Catchup Schedule PR 1
Catchup Schedule PR 1
Uploaded by
MichelleCopyright:
Available Formats
Catchup Schedule PR 1
Catchup Schedule PR 1
Uploaded by
MichelleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Catchup Schedule PR 1
Catchup Schedule PR 1
Uploaded by
MichelleCopyright:
Available Formats
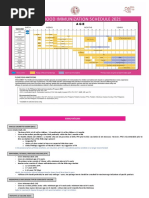
Catch-up Immunization Schedule for Persons Aged 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More
Than 1 Month BehindUnited States 2011 The table below provides catch-up schedules and minimum intervals between doses for children whose vaccinations have been delayed. A vaccine series does not need to be restarted, regardless of the time that has elapsed between doses. Use the section appropriate for the childs age
PERSONS AGED 4 MONTHS THROUGH 6 YEARS
Vaccine Hepatitis B1 Rotavirus2 Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis3 Minimum Age for Dose 1 Birth 6 wks 6 wks Dose 1 to Dose 2 4 weeks 4 weeks 4 weeks 4 weeks if first dose administered at younger than age 12 months Haemophilus influenzae type b4 6 wks 8 weeks (as final dose) if first dose administered at age 1214 months No further doses needed if first dose administered at age 15 months or older Minimum Interval Between Doses Dose 2 to Dose 3 8 weeks (and at least 16 weeks after first dose) 4 weeks2 4 weeks 4 weeks4 if current age is younger than 12 months 8 weeks (as final dose)4 if current age is 12 months or older andfirst dose administered at younger than age 12 months and second dose administered at younger than 15 months No further doses needed if previous dose administered at age 15 months or older 4 weeks if current age is younger than 12 months 8 weeks (as final dose for healthy children) if current age is 12 months or older No further doses needed for healthy children if previous dose administered at age 24 months or older 4 weeks 6 months 8 weeks (as final dose) This dose only necessary for children aged 12 months through 59 months who received 3 doses before age 12 months 6 months3 Dose 3 to Dose 4 Dose 4 to Dose 5
4 weeks if first dose administered at younger than age 12 months Pneumococcal5 6 wks 8 weeks (as final dose for healthy children) if first dose administered at age 12 months or older or current age 24 through 59 months No further doses needed for healthy children if first dose administered at age 24 months or older Inactivated Poliovirus6 Measles, Mumps, Rubella7 Varicella8 Hepatitis A9 6 wks 12 mos 12 mos 12 mos 4 weeks 4 weeks 3 months 6 months
8 weeks (as final dose) This dose only necessary for children aged 12 months through 59 months who received 3 doses before age 12 months or for children at high risk who received 3 doses at any age 6 months6
PERSONS AGED 7 THROUGH 18 YEARS
Tetanus,Diphtheria/ Tetanus,Diphtheria,Pertussis10 Human Papillomavirus11 Hepatitis A9 Hepatitis B1 Inactivated Poliovirus6 Measles, Mumps, Rubella7 7 yrs10 4 weeks 4 weeks if first dose administered at younger than age 12 months 6 months if first dose administered at 12 months or older Routine dosing intervals are recommended (females)11 6 months 4 weeks 4 weeks 4 weeks 3 months if person is younger than age 13 years 4 weeks if person is aged 13 years or older 8 weeks (and at least 16 weeks after first dose) 4 weeks6 6 months6 6 months if first dose administered at younger than age 12 months
9 yrs 12 mos Birth 6 wks 12 mos
Varicella8
12 mos
1.
2.
3. 4.
5.
Hepatitis B vaccine (HepB). Administer the 3-dose series to those not previously vaccinated. The minimum age for the third dose of HepB is 24 weeks. A 2-dose series (separated by at least 4 months) of adult formulation Recombivax HB is licensed for children aged 11 through 15 years. Rotavirus vaccine (RV). The maximum age for the first dose is 14 weeks 6 days. Vaccination should not be initiated for infants aged 15 weeks 0 days or older. The maximum age for the final dose in the series is 8 months 0 days. If Rotarix was administered for the first and second doses, a third dose is not indicated. Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine (DTaP). The fifth dose is not necessary if the fourth dose was administered at age 4 years or older. Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine (Hib). 1 dose of Hib vaccine should be considered for unvaccinated persons aged 5 years or older who have sickle cell disease, leukemia, or HIV infection, or who have had a splenectomy. If the first 2 doses were PRP-OMP (PedvaxHIB or Comvax), and administered at age 11 months or younger, the third (and final) dose should be administered at age 12 through 15 months and at least 8 weeks after the second dose. If the first dose was administered at age 7 through 11 months, administer the second dose at least 4 weeks later and a final dose at age 12 through 15 months. Pneumococcal vaccine. Administer 1 dose of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) to all healthy children aged 24 through 59 months with any incomplete PCV schedule (PCV7 or PCV13). For children aged 24 through 71 months with underlying medical conditions, administer 1 dose of PCV13 if 3 doses of PCV were received previously or administer 2 doses of PCV13 at least 8 weeks apart if fewer than 3 doses of PCV were received previously. A single dose of PCV13 is recommended for certain children with underlying medical conditions through 18 years of age. See age-specific schedules for details. Administer pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV) to children aged 2 years or older with certain underlying medical conditions, including a cochlear implant, at least 8 weeks after the last dose of PCV. A single revaccination should be administered after 5 years to children with functional or anatomic asplenia or an immunocompromising condition. See MMWR 2010;59(No. RR-11).
6. Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV). The final dose in the series should be administered on or after the fourth birthday and at least 6 months following the previous dose. A fourth dose is not necessary if the third dose was administered at age 4 years or older and at least 6 months following the previous dose. In the first 6 months of life, minimum age and minimum intervals are only recommended if the person is at risk for imminent exposure to circulating poliovirus (i.e., travel to a polio-endemic region or during an outbreak). 7. Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR). Administer the second dose routinely at age 4 through 6 years. The minimum interval between the 2 doses of MMR is 4 weeks. 8. Varicella vaccine. Administer the second dose routinely at age 4 through 6 years. If the second dose was administered at least 4 weeks after the first dose, it can be accepted as valid. 9. Hepatitis A vaccine (HepA). HepA is recommended for children aged older than age 23 months who live in areas where vaccination programs target older children, or who are at increased risk for infection, or for whom immunity against hepatitis A is desired. 10. Tetanus and diphtheria toxoids (Td) and tetanus and diphtheria toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine (Tdap). Doses of DTaP are counted as part of the Td/Tdap series. Tdap should be substituted for a single dose of Td in the catch-up series for children aged 7 through 10 years or as a booster for children aged 11 through 18 years; use Td for other doses. 11. Human papillomavirus vaccine (HPV). Administer the series to females at age 13 through 18 years if not previously vaccinated or have not completed the vaccine series. Quadrivalent HPV vaccine (HPV4) may be administered in a 3-dose series to males aged 9 through 18 years to reduce their likelihood of genital warts. Use recommended routine dosing intervals for series catch-up (i.e., the second and third doses should be administered at 1 to 2 and 6 months after the first dose). The minimum interval between the first and second doses is 4 weeks. The minimum interval between the second and third doses is 12 weeks, and the third dose should be administered at least 24 weeks after the first dose.
Information about reporting reactions after immunization is available online at http://www.vaers.hhs.gov or by telephone, 800-822-7967. Suspected cases of vaccine-preventable diseases should be reported to the state or local health department. Additional information, including precautions and contraindications for immunization, is available from the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines or telephone, 800-CDC-INFO (800-232-4636).
Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
You might also like
- Risk Assessment For Hot WorkDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment For Hot WorkLu Min Han89% (65)
- USMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsFrom EverandUSMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Manual Handling ChecklistDocument2 pagesManual Handling ChecklistHerry PrakosoNo ratings yet
- Tgs Example Crowd Control PlanDocument6 pagesTgs Example Crowd Control Planbootsevans100% (1)
- Slide Presentasi Hse PlanDocument16 pagesSlide Presentasi Hse PlanMuhammad Fadhil natsir100% (2)
- Vaccination Schedule For HorsesDocument3 pagesVaccination Schedule For HorsesKikiNo ratings yet
- Philippine Childhood Immunization Schedule 2019Document8 pagesPhilippine Childhood Immunization Schedule 2019Linius Cruz67% (3)
- Monthly Construction Site Inspection ChecklistDocument3 pagesMonthly Construction Site Inspection ChecklistMyolwinooNo ratings yet
- Generic Health and Safety Plan (EXAMPLE)Document57 pagesGeneric Health and Safety Plan (EXAMPLE)Oliver Youens100% (2)
- Figure 2. Catch-Up Immunization Schedule For Persons Ages 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More Than 1 Month Behind, U. S., 2013Document1 pageFigure 2. Catch-Up Immunization Schedule For Persons Ages 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More Than 1 Month Behind, U. S., 2013Alvaro FloresNo ratings yet
- Catchup Schedule PRDocument1 pageCatchup Schedule PRJesus A. Pineda GarciaNo ratings yet
- Recommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0-6 YearsDocument3 pagesRecommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0-6 YearsAlvaro FloresNo ratings yet
- 0 6yrs Schedule BWDocument1 page0 6yrs Schedule BWRyan ArdyantoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Vac + NotesDocument36 pagesPediatric Vac + NotesTrang Vu100% (1)
- Final PIDSP Immunization2024Document13 pagesFinal PIDSP Immunization2024John Michaelle SantosNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2021Document11 pagesChildhood Immunization Schedule 2021Paula QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedDocument11 pagesChildhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedPatricia Bernadette PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at BirthDocument5 pagesHepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at Birthannu panchalNo ratings yet
- IZSchedule0 6yrsDocument1 pageIZSchedule0 6yrsKaty ForemanNo ratings yet
- Catchup Schedule BWDocument4 pagesCatchup Schedule BWlcmurilloNo ratings yet
- Highlghts in Pediatric Infectious DiseasesDocument37 pagesHighlghts in Pediatric Infectious DiseasesLibay Villamor IsmaelNo ratings yet
- PertussisDocument11 pagesPertussissribaccayNo ratings yet
- IZSchedule0 6yrsDocument1 pageIZSchedule0 6yrsgeany2911No ratings yet
- Raymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM, MAN UNP-College of NursingDocument32 pagesRaymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM, MAN UNP-College of NursingrnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- The Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument26 pagesThe Expanded Program On ImmunizationJudee Marie MalubayNo ratings yet
- Summary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Document5 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Annie AnnaNo ratings yet
- 07 Childschd 6x4.5 1-Page PRDocument2 pages07 Childschd 6x4.5 1-Page PRSteluta GalbenusNo ratings yet
- HPV VaccineDocument1 pageHPV Vaccineeladewilase1No ratings yet
- Recommendations For Pneumococcal Vaccine Use in Children and TeensDocument1 pageRecommendations For Pneumococcal Vaccine Use in Children and TeensuknandiNo ratings yet
- 2022 2023 School Requirement K-12 202203231046460791Document1 page2022 2023 School Requirement K-12 202203231046460791sailorguardianlmNo ratings yet
- Catchup Schedule PR PDFDocument2 pagesCatchup Schedule PR PDFGama Adi SafutraNo ratings yet
- 10 Catchup Schedule PRDocument1 page10 Catchup Schedule PRdrsaharpakzadNo ratings yet
- Over-All Goal: To Reduce The Morbidity and Mortality Among Children Against The Most Common Vaccine-Preventable Specific GoalDocument9 pagesOver-All Goal: To Reduce The Morbidity and Mortality Among Children Against The Most Common Vaccine-Preventable Specific GoalRetiza EllaNo ratings yet
- Catch Up VaccinationDocument3 pagesCatch Up VaccinationSara Ilyas KhanNo ratings yet
- Jawaban B InggrisDocument4 pagesJawaban B InggrisMhd SholehNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: Gorgonia, Leanie Louise LDocument3 pagesHepatitis B: Gorgonia, Leanie Louise LLeanie LouiseNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenDocument1 pagePneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenPrincess Gutierrez RositaNo ratings yet
- WHO Immunization Schedule ChildrenDocument9 pagesWHO Immunization Schedule Childrenashchua21No ratings yet
- Immunization in ChildrenDocument28 pagesImmunization in ChildrensaripjunayyahNo ratings yet
- Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Catch-Up Guidance For Children 4 Months Through 18 Years of Age 2015Document3 pagesPneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Catch-Up Guidance For Children 4 Months Through 18 Years of Age 2015phobicmdNo ratings yet
- Immunization Schedule 27-07-2016Document2 pagesImmunization Schedule 27-07-2016SandraniNo ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument4 pagesVaccinesSam smithNo ratings yet
- Immunization Routine Table3Document9 pagesImmunization Routine Table3oweesheeNo ratings yet
- VACCINATION.Document4 pagesVACCINATION.ochidavi56No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Elements of Primary Health CareDocument12 pagesModule 4 - Elements of Primary Health CareAllyza Pholette DistorNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program of ImmunizationDocument20 pagesExpanded Program of ImmunizationgwynNo ratings yet
- Summary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Document6 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Risnu Nur MohammadNo ratings yet
- Vax 0-6Document2 pagesVax 0-6alvinmhNo ratings yet
- Epi Scheduale EnglishDocument1 pageEpi Scheduale EnglishKasun Senevirathne100% (2)
- VACCINATION1Document4 pagesVACCINATION1ochidavi56No ratings yet
- JC MarchDocument101 pagesJC MarchSubhashree SamantrayNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization RecordDocument4 pagesChildhood Immunization RecordJoseph Edward DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Haemophilus Influenzae Type B: Age Immunization Dose Notes Date GivenDocument4 pagesHaemophilus Influenzae Type B: Age Immunization Dose Notes Date Givenmail2saeedisNo ratings yet
- Final - Back 1 PDFDocument2 pagesFinal - Back 1 PDFesbat07No ratings yet
- ImmunizationsDocument64 pagesImmunizationsLily BeltranNo ratings yet
- Vaccinations For NJ SchoolsDocument2 pagesVaccinations For NJ SchoolskimtranpatchNo ratings yet
- Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Recommended Immunization Schedule For Children Aged 0 Through 18 Years - India, 2014 and Updates On ImmunizationDocument16 pagesIndian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Recommended Immunization Schedule For Children Aged 0 Through 18 Years - India, 2014 and Updates On Immunizationkrishna615No ratings yet
- Splenectomy: DisclaimerDocument5 pagesSplenectomy: DisclaimerMimi FatinNo ratings yet
- Immreqpk15 16Document4 pagesImmreqpk15 16api-234991765No ratings yet
- Vaccination ScheduleDocument2 pagesVaccination Scheduleratnakar_ghorpa9990No ratings yet
- Sara Michlle Immunization Tip SheetDocument2 pagesSara Michlle Immunization Tip SheetJan FloydNo ratings yet
- School Vaccine RequirementsDocument2 pagesSchool Vaccine RequirementsrkarlinNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2019Document8 pagesChildhood Immunization Schedule 2019Maribel LutzNo ratings yet
- Stanley Grogg, DODocument53 pagesStanley Grogg, DOminerva_stanciuNo ratings yet
- CHN1 Lec Session #17 SASDocument9 pagesCHN1 Lec Session #17 SASJhanna Mae BalbonNo ratings yet
- Published Assessment Report: VarilrixDocument4 pagesPublished Assessment Report: VarilrixkemalahmadNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Summative Test TLE 9Document1 pageQuarter 2 Summative Test TLE 9Jerome RamosNo ratings yet
- Important Terms in Industrial SecurityDocument2 pagesImportant Terms in Industrial Securitygracia100% (5)
- HEMP-Leader Engagement SOPAF GM-1Document64 pagesHEMP-Leader Engagement SOPAF GM-1ashveen_peddadu100% (2)
- 2 - Concrete MixerDocument2 pages2 - Concrete MixerRafee Pie50% (2)
- JSA-018 Lifting With Mobile CraneDocument5 pagesJSA-018 Lifting With Mobile CraneOmar Dhieb100% (2)
- FMDS1005 Disaster Recovery and Contingency Plan 2007Document8 pagesFMDS1005 Disaster Recovery and Contingency Plan 2007CarlosCastroNo ratings yet
- Punjab General Industries Private Limited: Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (HIRA)Document9 pagesPunjab General Industries Private Limited: Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (HIRA)Rohit VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- 8-Stop Work Authority - PPSXDocument8 pages8-Stop Work Authority - PPSXMohamed Mahmoud0% (1)
- SIL MethodologyDocument16 pagesSIL Methodologyhvananth100% (9)
- HIRACDocument9 pagesHIRACnarenmaniam100% (3)
- COSHH Assessment Form: Assessor (Employer/Supervisor Assessment Date Dates ReviewedDocument5 pagesCOSHH Assessment Form: Assessor (Employer/Supervisor Assessment Date Dates ReviewedEnus BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Expo Markers SdsDocument8 pagesExpo Markers SdsAman BaigNo ratings yet
- Nourah Safety Aed Safety & Quality Certifications & Diplomas 2Document5 pagesNourah Safety Aed Safety & Quality Certifications & Diplomas 2murthyNo ratings yet
- Managing Fire Safety: Tim Russell Essex County Fire and Rescue ServiceDocument21 pagesManaging Fire Safety: Tim Russell Essex County Fire and Rescue Servicekashifbutty2k100% (1)
- Sodium Bisulphite CAS No 7631-90-5: Material Safety Data Sheet Sds/MsdsDocument7 pagesSodium Bisulphite CAS No 7631-90-5: Material Safety Data Sheet Sds/MsdsMuhammad Iqbal ChandioNo ratings yet
- Airport Evacuation PlanDocument14 pagesAirport Evacuation Planandrewparnham0% (1)
- Vademecum para BomberosDocument34 pagesVademecum para BomberosAlvaro Buendia AyalaNo ratings yet
- Hand HygieneDocument1 pageHand Hygieneyopi kusumaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapJona Maguds100% (1)
- Man MadeDocument10 pagesMan MadeRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Eo BDRRMCDocument1 pageEo BDRRMCInternational Home Decors75% (4)
- G7 - Food Process-Q2-W7-LAS2Document1 pageG7 - Food Process-Q2-W7-LAS2Van TotNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: HI 93102-0 Primary Standard, 0 FTUDocument3 pagesSafety Data Sheet: HI 93102-0 Primary Standard, 0 FTUCuong CaoNo ratings yet
- Testing and CommisioningDocument2 pagesTesting and CommisioningKrishna PatilNo ratings yet