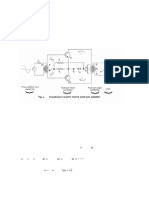
Comparison
Comparison
Uploaded by
SATYA TECHCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparison
Comparison
Uploaded by
SATYA TECHCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Comparison
Comparison
Uploaded by
SATYA TECHCopyright:
Available Formats
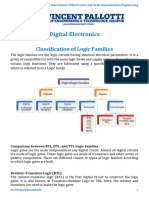
Logic Family (Silicon Technology) Introduction Features Limitations
1. RTL - In common use before the development - Low speed, high power dissipation
First logic family, require minimum number
of ICs. Common Emitter Configuration. of transistors. Low fan out, poor noise immunity
(Resistor Transistor Logic)
Logic 1: 1-3.6 V and Logic 0: 0.2V Operating speed <4MHz.
2. DCTL Direct coupled transistors. Simpler than RTL, easy to fabricate. Small logic swing, poor noise margin.
(Direct Coupled Transistor Logic) Base resistors of RTL are removed. Fewer components hence economical. Current hogging
Use diodes and transistors.
First circuit configuration designed into IC.
3. DTL Very small in size and high reliability at No low and constant output impedance
- Input is fed through diodes followed by in both states.
(Diode Transistor Logic) very low price.
transistor at the output side.
Greater fan out and improved noise margins.
4. TTL Use all transistors totem pole output. Fast switching time, larger fan out. Large current spike when switching
Function of diodes in DTL is performed Reduced silicon chip area. from low to high.
(Transistor-Transistor Logic) by multi-emitter transistor at input Easy to interface with other logic families. - Less noise immunity (0.4V)
- Merged Transistor Logic (MTL). High component density, less power
5. IIL Both PNP and NPN transistors are used. dissipation.
(Integrated Injection Logic) Low metal interconnection.
Poor noise immunity.
Designed around multi-collector
inverting transistors. Used in MSI and LSI designs.
Non saturated logic/Current mode logic. Require large silicon area, high power
Non-Saturated Logic 6.ECL - Compliment output/eliminates the need
Fastest logic family
dissipation (high cost).
ON - Active Mode of inverter. Used in very high frequency applications.
(Emitter Coupled Logic) Inconvenient voltage levels.
OFF Cut Off Mode No noise spikes, large fan out. Low noise margins.
Logic 1: -0.8 and Logic 0: -1.7
7.MOS Logic Use pMOS, nMOS or both with high
packaging density. Lower power dissipation. Larger propagation due to high output
MOS Logic Families (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Shorter rise and fall times. impedance.
Unipolar Transistor Technology) Logic) - Easy to design and fabricate Large fan-out. Noise margin is around 1V.
Less power drawn due to gate dielectric.
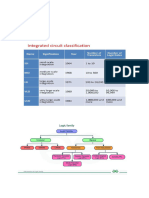
Parameter RTL IIL DTL HTL TTL ECL MOS CMOS
Basic Gate NOR NOR NAND NAND NAND OR-NOR NAND NOR-NAND
Fan Out 5 Depends on Injector Current 8 10 10-20 25 20 20-50
Power Dissipation 12 mW 6 nW -70 uW 8-12 mW 55 mW 10 mW 40-55 mW 0.2-10 mW 0.025-1.01 mW
Noise Immunity Nominal Poor Good Excellent Very Good Poor Good Very Good
Propagation Delay 12 nSec 25-30 nSec 30 nSec 4 nSec 10 nSec 1-2 nSec 300 nSec 70 nSec
Clock Rate 8 MHZ 72 MHz 4 MHz 35 MHz +60 MHz 2 MHz 10 MHZ
Speed X Power 144 Less than 1 300 100 100 60 70
You might also like
- KPMG GAAP Revenue RecognitionDocument1,109 pagesKPMG GAAP Revenue Recognitionel inNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Simulation History Matching and ForecastingDocument60 pagesReservoir Simulation History Matching and ForecastingnoorNo ratings yet
- Four Laws FinalDocument40 pagesFour Laws FinalsubesinghNo ratings yet
- 1zba4523 - 101 Load Loss CalculationDocument18 pages1zba4523 - 101 Load Loss CalculationRamaKrishna A100% (1)
- Comparison of Ic Logic FamiliesDocument1 pageComparison of Ic Logic FamiliesPiash DasNo ratings yet
- Comparison of IC Logic Families: April 2017Document2 pagesComparison of IC Logic Families: April 2017Jemshihas APNo ratings yet
- Comparison of I C Logic FamiliesDocument2 pagesComparison of I C Logic FamiliesVinod kumarNo ratings yet
- Comparison of I C Logic FamiliesDocument2 pagesComparison of I C Logic FamiliesK N KishoreNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Logic FamiliesDocument7 pagesComparison of Logic FamiliesVedantNo ratings yet
- Mendoza, Aldrin - Assignment2Document3 pagesMendoza, Aldrin - Assignment2Aldrin MndzNo ratings yet
- 7 Logic FamiliesDocument5 pages7 Logic FamiliesWade DachNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay State University: AC221: Fundamentals of Electronic CircuitsDocument8 pagesPresident Ramon Magsaysay State University: AC221: Fundamentals of Electronic CircuitsWade DachNo ratings yet
- Mendoza Assignment2Document3 pagesMendoza Assignment2Aldrin MndzNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Logic Family: (Electronics: PHYS4008)Document20 pagesLecture Notes For Logic Family: (Electronics: PHYS4008)Tanvir kabirNo ratings yet
- LOGIC FAMILYDocument5 pagesLOGIC FAMILYwonderingifiyNo ratings yet
- CoursTartarin STRI TRI L3 2024 Part2bDocument44 pagesCoursTartarin STRI TRI L3 2024 Part2bMinyar JabriNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: NIT Logic FamiliesDocument35 pagesDigital Electronics: NIT Logic FamiliesIroha IsshikiNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic FamilyDocument17 pagesDigital Logic Familydd3613667No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Digital Logic FamiliesDocument15 pagesUnit 5 - Digital Logic Familiesranjankushwaha712No ratings yet
- Basics: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document6 pagesBasics: Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)05851A0457No ratings yet
- slypa29Document36 pagesslypa29ricknmorty1103No ratings yet
- DS Unit 1 Logic FamiliesDocument55 pagesDS Unit 1 Logic Familiesanjaliumeshbhamare1234No ratings yet
- 1um 1064nm 3 Port Polarization Insensitive Optical CirculatorDocument2 pages1um 1064nm 3 Port Polarization Insensitive Optical CirculatorDK PhotonicsNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic FamiliesDocument28 pagesDigital Logic FamiliesRalphNo ratings yet
- This Experiment Is Individual!Document5 pagesThis Experiment Is Individual!Rachel MonesNo ratings yet
- DD - Lecture 1 - PCDocument31 pagesDD - Lecture 1 - PCRaju ReddyNo ratings yet
- ECEG3101-LC-Lec - 04 - Digital IC Families-1Document36 pagesECEG3101-LC-Lec - 04 - Digital IC Families-1Tsinat WondimuNo ratings yet
- Logic Families PDFDocument10 pagesLogic Families PDFBhavya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Full Adder Using Different XOR GatesDocument5 pagesDesign and Implementation of Full Adder Using Different XOR GatesEvans MuokiNo ratings yet
- 4logic FamiliesDigital Logic Gates TTL and CMOS Logic FamiliesDocument34 pages4logic FamiliesDigital Logic Gates TTL and CMOS Logic Familiessivaani sangeethaNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks ADICDocument21 pages2 Marks ADICRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Common Mode Inductors For Emi Filters Require Careful Attenuation To Core Material Selection (1995) (Magnetics)Document8 pagesCommon Mode Inductors For Emi Filters Require Careful Attenuation To Core Material Selection (1995) (Magnetics)mapo mfaNo ratings yet
- A1060204202 - 22152 - 28 - 2018 - 17891 - Logic Families PDFDocument18 pagesA1060204202 - 22152 - 28 - 2018 - 17891 - Logic Families PDFKarthik SînghNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Families ReviewerDocument4 pagesDigital Logic Families ReviewermatrishiapllenoNo ratings yet
- 18CSS201J AdeDocument148 pages18CSS201J AdeNilesh bibhutiNo ratings yet
- A Wideband - GHZ Noise Canceling Subthreshold Low Noise AmplifierDocument5 pagesA Wideband - GHZ Noise Canceling Subthreshold Low Noise AmplifierDHEERAJ KALRANo ratings yet
- Logic Families: ElectronicsDocument40 pagesLogic Families: ElectronicsPawan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Logic Gate - WikipediaDocument17 pagesLogic Gate - WikipediaElla Canonigo CanteroNo ratings yet
- Ecad 2 - MicroelectronicsDocument9 pagesEcad 2 - Microelectronicssherwincalma189No ratings yet
- Logic Families NotesDocument90 pagesLogic Families NotesRajat KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson8 DigitalLogicFamiliesDocument9 pagesLesson8 DigitalLogicFamiliesmatrishiapllenoNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Simulation of Integrated CircuitDocument7 pagesComparison and Simulation of Integrated Circuitapi-744376938No ratings yet
- Logic Family - Logic FamilyDocument4 pagesLogic Family - Logic FamilyCDAC VLSINo ratings yet
- LM 4811Document24 pagesLM 4811Avi Ben-EliyahuNo ratings yet
- 4401 ManualDocument4 pages4401 ManualBen RileyNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Families - Electronics TutorialDocument7 pagesDigital Logic Families - Electronics TutorialrakeluvNo ratings yet
- Logic FamiliesDocument18 pagesLogic FamiliesHiiiNo ratings yet
- Bca 1 STDocument42 pagesBca 1 STTushar PatelNo ratings yet
- LMH 6628Document24 pagesLMH 6628zhangce92066No ratings yet
- EEDP Lect 09 Logic FamiliesDocument34 pagesEEDP Lect 09 Logic Familiessiddu smartNo ratings yet
- 2004 CatalogDocument36 pages2004 CatalogiordacheNo ratings yet
- ES85X-3LCD03 SFP+ DatasheetDocument10 pagesES85X-3LCD03 SFP+ DatasheetCong NguyenNo ratings yet
- A 0.6-V Low-Power Variable-Gain LNA in 0.18-μm CMOS TechnologyDocument4 pagesA 0.6-V Low-Power Variable-Gain LNA in 0.18-μm CMOS TechnologyPranjal JalanNo ratings yet
- Abracon 2021 Antenna CatalogDocument42 pagesAbracon 2021 Antenna CatalogRudi SusantoNo ratings yet
- Chopper-Stabilized, Two Wire Hall-Effect Latch: Description Features and BenefitsDocument12 pagesChopper-Stabilized, Two Wire Hall-Effect Latch: Description Features and BenefitsMcOrtiz OrtizNo ratings yet
- EV Electro Voice - RE1000 Engineering Data SheetDocument2 pagesEV Electro Voice - RE1000 Engineering Data Sheetdd ffNo ratings yet
- 10MHz GateDriver EiceDRIVER 2EDF7275F 2EDF7175FDocument2 pages10MHz GateDriver EiceDRIVER 2EDF7275F 2EDF7175Falejo9719No ratings yet
- Group 6 (Wajahat Ali, Sufyan Ahmad, Rabia Shehzadi)Document18 pagesGroup 6 (Wajahat Ali, Sufyan Ahmad, Rabia Shehzadi)Saima KhanNo ratings yet
- Logic FamiliesDocument14 pagesLogic FamiliesAjay ReddyNo ratings yet
- IJETR011811Document6 pagesIJETR011811Anonymous gF0DJW10yNo ratings yet
- Logic FamiliesDocument14 pagesLogic Familiesnissi0% (1)
- Logic GateDocument11 pagesLogic GateedwardNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity and Radiated Emission of High-Speed Digital SystemsFrom EverandSignal Integrity and Radiated Emission of High-Speed Digital SystemsNo ratings yet
- 06_Chapter 1Document11 pages06_Chapter 1SATYA TECHNo ratings yet
- p2Document2 pagesp2SATYA TECHNo ratings yet
- staticDocument2 pagesstaticSATYA TECHNo ratings yet
- auto transformerDocument4 pagesauto transformerSATYA TECHNo ratings yet
- 2Document13 pages2SATYA TECHNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase LineDocument17 pages3 Phase LineSATYA TECHNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Viva Question AnswersDocument3 pagesData Structures Viva Question AnswersGrejoJobyNo ratings yet
- PVT Behavior of Fluids: Dr. M. SubramanianDocument58 pagesPVT Behavior of Fluids: Dr. M. SubramanianRama GaurNo ratings yet
- Budgeting Systems: Langfield-Smith, Thorne, Smith, Hilton Management Accounting, 7eDocument42 pagesBudgeting Systems: Langfield-Smith, Thorne, Smith, Hilton Management Accounting, 7ePhát TNNo ratings yet
- NSQC EDOOFA Exclusive Invitation To MARIST NYANGADocument2 pagesNSQC EDOOFA Exclusive Invitation To MARIST NYANGAbrendonstingNo ratings yet
- PB Mental Health Snapshot 4Document5 pagesPB Mental Health Snapshot 4amanda wuNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument9 pagesEntamoeba HistolyticaYash GautamNo ratings yet
- Ra 9379Document1 pageRa 9379Dave Ü DomosmogNo ratings yet
- Modeling Simulation and Performance Evaluation of Parabolic TroughDocument9 pagesModeling Simulation and Performance Evaluation of Parabolic TroughVikas PatelNo ratings yet
- A7rV Help GuideDocument535 pagesA7rV Help Guidesonyalpharumors100% (2)
- T&D - Unit1 - Mechanical Design of OH LinesDocument72 pagesT&D - Unit1 - Mechanical Design of OH LinesKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- VIVA - TarrifDocument1 pageVIVA - TarrifSrinivas VadtheNo ratings yet
- Tritaal/teentaal-Single Speed - (Thah)Document7 pagesTritaal/teentaal-Single Speed - (Thah)VARUN JAGANNATH KAUSHIKNo ratings yet
- The Sādhana For The Single Mudrā VajrasattvaDocument35 pagesThe Sādhana For The Single Mudrā VajrasattvaMarshal MHVHZRHLNo ratings yet
- Dessler - 04 Job AnalysisDocument12 pagesDessler - 04 Job AnalysisAlam SmithNo ratings yet
- Partnership Accounting With AnsDocument22 pagesPartnership Accounting With Ansjessica amorosoNo ratings yet
- Micro Processors: Case Study SummaryDocument6 pagesMicro Processors: Case Study SummaryNagesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- EN 12255 4 Wastewater Treatment Plants PDocument30 pagesEN 12255 4 Wastewater Treatment Plants PHoài An LêNo ratings yet
- LO 3. 25present A Range of Appetizer - Accompaniments of AppetizersDocument5 pagesLO 3. 25present A Range of Appetizer - Accompaniments of AppetizersRachel ReyesNo ratings yet
- OFS16.Reference R08.02Document7 pagesOFS16.Reference R08.02nana yaw100% (1)
- Folklore of The Freeway - Eric AvilaDocument256 pagesFolklore of The Freeway - Eric AvilaJuno IantoNo ratings yet
- Pathwaysrw 1 Unit6Document20 pagesPathwaysrw 1 Unit6Antioquia EnglishNo ratings yet
- Project Report Sem III (Gaurav.N.Kasat)Document66 pagesProject Report Sem III (Gaurav.N.Kasat)gaminghub069ytNo ratings yet
- DH 1208Document12 pagesDH 1208The Delphos HeraldNo ratings yet
- Winserver2 Volvo Viewinglibrary ST 160 2012 07 10 PDFDocument29 pagesWinserver2 Volvo Viewinglibrary ST 160 2012 07 10 PDFLuis JesusNo ratings yet
- Multilin f60 - ManualDocument724 pagesMultilin f60 - ManualcrismeragNo ratings yet
- HE Module 2 Day 5 6 7 HandoutsDocument7 pagesHE Module 2 Day 5 6 7 HandoutsKhloe Nicole AquinoNo ratings yet