Chip Sets
Chip Sets
Uploaded by
Drift GeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Chip Sets
Chip Sets
Uploaded by
Drift GeeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Chip Sets
Chip Sets
Uploaded by
Drift GeeCopyright:
Available Formats
8
CHIPSETS
CONTENTS AT A GLANCE AMD Chipset
AMD-640 chipset More on the AMD-640 system controller (Northbridge) More on the AMD-645 peripheral bus controller (Southbridge)
VIA Chipsets
Via Apollo P6 chipset Via Apollo VP3 chipset Via Apollo VP2 chipset Via Apollo VPX/97 chipset Via Apollo VP-1 chipset Via Apollo Master chipset
Intel Chipsets
Intel 430 VX Pentium chipset Intel 430 TX Pentium chipset Intel 430 HX Pentium chipset Intel 430 FX Pentium chipset Intel 430 MX mobile Pentium chipset Intel 440 FX Pentium Pro/II chipset Intel 450 GX/KX Pentium Pro chipset Intel 440 LX Pentium II chipset
SiS Chipsets OPTi Chipsets
OPTi discovery chipset OPTi Vendetta chipset FireStar chipset
Legacy and Support ICs Further Study
184
CHIPSETS
185
In the early days of the PC, motherboards (and pretty much every other device) were designed and built with discrete logic gates. If you were around in the days of the PC/XT and PC/AT, you probably remember the huge motherboards packed with over 150 to 200 individual ICs. Discrete ICs demanded a lot of power, and took up lots of room. It didnt take designers long to realize that standard functions of the PC (like floppy drive interface circuits, DMA controllers, or programmable interrupt controllers) could be integrated onto Application-Specific ICs (or ASICs). With the use of ASICs, PCs were able to drop their chip count, reduce construction costs, and reduce power requirements. But there are also performance advantages to such high levels of integration. Combining logic circuitry onto a single IC dramatically shortens the signal paths, and allows the circuit to operate at higher speeds. By optimizing the signal paths within the IC itself, performance could be improved even further. Designers quickly saw that they could integrate all the core logic needed to facilitate a complete PC in just a few highly integrated ICs. Because these chips were specifically designed to be used as a set on the motherboard, they were dubbed the chipset (Fig. 8-1). Today, chipsets play a leading role in the design and fabrication of modern personal computers. Where early motherboards could use hundreds of ICs, youd be hard-pressed to find more than 20 ICs on a current motherboard. In fact, chipsets are so important that new chipsets must be developed to support each new feature or CPU. For example, youll find that Intels 430 TX chipset supports features, such as SDRAM, dual CPUs, ACPI, and Ultra DMAbut the venerable 430 HX chipset does not. As a result, motherboards with a 430 HX chipset would have to be replaced with a motherboard using the 430 TX chipset
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
FIGURE 8-1
An Intel 440LX chipset. Intel Corporation
186
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-1 DETAILED CHIPSET MANUALS AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION AMD 640 chipset: Intel 430 FX Pentium chipset: Intel 430 HX Pentium chipset: Intel 430 VX Pentium chipset: Intel 430 TX Pentium chipset: Intel 450 GX/KX Pentium Pro chipset: Intel 440FX Pentium Pro chipset: Intel 440LX Pentium Pro chipset: Intel 430MX mobile Pentium chipset: VIA VT82C590 Apollo VP2: VIA VT82C595: VIA VT82C586B: VIA VT82C580 Apollo VPX: VIA VT82C580 Apollo VPX/97: VIA VT82C580 Apollo VP-1: VIA VT82C570M Apollo VP Master: VIA VT82C496 Pluto: SiS chipset family OPTi Vendetta http://www.amd.com/K6/k6docs/pdf/21090c.pdf http://developer.intel.com/design/pcisets/datashts/290518.htm http://developer.intel.com/design/pcisets/datashts/290551.htm http://developer.intel.com/design/pcisets/datashts/290553.htm http://developer.intel.com/design/pcisets/datashts/290559.htm http://developer.intel.com/design/pcisets/datashts/290523.htm http://developer.intel.com/design/pcisets/datashts/290549.htm http://developer.intel.com/design/pcisets/datashts/290564.htm http://developer.intel.com/design/pcisets/datashts/290525.htm http://www.via.com.tw/vp2586a.pdf http://www.via.com.tw/595.pdf http://www.via.com.tw/586b.pdf http://www.via.com.tw/vpx586a.pdf http://www.via.com.tw/580vpx.pdf http://www.via.com.tw/apollovp.pdf http://www.via.com.tw/apollovp.pdf http://www.via.com.tw/496pluto.pdf http://www.sisworld.com/ ftp://ftp.opti.com/pub/chipsets/system/vendetta/index.htm
before those features would be available. Ultimately, the overall features and capabilities of your PC are largely defined by the motherboard chipset (sometimes called core logic). This chapter is intended to familiarize you with many of the current chipsets in use today. If you want detailed technical information about todays chipsets, you can usually download the complete manual from the chipset manufacturers Web site (in Adobe Acrobats .PDF format). Table 8-1 lists the URLs for many chipset manuals.
The companion CD offers several utilities for the detection of core logic chipsets. For older motherboards, try SHOWS174.ZIP. For more recent systems, use CONF810E.ZIP, which also provides a complete assessment of system information (highly recommended).
There is a tremendous rivalry between the major chipset manufacturers. This chapter does not advocate the use of any given chipset (or manufacturer) over another, or attempt to make product recommendations. This chapter merely familiarizes you with the features of each chipset, and allows you to make objective assessments of system capabilities based upon the particular core logic in use.
AMD Chipsets
Although AMD (Advanced Micro Devices) is certainly no stranger to the CPU arena, they are relative newcomers to the chipset market. Traditionally, AMD relied on other chipset makers to support their line of CPUs (i.e., the 5x85, K5, and K6). However, not all chipset
AMD CHIPSETS
187
makers provided the optimum support for AMDs products. As a consequence, AMD has developed the 640 chipset for use with their K6 CPU.
AMD-640 CHIPSET
The AMD-640 chipset features two devices: the AMD-640 system controller, and the AMD-645 peripheral bus controller (Table 8-2). Working together, these chips can deliver numerous high-performance features that accelerate multimedia applications (especially those designed for MMX-type processors). The AMD-640 system controller has been optimized to accelerate AMD-K6 processor transactions, and also incorporates support for SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM)the most recent development in the evolution of main system memory. The AMD-645 peripheral bus controller features support for Ultra DMA/33, which allows the ATA/IDE interface to provide a 33MB/s data transfer rate. System performance is further increased with Type F DMA, which provides a 5 improvement over standard DMA transfers. Type F DMA reduces the system bus requirements for DMA transfers, providing the CPU with greater access to the ISA bus (less of a bottleneck during data transfers). Perhaps most important for AMD, the 640 chipset is backward-compatible with existing AMD and Intel CPUs.
TABLE 8-2 SUMMARY OF MOTHERBOARD CHIPSET COMPONENTS MASTER CHIPSET COMPONENT AMD-640 AMD-645 82437VX 82371SB 82438VX 82439TX 82371AB 82439HX 82371SB 82437FX 82371FB 82438FX 82437MX 82438MX 82371MX 82441FX 82442FX 82371SB 82451KX 82452KX 82453KX 82454KX 82451GX 82452GX 82453GX 82454GX 82443LX #NEEDED 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 or 2 4 1 1 1 or 2 1 FUNCTION System controller Peripheral bus controller System controller PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX3) Data path unit System controller PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX4) System controller PCI I/O IDE Xcelerator (PIIX3) System controller SA bridge, PCI/ISA/IDE Xcelerator (PIIX) Data path unit System controller Data path units PCI I/O IDE Xcelerator (MPIIX) PCI and memory controller Data bus accelerator PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX3) Memory interface component Data path unit Data controller PCI bridge Memory interface component Data path unit Data controller PCI bridge PCI AGP S t t ll
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
AMD-640 Intel 430 VX (Triton II*)
Intel 430 TX Intel 430 HX (Triton II*) Intel 430 FX (Triton*)
Intel 430 MX
Intel 440 FX (Natoma*)
Intel 450 KX (Orion*)
Intel 450 GX (Orion*)
I t l 440 LX
188
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-2 SUMMARY OF MOTHERBOARD CHIPSET COMPONENTS (CONTINUED) MASTER CHIPSET COMPONENT 82443LX 82371AB VT82C685VP VT82C586 VT82C687 VT82C597 VT82C586B VT82C595 VT82C586B VT82C585VPX VT82C586B or VT82C586A VT82C587VP VT82C585VP VT82C586 VT82C587VP VT82C575M VT82C576M VT82C577M VT82C416 5597 5596 5513 5571 5511 5512 5513 85C496 85C497 82C650 82C651 82C652 82C750 82C700 #NEEDED 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 FUNCTION PCI AGP System controller PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX4) System controller PCI/ISA/IDE/USB controller Memory controller System controller PCI/IDE/USB controller System controller PCI/IDE/USB controller System controller PCI/ISA/IDE/USB controller (97-compliant) PCI/ISA/IDE/USB controller (non-97) Share frame buffers System controller PCI/IDE/ISA/USB controller Share frame buffers System controller PCI/ISA/IDE controller Frame buffers Support controller Integrated system controller System controller USB controller Integrated system controller System controller Bus controller USB controller System controller Bus controller System Controller Bus controller Auxiliary PCI bus controller Integrated system controller Integrated system controller
Intel 440 LX VIA Apollo P6
VIA Apollo VP3 VIA Apollo VP2/97 VIA Apollo VPX/97
VIA Apollo VP-1
VIA Apollo Master
SiS 5597 (Jedi) SiS 5596 SiS 5571 (Trinity) SiS 551X
SiS 85C49X (486) OPTi Discovery
OPTi Vendetta OPTi Fire Star
TYPICAL CHIPSET FUNCTION DESIGNATIONS
s APIC: Advance Programmable Interrupt Controller s DBX: Data Bus Accelerator s DC: Data Controller s DP: Data Path s DPU: Data Path Unit s B: ISA Bridge s MIC: Memory Interface Component s PB: PCI Bridge s PIIX: PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator
PMC PCI
dM
ll
AMD CHIPSETS
189
TABLE 8-2 SUMMARY OF MOTHERBOARD CHIPSET COMPONENTS (CONTINUED) MASTER CHIPSET COMPONENT #NEEDED FUNCTION
s PMC: PCI and Memory Controller s PRMC: Power Management Controller s SC: System Controller s SMBA: Shared Memory Buffer Architecture s UMA: Unified Memory Architecture s USBC: Universal Serial Bus Controller
*Intel chipset code names are strictly unofficial, and Intel does not even acknowledge the use of code names.
MORE ON THE AMD-640 SYSTEM CONTROLLER (NORTHBRIDGE)
The AMD-640 system controller features the 64-bit Socket 7 interface, integrated writeback cache controller, system memory controller, and PCI bus controller. The Socket 7 interface has been optimized for the AMD-K6 processorproviding 3-1-1-1-1-1-1-1 transfer timing for both read and write transactions from PBSRAM (Pipeline Burst Static RAM) at 66 MHz. The memory controller features a data-buffering design that uses four cache lines (16 quad words or QW) of processor-to-DRAM or cache-to-DRAM write buffering with concurrent write-back capability to accelerate write-back and write-miss cycles. The integrated PCI bus controller features concurrent processor and PCI operation through a five-double word (or DW) posted write buffer design. PCI concurrency with DRAM or cache memory is achieved through a 48-double word post write buffer and 26double word prefetch buffer. The AMD-640 design also uses byte-merging, which optimizes processor-to-PCI throughput and reduces PCI bus traffic by converting consecutive processor addresses into burst PCI cycles. The controller minimizes PCI initiator read latency and DRAM access using techniques, such as snoop ahead, snoop filtering, forwarding cache write-backs to the PCI initiator, and merging L1 write-backs into the PCI-posted write buffers. The integrated PCI controller supports enhanced PCI bus commands, such as Memory-Read-Line, Memory-Read-Multiple, and Memory-Write-Invalidate. These features allow a PCI initiator to achieve the full 133-Mbps burst-transfer rate. The integrated PCI bus controller is fully compatible with the PCI local bus specification (revision 2.1). Table 8-3 offers the AMD-640 chipset features at a glance.
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
MORE ON THE AMD-645 PERIPHERAL BUS CONTROLLER (SOUTHBRIDGE)
The AMD-645 peripheral bus controller features an integrated ISA bus controller, enhanced master mode PCI EIDE controller with Ultra DMA/33 technology, ACPI-compatible Power Management Unit, USB controller, PS2-compatible keyboard/mouse controller, and Real-Time Clock (RTC) with extended 256-byte CMOS RAM. The on-chip EIDE controller has a dual-channel DMA engine with capability of interlaced dual-channel com-
190
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-3 AMD-640 CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s Optimized for the AMD-K6 processor s Provides SDRAM, EDO RAM, and FPM RAM support s Offers PCI concurrency s Supports Ultra DMA/33 s Includes Data path units s Includes PS/2 keyboard/mouse controller s Includes RTC s Backward compatible with other AMD and non-AMD processors s Offers USB support s Supports ACPI s Includes Plug-and-Play support
mands. High-bandwidth PCI transfers are achieved by an enhanced 16 double-word data FIFO with full scatter and gather capability. The integrated USB controller features a root hub with two ports having 18-level-deep data FIFOs and built-in physical layer transceivers. The USB controller also offers backward compatibility with legacy keyboard and PS/2 mouse support. The AMD-645 peripheral bus controller meets Microsoft Windows 95 Plug-and-Play requirements with steerable PCI interrupts, ISA interrupts, and DMA channels. The integrated power management unit is compliant with ACPI and APM, and provides dedicated input pins for external modem ring indication and power-on, five general-purpose I/O pins with option for I2C port, and 16 general-purpose pins that can be programmed as inputs or outputs.
Intel Chipsets
The Intel corporation provided the 8086 CPU that went into the first PC, and has led the way in CPU development ever since. Though competitors like AMD and Cyrix are narrowing the performance gap, Intel has managed to retain the lead in fast, high-performance CPUs, like the Pentium II. Because Intel is the first to release new CPUs, they are also ideally positioned to develop the chipsets to complement those CPUs. Intel is also a frequent collaborator with Microsoft in the proposal of new industry initiatives (such as ACPI and AGP), so they often have a head-start in supporting those initiatives. Intel offers a wide range of chipsets.
INTEL 430 VX PENTIUM CHIPSET
The Intel 430 VX chipset (also referred to as the Triton II chipset) is used in relatively recent Pentium-based PCs that are designed for low-end or end-user applications (e.g., multimedia, games, and personal productivity software). The 430 VX chipset integrates support for the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard, so home users can add a wide variety of Plug-and-Play digital input devices, such as mice, keyboards, joysticks, scanners, and cameras. The 430 VX supports concurrent PCI architecture, which maximizes system
INTEL CHIPSETS
191
performance with simultaneous activity on the CPU, PCI, and ISA buses. This generally improves video and audio performance for multimedia applications, and allows more high-speed peripherals in the systems without impacting the performance of the PCI bus. Improved EDO memory support, faster timing, and support for Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) are also included. Memory support also allows the Shared Memory Buffer Architecture (SMBA) option. The Intel 430VX PCIset consists of the 82437VX system controller, two 82438VX data paths, and the 82371SB PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX3). Although the 430 VX is generally considered to be a good performer, some features are noticeably absent. There is no support for multiple CPUs, and no support for ECC. The chipset will only handle up to 128MB of RAM (but only 64MB are cacheable). RAM timing is also a bit slower than the 430 HX, so 430 TX systems tend to be a bit slowereven when SDRAM is installed. Table 8-4 outlines the features of the 430 VX chipset.
INTEL 430 TX PENTIUM CHIPSET
The 430 TX chipset optimizes the capabilities of the Intel Pentium processor with MMX technology (Pentium MMX), and has found dual-duty in both desktop and mobile PCs.
TABLE 8-4 INTEL PENTIUM/MMX CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
CHIPSET 430 VX 430 TX 430 HX 430 FX 430 MX
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
Processor Voltage Dual CPUs Refresh RAS Lines 64-Mbit Support Max Memory Size Memory Types SDRAM (CL=2) EDO (66 MHz) MA Buffers ECC/Parity L2 Cache Type Cacheability PCI Support Concurrent PCI MTT SMBA Support Bridge Type USB Support IDE Support RTC Power Mgt. I/O Mgt.
Pentium 3.3 V(I/O) No CAS-before-RAS 5 No 128MB SDRAM/EDO/FPM 6-1-1-1 6-2-2-2 Integrated No Async, DRAM, Pburst 64MB PCI 2.1 Yes Yes Yes PIIX3 Yes BMIDE External N/A N/A
Pentium 3.3 V(I/O) No CAS-before-RAS 6 Yes 256MB SDRAM/EDO/FPM 6-1-1-1 5-2-2-2 Integrated No Pburst 64MB PCI 2.1 Yes Yes No PIIX4 Yes Ultra DMA Integrated ACPI SM Bus/GPIO
Pentium 3.3 V(I/O) Yes CAS-before-RAS 8 Yes 512MB EDO/FPM N/A 5-2-2-2 Integrated Yes Pburst 512MB PCI 2.1 Yes Yes No PIIX3 Yes BMIDE External N/A N/A
Pentium 3.3 V(I/O) No RAS Only 5 No 128MB EDO/SPM N/A 7-2-2-2 External No Async, Burst, Pburst 64MB PCI 2.0 No No No PIIX No BMIDE External N/A N/A
Pentium 3.3 V(I/O) No CAS-before- RAS 4 No 128MB EDO/SPM N/A 7-2-2-2 External No Async, Burst, Pburst 64MB PCI 2.0 No No No MPIIX No Normal IDE External SMI, APM N/A
192
CHIPSETS
Reduced power consumption enables new applications by delivering mobile-style power management to the desktop. The 430 TX chipset features Dynamic Power Management Architecture (DPMA)extending the battery life of mobile computers, and enabling new power-efficient desktop models. Support for the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) also improves power management. The 430 TX also supports the Ultra DMA disk drive protocol with the enhancements required for faster performance of todays multimedia applications. For higher memory throughput, the chip set supports Synchronous DRAM (or a mix of SDRAM and EDO RAM). Concurrent PCI support is available for the first time in a mobile PCI chip set, enabling faster and smoother video and audio performance. There is also support for the Universal Serial Bus (USB). With the outside the box Plug-and-Play capabilities of USB, the 430 TX chipset helps the integration of multimedia, I/O peripherals, and digital imaging devices. The 430 TX also implements a full System Management Bus (SMBus) host controller with three-wire interfacethrough which the system can communicate with simple monitoring controllers. For example, Smart Battery devices can provide information to the power-management charging system via the SMBus. The user can then be informed of the current battery state, along with an accurate prediction of the available operating time (or remaining time to fully charge the battery). Table 8-4 compares the features of the 430 TX. The 430 TX chipset is a two-chip solution consisting of the 82439TX system controller, and the 82371AB PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator. The 430 TX forms a host-to-PCI bridge, provides the second level (L2) cache control, and offers a full 64-bit data path to main memory. The system controller integrates the cache and main memory DRAM control functions, and provides bus control for transfers between the CPU, cache, main memory, and the PCI bus. The L2 cache controller supports write-back cache for cache sizes of 256KB and 512KB (cache-less designs are also supported).
INTEL 430 HX PENTIUM CHIPSET
The venerable 430 HX chipset (unofficially dubbed Triton II) is perhaps the most wellknown and well-respected Pentium chipset ever produced. With uncompromised EDO RAM timing, the 430 HX matches the performance of an asynchronous L2 cache-based system (without the cache). It supports 64Mbit DRAM, and offers 8 RAS lines (for up to 512MB of system memory). Memory address buffers are built into the system controller. Integrated deep-posting and FIFO buffers enable concurrent activity on both sides of the system controller and data paths for improved CPU utilization. ECC and parity memory support are integrated into the chip set, along with dual CPU support. The 430 HX supports concurrent PCI architecture and the Universal Serial Bus (USB). The 430 HX chipset consists of the 82439HX system controller and the 82371SB PCI I/O IDE Xcelerator (PIIX3). Table 8-4 lists the features of the 430 HX.
INTEL 430 FX PENTIUM CHIPSET
The 430 FX chipset (or Triton as it is unofficially known) was the first Intel Pentium chipset to become extremely successfulso successful, in fact, that it is largely deemed to be the undoing of other competitors like ETEQ, UMC, and ALI. It was also the first x86type chipset using EDO RAM (and is responsible for EDO now being a standard RAM
INTEL CHIPSETS
193
type). Although the 430 FX is now obsolete, it is still considered to be a decent performer. Table 8-4 lists the specifications for the 430 FX chipset. The 430 FX chipset consists of the 82437FX system controller, two 82438FX Data Paths, and the 82371FB PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (or PIIX). The chipset forms a host-to-PCI bridge, provides second level (L2) cache control, and supports a full 64-bit data path to main memory. The system controller integrates the cache and main memory DRAM control functions, and provides bus control for transfers between the CPU, cache, main memory, and the PCI bus. The L2 cache controller supports a write-back cache for cache sizes of 256KB and 512KB (cache-less designs are also supported). Cache memory can be implemented with either standard, burst, or pipelined burst SRAMs. An external Tag RAM is used for the address tag, and an internal Tag RAM handles the cache line status bits. The system controller supports up to 128MB of main memory. An optimized PCI interface allows the CPU to sustain a high bandwidth to the graphics frame buffer at all frequencies. Using the snoop-ahead feature, the system controller allows PCI masters to achieve full PCI bandwidth. The data paths provide the connections between the CPU/cache, main memory, and PCI bus.
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
INTEL 430 MX MOBILE PENTIUM CHIPSET
The 430 MX chipset is the first of Intels complete mobile chipset solutions for the Pentium processor. The 430 MX uses many architectural innovations developed for the 430 FX chipset designed for desktop computers, and was designed for such uses as ProShare, high-speed Ethernet, and audio/graphic-intensive applications. The 430 MX chipset is ideally suited for any application that requires a faster bus (from 25 to 33MHz) for greater performance. The 430 MX supports EDO RAM and pipelined-burst SRAM. Its architecture provides greater than 100 MB/s PCI data streaming. The highly integrated Mode 4 local bus IDE controller improves the operation of fast hard drives. In addition, its integrated Plug-andPlay port makes systems easier to use and increases performance by transforming ISA motherboard peripherals into pseudo-PCI devices. As a mobile chipset, the 430 MX benefits from Advanced Power Management (APM) support. The 430 MX chipset consists of the 82437MX system controller, two 82438MX data paths, and the 82371MX PCI I/O IDE Xcelerator (or MPIIX). The 430 MX forms a hostto-PCI bridge, provides the second level (L2) cache control, and supports a full 64-bit data path to main memory. The 82371MX MPIIX provides the bridge between the PCI bus and the ISA-like Extended I/O expansion bus. In addition, the 82371MX has an IDE interface that supports two IDE devicesproviding an interface for IDE hard disks and CD-ROM drives. The MPIIX integrates many common I/O functions used in ISA-based PC systems a seven-channel DMA controller, two 82C59 interrupt controllers, a 8254 timer/counter, Intel SMM power management support, and control logic for NMI generation. Chip-select decoding is provided for the BIOS, real-time clock, and keyboard controller. Edge/level interrupts and interrupt steering are supported for PCI Plug-and-Play compatibility.
INTEL 440 FX PENTIUM PRO/II CHIPSET
The 440 FX chipset (unofficially referred to as the Natoma chipset) is a highly integrated solution for supporting Pentium II and Pentium Pro processors in mainstream business
194
CHIPSETS
systems. This second-generation chipset optimizes system performance for 32-bit application software in 32-bit operating system environments, and will support multiple CPUs. Based on concurrent PCI architecture, the 440 FX chipset includes a multi-transaction timer (MTT) for enhanced video transfer and higher frame rates, and a passive release mechanism for improved MPEG and audio performance. There is also enhanced write performance for full utilization of write buffers (to improve host-based processing applications) and PCI-delayed transactions to ensure CPU-to-ISA write control compatibility with the PCI 2.1 specification. The 440 FX chipset is slated for compact designs implemented in a four-layer board (in either the ATX, baby AT, or LPX form factors). The chipset supports up to 1GB maximum memory size using flexible memory options including EDO RAM. Memory is further enhanced with ECC support. The 440 FX also utilizes the PIIX3allowing motherboards to use the same I/O subsystems as those used with the 430 HX and 430 VX. Universal Serial Bus (USB) support allows for Plug-and-Play connectivity outside the box, and Bus Master IDE (BMIDE) handles access for fast hard drives. Table 8-5 lists the features for a 440 FX chipset. The 440 FX chipset consists of the 82441FX PCI and memory controller, the 82442FX data bus accelerator, and the 82371SB PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (or PIIX3).
TABLE 8-5 INTEL PENTIUM PRO/II CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE CHIPSET Processor Voltage Dual CPUs Refresh RAS Lines 64-Mbit Support Max Memory Size Memory Types Memory Interleave ECC/Parity PCI Support Concurrent PCI MTT SMBA Support Bridge Type USB Support IDE Support RTC Power Mgt. I/O Mgt. 440 FX Pentium Pro Pentium II GTL+ Yes RAS only or CAS-before-RAS 8 Yes 1GB EDO/FPM/BEDO No Yes PCI 2.1 Yes Yes No PIIX3 Yes BMIDE External SMM N/A 450 GX Pentium Pro GTL+ Up to quad processor CAS-before-RAS 16 Yes 8GB FPM 4-way, 2-way, non Yes* PCI 2.0 N/A No No Not included N/A** N/A*** N/A SMM N/A 450 KX Pentium Pro GTL+ Yes CAS-before-RAS 8 Yes 1GB FPM 2-way, non Yes* PCI 2.0 N/A No No Not included N/A** N/A*** N/A SMM N/A
Notes: *ECC only on memory and parity on host bus **Some motherboard implementations include the 82371SB, which is capable of USB ***Some motherboard implementations include the 82371FB, which is capable of bus master IDE
INTEL CHIPSETS
195
INTEL 450 GX/KX PENTIUM PRO CHIPSET
The 450 GX chipset (known as the Orion chipset) is designed to support Pentium Pro processor servers and scientific systemsespecially those which use multiple CPUs (up to four). By comparison, the 450 KX (also sometimes referred to as Orion) is aimed at designers of workstations and high-performance desktops with one or two CPUs. In actuality, the 450 GX/KX chipsets are rarely used because of the many features the chipsets lack. Neither supports concurrent PCI, USB, or any form of I/O management. When compared with other contemporary chipsets, the 450 GX/KX are simply not as competitive as the more recent 440 FX chipset. Table 8-5 highlights the features of the 450 GX/KX chipset.
INTEL 440 LX PENTIUM II CHIPSET
The 440 LX chipset is the first in a series of AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) chipsets from Intel designed to optimize the performance of a Pentium II processor. This is seen as a major new computing platform for small business, large business, and home users alike. The 440 LX chipset with AGP extends the system bandwidth to the graphics controller, and optimizes the system bandwidth and concurrency with the implementation of Quad Port Acceleration (QPA). QPA provides four-port concurrent arbitration of the processor bus, graphics bus, PCI bus, and SDRAM. The 440 LX chipset also offers advanced power management and fast resume from powered-down states through Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI). This enables local power down operation, with remote wake up for off-hours maintenance. Application performance for 3D graphics are improved. AGP gives PCs the capability to handle memory-intensive 3D graphics applications, providing the faster performance and enabling larger textures out of main memoryresulting in more life-like image detail. The 82443LX PCI AGP system controller integrates a host-to-PCI bridge, optimized DRAM controller and data path, and an Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) interface into a single chip. The I/O subsystem portion of the 440 LX is the 82371AB, which provides an ISA bridge, a PCI ISA IDE Xcelerator (PIIX4), and USB controller. Table 8-6 lists the features for the 440LX chipset.
TABLE 8-6 INTEL PENTIUM II CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE CHIPSET Processor Voltage Dual CPUs DRAMRefresh RAS Lines 64 Mbit Support Max. Memory Size Memory Types Memory Interleave ECC/Parity 440 LX Pentium II GTL+ Yes CAS-before-RAS 8 Yes 1GB EDO, 512MB SDRAM EDO/SDRAM No Yes
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
196
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-6 INTEL PENTIUM II CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE (CONTINUED) CHIPSET ECC/Parity PCI Support Concurrent PCI AGP compliant 1 Support 2 Support PIPE SEA MTT SMBA Support Bridge Type USB Support IDE Support RTC Power Mgt. I/O Mgt. 440 LX Yes PCI 2.1 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No PIIX4 Yes BMIDE and Ultra DMA/33 Integrated SMM and ACPI SMBus/GP10
VIA Chipsets
Founded in 1987, VIA is perhaps the greatest threat to Intels dominance of the chipset market. Their line of Apollo chipsets has provided an effective alternative for the support of Intel Pentium/MMX/Pro, AMD K5 and K6, and Cyrix 6x86 and M2 CPUs. VIA chipsets are generally recognized as full-featured, high-performance solutions that are used on many motherboards. VIA also produces a selection of network and peripheral controller ICs for computer applications.
VIA APOLLO P6 CHIPSET
VIAs VT82C680 Apollo P6 is a high-performance energy-efficient chipset for PCI/ISA desktop and notebook PC systems based on 64-bit Intel Pentium Pro processors. The chipset supports multiple Pentium Pro configurations (based on Intel GTL+), and handles up to 66MHz external CPU bus speed. The chipset also supports the Pentium Pro CPU multi-phase protocols for split transactions and eight level deep in-order queue for optimal CPU throughput. The DRAM and PCI bus are also independently powered so that each of the buses can be run at 3.3 V or 5 V (the ISA bus always runs at 5 V). The main features of the Apollo P6 chipset are listed in Table 8-7.
VIA APOLLO VP3 CHIPSET
The Apollo VP3 is a high-performance, two-chip chipset for the implementation of AGP, PCI, and ISA bus architectures in desktop and notebook PC systems, based on 64-bit Socket-
VIA CHIPSETS
197
7 CPUs (including Intel Pentium and Pentium MMX, AMD K5 and K6, and Cyrix/IBM 6x86 and 6x86MX processors). The Apollo VP3 chipset consists of the VT82C597 system controller and the VT82C586B PCI-to-ISA bridge. The VT82C597 system controller provides superior performance between the CPU, optional synchronous cache, DRAM, AGP bus, and the PCI bus with pipelined, burst, and concurrent operation. The VT82C597 complies with the Accelerated Graphics Port Specification 1.0 and features a 66MHz master system bus. It is interesting to notice that the VP3 chipset is one of the few that provide AGP support for non-Pentium Pro processors. The key features for the chipset are shown in Table 8-8.
VIA APOLLO VP2 CHIPSET
The two-chip VIA Apollo VP2/97 is the industrys most highly integrated, high-performance Socket 7 compliant chipset. With ECC, Microsoft PC-97 compliance, SDRAM, 512MB DRAM, and 2MB cache support, the VP2/97 offers remarkable versatility for Intel Pentium, Pentium MMX, Cyrix/IBM 6x86 and 6x86MX, and AMD K5 and K6 MMX processors. The Apollo VP2/97 builds on the VIA VT82C580VP Apollo VP (widely recognized as a leading Socket 7 chipset). Additional performance related features include a fast DRAM
TABLE 8-7 VIA APOLLO P6 CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s Highly integrated 3-chip solution s Fast DRAM controller s Intelligent PCI bus controller s Enhanced master-mode PCI IDE controller s Plug-and-Play controller with two Windows 95-compliant Plug-and-Play ports s Integrated USB interface with hub and dual function ports s Integrated power management, providing normal, doze, sleep suspend and conserve modes s GTL+ bus-driver/receiver compatible with Intel fast DRAM controller specifications s Up to 1GB of banked DRAM
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
TABLE 8-8 VIA APOLLO VP3 CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s PC-97 compatible using VT82C586B with ACPI power management. s Includes Ultra-DMA/33, EIDE, USB, and Keyboard/PS2-mouse interfaces. s Includes RTC/CMOS on-chip. s Supports 64-bit Socket 7 CPUs, 64-bit system memory, 32-bit PCI, and 32-bit AGP interfaces. s 3.3-V and sub-3.3-V interface to CPU. s 3.3-V (5-V tolerant) DRAM, AGP, and PCI interface. s AGP v1.0 compliant. s PCI buses are synchronous to host CPU bus. s 33MHz operation on the primary PCI bus. s 66MHz PCI operation on the AGP bus. s Concurrent CPU and AGP access. s Supports FPM RAM, EDO RAM, and SDRAM.
198
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-9 VIA APOLLO VP2 CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s PC-97 compliance includes an extension to ACPI/OnNow. s Integrated Universal Serial Bus controller. s Enhanced master-mode PCI IDE controller with extension to Ultra-DMA/33. s Support for up to 512MB DRAM with ECC. s DRAM controller with FPM/EDO/SDRAM support in mixed combinations of 32-bit or 64-bit data
bus widths.
s Intelligent PCI bus controller offering concurrent PCI master/CPU/IDE operations, and zero
wait-state PCI master and slave burst-transfer rates.
s Integrated KeyBoard Controller (KBC) and Real-Time Clock (RTC). s Supports Pentium, Pentium MMX, Cyrix 6x86 and M2, and AMD K5 and K6 MMX. s Advanced cache controller with burst synchronous cache SRAM support up to 2MB. s Plug-and-Play controller and PCI-to-ISA bridge.
controller with support for SDRAM, EDO, BEDO, and FPM DRAM types in mixed combinations with 32-/64-bit data bus widths and row and column addressing, a deeper buffer with enhanced performance, an intelligent PCI bus controller with concurrent PCI master/CPU/IDE operations, and zero-wait-state PCI master and slave burst transfer rates. The Apollo VP2/97 features the VIA VT82C586B PCI-IDE controller chip, which supports ACPI/OnNow, Ultra-DMA/33, and USB technologies. Table 8-9 lists the main features of the chipset.
VIA APOLLO VPX/97 CHIPSET
The VIA VT82C580VPX Apollo VPX/97 core logic chipset is a high-performance fourchip solution for Socket 7 main boards supporting Intel Pentium, Pentium MMX, Cyrix/ IBM 6x86 and 6x86MX, and AMD K5 and K6 MMX processors. To enable proper implementation of the Cyrix/IBM 6x86 200+ processor, the chipset features an asynchronous CPU bus that operates at either 66 or 75MHz speeds. Apollo VPX/97 also supports the Cyrix/IBM linear burst mode. The Apollo VPX/97 features a fast DRAM controller with support for SDRAM, EDO, BEDO and FPM DRAM types in mixed combinations of 32- or 64-bit data bus widths. Additional features include a deeper buffer with enhanced performance, an intelligent PCI bus controller with concurrent PCI master/CPU/IDE operations, and zero-wait-state PCI master and slave burst transfer rates. There is support for up to 2MB of L2 cache, and up to 512MB of DRAM. The VIA Apollo VPX/97 features the VIA VT82C586B PCI-IDE controller chip that complies with the Microsoft PC-97 industry standard by supporting ACPI/OnNow, Ultra-DMA/33, and USB technologies. Table 8-10 lists the key features of the Apollo VPX/97.
VIA APOLLO VP-1 CHIPSET
The VT82C580VP Apollo VP-1 is a four-chip solution for PCI/ISA desktop and notebook PCs based on Pentium, AMD K5x86, and Cyrix 6x86 CPUs. Apollo VP-1 features func-
VIA CHIPSETS
199
tions designed to bypass conventional board-level bottlenecks (including burst and normal EDO RAM, FPM RAM, and SDRAM support, burst SRAM and cache module support, and an on-board dual-channel enhanced-master-mode PCI IDE controller that supports up to four Enhanced IDE (EIDE) devices. The VIA Apollo VP-1 chipset consists of one VT82C585VP system controller, a VT82C586 PCI/IDE/ISA/USB controller, and two VT82C587VP share frame buffers. The features of the VP-1 are listed in Table 8-11.
VIA APOLLO MASTER CHIPSET
The VT82C570M Apollo Master is an older chipset for PCI/ISA desktop PCs, based on Intel Pentium, AMD K5x86, and Cyrix 6x86 CPUs. The VIA Apollo Master consists of a VT82C575M system controller, a VT82C576M PCI/ISA/IDE controller, two VT82C577M frame buffers, and a VT82C416 support IC. Few features would now be considered advanced, but Table 8-12 lists the main features.
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
TABLE 8-10 VIA APOLLO VPX/97 CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s Asynchronous CPU bus, which is operational at either 66/75MHz. s PC-97 compliance includes extension to ACPI/OnNow. s Integrated Universal Serial Bus controller. s Enhanced master-mode PCI IDE controller with extension to Ultra-DMA/33. s Support for up to 512MB DRAM. s DRAM controller with FPM/EDO/SDRAM support in mixed combinations with 32-bit or 64-bit
data bus widths.
s Intelligent PCI bus controller offering concurrent PCI master/CPU/IDE operations, and zero-
wait-state PCI master and slave burst-transfer rates.
s Integrated Keyboard Controller (KBC) and Real-Time Clock (RTC). s Supports the Pentium, Pentium MMX, Cyrix 6x86 and M2, and AMD K5 and K6 MMX. s Advanced cache controller with burst synchronous cache SRAM supports up to 2MB. s Integrated Plug-and-Play controller and PCI-to-ISA bridge. s Multiple processor support.
TABLE 8-11 VIA APOLLO VP-1 CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s PCI/ISA Green PC ready s Integrated Universal Serial Bus support and intelligent PCI Bus controller. s Unified Memory Architecture includes SDRAM and BEDO support. s Fast DRAM Controller with support for various DRAM modes (32-bit or 64-bit data width). s Enhanced master-mode IDE controller with support for up to four devices. s Integrated cache controller. s Shared frame buffers. s Integrated Plug-and-Play controller and Power-Management Unit. s Integrated PCI-to-ISA bridge.
200
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-12 VIA APOLLO MASTER CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s PCI/ISA green chipset. s Fast DRAM controller. s Master-mode PCI bus controller. s Enhanced master-mode PCI IDE controller supports up to four devices. s Windows 95 Plug-and-Play compliant. s Power-Management Unit. s Supports Intel Pentium, AMD K5, and Cyrix 6x86 CPUs. s Synchronous ISA bus controller.
TABLE 8-13 SIS5597 CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s Single-chip solution with the 5597 (Jedi chip). s Pentium/PCI/ISA low-cost core logic with integrated VGA controller. s 64-bit PCI/Host graphic and video accelerator. s Meets PC-97 and ACPI requirements. s PCI Burst Write. s Supports the universal serial bus. s Integrated Direct-Draw hardware accelerator. s 85Hz vertical refresh rate.
SiS Chipsets
SiS is another major manufacturer of chipsets that support core logic (motherboards), as well as mobile PCs and multimedia applications. Although SiS is a bit behind VIA and Intel in chipset development, they are rather unique in the inclusion of video-accelerator hardware into the chipset (particularly in their later products). This makes SiS chipsets particularly appealing to entry-level PCs, where minimizing cost is very important. Because SiS products are not as widely used as other chipsets, youll find summaries of SiS chipset features in the following tables:
s s s s s
SiS5597 chipset; Table 8-13 SiS5596 chipset; Table 8-14 SiS5571 chipset; Table 8-15 SiS551X chipset; Table 8-16 SiS85C49X chipset; Table 8-17
OPTi Chipsets
Founded in 1989, OPTi is a well-known supplier of core logic and multimedia chipsets to manufacturers of desktop and mobile computer products worldwide. Although the
OPTI CHIPSETS
201
TABLE 8-14 SIS5596 CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s Two-chip solution with the 5596 and 5513. s Pentium low-cost core logic with integrated VGA controller. s Supports Intel Pentium CPUs (and other compatible CPUs) at 66/60/50MHz. s Integrated high-performance video/graphics accelerator. s Integrated L2 cache controller supporting up to 1MB of L2 cache. s Integrated high-performance DRAM controller (FPM and EDO RAM). s Supports up to 512MB of main system memory. s Integrated PCI bus support. s Supports super-high-resolution graphic modes up to 1280 1024. s Supports a virtual screen up to 2048 2048. s Microsoft Video for Windows-compliant.
2
TABLE 8-15 SIS5571 CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s Pentium/PCI/ISA high-performance core logic. s Single-chip solution with the 5571 (Trinity chip). s Supports Intel Pentium CPUs (and other compatible CPUs) at 66/60/50 MHz. s Integrated L2 cache controller supporting up to 1MB of L2 cache. s Integrated high-performance DRAM controller supporting up to 384MB of main system memory. s Concurrent CPU and PCI operations. s Integrated post-write buffers and read prefetch buffers to increase system performance. s Supports five external PCI masters. s Includes an enhanced PCI IDE master/slave controller. s Integrated universal serial bus controller. s ISA-compatible and Fast Type-F DMA cycles supported.
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
TABLE 8-16 SIS551X CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s Pentium/PCI/ISA core logic. s Three-chip solution with the 5511, 5512, and 5513. s Supports Intel Pentium CPUs (and other compatible CPUs) at 66/60/50MHz. s Integrated second-level (L2) cache controller. s Integrated DRAM controller. s Provides high-performance PCI arbiter and integrated PCI bridge. s Supports the full 64-bit Pentium data bus. s Provides 32-bit interface to the PCI bus. s Includes enhanced DMA functions and integrated interrupt controllers. s Integrated KeyBoard Controller (KBC) and Real-Time Clock (RTC). s Includes a fast PCI IDE master/slave controller. s Includes a USB interface. s On-board Plug-and-Play support.
202
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-17 SIS85C49X CHIPSET FEATURES AT A GLANCE
s 486 PCI/ISA core logic chipset. s A two-chip solution using the 85C496 and 85C497. s Supports the Intel 486 (and other compatible CPUs) at 50/40/33/25MHz. s Includes an L2 cache controller and DRAM controller. s Supports VESA bus specification Rev 2.0p. s Supports PCI bus specification Rev 2.0. s Supports up to four external PCI masters.
chipsets by Intel and VIA have pushed OPTi into the background, they continue to produce some respected motherboard chipsets.
OPTI DISCOVERY CHIPSET
The OPTi Discovery chipset (82C650/651) provides a highly integrated solution for a wide range of fully compatible, high-performance PC platforms, based on the Intel Pentium Pro processor. The Discovery chipset is comprised of two chips, the 82C650 system controller, and the 82C651 bus controller (and an optional third chipthe 82C652 which provides an auxiliary PCI bus that can be used as the AGP port). It provides 64-bit core logic, integrated PCI (revision 2.1), support for a second host-to-PCI device (the 82C652), support for all popular memory technologies, sophisticated power management features, as well as optional support for Unified Memory Architecture (UMA) and the Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP). The deep buffers and several levels of pipelining minimize system level latencies and maximize/sustain throughputs for all the major subsystems. Support for parity/ECC protection provides enhanced levels of fault tolerance to greatly improve the reliability of the system.
OPTI VENDETTA CHIPSET
The OPTi Vendetta (82C750) single-chip core logic unit provides a highly integrated solution for high-performance PC platforms. It supports the Intel 3.3-V Pentium, Cyrix 6x86, and AMD 5K86. In addition to supporting a wide range or platform designs, the 82C750 feature set also includes audio and one-game-port functionality, common architecture support, isolated primary/secondary Ultra-DMA IDE support, and dual USB ports. This makes the Vendetta an ideal choice for multimedia-based end-user systems.
FIRESTAR CHIPSET
OPTis FireStar single-chip core logic combines high-performance features with spacesaving design ideal for mobile applications. This solution is based on the Intel 3.3-V and 2.5-V (split voltage) Pentium MMX, Cyrix M2, and AMD K6 processors. FireStar also allows FPM DRAM, EDO DRAM, or Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) as options when
LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS
203
designing the system. The highly concurrent cycles and deep-buffering features of FireStar also improve the systems performance. For power-management applications, FireStar offers power-saving modes for extended battery life and provides true CPU-temperature monitoring. In STPGNT mode, CPU power consumption can be reduced by 80%. In STPCLK mode, CPU power consumption can be reduced by as much as 99%. FireStar also features advanced fail-safe thermal management, full peripheral activity tracking and power-off control, Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) support, and Advanced Power Management (APM), as well as suspend to memory and suspend to disk power-management options.
Legacy and Support ICs
Although this chapter is intended to highlight many of the most popular motherboard chipsets in use today, there are a great many more older chips and chipsets still in the field. The myriad of 386 and 486-class systems still in service almost guarantee that youll encounter these legacy chips sooner or later. It is almost impossible to adequately list all the chips and chipsets that have been used in PCs throughout the years, but Table 8-18 attempts to cover the more popular devices (as well as other support ICs, which might still be in use).
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
TABLE 8-18 A BRIEF LISTING OF LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS
ACC 82010 Chipset (i286/i386 systems motherboard chipset)
IC ACC2000 ACC2100 ACC2210 ACC2220 FUNCTION Integrated peripheral controller System controller Data bus buffer Address bus buffer
ACC 82020 Chipset (i286/i386 systems motherboard chipset)
IC ACC2000 ACC2120 ACC2210 ACC2220 ACC2300 ACC2500 ACC2030 ACC2035 FUNCTION Integrated peripheral controller Enhanced system controller Data bus buffer Address bus buffer Page-interleaved memory controller System controller Single-chip i286 system controller Single-chip i386SX system controller
204
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-18 A BRIEF LISTING OF LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS (CONTINUED)
Acer Labs (motherboard chipsets)
IC M1521-A/1523 M1541/1533 FUNCTION Aladdin III Aladdin IV
Chips & Technologies CS8230 Chipset (CHIPset i286 motherboard chipset)
IC 82C201 82C202 82C203 82C204 82C205 FUNCTION System controller RAM/ROM decoder and I/O controller High-address bus buffer Low-address bus buffer Data bus buffer and parity generator
Chips & Technologies CS8221 Chipset (NEAT i286 motherboard chipset)
IC 82C211 82C212 82C215 82C206 FUNCTION System controller and extended CMOS RAM control logic I/O and memory decode logic Parity logic and bus buffers Integrated peripheral controller
Chips & Technologies CS8233 Chipset (PEAK i386 motherboard chipset)
IC 82C311 82C316 82C315 82C452 82C601 82C765 FUNCTION CPU, cache, DRAM controller Peripheral controller Bus controller Super VGA controller Single-chip peripheral controller Single-chip floppy-disk controller
Chips & Technologies CB8291/CB8295 Chipset (ELEAT i286/i386 motherboard chipsets)
IC 82C235 82C450 82C451 82C710 82C711 FUNCTION SCAT system controller 1MB DRAM VGA graphics controller Integrated VGA graphics controller Universal peripheral controller Universal peripheral controller II
Chips & Technologies CS8230/CS8231 Chipset (i386DX motherboard chipsets)
IC 82C206 82C301 82C302 FUNCTION Integrated peripheral controller Bus controller P /i l ll
LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS
205
TABLE 8-18 A BRIEF LISTING OF LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS (CONTINUED) 82C302 82C303 82C304 82C305 82C306 82C307 Page/interleave memory controller High-address bus buffer Low-address bus buffer Data bus buffers Control buffer Cache/DRAM controller
Chips & Technologies CS8238 Chipset (i386DX motherboard chipset for MCA bus systems) IC FUNCTION
82C226 82C233 82C321 82C322 82C325 System peripheral controller DMA controller CPU/microchannel controller Page interleave/EMS controller Data bus buffer
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
Chips & Technologies CS8281 Chipset (NEATsx i386SX motherboard chipset) IC FUNCTION
82C206 82C215 82C811 82C812 Integrated peripherals controller Data and address buffer CPU and bus controller Page interleave/EMS controller
Chips & Technologies CS8285 Chipset (PEAKset/SX i386SX motherboard chipset)
IC 82C235 82C835 FUNCTION System controller Cache controller
Chips & Technologies CS82310 Chipset (PEAKset i386DX/i486SX/i486DX motherboard chipset)
IC 82C351 82C355 82C356 FUNCTION CPU/cache/DRAM controller Data buffer Integrated peripheral controller
Chips & Technologies CHIPS 280 Chipset (PS/2 Model 80 i386DX motherboard chipset for MCA bus)
IC 82C226 82C233 82C321 82C322 82C325 82C450 FUNCTION Page interleave/EMS controller DMA controller CPU/microchannel controller Page interleave/EMS controller Data bus buffer and controller 1MB DRAM VGA hi t ll
206
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-18 A BRIEF LISTING OF LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS (CONTINUED) 82C450 C 82C607 1MB DRAM VGA (graphics controller CS C /S S Multi-function controller )
ETEQ Microsystems 82C390SX Chipset (Panda i386DX motherboard chipset)
IC 82C390SX FUNCTION CPU, cache, and DRAM controller
ETEQ Microsystems 82C4901/82C4902 Chipset (Bengal i386DX motherboard chipset)
IC 82C4901 82C4902 FUNCTION CPU, cache, and DRAM controller Data bugger and MCP interface controller
ETEQ Microsystems ET2000 Chipset (i386DX/i486SX/i486DX motherboard chipset for EISA bus)
IC ET2001 ET2002 ET2003 ET2004 FUNCTION EISA bus controller EISA data buffer EISA integrated peripheral controller EISA cache/memory controller
ETEQ Microsystems ET6000 Chipset (Cheetah i486SX motherboard chipset)
IC ET6000 FUNCTION System controller
Faraday FE3600B Chipset (motherboard chipset)
IC FE3001 FE3010 FE3021 FE3031 FUNCTION System controller Peripheral controller Address bus and memory control logic Parity and data bus controller
Integrated Technology Express (motherboard chipsets)
IC IT8330G IT8331G FUNCTION Platinum Platinum plus
Intel 82350/DT EISA Chipset (i386DX/i486SX/i486DX chipset for EISA bus)
IC 82077 82352 82353 FUNCTION Floppy-disk controller EISA bus buffer Ad dd t th
LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS
207
TABLE 8-18 A BRIEF LISTING OF LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS (CONTINUED) 82353 Faraday FE3600B Chipset (motherboard chipset) Advanced data path 82357 Integrated peripheral controller 82358 EISA bus controller 82359 DRAM controller
Intel Peripheral Controllers (other ICs)
IC 8206 8207 82078 82091AA 82350 82351 82355 82C08 82C54 82C55A FUNCTION Error detection and correction unit Dual-port dynamic RAM controller Single-chip floppy-disk controller Advanced integrated peripheral (AIP) EISA chip set Local I/O EISA support peripheral (LIO.E) Bus master interface controller (BMIC) Dynamic RAM controller Programmable interval timer Programmable peripheral interface
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
OPTI Chipset (i286/i386 motherboard chipset)
IC 82C381 82C382 FUNCTION System and cache memory controller Direct-mapped page-interleaved memory controller
OPTI 386WB Chipset (i386DX motherboard chipset)
IC 82C206 82C391 82C392 FUNCTION Integrated peripheral controller System controller Data bus controller
OPTI 486SXWB Chipset (i486SX motherboard chipset)
IC 82C206 82C392 83C493 FUNCTION Integrated peripheral controller Data bus controller System controller
OPTI 386/486WB Chipset (i386DX/i486SX/i486DX motherboard chipset for EISA bus)
IC 82C681 82C682 82C686 82C687 FUNCTION EISA bus controller Memory/cache controller Integrated peripheral controller Data bus controller
208
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-18 A BRIEF LISTING OF LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS (CONTINUED)
OPTi Other Support ICs
IC 82C566/7/8-MAX 82C814 82C824 92C178 82C931 FUNCTION Viper Max chipset Mobile PC docking controller PC card controller PCI/LCD controller Audio controller
SiS Other Support ICs
IC 5581 6204 6205 6225 6226 6326 5107 5131 5120 8132 8164 SiS5581 SiS6204 SiS6205 SiS6225 SiS6226 SiS6326 SiS5107 SiS5131 SiS5120 SiS8132 SiS8164 FUNCTION Core logic (Jessie chip) ISA video controller High-performance PCI 2D graphics and video accelerator MPEG1 PCI/2D graphics and video accelerator MPEG2 PCI/AGP/2D graphics and video accelerator MPEG2 PCI/AGP/3D graphics and video accelerator Hot docking controller PCMCIA/ISA controller Single chip notebook solution 128KB pipelined burst SRAM 256KB pipelined burst SRAM
Suntec Chipset (i286 motherboard chipset)
IC ST62C201 ST62C202 ST62C008 ST62C010 ST62BC001 ST62BC002 ST62BC003 ST62BC004 ST62C005 ST62C006 FUNCTION System bus controller Memory controller Integrated peripheral controller Address bus controller System controller High address controller Low address controller Data buffer I/O control, DMA page register Integrated peripheral controller
Suntec Chipset (i286/i386SX motherboard chipset)
IC GS62C101 GS62C102 FUNCTION System, data bus, timer, and interrupt controller Memory, DMA, and I/O controller
LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS
209
TABLE 8-18 A BRIEF LISTING OF LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS (CONTINUED)
Suntec Chipset (i286 motherboard chipset) Symphony Labs HAYDN AT Chipset (i386SX/i386DX/i486SX/i486SLC/i486DX motherboard chipset) IC FUNCTION IC FUNCTION
SL82C362 SL82C461 SL82C465 Bus controller System controller Cache controller
Symphony Labs Mozart Chipset (i386SX/DX/i486SX/SLC/DX motherboard chipset for EISA bus)
IC SL82C471 SL82C472 SL82C473 FUNCTION CPU, cache, and DRAM controller EISA bus controller EISA DMA controller
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
Western Digital Chipset (motherboard chipset)
IC 75C10 75C20 75C30 76C10 WD6000 WD6010 WD6020 WD6036 FUNCTION Single-chip 286 AT controller Floppy-drive, hard-drive, and real-time clock controller Serial- and parallel-port controller High-speed single i286 system controller System, interrupt, and timer controller DMA, reset, and parity controller Address and data bus controller DRAM/cache memory controller
VIA Chipset (FLEXSET motherboard chipset)
IC SL9011 SL9020 SL9023 SL9030 SL9090 SL9095 SL9151 SL9152 SL9250 SL9251 SL9252 SL9350 SL9351 SL9352 FUNCTION System controller Data bus controller Address controller Integrated peripheral controller Universal clock IC Power-management IC i286 page-interleave memory controller i286 system and memory controller i386SX Page-mode memory controller i386SX Page-interleave memory controller i386SX System and memory controller i386DX Page-mode memory controller i386DX Page-mode memory controller i386DX System and memory controller
210
CHIPSETS
TABLE 8-18 A BRIEF LISTING OF LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS (CONTINUED)
VLSI Technology Chipset (VL82CPCAT-16/20 motherboard chipset) VIA Other Support ICs
IC VT86C100 VT86C926 VT86C916 VT83C572 VT83C469 VT83C465 VT8225 VT82C887 VT82C885 VT82C42 FUNCTION Rhine fast ethernet controller (10/100 BaseT) Amazon PCI 10BaseT fast ethernet controller Nile ISA 10BaseT fast ethernet controller PCI-to-USB bridge PCMCIA socket controller PCMCIA controller Clock generator Real-Time Clock (RTC) Real-Time Clock (RTC) KeyBoard Controller (KBC)
VLSI Technology Chipset (TOPCAT i286/i386SX motherboard chipset)
IC VL82C331 VL82C320 VL82C106 FUNCTION ISA bus controller System controller Multi-function controller
VLSI Technology Chipset (TOPCAT i386DX motherboard chipset)
IC VL82C106 VL82C311 VL82C322 VL82C330 FUNCTION Multi-function controller ISA bus controller Data buffer System controller
VLSI Technology Chipset (VL82CPCAT-16/20 motherboard chipset)
IC VL82C100 VL82C201 VL82C202 VL82C203 VL82C204 FUNCTION Peripheral controller System controller Memory controller Address buffer Data buffer
VLSI Other Support ICs
IC Polaris VAS96031 VL82C829 VMS110 VMS230 FUNCTION Alpha system controller Pier 39 PCI-to-Mac I/O bridge controller Songbird 3D audio accelerator 16-bit DES coprocessor Gh Rid DES d RSA i
FURTHER STUDY
211
TABLE 8-18 A BRIEF LISTING OF LEGACY AND SUPPORT ICS (CONTINUED)
VLSI Technology Chipset (VL82CPCAT-16/20 motherboard chipset) VES2030 MPEG 2 transport demultiplexer subsystem ACTIS Actis single-chip VLSI ISDN data processor IC FUNCTION ENDEC+ Fiber-channel ENDEC Firefly Chipset fiber-channel ASSP solution GSM GSM power and flexibility in a single chip RubyII Advanced communication processor SC2000 Universal timeslot interchange SC4000 Universal timeslot interchange VCS94250 Apollo serial storage architecture VIP Single-chip VLSI ISDN subscriber processor VN567200 VN567200 ATM Quad Uni Zilog Chipset (motherboard chipset)
IC P90 P91 P92 FUNCTION System, interrupt, DMA, clock, and refresh controller Memory controller Address and data-bus controllers
2
SYSTEM DATA AND TROUBLESHOOTING
Zymos Chipset (motherboard chipset)
IC POACH/XTB POACH1 POACH2 POACH4 POACH6 POACH7 POACH8 FUNCTION Single-chip XT controller System clock, bus controller, interrupt controller, and RTC DMA, timer, refresh, and I/O controller Single-chip XT controller High-speed i386DX/i486 system controller System clock, bus controller, interrupt controller, and RTC DMA, timer, refresh, and I/O controller
Further Study
This finishes up Chapter 8. Be sure to review the glossary and chapter questions on the accompanying CD. If you have access to the Internet, take some time to review a few of the chipset makers: AMD: http://www.amd.com Intel: http://developer.intel.com/design/pcisets/
212
CHIPSETS
VIA: http://www.via.com.tw/ SIS: http://www.sisworld.com/ Opti: http://www.opti.com VLSI: http://www.vlsi.com
You might also like
- JCM Manuals and DocumentationDocument2 pagesJCM Manuals and Documentationleonel botesNo ratings yet
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- Schematics Foxcom H61MD - HW-20130125Document48 pagesSchematics Foxcom H61MD - HW-20130125anhxco0% (1)
- PHILIPS Chassis EP1.1U AA Service ManualDocument101 pagesPHILIPS Chassis EP1.1U AA Service ManualtecatronicNo ratings yet
- MSI - MS-7680 - H61 - Socket 1155Document34 pagesMSI - MS-7680 - H61 - Socket 1155andrealves-tecNo ratings yet
- Mboard TshootingDocument29 pagesMboard TshootingDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- PLC SlidesDocument46 pagesPLC Slidesdonatchange100% (1)
- Ti VDP Programmers Guide PDFDocument72 pagesTi VDP Programmers Guide PDFhelderdNo ratings yet
- ATX Power Supply Connector Pinout and Wiring @Document3 pagesATX Power Supply Connector Pinout and Wiring @costelchelariuNo ratings yet
- Optiplex 780 Arrowhead RA03Document43 pagesOptiplex 780 Arrowhead RA03João Luis N. Do AmaralNo ratings yet
- JM20337 JMicronDocument2 pagesJM20337 JMicronRuben Perez AyoNo ratings yet
- Tina Ti Spice ModelsDocument17 pagesTina Ti Spice Modelsdragos_bondNo ratings yet
- Motorola Master Selection Guide RFDocument40 pagesMotorola Master Selection Guide RFAbrham Yair Aguilar Rodriguez100% (1)
- Tyco CircularConnectorsDocument84 pagesTyco CircularConnectorsmicrorameshNo ratings yet
- MS-7788 r30 PDFDocument34 pagesMS-7788 r30 PDFLuis Sena0% (1)
- Ssc5x86h ManDocument29 pagesSsc5x86h ManValdenir DuarteNo ratings yet
- TMS9918A TMS9928A TMS9929A Video Display Processors Data Manual Nov82Document105 pagesTMS9918A TMS9928A TMS9929A Video Display Processors Data Manual Nov82Dan PedersenNo ratings yet
- Ascend Y625 PDFDocument63 pagesAscend Y625 PDFCelublack CkNo ratings yet
- MB8719Document3 pagesMB8719mivica2No ratings yet
- Apple Macbook A1181 (K36C MLB)Document76 pagesApple Macbook A1181 (K36C MLB)GabrielMarteelNo ratings yet
- OP25 Windows 10 Virtual Machine Setup Guide July 10, 2022Document30 pagesOP25 Windows 10 Virtual Machine Setup Guide July 10, 2022ValerioNo ratings yet
- Kenwood Hard To Find Wiring ListDocument6 pagesKenwood Hard To Find Wiring ListTodd HoferNo ratings yet
- Micro M+Document5 pagesMicro M+eliminar100% (1)
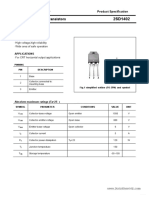
- D1402Document3 pagesD1402ban4444No ratings yet
- Esquema Eletrico MpmovieDocument1 pageEsquema Eletrico MpmovieMaurilio Caetano100% (1)
- HP W19e LCD Monitor Service ManualDocument112 pagesHP W19e LCD Monitor Service Manualoyrrb100% (1)
- USBCNC Breakout Board User ManualDocument40 pagesUSBCNC Breakout Board User ManualChaveiro GoldNo ratings yet
- Acer Aspire 5570 SchematicDocument29 pagesAcer Aspire 5570 Schematicbeppino_andoNo ratings yet
- DH67GD DH67BL TechProdSpecDocument92 pagesDH67GD DH67BL TechProdSpecjagan2003No ratings yet
- FETs DatabookDocument189 pagesFETs DatabookTito Titon0% (1)
- Osd Oscilloscope SchematicDocument1 pageOsd Oscilloscope SchematicSebastian Costa100% (1)
- Catalog of HuntronDocument0 pagesCatalog of Huntronnj23dublin100% (1)
- 1996 Harris Power MOSFET SupplementDocument378 pages1996 Harris Power MOSFET SupplementCeaser EliNo ratings yet
- Sata Ide 2 ManualDocument10 pagesSata Ide 2 ManualSor MiNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Manaul Sata Sis 964Document41 pagesMotherboard Manaul Sata Sis 964Hercilio De Alcântara SilvaNo ratings yet
- Soldering Station WSD 81 Weller 2Document10 pagesSoldering Station WSD 81 Weller 2Saheer AmbadanNo ratings yet
- 1984 MOS Memory Data BookDocument468 pages1984 MOS Memory Data Bookiimro20032765No ratings yet
- Electronic Stethoscope-2Document2 pagesElectronic Stethoscope-2subhadeep41No ratings yet
- 300 Series Chipset On Package PCH Datasheet Vol 2 PDFDocument1,345 pages300 Series Chipset On Package PCH Datasheet Vol 2 PDFasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- JM20337 Datasheet v1.1Document15 pagesJM20337 Datasheet v1.1Mehmet DemirNo ratings yet
- Hacking Your CMOS BIOSDocument2 pagesHacking Your CMOS BIOSRafique AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lenovo DMI DecodeDocument14 pagesLenovo DMI DecodeMarcelloNo ratings yet
- Description: 600-12010-BASE-QS1Document24 pagesDescription: 600-12010-BASE-QS1jayixi4827100% (1)
- Apple 2 Computer Information - Document 532 - Schematic 050-0051-DDocument5 pagesApple 2 Computer Information - Document 532 - Schematic 050-0051-DGabriel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Samsung RV508 SCALA-15UL-IstanbulDocument74 pagesSamsung RV508 SCALA-15UL-IstanbulWade Dyer0% (2)
- Fujitsu FPCPR231 Docking StationDocument1 pageFujitsu FPCPR231 Docking StationKlausNo ratings yet
- Robot OttoDocument17 pagesRobot OttoMarcio ScarduaNo ratings yet
- Intel Strongarm Sa-1111 Microprocessor Companion Chip: Developer'S ManualDocument176 pagesIntel Strongarm Sa-1111 Microprocessor Companion Chip: Developer'S Manualjohn michelNo ratings yet
- 21 - Trainee (Stores) Engineering: Ç'U Iqflrdk J'¡ (Kyk %& Ç'U Iqflrdk La ( K %&Document16 pages21 - Trainee (Stores) Engineering: Ç'U Iqflrdk J'¡ (Kyk %& Ç'U Iqflrdk La ( K %&Sravan KanigantiNo ratings yet
- GA-H61M-DS2 R201 Schematic PDFDocument30 pagesGA-H61M-DS2 R201 Schematic PDFscobaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Industrial Motherboard 0128Document75 pages1.3 Industrial Motherboard 0128prasad_nnpNo ratings yet
- imageRUNNER 2545 (I) 2535 (I) 2530 (I) 2525 (I) 2520 (I) User Guide ENDocument650 pagesimageRUNNER 2545 (I) 2535 (I) 2530 (I) 2525 (I) 2520 (I) User Guide ENnyrvanNo ratings yet
- MB945 - User Manual - V1.0BDocument77 pagesMB945 - User Manual - V1.0Bpablo salvatierraNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument31 pagesUnit Ikiran Naik PoojariNo ratings yet
- GAMING HACKINTOSH READY 2.8GHZ Quad I7 6GB 1TB PC MACDocument5 pagesGAMING HACKINTOSH READY 2.8GHZ Quad I7 6GB 1TB PC MACusernamewiserNo ratings yet
- MB865 User'S Manual: LGA775 Pentium 4 Intel 865G Industrial MotherboardDocument64 pagesMB865 User'S Manual: LGA775 Pentium 4 Intel 865G Industrial Motherboardcharst pNo ratings yet
- Digi Lite MotherboardDocument12 pagesDigi Lite Motherboardrajesh_r450No ratings yet
- AN8 Series: AMD Athlon 64/64FX System Board Socket 939 User's ManualDocument104 pagesAN8 Series: AMD Athlon 64/64FX System Board Socket 939 User's ManualbelcazarNo ratings yet
- Manuel Laptop c40Document98 pagesManuel Laptop c40MilanNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorDocument12 pages1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorTuesept Anne Vargas UrgenteNo ratings yet
- User' User' User' User' User'sssss Manual Manual Manual Manual ManualDocument86 pagesUser' User' User' User' User'sssss Manual Manual Manual Manual Manualti08077762No ratings yet
- Assembly ProceduresDocument40 pagesAssembly Proceduresapi-26355935No ratings yet
- Preventive MaintenanceDocument14 pagesPreventive MaintenanceDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Video AdaptersDocument45 pagesVideo AdaptersDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Upgrading A P - SupplyDocument7 pagesUpgrading A P - SupplyDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Serial PortDocument16 pagesSerial PortDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Upgrading A MicroprocessrDocument10 pagesUpgrading A MicroprocessrDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Syst Data and TshootingDocument19 pagesSyst Data and TshootingDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Removable Media DrivesDocument25 pagesRemovable Media DrivesDrift Gee100% (1)
- PC Cards Adn PeripheralsDocument38 pagesPC Cards Adn PeripheralsDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Paralel Port TshootingDocument13 pagesParalel Port TshootingDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Plug and PlayDocument28 pagesPlug and PlayDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Monitor Testing and Alignment: Contents at A GlanceDocument16 pagesMonitor Testing and Alignment: Contents at A GlanceDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Other Interfaces and Technologies: Contents at A GlanceDocument19 pagesOther Interfaces and Technologies: Contents at A GlanceDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- MCA Bus OperationsDocument10 pagesMCA Bus OperationsDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Modems and Fax CardsDocument55 pagesModems and Fax CardsDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Mice and TrackballsDocument18 pagesMice and TrackballsDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Memory MgrsDocument30 pagesMemory MgrsDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Laser and LED PrintersDocument55 pagesLaser and LED PrintersDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument34 pagesIndexDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Hard DrivesDocument52 pagesHard DrivesDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Floppy DrivesDocument20 pagesFloppy DrivesDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Virtual Appliance Manager 8.4.0 Installation GuideDocument62 pagesVirtual Appliance Manager 8.4.0 Installation GuideFarha AzadNo ratings yet
- Poly Studio P15 Data SheetDocument2 pagesPoly Studio P15 Data SheetSchool PracticeNo ratings yet
- Shared Memory Based Communication Between Collocated Virtual MachinesDocument24 pagesShared Memory Based Communication Between Collocated Virtual MachinesDmitry StarikovNo ratings yet
- NSX NEW Icon Library - CommunitiesDocument19 pagesNSX NEW Icon Library - CommunitiesMoises ToroNo ratings yet
- Chiken Mod v1 MedDocument210 pagesChiken Mod v1 MedYayaNo ratings yet
- Email MarketingDocument16 pagesEmail MarketingMajorNo ratings yet
- FreeVideoToMP3Converter LogDocument92 pagesFreeVideoToMP3Converter Logesie_32No ratings yet
- Aco Hydraulic Design Software: Aco Multidrain M100D SystemDocument1 pageAco Hydraulic Design Software: Aco Multidrain M100D SystemJosephRusselVizmanosNo ratings yet
- Brksec 2663Document102 pagesBrksec 2663Amit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Short Notes IctDocument7 pagesShort Notes IctNoor Syafiq100% (2)
- Cloud Service Map: Microsoft Azure & AWSDocument37 pagesCloud Service Map: Microsoft Azure & AWSdonna.nixNo ratings yet
- (InfoAcademy) CyberOpsAssociate-Sedinta13Document34 pages(InfoAcademy) CyberOpsAssociate-Sedinta13Chip CiprianNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology, Calicut: Department of Architecture and PlanningDocument20 pagesNational Institute of Technology, Calicut: Department of Architecture and PlanningDriya HariNo ratings yet
- Cac Phan Mem Quan Ly Tuoi PDFDocument336 pagesCac Phan Mem Quan Ly Tuoi PDFNguyen Van KienNo ratings yet
- Lciit Wistron Tahoe SFF (14087-1 Df9dh)Document55 pagesLciit Wistron Tahoe SFF (14087-1 Df9dh)pushp raj gaurawNo ratings yet
- Pharo by ExampleDocument376 pagesPharo by ExamplePetrNo ratings yet
- Dr. Avinash Gautam CSIS, BITS Pilani: Java Collection Framework: Maps and SetsDocument19 pagesDr. Avinash Gautam CSIS, BITS Pilani: Java Collection Framework: Maps and SetssaisounyaNo ratings yet
- DBA Service Datasheet 2Document3 pagesDBA Service Datasheet 2Venky AllaNo ratings yet
- Error "Too Many Files Open"Document5 pagesError "Too Many Files Open"iftikhar ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - StackDocument36 pagesChapter - 4 - Stacktarekegnworku5No ratings yet
- Salvation of The Child Stuck Into The Borehole PAPER ID: 19011Document21 pagesSalvation of The Child Stuck Into The Borehole PAPER ID: 19011buvi RKNo ratings yet
- How To Write and Present Technical Papers: R. K. RathoreDocument22 pagesHow To Write and Present Technical Papers: R. K. RathorerrathoreNo ratings yet
- Informatica - HOW To-Optimize PowerCenter Bulk Load To Microsoft SQL ServerDocument2 pagesInformatica - HOW To-Optimize PowerCenter Bulk Load To Microsoft SQL ServerChristian AcostaNo ratings yet
- hp3330mt PDFDocument4 pageshp3330mt PDFB Joseph ParhusipNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Generative Model Based On Gradient Descent and Mean Square ErrorDocument8 pagesA Simplified Generative Model Based On Gradient Descent and Mean Square ErrorOmar Lopez-RinconNo ratings yet
- Examen Ingles Taller 4Document9 pagesExamen Ingles Taller 4Amparo Gomez SuarezNo ratings yet
- 1 PRACTICAL TASK. Computer Networks BasicsDocument1 page1 PRACTICAL TASK. Computer Networks BasicsDianka BodnarNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu ESPRIMO P900 E90+ Desktop PC: Data SheetDocument9 pagesFujitsu ESPRIMO P900 E90+ Desktop PC: Data SheetTea AlexNo ratings yet
- TEXTILEDocument45 pagesTEXTILEAsif AnwarNo ratings yet