Reproduction Worksheet
Uploaded by
-Bleh- WalkerReproduction Worksheet
Uploaded by
-Bleh- WalkerName: Block: Date:
Biology 12 - The Reproductive System!
• Part A: Definitions: Please define or explain the following terms, in your OWN WORDS, in as few words as
clarity allows.
a) testes
b) scrotum
c) seminiferous tubules
d) epididymis
e) sperm
f) vas deferens
g) acrosome
h) spermatogenesis
i) penis
j) Interstitial cells
k) Sertoli cells
l) Semen
m) seminal fluid
n) seminal vesicles
o) prostate gland
p) Cowper’s glands
q) urethra
r) testosterone
s) FSH (in males)
t) LH (in males)
u) ovaries
v) oviducts
w) uterus
x) cervix
y) vagina
z) follicles
aa) oocyte
bb) zona pellucida
cc) ovulation
dd) corpus luteum
ee) clitoris
ff) hypothalamus
gg) FSH
RAYCROFT Worksheet - Reproduction - Page 1 of 4
Part B: Fill In The Blanks
1. The part of the male reproductive system that creates an antacid secretion is called the ________________
________________.
2. Semen is composed of ________________, which is made in the ________________tubules, and
secretions from the ________________gland, ________________glands, and
________________vesicles.
3. The seminal vesicles secrete a fluid that is rich in the monosaccharide ________________, which serves
as ________________for the sperm.
4. Cowper’s glands secrete a fluid that acts as a ________________.
5. The ________________cells in the testes produce testosterone in response to the hormone LH.
6. The hormone ________________promotes spermatogenesis.
7. The male hormone testosterone is a ________________hormome, meaning that it is ________________-
soluble. Like all steroid hormones, it is derived from the steroid hormone ________________.
8. ________________is made inside the seminiferous tubules and sent from there to the
________________for storage.
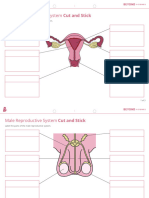
9. Label the diagram of the male reproductive system.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
10. List the structures through which sperm passes in order, from the following list: epididymis, seminiferous
tubules, urethra, penis, vas deferens. ________________________________, ________________,
________________________________, ________________, ________________
11. Label the parts of the diagram of the sperm cell and list a function for each part:
Name Function
W
X
Y
Z
12. List 3 function of testosterone
A
B
C
13. The ____________produces the hormone GnRH when testosterone and ___________levels are
________.
14. This causes the ________________pituitary gland to release ________________and ________________.
15. LH causes ________________cells in the testes to release more ________________.
RAYCROFT Worksheet - Reproduction - Page 2 of 4
Name: Block: Date:
16. FSH causes the seminiferous tubules to absorb more ________________, which in turn causes them to
produce more ________________. As it makes more sperm, it also releases more of the hormone
________________. High levels of this hormone feedback to the ________________and
________________, causing them to release less of their hormones.
17. Label the following diagram and give a function for each labeled part.
Name Function
18. List 3 functions of estrogen:
A
B
C
19. The entrance to the uterus is called the ________________.
20. The female erectile organ containing many sensory nerve receptors is called the ________________.
21. the menstrual cycle lasts on average _____days. Day 1 is the first day that ________________starts, and
usually finishes by day 5.
22. During menstruation, levels of female ________________are low.
23. In the follicular phase (days 1 – 14), low levels of hormones are detected by the hypothalamus, which
releases ________________. This is sent to the pituitary gland, which releases _________and
_________.
24. FSH causes several immature ____________, along with their surrounding ________________cells, in the
ovaries to begin to develop. The developing follicle cells release increasing amounts of
________________.
25. This hormone is responsible for the ________________phase of the uterine cycle. In the uterus,
________________vessels and ________________proliferate.
26. Rising levels of estrogen cause the release of a large amount of LH on about day 13 which causes
________________.
27. Ovulation normally occurs on day ________________. In ovulation, the ________________is released
from the ovary, leaving behind the ________________cells, which go on to form the ________________
________________. This structure continues to release the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Of
these two hormones, ________________is most important for the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle. This
hormone cause the ________________phase of the uterine cycle. The uterine glands mature and release
a thick mucus, and the endometrium ________________in thickness.
28. High levels of ________________cause ________________feedback to the anterior pituitary, shutting
down the release of _________. Lower levels of LH cause the __________________ ______________to
disintegrate. Since it is breaking down, it can no longer release estrogen and progesterone.
29. Low levels of female ________________by day 28 will cause the uterine ________________to be shed,
and the cycle will start anew.
30. However, if fertilization happens, the ________________cycle will be interrupted. Fertilization usually
occurs in the upper ________________. The fertilized egg is first called a ZYGOTE and then an
________________as it divides through mitosis.
RAYCROFT Worksheet - Reproduction - Page 3 of 4
31. The embryo, upon reaching the UTERUS, will embed itself into the endometrium. This is called
________________.
32. A shared set of membranes called the placenta forms around the embryo. This will begin to secrete the
hormone HCG, which temporarily maintains the corpus luteum.
33. As the placenta develops and matures, it makes its own ________________and ________________. This
will maintain the uterine lining so that ________________does not occur during pregnancy.
34. After 9 months, the fetus is ready to be born. The pressure of the baby’s head against the cervix causes a
nerve impulse to be sent to the hypothalamus. This causes the hypothalamus to release the hormone
________________to the pituitary, which releases it into the blood. This hormone causes
________________. It operates on a ________________feedback loop. The hormone causes the uterine
muscles to ________________with ever greater intensity until the baby is pushed out of the uterus through
the ________________, which serves as the birth canal.
35.
RAYCROFT Worksheet - Reproduction - Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- SCIENCE-10-Q3 WORKSHEET REVISED COPY-week-1-771% (7)SCIENCE-10-Q3 WORKSHEET REVISED COPY-week-1-746 pages
- Anatomy of The Reproductive System No PathoNo ratings yetAnatomy of The Reproductive System No Patho5 pages
- Acfrogco0l3vjrnkqmbmadvtgnuzmglrgnre Wi50x5h89xxy9bgtsvwkh9b65itlr8kiwdrbzk3rsaoi9jxiigwyysp7 1cox7hrso8eojxvxme7 Currdjedquyh79gf Qnl2dxwtd3jtouizuNo ratings yetAcfrogco0l3vjrnkqmbmadvtgnuzmglrgnre Wi50x5h89xxy9bgtsvwkh9b65itlr8kiwdrbzk3rsaoi9jxiigwyysp7 1cox7hrso8eojxvxme7 Currdjedquyh79gf Qnl2dxwtd3jtouizu2 pages
- Anatomy and Physiology/Lymphatic System Chapter 10-ObjectivesNo ratings yetAnatomy and Physiology/Lymphatic System Chapter 10-Objectives9 pages
- Worksheet. Chapter 12. Human Reproductive SystemNo ratings yetWorksheet. Chapter 12. Human Reproductive System2 pages
- 607107-Guided Notes - Human Reproduction and DevelopmentNo ratings yet607107-Guided Notes - Human Reproduction and Development6 pages
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Quarter 3 Sci10 Week 1-2No ratings yetLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Quarter 3 Sci10 Week 1-25 pages
- Science 10 Hormoses and the Reproductive System LAS (1)No ratings yetScience 10 Hormoses and the Reproductive System LAS (1)6 pages
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Quarter 3 Sci10 Week 1-2 For RemediationNo ratings yetLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Quarter 3 Sci10 Week 1-2 For Remediation6 pages
- NUMC 101B Endocrine System Laboratory Exercise100% (1)NUMC 101B Endocrine System Laboratory Exercise17 pages
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual CycleNo ratings yetScience: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual Cycle26 pages
- One Word Questions - Physiology - Fill Ups and Location Type QuestionsNo ratings yetOne Word Questions - Physiology - Fill Ups and Location Type Questions16 pages
- Endocrine and Nervous Overview - 2-CombinedNo ratings yetEndocrine and Nervous Overview - 2-Combined10 pages
- Female Reproductive System, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandFemale Reproductive System, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Sperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ovum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- MM ACADEMY 1ST SUNDAY TEST 26.1.2025 BY STUDY CORNERNo ratings yetMM ACADEMY 1ST SUNDAY TEST 26.1.2025 BY STUDY CORNER10 pages
- Analytical Techniques AS Chemistry QP WS Hard MSNo ratings yetAnalytical Techniques AS Chemistry QP WS Hard MS16 pages
- 2021 Level LS Physics Basic Questions Chap 1-5 (BTG)No ratings yet2021 Level LS Physics Basic Questions Chap 1-5 (BTG)65 pages
- Allah in Relationship With The Created WorldNo ratings yetAllah in Relationship With The Created World4 pages
- 2021 Level L Biology Practical Based QuestionsNo ratings yet2021 Level L Biology Practical Based Questions61 pages
- G10 Science Q3 The Human Reproductive System - PresentationNo ratings yetG10 Science Q3 The Human Reproductive System - Presentation37 pages
- Name: - Score: - Summative Test No. 1 in Science Second Quarter100% (2)Name: - Score: - Summative Test No. 1 in Science Second Quarter19 pages
- Parts and Description of The Male Reproductive SystemNo ratings yetParts and Description of The Male Reproductive System25 pages
- Lesson 4 - Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionNo ratings yetLesson 4 - Anatomy and Physiology of Reproduction34 pages
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMNo ratings yetANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM6 pages
- Science 6 - q1 - Unit 1 - Lesson 1 - The Human Reproductive SystemNo ratings yetScience 6 - q1 - Unit 1 - Lesson 1 - The Human Reproductive System133 pages
- Vaginismus A Review of The Literature On The Classification Diagnosis, Etiology and Treatment TranslateNo ratings yetVaginismus A Review of The Literature On The Classification Diagnosis, Etiology and Treatment Translate14 pages
- Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemNo ratings yetPhysiology of Female Reproductive System22 pages
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5From EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5
- Acfrogco0l3vjrnkqmbmadvtgnuzmglrgnre Wi50x5h89xxy9bgtsvwkh9b65itlr8kiwdrbzk3rsaoi9jxiigwyysp7 1cox7hrso8eojxvxme7 Currdjedquyh79gf Qnl2dxwtd3jtouizuAcfrogco0l3vjrnkqmbmadvtgnuzmglrgnre Wi50x5h89xxy9bgtsvwkh9b65itlr8kiwdrbzk3rsaoi9jxiigwyysp7 1cox7hrso8eojxvxme7 Currdjedquyh79gf Qnl2dxwtd3jtouizu
- Anatomy and Physiology/Lymphatic System Chapter 10-ObjectivesAnatomy and Physiology/Lymphatic System Chapter 10-Objectives
- 607107-Guided Notes - Human Reproduction and Development607107-Guided Notes - Human Reproduction and Development
- Science 10 Hormoses and the Reproductive System LAS (1)Science 10 Hormoses and the Reproductive System LAS (1)
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Quarter 3 Sci10 Week 1-2 For RemediationLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Quarter 3 Sci10 Week 1-2 For Remediation
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual CycleScience: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Feedback Mechanisms Involved in The Regulating Processes of Menstrual Cycle
- One Word Questions - Physiology - Fill Ups and Location Type QuestionsOne Word Questions - Physiology - Fill Ups and Location Type Questions
- Female Reproductive System, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandFemale Reproductive System, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related Conditions
- Sperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related Conditions
- Ovum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related Conditions
- MM ACADEMY 1ST SUNDAY TEST 26.1.2025 BY STUDY CORNERMM ACADEMY 1ST SUNDAY TEST 26.1.2025 BY STUDY CORNER
- 2021 Level LS Physics Basic Questions Chap 1-5 (BTG)2021 Level LS Physics Basic Questions Chap 1-5 (BTG)
- G10 Science Q3 The Human Reproductive System - PresentationG10 Science Q3 The Human Reproductive System - Presentation
- Name: - Score: - Summative Test No. 1 in Science Second QuarterName: - Score: - Summative Test No. 1 in Science Second Quarter
- Parts and Description of The Male Reproductive SystemParts and Description of The Male Reproductive System
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
- Science 6 - q1 - Unit 1 - Lesson 1 - The Human Reproductive SystemScience 6 - q1 - Unit 1 - Lesson 1 - The Human Reproductive System
- Vaginismus A Review of The Literature On The Classification Diagnosis, Etiology and Treatment TranslateVaginismus A Review of The Literature On The Classification Diagnosis, Etiology and Treatment Translate