0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 viewsHepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at Birth
Hepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at Birth
Uploaded by
annu panchal1. The document provides vaccination recommendations for various diseases. It outlines the recommended vaccines, doses, and timing for diseases like hepatitis B, rotavirus, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, pneumococcal, polio, influenza, measles, mumps, rubella, varicella, hepatitis A, meningococcal, tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis, and human papillomavirus.
2. Specific details are provided for each vaccine including the minimum age, number of doses, timing between doses, and catch-up recommendations. High-risk groups and international travel are also addressed.
3
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Hepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at Birth
Hepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at Birth
Uploaded by
annu panchal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views5 pages1. The document provides vaccination recommendations for various diseases. It outlines the recommended vaccines, doses, and timing for diseases like hepatitis B, rotavirus, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, pneumococcal, polio, influenza, measles, mumps, rubella, varicella, hepatitis A, meningococcal, tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis, and human papillomavirus.
2. Specific details are provided for each vaccine including the minimum age, number of doses, timing between doses, and catch-up recommendations. High-risk groups and international travel are also addressed.
3
Original Title
immunization
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
1. The document provides vaccination recommendations for various diseases. It outlines the recommended vaccines, doses, and timing for diseases like hepatitis B, rotavirus, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, pneumococcal, polio, influenza, measles, mumps, rubella, varicella, hepatitis A, meningococcal, tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis, and human papillomavirus.
2. Specific details are provided for each vaccine including the minimum age, number of doses, timing between doses, and catch-up recommendations. High-risk groups and international travel are also addressed.
3
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views5 pagesHepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at Birth
Hepatitis B (Hepb) Vaccine. (Min Age: Birth) at Birth
Uploaded by
annu panchal1. The document provides vaccination recommendations for various diseases. It outlines the recommended vaccines, doses, and timing for diseases like hepatitis B, rotavirus, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, pneumococcal, polio, influenza, measles, mumps, rubella, varicella, hepatitis A, meningococcal, tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis, and human papillomavirus.
2. Specific details are provided for each vaccine including the minimum age, number of doses, timing between doses, and catch-up recommendations. High-risk groups and international travel are also addressed.
3
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
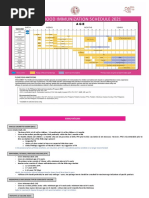
1. Hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine. (Min age: birth)
At birth:
• HBsAg-negative mother: administer 1 dose of monovalent HepB vaccine within 24hrs of birth
for infants ≥2,000g. For infants <2000g, give 1 dose at chronological age 1 month or
hospital discharge.
• HBsAg-positive mother: administer 1 dose of monovalent HepB vaccine and 0.5mL of hepatitis
B immune globulin (HBIG) within 12hrs of birth, regardless of birth weight. Test for
HBsAg and antibody to HBsAg (anti-HBs) at age 9–12mos or 1–2mos after final dose if
the series was delayed.
• Unknown HBsAg status: administer HepB vaccine within 12hrs of birth, regardless of birth
weight (add 0.5mL of HBIG for infants <2000g). Determine mother's HBsAg status as
soon as possible and, if she is HBsAg-positive, also give HBIG for infants weighing
≥2,000g (no later than age 1wk).
Doses after the birth dose:
• The 2nd dose should be administered at age 1 or 2mos. Monovalent HepB vaccine should be
used for doses administered before age 6wks.
• Infants who did not receive a birth dose should receive 3 doses of a HepB-containing vaccine on
a schedule of 0, 1–2mos, and 6mos starting as soon as feasible.
• Administer the 2nd dose 1–2mos after the 1st dose (min interval of 4wks), administer the 3rd
dose at least 8wks after the 2nd dose AND at least 16wks after the 1st dose. The final (3rd
or 4th) dose in the HepB vaccine series should be administered no earlier than age 24wks.
• Administration of a total of 4 doses of HepB vaccine is permitted when a combination vaccine
containing HepB is administered after the birth dose.
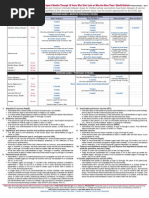
2. Rotavirus (RV) vaccine. (Min age: 6wks for both RV1 [Rotarix] and RV5 [RotaTeq])
• Administer a series of RV vaccine to all infants as follows:
1. If RV1 is used, administer a 2-dose series at 2 and 4mos of age.
2. If RV5 is used, administer a 3-dose series at ages 2, 4, and 6mos.
3. If any dose in series was RV5 or vaccine product is unknown for any dose in the series, a total
of 3 doses of RV vaccine should be given.
3. Diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis (DTaP) vaccine. (Min age: 6wks. Exception:
DTaP-IPV [Kinrix, Quadracel]: 4yrs)
• Administer a 5-dose series of DTaP vaccine at ages 2, 4, 6, 15–18mos, and 4–6yrs. The 4th dose
may be administered as early as age 12mos, provided at least 6mos have elapsed since the
3rd dose. The 4th dose of DTaP need not be repeated if given at least 4mos after the 3rd
dose of DTaP and the child was ≥12mos of age.
• 5th dose of DTap vaccine is not needed if 4th dose was given ≥4yrs of age.
4. Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine. (Minimum age: 6wks for PRP-T
[ACTHIB, DTaP-IPV/Hib (Pentacel), Hiberix] and PRP-OMP [PedvaxHIB])
• Administer a 4-dose Hib vaccine series at 2, 4, 6, and 12–15mos for ActHIB, Hiberix, or
Pentacel. For PedvaxHIB, administer a 3-dose series at 2, 4, and 12–15mos.
• For catch-up vaccination recommendations, refer to the 2018 Catch-Up Vaccination Schedule: 4
Months–18 years chart.
• Persons with high-risk conditions: refer to the ACIP 2018 Immunization Schedule footnotes.
5. Pneumococcal vaccines. (Min age: 6wks for PCV13, 2yrs for PPSV23)
Routine vaccination with PCV13:
• Administer a 4-dose series of PCV13 vaccine at ages 2, 4, 6mos and at age 12–15mos.
• Persons with high-risk conditions: refer to the ACIP 2018 Immunization Schedule footnotes.
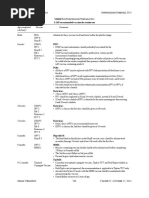
6. Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV). (Min age: 6wks)
• Administer a 4-dose series of IPV at ages 2, 4, 6–18mos and 4–6yrs. The final dose in the series
should be administered on or after the 4th birthday and at least 6mos after the previous
dose.
• If both OPV (trivalent) and IPV were given as part of a series, a total of 4 doses should be given
to complete the series. Doses should be at least 4wks apart, with the final dose given on or
after the 4th birthday and at least 6mos after the previous dose. If only OPV were given,
and all doses given before 4yrs of age, 1 dose of IPV should be given at age ≥4yrs, at least
6mos after last OPV dose.
7. Influenza vaccines. (Min age: 6mos for inactivated influenza vaccine [IIV]; 18yrs for
recombinant influenza vaccine [RIV])
• Administer an age-appropriate formulation and dose of influenza vaccine annually to all children
beginning at age 6mos. For the 2017−2018 season, use of live attenuated influenza vaccine
(LAIV) is not recommended.
For children aged 6mos–8yrs:
• For the 2017–2018 season, administer 2 doses at least 4wks apart to children who have not
previously received ≥2 doses before July 1, 2017.
For children aged ≥9yrs:
• Administer 1 dose.
8. Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. (Min age: 12mos)
• Administer a 2-dose series of MMR vaccine at ages 12–15mos and 4–6yrs. The 2nd dose may be
given as early as 4wks after the 1st dose.
• Administer 1 dose of MMR to infants aged 6–11mos before departure from the U.S. for
international travel. These children should be revaccinated with 2 doses, the 1st at age 12–
15mos (12mos for children in high-risk areas), and the 2nd dose at least 4wks later.
Unvaccinated children ≥12mos should receive 2 doses at least 4 wks apart before
departure.
• Administer 1 dose of MMR to children ≥12mos who previously received ≤2 doses of mumps-
containing vaccine and are identified by a public health authority to be at high risk during a
mumps outbreak.
9. Varicella (VAR) vaccine. (Min age: 12mos)
• Administer a 2-dose series of VAR vaccine at ages 12–15mos and 4–6yrs. The 2nd dose may be
administered as early as 3mos after the 1st dose. If the 2nd dose was given at least 4wks
after the 1st dose, it can be accepted as valid.
10. Hepatitis A (HepA) vaccine. (Min age: 12mos)
• Initiate the 2-dose HepA vaccine series, separated by 6–18mos, for children aged 12–23mos. If
the series begun before age 2yrs, 2 doses should be completed even if the child turns 2
before the 2nd dose is given.
• Unvaccinated children ≥2yrs may receive the HepA vaccine series if desired. Separate doses by
at least 6mos.
• High-risk groups that should be vaccinated: refer to the ACIP 2018 Immunization Schedule
footnotes.
11. Meningococcal vaccines. (Min age: 9mos for MenACWY-D [Menactra], 2mos for
MenACWY-CRM [Menveo], 10yrs for serogroup B meningococcal [MenB] vaccines:
MenB-4C [Bexsero] and MenB-FHbp [Trumenba])
• MenACWY vaccination (Menactra, Menveo):
—Administer a 2-dose series at 11–12yrs and 16yrs.
—If Menactra is used, give either before or at the same time as DTaP.
• MenB vaccination (Bexsero, Trumenba):
—Persons 16–23yrs (16–18yrs preferred) not at increased risk may receive, at clinical
discretion, 2 doses of Bexsero at least 1 month apart or 2 doses of Trumenba at least 6mos
apart (if 2nd Trumenba dose given too soon, administer a 3rd dose at least 4mos after the
2nd dose).
—The two MenB vaccines are not interchangeable.
• Persons with high-risk conditions or those traveling to or living in countries where
meningococcal disease is hyperendemic or epidemic: refer to the ACIP 2018 Immunization
Schedule footnotes.
12. Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Tdap) vaccine. (Min age: 11yrs for routine
vaccination, 7yrs for catch-up)
• Give 1 dose of Tdap vaccine to all adolescents aged 11–12yrs.
• Tdap can be administered regardless of the interval since the last tetanus and diphtheria toxoid-
containing vaccine.
• Administer 1 dose of Tdap vaccine to pregnant adolescents during each pregnancy (preferably
during the early part of gestational weeks 27−36).
• For catch-up vaccination recommendations, refer to the 2018 Catch-Up Vaccination Schedule: 4
Months–18 years chart.
13. Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines. (Minimum age: 9yrs for 4vHPV [Gardasil] and
9vHPV [Gardasil 9])
• Adolescents age 11–12yrs (can start at age 9yrs) and through 18yrs (if not previously adequately
vaccinated) should receive HPV vaccine series. Number of doses is dependent on age at
initial vaccination:
—Initiated at age 9–14yrs: administer a 2-dose series at least 5mos apart at 0 and 6–12
mos. If 2nd dose given too soon, administer a 3rd dose at least 12wks after the 2nd dose
and at least 5mos after the 1st dose.
—Initiated at age ≥15yrs: administer a 3-dose series at 0, 1–2, and 6mos. The 1st and 2nd
dose should be at least 4wks apart, the 2nd and 3rd dose at least 12wks apart, and the 1st
and 3rd dose at least 5mos apart. If given too soon, repeat doses at or after the minimum
interval since the most recent dose.
• No additional doses are needed for persons who have completed a valid series with any HPV
vaccine.
• Administer HPV vaccine beginning at age 9yrs to children with any history of sexual abuse or
assault.
• Immuno compromised children should receive a 3-dose series at 0, 1–2, and 6mos, regardless of
age at vaccine initiation.
• HPV vaccination is not recommended for pregnancy. However, pregnancy testing is not needed
before vaccination. If found to be pregnant after initiating the vaccination series, no
intervention is needed; the remainder of the series should be delayed until completion of
pregnancy.
You might also like
- Maternity Care Guidelines - 24 November 2023Document266 pagesMaternity Care Guidelines - 24 November 2023Khodani100% (1)
- USMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsFrom EverandUSMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Basic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityDocument1 pageBasic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityTechnoShindoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Childhood Immunization Schedule 2019Document8 pagesPhilippine Childhood Immunization Schedule 2019Linius Cruz67% (3)
- Pedigree Case StudiesDocument24 pagesPedigree Case StudiesIan Galang50% (2)
- 0 6yrs Schedule BWDocument1 page0 6yrs Schedule BWRyan ArdyantoNo ratings yet
- IZSchedule0 6yrsDocument1 pageIZSchedule0 6yrsKaty ForemanNo ratings yet
- Recommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0-6 YearsDocument3 pagesRecommended Immunization Schedule For Persons Aged 0-6 YearsAlvaro FloresNo ratings yet
- Catchup Schedule PRDocument1 pageCatchup Schedule PRJesus A. Pineda GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Vac + NotesDocument36 pagesPediatric Vac + NotesTrang Vu100% (1)
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2021Document11 pagesChildhood Immunization Schedule 2021Paula QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedDocument11 pagesChildhood Immunization Schedule 2021 EditedPatricia Bernadette PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Figure 2. Catch-Up Immunization Schedule For Persons Ages 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More Than 1 Month Behind, U. S., 2013Document1 pageFigure 2. Catch-Up Immunization Schedule For Persons Ages 4 Months Through 18 Years Who Start Late or Who Are More Than 1 Month Behind, U. S., 2013Alvaro FloresNo ratings yet
- Summary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Document5 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Annie AnnaNo ratings yet
- 07 Childschd 6x4.5 1-Page PRDocument2 pages07 Childschd 6x4.5 1-Page PRSteluta GalbenusNo ratings yet
- Final PIDSP Immunization2024Document13 pagesFinal PIDSP Immunization2024John Michaelle SantosNo ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument4 pagesVaccinesSam smithNo ratings yet
- Highlghts in Pediatric Infectious DiseasesDocument37 pagesHighlghts in Pediatric Infectious DiseasesLibay Villamor IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Catchup Schedule PR 1Document1 pageCatchup Schedule PR 1MichelleNo ratings yet
- IZSchedule0 6yrsDocument1 pageIZSchedule0 6yrsgeany2911No ratings yet
- Raymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM, MAN UNP-College of NursingDocument32 pagesRaymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM, MAN UNP-College of NursingrnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Summary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Document6 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Child Teen Immunization: (Age Birth Through 18 Years)Risnu Nur MohammadNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program of ImmunizationDocument20 pagesExpanded Program of ImmunizationgwynNo ratings yet
- Table I-IAP Immunization Schedule 2016-FinalDocument6 pagesTable I-IAP Immunization Schedule 2016-Finalsheb2004No ratings yet
- PertussisDocument11 pagesPertussissribaccayNo ratings yet
- The Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument26 pagesThe Expanded Program On ImmunizationJudee Marie MalubayNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Elements of Primary Health CareDocument12 pagesModule 4 - Elements of Primary Health CareAllyza Pholette DistorNo ratings yet
- IMMUNIZATION ScheduleDocument2 pagesIMMUNIZATION Schedulejhonny100% (1)
- Karla May C. Gentapan, M.D. Post-Graduate Medical Intern DMSFI Department of PediatricsDocument66 pagesKarla May C. Gentapan, M.D. Post-Graduate Medical Intern DMSFI Department of PediatricsCyril James Tagud BualNo ratings yet
- ImmunizationDocument30 pagesImmunizationSamar MohsnNo ratings yet
- ImmunizationsDocument64 pagesImmunizationsLily BeltranNo ratings yet
- 7-18yr Schedule For Immunizations, CDC 2008Document1 page7-18yr Schedule For Immunizations, CDC 2008Tracy100% (1)
- HPV VaccineDocument1 pageHPV Vaccineeladewilase1No ratings yet
- Stanley Grogg, DODocument53 pagesStanley Grogg, DOminerva_stanciuNo ratings yet
- Summary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years and Older)Document5 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years and Older)Hannah Caburian RemoNo ratings yet
- V - Immunization ScheduleDocument1 pageV - Immunization ScheduleFranceNo ratings yet
- Immunization in ChildrenDocument28 pagesImmunization in ChildrensaripjunayyahNo ratings yet
- Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Recommended Immunization Schedule For Children Aged 0 Through 18 Years - India, 2014 and Updates On ImmunizationDocument16 pagesIndian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Recommended Immunization Schedule For Children Aged 0 Through 18 Years - India, 2014 and Updates On Immunizationkrishna615No ratings yet
- 2022 2023 School Requirement K-12 202203231046460791Document1 page2022 2023 School Requirement K-12 202203231046460791sailorguardianlmNo ratings yet
- Childhood Immunization Schedule 2019Document8 pagesChildhood Immunization Schedule 2019Maribel LutzNo ratings yet
- Over-All Goal: To Reduce The Morbidity and Mortality Among Children Against The Most Common Vaccine-Preventable Specific GoalDocument9 pagesOver-All Goal: To Reduce The Morbidity and Mortality Among Children Against The Most Common Vaccine-Preventable Specific GoalRetiza EllaNo ratings yet
- Updates in Iraq National Program of Immunization 2012Document36 pagesUpdates in Iraq National Program of Immunization 2012Husain TamimieNo ratings yet
- IMUNISASI2Document29 pagesIMUNISASI2RatnaSuryatiNo ratings yet
- Published Assessment Report: VarilrixDocument4 pagesPublished Assessment Report: VarilrixkemalahmadNo ratings yet
- Immunization ScheduleDocument2 pagesImmunization ScheduleTracy100% (1)
- Recommended Immunization - Canadian Immunization Guide - Seventh Edition - 2006Document2 pagesRecommended Immunization - Canadian Immunization Guide - Seventh Edition - 2006Maja MudriNo ratings yet
- F1 - Frequently Asked Questions On Immunization DVLMDocument25 pagesF1 - Frequently Asked Questions On Immunization DVLMMAHAMMAD ANWAR ALINo ratings yet
- Summary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years and Older)Document5 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years and Older)Moshe KalvivindNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: Gorgonia, Leanie Louise LDocument3 pagesHepatitis B: Gorgonia, Leanie Louise LLeanie LouiseNo ratings yet
- Jawaban B InggrisDocument4 pagesJawaban B InggrisMhd SholehNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program On ImmunuzationDocument37 pagesExpanded Program On ImmunuzationRose AnnNo ratings yet
- VACCINATION.Document4 pagesVACCINATION.ochidavi56No ratings yet
- Publicly Funded Immunization Schedules For Ontario - January 2009Document4 pagesPublicly Funded Immunization Schedules For Ontario - January 2009sharmas56No ratings yet
- CDC Healthcare Personnel Vaccination RecommendationsDocument1 pageCDC Healthcare Personnel Vaccination RecommendationsdocktpNo ratings yet
- JC MarchDocument101 pagesJC MarchSubhashree SamantrayNo ratings yet
- VACCINATION1Document4 pagesVACCINATION1ochidavi56No ratings yet
- Vaccinations For NJ SchoolsDocument2 pagesVaccinations For NJ SchoolskimtranpatchNo ratings yet
- Immunization Schedule 27-07-2016Document2 pagesImmunization Schedule 27-07-2016SandraniNo ratings yet
- What's New On The Child and Adolescent Immunization SchedulesDocument30 pagesWhat's New On The Child and Adolescent Immunization SchedulesMark ReinhardtNo ratings yet
- Immunisation ScheduleDocument3 pagesImmunisation SchedulejegathesmsjsNo ratings yet
- Sara Michlle Immunization Tip SheetDocument2 pagesSara Michlle Immunization Tip SheetJan FloydNo ratings yet
- Nurul Hassanah Binti MuslimDocument11 pagesNurul Hassanah Binti MuslimLi FaungNo ratings yet
- Health Advice and Immunizations for TravelersFrom EverandHealth Advice and Immunizations for TravelersNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Bodies - AnpDocument14 pagesRegulatory Bodies - Anpannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON Role of Research, Leadership and Management in NursingDocument22 pagesSeminar ON Role of Research, Leadership and Management in Nursingannu panchal100% (1)
- Clinical Presentation.Document12 pagesClinical Presentation.annu panchalNo ratings yet
- Transcultural NursingDocument11 pagesTranscultural Nursingannu panchal100% (1)
- Water BirthDocument9 pagesWater Birthannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Genetics and Common Genetic DisordersDocument88 pagesBasic Concepts in Genetics and Common Genetic Disordersannu panchalNo ratings yet
- King TheoryDocument59 pagesKing Theoryannu panchalNo ratings yet
- FetalcirculationDocument32 pagesFetalcirculationannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Fetal SkullDocument33 pagesFetal Skullannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument34 pagesEctopic Pregnancyannu panchalNo ratings yet
- 4physiologyofpuerperium 180930161559Document54 pages4physiologyofpuerperium 180930161559annu panchalNo ratings yet
- Gynecological ProblemDocument40 pagesGynecological Problemannu panchalNo ratings yet
- PartographDocument3 pagesPartographannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Development of PlacentaDocument15 pagesDevelopment of Placentaannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Amniotic FluidDocument34 pagesAmniotic Fluidannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Course Plan CommunityDocument6 pagesCourse Plan Communityannu panchalNo ratings yet
- EclampsiaDocument36 pagesEclampsiaannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument67 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Systemannu panchalNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT ON DRUGS AND PROCEDURES PERMITTED TO BE USED BY NURSE MIDWIVES BY GoIDocument5 pagesASSIGNMENT ON DRUGS AND PROCEDURES PERMITTED TO BE USED BY NURSE MIDWIVES BY GoIannu panchal100% (1)
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bengaluru, KarnatakaDocument25 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bengaluru, Karnatakaannu panchalNo ratings yet
- The Voice of Nursing: Community of Practice Forums (Cop) ForumsDocument18 pagesThe Voice of Nursing: Community of Practice Forums (Cop) Forumsannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Recruitment Process: Subject: Nursing ManagementDocument12 pagesAssignment On Recruitment Process: Subject: Nursing Managementannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, KarnatakaDocument16 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, Karnatakaannu panchalNo ratings yet
- List of Clinical Assignments: Requirement List First Year B.Sc. NursingDocument7 pagesList of Clinical Assignments: Requirement List First Year B.Sc. Nursingannu panchalNo ratings yet
- FP2020 VisionDocument197 pagesFP2020 Visionannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Audiovisualaids CETDocument43 pagesAudiovisualaids CETannu panchalNo ratings yet
- 4-H Vermicomposting: A Fifth-Grade School Enrichment ProgramDocument11 pages4-H Vermicomposting: A Fifth-Grade School Enrichment Programannu panchalNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Waste DisposalDocument17 pagesLESSON PLAN Waste Disposalannu panchal100% (1)
- Drug Addiction and Drug AbuseDocument23 pagesDrug Addiction and Drug Abuseannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Q.I. Answer in Detail Any Two - (2x10 20) Q.I. Answer in Detail Any Two - (2x10 20)Document2 pagesQ.I. Answer in Detail Any Two - (2x10 20) Q.I. Answer in Detail Any Two - (2x10 20)annu panchalNo ratings yet
- Lose 7 Pounds of Stubborn Belly Fat Just in 3 DaysDocument22 pagesLose 7 Pounds of Stubborn Belly Fat Just in 3 DaysAnusha0% (1)
- Research EditedDocument77 pagesResearch EditedCindy Macaranas SorianoNo ratings yet
- Wa0005.Document2 pagesWa0005.schauhal69No ratings yet
- Digilaser 203: Computerised Laser TherapyDocument1 pageDigilaser 203: Computerised Laser TherapyLakshmanan SethupathiNo ratings yet
- Cgwilson CV Oct15Document3 pagesCgwilson CV Oct15api-273022942No ratings yet
- Issues With Surgical GuidesDocument2 pagesIssues With Surgical GuidesDrMarkHoganNo ratings yet
- Health and Skill Related Components of Physical FitnessDocument6 pagesHealth and Skill Related Components of Physical FitnessJovanne CabaluNo ratings yet
- WJCC 3 156Document8 pagesWJCC 3 156Jorianditha RamadhanNo ratings yet
- High Risk New BornDocument12 pagesHigh Risk New BornM. jehovah Nissie YeshalomeNo ratings yet
- The Health and Wellbeing of Adults Working in Early Childhood EducationDocument7 pagesThe Health and Wellbeing of Adults Working in Early Childhood EducationNICOLETA-CRISTINA GRIGORENo ratings yet
- Before Puberty The PH of The Vagina IsDocument3 pagesBefore Puberty The PH of The Vagina IsAhmad HamdanNo ratings yet
- Clade X Model PDFDocument5 pagesClade X Model PDFAlexandre Rocha Lima e MarcondesNo ratings yet
- Resume CV MD Physician Orthopedic Oncologist Board Certified General Surgeon Illinois or Northen Indiana Post Medical Resume Physician CVDocument4 pagesResume CV MD Physician Orthopedic Oncologist Board Certified General Surgeon Illinois or Northen Indiana Post Medical Resume Physician CVRick WhitleyNo ratings yet
- A First Longitudinal Growth Study of Stature and Weight of The School Children From Jessore District in BangladeshDocument17 pagesA First Longitudinal Growth Study of Stature and Weight of The School Children From Jessore District in BangladeshIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Aria 2010Document14 pagesAria 2010zeegerzNo ratings yet
- OET - Nursing - Writing - Case Notes - Ann BallardDocument3 pagesOET - Nursing - Writing - Case Notes - Ann Ballard7meghamNo ratings yet
- The Intelligent Patients Guide To The Doctor Patient Relationship PDFDocument303 pagesThe Intelligent Patients Guide To The Doctor Patient Relationship PDFIstrate Cristian100% (2)
- (FINAL) Legalization of Medical Marijuana Affirmative SpeechDocument5 pages(FINAL) Legalization of Medical Marijuana Affirmative SpeechKaye SantosNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 OutlineDocument6 pagesCh. 1 OutlineVal Maureen Codina SinchakNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Department of Oral Medicine, Diagnosis and RadiologyDocument37 pagesCase Presentation: Department of Oral Medicine, Diagnosis and RadiologyDanzo VinsmokeNo ratings yet
- MCQs TrickyDocument5 pagesMCQs TrickyMonica Shrivastava SharmaNo ratings yet
- TB PamphletDocument2 pagesTB PamphletMuhammad Kamal0% (1)
- Cardiac Diseases in PregnancyDocument13 pagesCardiac Diseases in PregnancyAbdullah MatarNo ratings yet
- Endovascular Surgery CP - DR Sahal FatahDocument34 pagesEndovascular Surgery CP - DR Sahal FatahRaymond AdiwicaksanaNo ratings yet
- Cpe Ecfvg Appendix of Common DiagnosesDocument9 pagesCpe Ecfvg Appendix of Common DiagnosesMayank Mj PatelNo ratings yet
- Bibliografie BunaDocument4 pagesBibliografie BunaAndreea IrimiaNo ratings yet
- Lessthan 60Document8 pagesLessthan 60api-160333876No ratings yet