0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsWeygan NCP
Weygan NCP
Uploaded by
Kate WeyganThe document contains two nursing care plans. The first plan addresses a patient with hyperthermia and includes assessments, goals, interventions and evaluations to monitor vital signs, assess for signs of hyperthermia, administer medications, and encourage fluid intake. The second plan addresses ineffective airway clearance and includes assessments, goals, interventions and evaluations to monitor respirations, assess consciousness and hydration, elevate the head of the bed, maintain hydration, and encourage deep breathing exercises.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Weygan NCP
Weygan NCP
Uploaded by
Kate Weygan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesThe document contains two nursing care plans. The first plan addresses a patient with hyperthermia and includes assessments, goals, interventions and evaluations to monitor vital signs, assess for signs of hyperthermia, administer medications, and encourage fluid intake. The second plan addresses ineffective airway clearance and includes assessments, goals, interventions and evaluations to monitor respirations, assess consciousness and hydration, elevate the head of the bed, maintain hydration, and encourage deep breathing exercises.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document contains two nursing care plans. The first plan addresses a patient with hyperthermia and includes assessments, goals, interventions and evaluations to monitor vital signs, assess for signs of hyperthermia, administer medications, and encourage fluid intake. The second plan addresses ineffective airway clearance and includes assessments, goals, interventions and evaluations to monitor respirations, assess consciousness and hydration, elevate the head of the bed, maintain hydration, and encourage deep breathing exercises.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesWeygan NCP
Weygan NCP
Uploaded by
Kate WeyganThe document contains two nursing care plans. The first plan addresses a patient with hyperthermia and includes assessments, goals, interventions and evaluations to monitor vital signs, assess for signs of hyperthermia, administer medications, and encourage fluid intake. The second plan addresses ineffective airway clearance and includes assessments, goals, interventions and evaluations to monitor respirations, assess consciousness and hydration, elevate the head of the bed, maintain hydration, and encourage deep breathing exercises.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Weygan, Deborah-kate A.
BSN 2B2
Actual Nursing Care Plan 1
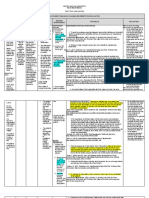
Assessment Goals Nursing interventions Rationale Evaluation
DATA STG: DX: STG:
Subjective: Within 4 hours of Nursing 1. Monitor vital signs. >To establish baseline >Goal Met
N/A Interventions and Health data. The patient was able to
Teachings, the patient will 2. Assess for signs of >To establish appropriate maintain normal core
be able to, maintain core Hyperthermia such as: interventions. temperature as evidenced
temperature within the poor skin turgor, dry oral by latest temperature of
normal range as membranes, dry lips, and 36.6.
Objective: manifested by decreased warm skin. >Dysrhythmias are
>Skin warm to touch temperature of 37.8 to 3. Monitor heart rate and common due to electrolyte
>Diaphoresis 36.6. rhythm. imbalance, dehydration, LTG:
>Temperature-37.8 C and direct effects of >Goal Met
hyperthermia on blood The patient was able to
Nursing Diagnosis: LTG: and cardiac tissue. demonstrate improved
>Hyperthermia Within 8 hours of Nursing level of ease and comfort
Interventions and Health as evidenced by the
Teachings, the patient will >To treat underlying patient feels comfortable
be able to demonstrate cause. and has good sleep
improved level of ease and pattern.
comfort. TX: >To promote rapid core
1. Administer medications cooling.
as prescribed.
2. Assist with internal >Exposing skin to room
cooling method like tepid air decreases heat and
sponge bath. increases evaporative
3. Loosen or remove cooling.
excess clothing and
covers. >Excessive cooling or
cooling too rapidly may
cause shivering, which
4. Modify cooling increases metabolic rate
measures based on the and temperature.
patient’s physical Shivering should be
response. avoided as it will hinder
cooling efforts.
>Promotes comfort and
helps chilling since
diaphoresis occurs during
defervescence.
5. Keep clothing and bed
linens dry. >If the client is alert
enough to swallow,
provide cool liquids to
help lower the body
EDX: temperature. Additionally,
1. Encourage adequate if the patient is dehydrated
fluid intake. or diaphoretic, fluid loss
contributes to fever.
>Fever is reportable,
especially in infants and
young children with or
without other symptoms
and in older children if it
is unresponsive to
2. Instruct the parent to antipyretic and fluids,
measure the child’s because it accompanies a
temperature, and what treatable infection(viral or
symptoms to report to the bacterial).
physician. >To prevent dehydration.
3.Discuss with the mother
the importance of
adequate fluid intake at all
times and ways to improve
hydration status when ill.
ACTUAL NURSING CARE PLAN 2
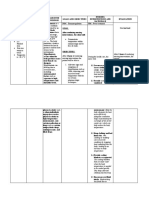
Assessment Goals Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Data STG: DX: STG:
Subjective: Within 4 hours of Nursing 1. Monitor respirations and >To establish baseline GOAL MET
N/A Interventions and breath sounds, noting rate data and interventions. >After 4 hour of Nursing
Therapeutic Managements and sounds. >This information is Interventions and
the patient will be able to, 2. Assess level of essential for identifying Therapeutic
demonstrate behaviors to consciousness/ potential for airway Managements, the
Objective: improve or maintain clear cognition and ability to problems, providing patient was able to
>Non-Productive and airway. protect own airway. baseline level of care demonstrate behaviors to
Ineffective cough needed, and influencing improve or maintain
>Not in distress choice of interventions. clear airway.
LTG: Within 8 hours of >Airway clearance is
Nursing Interventions and hindered by inadequate
Therapeutic Management, hydration and the
the patient will be able to 3. Assess the patient’s thickening of secretions.
Nursing Diagnosis: maintain airway patency. hydration status. LTG:
Ineffective Airway >Doing so would lower GOAL MET
Clearance the diaphragm and >After 8 hours of
promote chest expansion, Nursing Interventions
mobilization and to and Therapeutic
TX: breathe readily. managements, the
1. Elevate the head of the >Fluids help maintain patient was able to
head of the bed and keep the hydration and increase maintain airway patency.
patient on a moderate high ciliary action to remove
back rest. secretions and reduce
viscosity.
2. Maintain adequate >A sitting position
hydration, especially warm permits maximum lungs
liquids. excursion and chest
expansion.
>To relax smooth
respiratory musculature,
3. Place patient with proper deduce airway edema,
body alignment for and mobilize secretions.
maximum breathing pattern.
4. Administer medications
(expectorants, anti- >To maximize effort.
inflammatory agents)
>This prevent fatigue.
EDX: >Hydration can help
1. Encourage deep-breathing prevent the accumulation
exercise and coughing of viscous secretions and
exercises. improve airway
2. Encourage adequate rest. clearance.
3. Encourage increased fluid
intake and warm liquids.
DRUG STUDY
You might also like
- NCP Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP Electrolyte ImbalanceGertrude Araneta Javier94% (16)
- Fromm Reichmann, LonelinessDocument16 pagesFromm Reichmann, Lonelinessrachel.avivNo ratings yet
- Fever NCPDocument5 pagesFever NCPNikael Patun-og100% (1)
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument2 pagesNCP LeptospirosisLouise Anne Asuncion OclimaNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 6 - Demo COTDocument36 pagesMAPEH 6 - Demo COTLucena GhieNo ratings yet
- Benign Febrile ConvulsionDocument9 pagesBenign Febrile ConvulsionRoxanne Mae Marcelo Badongen100% (1)
- Urdaneta City University: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesUrdaneta City University: Nursing Care PlanDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- NCP Fever FinalDocument3 pagesNCP Fever FinalAllyssa Jane PragadosNo ratings yet
- NCP PediaDocument6 pagesNCP PediaJohn Kenley FerryNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument5 pagesHyperthermiaRapunzel Leanne100% (1)
- NCP TahbsoDocument18 pagesNCP TahbsoUzziah Dharambai GurbuxaniNo ratings yet
- Long Term: PT Will Demonstrate Increased Tolerance To Activity by DischargeDocument18 pagesLong Term: PT Will Demonstrate Increased Tolerance To Activity by DischargeMary Ann Ebol0% (1)
- Final-Na-Ncp-Nagyd-Ni 2Document9 pagesFinal-Na-Ncp-Nagyd-Ni 2Crezel Jean Casango AnNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Soure: Marilyn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr "Nursespocket Guide."14th Ed.p.784Document30 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Soure: Marilyn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr "Nursespocket Guide."14th Ed.p.784Jesil MarolinaNo ratings yet
- A CASE STUDY AND JOURNAL READING ONDocument16 pagesA CASE STUDY AND JOURNAL READING ONMatthew CalaraNo ratings yet
- Cor Jesu College, Inc., College of Health Sciences Sto. Rosario, Tres de Mayo, Digos CityDocument6 pagesCor Jesu College, Inc., College of Health Sciences Sto. Rosario, Tres de Mayo, Digos City2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet
- Hypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. DungcaDocument2 pagesHypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. DungcaJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- NCP Case PresDocument2 pagesNCP Case PresAnton QueralNo ratings yet
- NCP CholeDocument15 pagesNCP CholeEly Chelle AbuelNo ratings yet
- Wong Actual-NcpDocument2 pagesWong Actual-Ncpbulok netflakesNo ratings yet
- Cardenas Pericare:cath:urineDocument9 pagesCardenas Pericare:cath:urineChristeen Lyzet CardenasNo ratings yet
- Franz - NCP (Pedia) - YeyyyyDocument7 pagesFranz - NCP (Pedia) - YeyyyyJohn Kenley FerryNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAlyssa Moutrie Dulay Arabe100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAriaNo ratings yet
- Gender: FemaleDocument9 pagesGender: FemaleNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document10 pagesPresentation 1Olivelhynn BernaldoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Acute Bacterial MeningitisDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis Acute Bacterial MeningitisJane NuevaNo ratings yet
- NCPPPPDocument6 pagesNCPPPPIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument3 pagesHyperthermia NCPkaylejordan_29100% (2)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)
- Hyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLODocument4 pagesHyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLOMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis - Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesToxoplasmosis - Nursing Care PlanJulia Trisha MasukolNo ratings yet
- NCP Sample 1Document9 pagesNCP Sample 1Vincent BarcenillaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Child Nursing CareDocument3 pagesChild Nursing Carelina solihanNo ratings yet
- Viernes, Jericho NCP CimcDocument2 pagesViernes, Jericho NCP CimcJayson Respicio jr.No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationGenevieve Ann Abogada SuperioNo ratings yet
- Anemia NCPDocument20 pagesAnemia NCPNursidar Pascual Mukattil80% (5)
- "Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" AsDocument4 pages"Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" Ashanna caballoNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Sleep Pattern and Hypothermia (Care of Older Adult Issues)Document4 pagesNCP Disturbed Sleep Pattern and Hypothermia (Care of Older Adult Issues)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- NCPNICUDocument2 pagesNCPNICUJielyn San MiguelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On FeverDocument15 pagesNursing Care Plan On Feverkamini Choudhary100% (2)
- Dnrle Influenza NCPDocument3 pagesDnrle Influenza NCPEna RodasNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorhagic Fever (DHF)Document30 pagesDengue Hemorhagic Fever (DHF)Octa VianiNo ratings yet
- Dela Cena Geria NCP HyperthermiaDocument8 pagesDela Cena Geria NCP HyperthermiaBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument3 pagesHyperthermia NCPKate WeyganNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument7 pagesVital SignsEmeroot RootNo ratings yet
- Chona NCP 2Document3 pagesChona NCP 2Jan Mark SotoNo ratings yet
- Garcia Jomari A. BSN 2h Kawa-NcpDocument6 pagesGarcia Jomari A. BSN 2h Kawa-NcpRaid GarciaNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesHyperthermiapamgee100% (11)
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanSheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- NCP CASE STUDY - Acute PyelonephritisDocument9 pagesNCP CASE STUDY - Acute PyelonephritisyasiraNo ratings yet
- PDF NCP Electrolyte Imbalance - CompressDocument3 pagesPDF NCP Electrolyte Imbalance - Compressclaire yows100% (1)
- HyperthermiaDocument5 pagesHyperthermiaCarey Jamille YadanNo ratings yet
- Actual NCP Pt.Document2 pagesActual NCP Pt.Kate WeyganNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Independent: Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Independent: Short TermKen IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Feliciano, Troy Ivan Silva, Queenie Rose V. BSN 3-C: Rationale: To Track The Changes of Client's ConditionDocument4 pagesFeliciano, Troy Ivan Silva, Queenie Rose V. BSN 3-C: Rationale: To Track The Changes of Client's ConditionQueenie SilvaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia - NCPDocument5 pagesHyperthermia - NCPCarey Jamille YadanNo ratings yet
- ASKEP HIPERTERMI (English)Document7 pagesASKEP HIPERTERMI (English)SaamNo ratings yet
- Living Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineFrom EverandLiving Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineNo ratings yet
- Thyroidectomy Diet: A Beginner's 2-Week Step-by-Step Guide After Thyroid Gland Removal, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandThyroidectomy Diet: A Beginner's 2-Week Step-by-Step Guide After Thyroid Gland Removal, With Sample Recipes and a Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- How to Energize Your Life: 15 Simple Habits for a Boosted YouFrom EverandHow to Energize Your Life: 15 Simple Habits for a Boosted YouNo ratings yet
- CFS-CT CP 670 CP 673 CP 676: Safety Data SheetDocument8 pagesCFS-CT CP 670 CP 673 CP 676: Safety Data SheetforotherNo ratings yet
- Poshan Abhiyaan Progress ReportDocument7 pagesPoshan Abhiyaan Progress ReportSBP HazaribaghNo ratings yet
- Mljekarstvo 5 9 2009 p201 p208Document8 pagesMljekarstvo 5 9 2009 p201 p208serbian_freemanNo ratings yet
- Muhssin Abdul-Shaheed Ramadan: Professional Development ProgramDocument1 pageMuhssin Abdul-Shaheed Ramadan: Professional Development ProgramMuhssin abdulsheedNo ratings yet
- FK-NM SDSDocument12 pagesFK-NM SDSMEY PAPERNo ratings yet
- Cesc Communication LetterDocument2 pagesCesc Communication LetterMarvin VersozaNo ratings yet
- Olympus CV180 User Manual-CAP6 'N' 7 FUSE REPLACEMENT 'N' CARE, STORAGE AND DISPOSALDocument4 pagesOlympus CV180 User Manual-CAP6 'N' 7 FUSE REPLACEMENT 'N' CARE, STORAGE AND DISPOSALSandra OrduñaNo ratings yet
- 6 Tecar Vs Tens in Phantom Limb PainDocument8 pages6 Tecar Vs Tens in Phantom Limb PainSilvia PluisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Sigmund Freud Psychoanalytic Theory Part IDocument54 pagesLesson 3. Sigmund Freud Psychoanalytic Theory Part IClarizza Joy J. CuizonNo ratings yet
- Doctors List at Icf HospitalDocument4 pagesDoctors List at Icf HospitalMunusamy RajiNo ratings yet
- Nutrifactor - Nuroton Is Marvelous Supplement For Mood & Brain FunctionsDocument2 pagesNutrifactor - Nuroton Is Marvelous Supplement For Mood & Brain FunctionsMuhammad BabarNo ratings yet
- Sika Line Marking PaintDocument7 pagesSika Line Marking Paintfaisal nadeemNo ratings yet
- 2009 IChem EHazards XXIPaper 127Document13 pages2009 IChem EHazards XXIPaper 127Okechukwu KaluNo ratings yet
- MSDS Pe Wax Msa-500Document7 pagesMSDS Pe Wax Msa-500Usama WalyNo ratings yet
- Radserve InfoDocument98 pagesRadserve InfoOyetola AnuoluwaNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 Team 1Document7 pagesNCP 1 Team 1janalthea.dautilNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Presentation AssignmentDocument3 pagesClinical Case Presentation Assignmentapi-738548992No ratings yet
- Module 2 - The Basics of First AidDocument6 pagesModule 2 - The Basics of First AidRonald Michael QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Capillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestDocument4 pagesCapillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestGerly MaglangitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assesment 2019Document17 pagesNursing Assesment 2019Jemmy KherisnaNo ratings yet
- Traditional Management MethodsDocument5 pagesTraditional Management MethodsChristopher R. Bañez IINo ratings yet
- Different Settlement PatternsDocument14 pagesDifferent Settlement PatternsPrince Rizaldy S. Heti-ayonNo ratings yet
- Practical 3 MnabDocument12 pagesPractical 3 MnabSabby SaberonNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Major Project Management Problems in The Research and 9777Document6 pagesAnalysis of Major Project Management Problems in The Research and 9777Abhishek JainNo ratings yet
- Labour AnalysisDocument56 pagesLabour AnalysisArizky Margo AgungNo ratings yet
- Mastopexia en MultiplanosDocument9 pagesMastopexia en Multiplanossicemiv761No ratings yet
- Project Planning ManuscriptDocument7 pagesProject Planning ManuscriptEloisa CellonaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Somatic Work Part 3Document13 pagesIntro To Somatic Work Part 3William100% (1)