a designated point
specified by local regulations.
5. Sewer Lateral:
The section of the house sewer line that extends from the building
to the main sewer line in the street is often referred to as the sewer
lateral. This lateral ensures a smooth flow of wastewater from the
house to the larger sewer system.
6. Connection to Street Sewers:
The connection to street sewers involves joining the house sewer
line with the main sewer line in the public or municipal sewer
system. This connection is established using appropriate fittings
and methods, ensuring a secure and watertight link.
7. Inspections and Regulations:
Local building codes and regulations typically govern the
connection of house drains to street sewers. Inspections may be
required to verify that the connection meets safety and sanitation
standards. It's essential to comply with these regulations to ensure
the proper functioning of the overall sewage system.
8. Maintenance and Repairs:
Regular maintenance is crucial to prevent blockages and ensure the
efficient flow of wastewater. If issues arise with the connection to
street sewers, repairs may be necessary. This may involve
addressing blockages, replacing damaged pipes, or making
adjustments to ensure compliance with local regulations.
9. Permits:
In many jurisdictions, obtaining permits from local authorities is a
prerequisite for making connections to street sewers. This helps
ensure that the work is done in accordance with established
standards and regulations.
10. Environmental Considerations:
The proper connection of house drains to street sewers is not only
essential for the safety and health of occupants but also for
environmental protection. Wastewater is directed to treatment
facilities, preventing contamination of natural water sources.
The connection of house drains to street sewers involves the integration of a
building's plumbing system with the larger municipal sewage network,
following local regulations and standards to ensure proper functionality and
environmental responsibility.
You might also like
- Dealers Guide To Chemical Restoration of Postal StampsDocument40 pagesDealers Guide To Chemical Restoration of Postal Stampspeter smith100% (3)
- Module 1 - Building Plumbing System - IntroductionDocument3 pagesModule 1 - Building Plumbing System - IntroductionRochelleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Building Planning & Architecture - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument12 pagesUnit 1 - Building Planning & Architecture - WWW - Rgpvnotes.indeepak ujjainyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Building Planning & Architectural - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument12 pagesUnit 3 - Building Planning & Architectural - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inMohd Naif FirozNo ratings yet
- ME 428 Building Drainage SystemDocument11 pagesME 428 Building Drainage SystemJorwel Vincent E. VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing (AutoRecovered)Document3 pagesPlumbing (AutoRecovered)nicsNo ratings yet
- Sanitary FittingsDocument6 pagesSanitary Fittingsgsenv20r09No ratings yet
- M1 - Plumbing FixturesDocument19 pagesM1 - Plumbing FixturesazulaNo ratings yet
- PLUMBINGDocument10 pagesPLUMBINGYagesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- q4 Technical Drafting 9 Students Handouts 2Document2 pagesq4 Technical Drafting 9 Students Handouts 2ffsqg7r4xjNo ratings yet
- Reaserch PaperDocument5 pagesReaserch PaperJohn Michael PascuaNo ratings yet
- Design of Plumbing Systems Inside Buildings1Document17 pagesDesign of Plumbing Systems Inside Buildings1Thurya BenissaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Sanitary SystemDocument36 pagesGroup 3 - Sanitary SystemAyesa AgravanteNo ratings yet
- Dr.S.Sreedhar Reddy, Assistant Professor University of Nizwa, NizwaDocument50 pagesDr.S.Sreedhar Reddy, Assistant Professor University of Nizwa, Nizwassreedharreddy0% (1)
- Dr.S.Sreedhar Reddy, Assistant Professor University of Nizwa, NizwaDocument40 pagesDr.S.Sreedhar Reddy, Assistant Professor University of Nizwa, NizwaID Pritesh ModiNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Plumbing SystemsDocument5 pagesWater Supply Plumbing Systemsashe zinabNo ratings yet
- Plumbing 010Document79 pagesPlumbing 010Lyka Jane MercadoNo ratings yet
- 41 M4 GuiangDocument3 pages41 M4 GuiangJohn Zander GuiangNo ratings yet
- CE314 (Assignment1)Document1 pageCE314 (Assignment1)Hanni PhamNo ratings yet
- Blue and Minimalist Corporate PresentationDocument36 pagesBlue and Minimalist Corporate PresentationRenzpaul CuetoNo ratings yet
- Drainage SystemDocument2 pagesDrainage Systemsultanbadii12No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of SanitationDocument44 pagesBasic Principles of SanitationKaushik Jayaveeran67% (12)
- Sewerage System Enviornmental EngineeringDocument32 pagesSewerage System Enviornmental EngineeringShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- PLUMBING SYSTEM-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesPLUMBING SYSTEM-WPS OfficeLea MaligsayNo ratings yet
- U2MIDTERMDocument11 pagesU2MIDTERMsheenazxx95No ratings yet
- DraftDocument42 pagesDraftmyprojectstudy100% (2)
- Research 3Document9 pagesResearch 3Edgiecylin S. GALENONo ratings yet
- CTD 202Document28 pagesCTD 202omahs514No ratings yet
- Chapter7-Plumbing system-WS&SEDocument30 pagesChapter7-Plumbing system-WS&SERwagatare civilcontractorsNo ratings yet
- Properties of PlumbingDocument4 pagesProperties of PlumbingvicentiopaulNo ratings yet
- Drainage Systems 1601091Document10 pagesDrainage Systems 1601091Subrata Kumar DattaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 and 8-WS&SEDocument72 pagesChapter 7 and 8-WS&SEKunduwera MethodeNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Domestic Plumbing: 1. Single Stack SystemDocument4 pagesUnit-V Domestic Plumbing: 1. Single Stack SystemVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Tle q4 M1to3Document12 pagesTle q4 M1to3Syrart's Digitally Art'sNo ratings yet
- Case Study On The Application of A Proper PlumbingDocument25 pagesCase Study On The Application of A Proper PlumbingJeremie SaragaNo ratings yet
- Extended Abstract V2Document10 pagesExtended Abstract V2Luis MogrovejoNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Materials, Traps, Ventilation, Fixtures and InstallationDocument3 pagesPlumbing Materials, Traps, Ventilation, Fixtures and InstallationAldea ChanNo ratings yet
- TLE - PlumbingDocument20 pagesTLE - PlumbingsaglebalNo ratings yet
- Ulo 1 Assignments 03-16-2023 (Garcia)Document2 pagesUlo 1 Assignments 03-16-2023 (Garcia)Griffin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Transportation, Different Modes of Transportation, Characteristics of Road Transport, Scope of Highway and Traffic EngineeringDocument5 pagesImportance of Transportation, Different Modes of Transportation, Characteristics of Road Transport, Scope of Highway and Traffic EngineeringArteezy BabaevNo ratings yet
- Rain and Ground Water Drainage Systems For Buildings: Eduardo João Vindeirinho RinoDocument11 pagesRain and Ground Water Drainage Systems For Buildings: Eduardo João Vindeirinho RinoVishwas GhanNo ratings yet
- Bu1 Lesson 4Document66 pagesBu1 Lesson 4Ysa CambaNo ratings yet
- Sewage: Sullage: Plumbing/Drainage System: Sewer: Soil PipeDocument2 pagesSewage: Sullage: Plumbing/Drainage System: Sewer: Soil PipeMuhammad Nouman KhanNo ratings yet
- The House Sewer House Sewer Is Defined As, That Portion of The Horizontal Drainage System, Which Starts FromDocument2 pagesThe House Sewer House Sewer Is Defined As, That Portion of The Horizontal Drainage System, Which Starts FromStanley Scott ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Design Population 8410 Persons: V 1/n R SDocument5 pagesDesign Population 8410 Persons: V 1/n R SFortiter FysproNo ratings yet
- Basic Principle of Sanitary and Plumbing DesignDocument52 pagesBasic Principle of Sanitary and Plumbing DesignCasandra TellesNo ratings yet
- Sanitary DesignDocument59 pagesSanitary DesignKHA120096 Student100% (2)
- C11 Demonstrate A Knowledge of Relevant StandardsDocument7 pagesC11 Demonstrate A Knowledge of Relevant StandardsSharvin MungurNo ratings yet
- Part-5 EU2Document20 pagesPart-5 EU2ashNo ratings yet
- M.E Group 3 ReportDocument43 pagesM.E Group 3 ReportDimple LapuzNo ratings yet
- Technical Terms: 1. PlumbingDocument7 pagesTechnical Terms: 1. PlumbingParth AnajwalaNo ratings yet
- Finals CE 314 - 084736Document7 pagesFinals CE 314 - 084736BASITO, CHRISTIAN PAUL B.No ratings yet
- House DrainageDocument37 pagesHouse DrainageSubhashish .DeyNo ratings yet
- Arch ScienceDocument6 pagesArch SciencehanaNo ratings yet
- What's Bugging Your Pipes: How Microorganisms Affect Plumbing SystemsFrom EverandWhat's Bugging Your Pipes: How Microorganisms Affect Plumbing SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Outdoor Plumbing Projects: Installing and Maintaining Sprinklers, Pools, and Other Water Features: Homeowner Plumbing Help, #6From EverandOutdoor Plumbing Projects: Installing and Maintaining Sprinklers, Pools, and Other Water Features: Homeowner Plumbing Help, #6No ratings yet
- Plumbing Book for Beginners: A Comprehensive DIY Guide to Plumbing System Fundamentals for Homeowners on Kitchen and Bathroom Sink, Drain, Toilet Repairs or Replacements: Homeowner Plumbing Help, #1From EverandPlumbing Book for Beginners: A Comprehensive DIY Guide to Plumbing System Fundamentals for Homeowners on Kitchen and Bathroom Sink, Drain, Toilet Repairs or Replacements: Homeowner Plumbing Help, #1No ratings yet
- Thesis Complete RevisedDocument26 pagesThesis Complete RevisedCarl Joseph Moredo50% (2)
- Francis Abaigar-Cot-English-4-Main-IdeaDocument11 pagesFrancis Abaigar-Cot-English-4-Main-IdeaFrancis AbaigarNo ratings yet
- Peoria County Booking Sheet 08/28/15Document10 pagesPeoria County Booking Sheet 08/28/15Journal Star police documentsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Notes (Properties of Fluid) PDFDocument23 pagesChapter 1 - Notes (Properties of Fluid) PDFHappy Ocean100% (1)
- Delivery Note - IBRU-BOC-PU-1160Document2 pagesDelivery Note - IBRU-BOC-PU-1160Santosh SridharNo ratings yet
- On The: An Interview With Dr. Leo ChengDocument1 pageOn The: An Interview With Dr. Leo ChengJulio Mauricio Vidaurre-RuizNo ratings yet
- Radio Program Liver Cancer and Depression 0126223 NarrativeDocument5 pagesRadio Program Liver Cancer and Depression 0126223 NarrativeMae Francesca Isabel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 12 2Document8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 12 2Rizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- Tiffany Chin CVDocument4 pagesTiffany Chin CVapi-455548272No ratings yet
- 2 Organ SystemsDocument5 pages2 Organ SystemsBeaNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Focus ReviewDocument9 pagesKaplan Focus ReviewSaidel ElizondoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: B13.4 DNA and The Human Genome Project: Connector: Questions On Prior Learning Linked To Todays LessonDocument46 pagesLesson Title: B13.4 DNA and The Human Genome Project: Connector: Questions On Prior Learning Linked To Todays LessonBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Data SF 2400Document2 pagesData SF 2400Francisco SalazarNo ratings yet
- Plaintiff-Appellee vs. vs. Defendant-Appellant Eliezer S. Tengco The Office of The Solicitor GeneralDocument10 pagesPlaintiff-Appellee vs. vs. Defendant-Appellant Eliezer S. Tengco The Office of The Solicitor GeneralGerard TinampayNo ratings yet
- Delayed Coking: Chapter 5Document34 pagesDelayed Coking: Chapter 5Arumugam Ramalingam100% (1)
- Pulsar45 OpmanualDocument28 pagesPulsar45 OpmanualNilson HurtadoNo ratings yet
- 500 QuestionsDocument54 pages500 QuestionsdprincebuchikoyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Surgical Sutures Review NotesDocument4 pagesBasics of Surgical Sutures Review NotesjeshemaNo ratings yet
- Product Description: 7.9 - 11.0 GHZ 15 W Gan Power AmplifierDocument26 pagesProduct Description: 7.9 - 11.0 GHZ 15 W Gan Power AmplifierBabak SaranNo ratings yet
- Performance of Functionally Modified Epoxy Nano Composites For FRP ApplicationsDocument7 pagesPerformance of Functionally Modified Epoxy Nano Composites For FRP ApplicationsHOD CIVIL DEPARTMENTNo ratings yet
- EsrDocument5 pagesEsrVirendra Singh Rajput100% (1)
- Basic Communication As NutritionistsDocument58 pagesBasic Communication As NutritionistsRima AuliyaNo ratings yet
- 11 BibliographyDocument24 pages11 BibliographyMehmudNo ratings yet
- Typhoon Yolanda: An Analysis On The Impact of Natural Disasters and Effectiveness of Disaster ManagementDocument7 pagesTyphoon Yolanda: An Analysis On The Impact of Natural Disasters and Effectiveness of Disaster ManagementAl TheaNo ratings yet
- GRP Non Circular Pipe SystemsDocument16 pagesGRP Non Circular Pipe Systemsseby_77No ratings yet
- Hempel Interior Filler 38840Document3 pagesHempel Interior Filler 38840Noman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Causes of Poverty in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesCauses of Poverty in The PhilippinesSannyboy Paculio DatumanongNo ratings yet
- Tools Kawasaki 2009 Recommended ItemsDocument5 pagesTools Kawasaki 2009 Recommended ItemsBrianCookNo ratings yet
- Polyurea Grease Mobil SHC PolyrexDocument2 pagesPolyurea Grease Mobil SHC PolyrextribolasNo ratings yet