SciFiSH SDLP
SciFiSH SDLP
Uploaded by
john sibayanCopyright:
Available Formats
SciFiSH SDLP
SciFiSH SDLP
Uploaded by
john sibayanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
SciFiSH SDLP
SciFiSH SDLP
Uploaded by
john sibayanCopyright:
Available Formats
A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 3
I. Objectives
At the end of the lesson pupils will be able to;
a. differentiate vertebrate and invertebrate animals, (S3LT-IIc-d-3)
b. volunteer in answering questions about the topic; and
c. value the importance of vertebrate and invertebrate animals in our environment
through observation.
II. Subject matter
Topic: Classification of Animals
Reference: K-12 Curriculum guide
Values integration: Voluntarism and Active participation
Material: Flat screen tv, Power point presentation, Cut-out pictures
III. Learning procedure
A. Preliminary activity
1. Review
Anyone from the class, what was our topic last meeting?
What did you learn from our discussion?
2. Motivation
Let’s play a guessing game.
“Guess the animals in the pictures”
What do you see in the picture?
Does it have a bone?
What does it do, can it fly or swim?
B. Developmental activity
a. Presentation
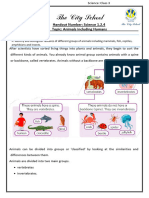
Classification of animals, it means grouping animals according to
similarity. Classification of animals, covers the animal kingdom
wherein, they are classified as vertebrate and invertebrate animals.
1. Vertebrate Animals
-An animal that has a backbone and skeleton.
Subgroup of Vertebrate Animals
a. Mammals - warm blooded animals, with fur or hair. They live
on land and water.
Examples: lion, dog, dolphin.
Does every mammal have four limbs/legs?
b. Birds – warm blooded animals, with wings, feathers, beaks
and two legs. They live on land and air.
Examples: penguin, chicken, eagle.
Does every bird fly?
c. Reptiles - cold blooded animals, that has scales instead of
fur or feathers. They live on both land and water.
Examples: crocodile, turtle, snake.
d. Amphibians - cold blooded animals, that don’t have scales
but they have moist or smooth skin. They live on land and
water.
Examples: frogs, newts, salamanders.
e. Fish - cold blooded animals, that has gills but lack limbs.
They live in water.
Examples: shark, gold fish, swordfish.
What are the similarities and differences of vertebrate
animals?
What type of vertebrate animals, lay eggs and give live
births?
2. Invertebrate Animals
-animals without backbone or bony skeleton.
Subgroup of invertebrate animals
a. Cnidarias – are soft-bodied stinging animals that live in water.
Examples: corals, jellyfish, sea anemone.
b. Echinoderms – are group of animals that live in on the ocean
floor. They have spiny, and bumpy skins.
Examples: starfish, sea cucumber, sea urchin.
c. Mollusks – are animals that has a soft body, and some are
covered with shells.
Examples: snail, octopus, squid.
d. Annelids – are animals that has a soft body, no legs, and no
shell. Also called as segmented worms.
Example: earthworm, leeches, ragworm.
e. Arthropods - animals that have a hard-outer shell. Includes
arachnids and insects.
Examples: cockroach, crabs, spiders.
What is the difference between arachnids and insects?
What is the difference between vertebrate and invertebrate
animals? What can you say about the size?
b. Application
Divide the class into two groups and distribute the cut-out pictures in
each group.
Place the cut-outs in their corresponding column or classification.
Vertebrate Animals Invertebrate Animals
C. Generalization
What was our topic for today?
What are the two classifications of animals that we discuss?
How many subgroups of invertebrate and vertebrate animals did we discuss?
IV. Evaluation
A. Read and answer. Write T if the statement is true and F if the statement is false.
1. Vertebrate animals are animals that has a backbone and skeleton.
2. Classification of animals, covers the animal kingdom.
3. Mammals are animals with gills and can breathe under water.
4. Invertebrate animals are animals without backbone or bony skeleton.
B. Write three (3) subgroups/types of vertebrate and invertebrate animals.
Vertebrate animal subgroups:
1.
2.
3.
Invertebrate animal subgroups:
1.
2.
3.
V. Assignment
Write examples of vertebrate and invertebrate animals, two (2) examples each
subgroup. Write it in your notebook.
Prepared by: Checked by:
Epak, Jethro Mrs. Delia Sumeg-ang
Sibayan, John
You might also like
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 6 Quarter 2 VertebratesDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 6 Quarter 2 VertebratesCid Poniente100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - VertebratesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Vertebrateslrac_adazol87% (15)
- Classifying Vertebrates 2nd Grading Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesClassifying Vertebrates 2nd Grading Lesson PlanJermeeNo ratings yet
- VertebratesDocument6 pagesVertebratesNillyn Dela Cera MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Casas 7es Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesCasas 7es Lesson PlanMark Kenette RedonaNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Q2-W4Document68 pagesScience 6 Q2-W4NORANo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlanGR Ac IaNo ratings yet
- Karlo Cot q2Document7 pagesKarlo Cot q2karlo bernaldezNo ratings yet
- Cot ScienceDocument4 pagesCot Sciencevictor jr. regala100% (2)
- DAILY LESSON PLAN Science 6Document6 pagesDAILY LESSON PLAN Science 6judyannmaranancortez0927100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in General BiologyDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in General BiologyJENNICA GRACE E. YNCHAUSTINo ratings yet
- Science SSESDocument3 pagesScience SSESJnz OlanNo ratings yet
- Science6 Q2 Mod5 AnimalsCharacteristicsofInvertabrates V4Document15 pagesScience6 Q2 Mod5 AnimalsCharacteristicsofInvertabrates V4France Kenneth SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan VertebratesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan VertebratesPrakasha B GNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Science 4 VertebratesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Science 4 VertebratesRoselyn Roco100% (2)
- Science6 - Q2 - Lesson Plan On Determine The Distringuishing Characteristics of VertebratesDocument6 pagesScience6 - Q2 - Lesson Plan On Determine The Distringuishing Characteristics of VertebratesMaria Theresa DemeterioNo ratings yet
- Science and Health V: 38. DateDocument2 pagesScience and Health V: 38. DateRichardDumlaoNo ratings yet
- Caraga Central Elementary School VI Janneth M. Tipudan Science Second I. Objectives A. Content Standard B. Performance StandardsDocument5 pagesCaraga Central Elementary School VI Janneth M. Tipudan Science Second I. Objectives A. Content Standard B. Performance StandardsRey Abdon IbañezNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Q2 W4Document80 pagesScience 6 Q2 W4Jovy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 6Document5 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6Dh ELNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 6 - SMILE LP - Quarter 2 - Week 4 - 5 - VERTEBRATES AND INVERTEBRATESDocument9 pagesSCIENCE 6 - SMILE LP - Quarter 2 - Week 4 - 5 - VERTEBRATES AND INVERTEBRATESAnieda SabileNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 6 Quarter 2 VertebratesDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 6 Quarter 2 VertebratesRoxieth Comendador BokingkitoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan VertebratesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Vertebratesjenina dionisio100% (1)
- Animals Without BackbonesDocument29 pagesAnimals Without BackbonesAna Liza DegamoNo ratings yet
- Demo Lesson in Science No.2Document9 pagesDemo Lesson in Science No.2almaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - GS - Animals (Class 3)Document2 pagesQuestion Bank - GS - Animals (Class 3)GaneshkumarAnbukkani100% (2)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology 2 (Grade 12)Document7 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology 2 (Grade 12)Gomez Agustin Leslie100% (1)
- InvertebratesDocument13 pagesInvertebratesIvy Joy Cantomayor LazonaNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates PDFDocument13 pagesInvertebrates PDFNutmegNo ratings yet
- Science6 Q2 Mod4 AnimalsCharacteristicsofVertabrates V4Document17 pagesScience6 Q2 Mod4 AnimalsCharacteristicsofVertabrates V4Francois SorianoNo ratings yet
- Review AnimalsDocument28 pagesReview AnimalsyffgolvhgNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2q Sci - Docx 2024 25Document6 pagesLesson Plan 2q Sci - Docx 2024 25Grace NaduaNo ratings yet
- Class V G.Science First Term Notes of Unit 1 New 2024-25Document9 pagesClass V G.Science First Term Notes of Unit 1 New 2024-25sanaazhar227No ratings yet
- Q2 G6 Science M2Document20 pagesQ2 G6 Science M2Noel B. InuguidanNo ratings yet
- COT - 4a's LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 6 - SY 2021-2022Document6 pagesCOT - 4a's LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 6 - SY 2021-2022KJMD Kent Joshua M. Dumam-ag100% (10)
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4 Animals: Characteristics of VertebratesDocument18 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 4 Animals: Characteristics of VertebratesAsela O. Arias100% (3)
- Week 6 Sept.23-26, 2019Document13 pagesWeek 6 Sept.23-26, 2019Heidi Dalyagan DulnagonNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Bio Chap Answer - Key - 3Document6 pagesClass 7 Bio Chap Answer - Key - 3Laiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Karlo Cot q2Document7 pagesKarlo Cot q2karlo bernaldezNo ratings yet
- Class 4 Subject Science Chapter 3 Animal KingdomDocument3 pagesClass 4 Subject Science Chapter 3 Animal KingdomShubhjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in Science 4 Quarter 2Document8 pagesActivity Sheet in Science 4 Quarter 2Mhadz Reyes100% (7)
- q2 Week 5, Day 1 Cot 2 FinalDocument3 pagesq2 Week 5, Day 1 Cot 2 FinalUziel Joy TapangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PDFDocument5 pagesLesson Plan PDFMargie lajotNo ratings yet
- 1.2.4 Handout (Vertebrates)Document3 pages1.2.4 Handout (Vertebrates)mfatehkhanNo ratings yet
- Science6 Q2 Mod5 AnimalsCharacteristicsofInvertabrates V4Document16 pagesScience6 Q2 Mod5 AnimalsCharacteristicsofInvertabrates V4Asela O. Arias100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Animals EverywhereDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Animals Everywherearpita bhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Science6 Q2 - Lesson On Determine The Distinguishing Characteristics of VertebratesDocument50 pagesScience6 Q2 - Lesson On Determine The Distinguishing Characteristics of VertebratesMaria Theresa DemeterioNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 5Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade 5MordecaiNo ratings yet
- How Animals SurviveDocument3 pagesHow Animals SurviveDebolina BaishyaNo ratings yet
- 1st Cot Sc3444Document7 pages1st Cot Sc3444Lynn LynnNo ratings yet
- Biology WorkbookDocument9 pagesBiology WorkbookumeshlpsNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Science 4Document47 pagesWeek 2 - Science 4Jean Marie GomezNo ratings yet
- Inbound 6311546274918139139Document17 pagesInbound 6311546274918139139Ralf Joseph CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Unit Animals Lesson 1 Classifying CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesUnit Animals Lesson 1 Classifying Characteristicsapi-545554684No ratings yet
- Science Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 4-5)Document26 pagesScience Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 4-5)Denver TamayoNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson Plan in Science 6, 2nd Gradimg.Document8 pagesCot Lesson Plan in Science 6, 2nd Gradimg.princess nicole lugtuNo ratings yet
- Animal ClassificationsvertebratesandinverDocument27 pagesAnimal ClassificationsvertebratesandinverSana Ishtiaq100% (1)
- Class 4 - Science Chapter - 3 Adaptations in AnimalsDocument8 pagesClass 4 - Science Chapter - 3 Adaptations in AnimalsBhawna Kapoor100% (1)
- Why There Is No Theory in Comparative PsychologyDocument14 pagesWhy There Is No Theory in Comparative PsychologyLuiz Helvécio Marques SegundoNo ratings yet
- (Everybody Up 4 - Unit 5 & 6) : Revision Worksheet 2Document2 pages(Everybody Up 4 - Unit 5 & 6) : Revision Worksheet 2Minh HằngNo ratings yet
- P-27 Geological Time ScaleDocument2 pagesP-27 Geological Time ScaleFelix Joshua.B 10 BNo ratings yet
- Bestiary of The BeyondDocument128 pagesBestiary of The Beyondalexhow100% (3)
- Scientific Names of Animals and BirdsDocument3 pagesScientific Names of Animals and BirdsNAYAN JYOTI KALITA100% (1)
- Manual D&D 5e - Dragão PrismáticoDocument5 pagesManual D&D 5e - Dragão PrismáticoMurillo VazNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade IiiDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade IiiBhen GieNo ratings yet
- Pre-A1 Week 19-Lets Help Endangered Animals EdwinDocument6 pagesPre-A1 Week 19-Lets Help Endangered Animals EdwinJhon brayan Espinosa salazarNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension The Adventure BeginsDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension The Adventure BeginsShayma ReyadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Soil OrganismsDocument32 pagesLesson 8 Soil OrganismsJosue A. Sespene Jr.No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan For Classroom Observation: Angelico J. Medina Memorial SchoolDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan For Classroom Observation: Angelico J. Medina Memorial SchoolMs. AyyaNo ratings yet
- ZOOLOGYDocument4 pagesZOOLOGYsyamprasadNo ratings yet
- Dinosaurs of The Lost Valley (8045960)Document87 pagesDinosaurs of The Lost Valley (8045960)Gon_1313100% (2)
- Animal KingdomDocument5 pagesAnimal Kingdommickey.jaduNo ratings yet
- TLE 158 Different Types of FowlDocument6 pagesTLE 158 Different Types of FowlSushi WasabiNo ratings yet
- Kosa Kata Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesKosa Kata Bahasa InggrisMUHAMMAD IQBALNo ratings yet
- Natural Classification of Organisms Based On Criteria (2021)Document17 pagesNatural Classification of Organisms Based On Criteria (2021)Alisha JasaniNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 4th Quarter - ACTIVITY #1-5Document7 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 4th Quarter - ACTIVITY #1-5Kimberly AyusoNo ratings yet
- Zoology 4Document18 pagesZoology 4danishNo ratings yet
- World Distribution of Plants and AnimalsDocument19 pagesWorld Distribution of Plants and AnimalsNeesha 0114No ratings yet
- Materi News ItemDocument3 pagesMateri News ItemlasintusmanaluNo ratings yet
- A Large-Sized Mammalian Coprolite Containing Ground Sloth OsteodermsDocument12 pagesA Large-Sized Mammalian Coprolite Containing Ground Sloth OsteodermsCrocodilo VasconcelosNo ratings yet
- Alaska Kushtaka ? Origin Tlingit Folklore Description Shape-Shifting Crea - 20241101 - 005353 - 0000Document49 pagesAlaska Kushtaka ? Origin Tlingit Folklore Description Shape-Shifting Crea - 20241101 - 005353 - 0000castile.dungeonNo ratings yet
- Death Save Repeat - Level Adjustment GuideDocument4 pagesDeath Save Repeat - Level Adjustment Guidetalanjones2000No ratings yet
- GY 112 Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesGY 112 Lecture NotesSyed Jabed Miadad AliNo ratings yet
- Bakkegard Et Al 2022 - INVENTARIO HERPETOLÓGICO DE LA BASE NAVAL DE GTMODocument15 pagesBakkegard Et Al 2022 - INVENTARIO HERPETOLÓGICO DE LA BASE NAVAL DE GTMOManuel IturriagaNo ratings yet
- Galapagos Darwin, Evolution, and ENTDocument4 pagesGalapagos Darwin, Evolution, and ENTkevin eNo ratings yet
- 7 A Gorilla in The GuestDocument2 pages7 A Gorilla in The GuestKshiteej Kabra17% (6)
- Introduction To InsectsDocument28 pagesIntroduction To InsectsHariprasanth SekarNo ratings yet
- G11 Worksheet AK Ch24 L1 AnimalsDocument5 pagesG11 Worksheet AK Ch24 L1 AnimalsLayal AlsoufiNo ratings yet