0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsChapter2 non CS
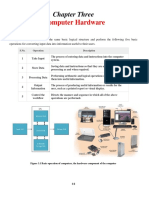
A digital computer consists of input devices (like keyboards and mice), output devices (such as monitors and printers), memory (including RAM and ROM), and a Central Processing Unit (CPU). Input devices allow users to enter data, while output devices present processed information. Memory systems include primary memory for short-term storage and secondary memory for long-term storage, with virtual memory techniques enhancing multitasking capabilities.
Uploaded by
maniaconnztCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsChapter2 non CS
A digital computer consists of input devices (like keyboards and mice), output devices (such as monitors and printers), memory (including RAM and ROM), and a Central Processing Unit (CPU). Input devices allow users to enter data, while output devices present processed information. Memory systems include primary memory for short-term storage and secondary memory for long-term storage, with virtual memory techniques enhancing multitasking capabilities.
Uploaded by
maniaconnztCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 10
Basic Structure of a Digital
Computer
For Non-CS students
Basic Structure of a Digital Computer
●
A Digital Computer typically consists of :
●
Input Devices: These devices allow users to enter data and
instructions into the computer. Examples include keyboards, mice,
scanners, and microphones.
●
Output Devices: These devices display the results of the computer's
processing. Examples include monitors, printers, and speakers.
●
Memory: This component stores data and instructions.
●
Central Processing Unit (CPU): The "brain" of the computer,
responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
Basic Structure of a Digital Computer
Fig : Block diagram of a Digital Computer
Memory system of a Digital Computer
●
Primary Memory (RAM):
●
Volatile, meaning data is lost when power is turned off.
●
Used for short-term storage of active programs and data.
●
Faster access speeds for quicker data retrieval. Secondary Memory:
●
Secondary Memory (ROM):
●
Non-volatile, retaining data even when power is off.
●
Used for long-term storage of programs, data, and operating systems.
●
Slower access speeds compared to RAM.
●
Includes devices like hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and USB
drives.
Memory system of a Digital Computer
●
Virtual memory is a memory management technique that gives
an illusion of more memory than physically available.
●
It uses a portion of the hard disk as virtual memory.
●
It improves multitasking and allows running larger programs.
●
It uses techniques like paging and segmentation.
Input Devices
●
Input devices are essential for interacting with computers. They
allow users to enter data and commands into the system.
Common input devices include keyboards for text input, mice
for navigation and selection, scanners for digitizing images, and
microphones for voice input.
Input Devices
●
Keyboards: The most common input device used to enter text and
commands.
●
Mice: Pointing devices used to control the cursor on the screen.
●
Scanners: Devices that convert physical documents into digital images.
●
Microphones: Used to capture audio input, such as voice commands or
music.
●
Webcams: Capture video and still images.
●
Joysticks and Gamepads: Used for gaming and other interactive
applications.
Output Devices
●
Output devices allow computers to present information to users.
Common output devices include monitors to display visual
information, printers to produce hard copies, and speakers to
generate audio output. More specialized output devices include
projectors, plotters, and voice synthesizers.
Output Devices
●
Monitors: Display visual information on a screen.
●
Printers: Produce hard copies of documents or images.
●
Speakers: Produce audio output.
●
Projectors: Display images or videos on a large screen.
●
Plotters: Used to create large-format prints, such as
architectural drawings or engineering blueprints.
Thank You
You might also like
- Edexcel IGCSE ICT Chapter 1 (Digital Devices)67% (6)Edexcel IGCSE ICT Chapter 1 (Digital Devices)12 pages
- Input, Output and Storage Devices - NotesNo ratings yetInput, Output and Storage Devices - Notes1 page
- Lesson 3 - Basic Components of Computer SystemsNo ratings yetLesson 3 - Basic Components of Computer Systems8 pages
- 1_CLO1_Fundamental Components of a Computer SystemNo ratings yet1_CLO1_Fundamental Components of a Computer System18 pages
- Unit 1.2 Components of A Computer System.No ratings yetUnit 1.2 Components of A Computer System.35 pages
- Lecture 04 - Input Output Storage DevicesNo ratings yetLecture 04 - Input Output Storage Devices43 pages
- Introduction to Computers and Computer Hardware and Computer Components (1)No ratings yetIntroduction to Computers and Computer Hardware and Computer Components (1)6 pages
- Fdre Air Force Education and Training Center: Hardware PeripheralsNo ratings yetFdre Air Force Education and Training Center: Hardware Peripherals53 pages
- Chapter 2 - Operating System Hardware ComponentsNo ratings yetChapter 2 - Operating System Hardware Components25 pages
- CHAPTER 1.2 Elements of Computer System and Categories of Computer PeripheralsNo ratings yetCHAPTER 1.2 Elements of Computer System and Categories of Computer Peripherals23 pages
- Unit 1-Computer Organisation Study NotesNo ratings yetUnit 1-Computer Organisation Study Notes13 pages
- Introduction To Computer: Engr - Laila NadeemNo ratings yetIntroduction To Computer: Engr - Laila Nadeem12 pages
- Computer Orgnization: Dr. Chaitali ShahNo ratings yetComputer Orgnization: Dr. Chaitali Shah38 pages
- real year 10 Int'g ICT first term E-noteNo ratings yetreal year 10 Int'g ICT first term E-note29 pages
- Unit 1 - Types and Componenets of Computer SystemsNo ratings yetUnit 1 - Types and Componenets of Computer Systems14 pages
- Field Configuration Guide: 2015-2016 FIRST Tech ChallengeNo ratings yetField Configuration Guide: 2015-2016 FIRST Tech Challenge11 pages
- Creating AVD. The First Application. Android Project StructureNo ratings yetCreating AVD. The First Application. Android Project Structure6 pages
- 10.6.11 Lab - Use Tera Term To Manage Router Configuration Files - ILMNo ratings yet10.6.11 Lab - Use Tera Term To Manage Router Configuration Files - ILM11 pages
- Course Objectives: ICND1: Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 1No ratings yetCourse Objectives: ICND1: Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 13 pages
- How To Access OS5 X32 RAID Data From OS5 X64 System V0.3No ratings yetHow To Access OS5 X32 RAID Data From OS5 X64 System V0.34 pages
- Laboratory Exercise 9: Procedure Calls, Stack and ParametersNo ratings yetLaboratory Exercise 9: Procedure Calls, Stack and Parameters6 pages
- Windows, Visual Studio 2010 and Allegro 5No ratings yetWindows, Visual Studio 2010 and Allegro 53 pages
- Network Layer: Logical Addressing: Dr. Kunwar Pal Dept. of CSE NIT JalandharNo ratings yetNetwork Layer: Logical Addressing: Dr. Kunwar Pal Dept. of CSE NIT Jalandhar58 pages
- Poweredge R730 and R730Xd: Technical GuideNo ratings yetPoweredge R730 and R730Xd: Technical Guide64 pages
- LEXMARK T640, T642, T644 4061-Xx0 Parts, Service ManualNo ratings yetLEXMARK T640, T642, T644 4061-Xx0 Parts, Service Manual422 pages
- Cad System Hardware: Design Workstations. The Workstation Is The Interface Between ComputerNo ratings yetCad System Hardware: Design Workstations. The Workstation Is The Interface Between Computer5 pages
- Main Functions of An Operating System: 2017 Me 302 M. Usama Bin ManzoorNo ratings yetMain Functions of An Operating System: 2017 Me 302 M. Usama Bin Manzoor4 pages
- PJL Commands-Druckerzähler Setzen HP2015dnNo ratings yetPJL Commands-Druckerzähler Setzen HP2015dn3 pages
- Configuring & Troubleshooting Windows Server 2008 Active Directory Domain ServicesNo ratings yetConfiguring & Troubleshooting Windows Server 2008 Active Directory Domain Services2 pages
- Gas Chromatography Driver Pack: Galaxie 2010 Chromatography Data SystemNo ratings yetGas Chromatography Driver Pack: Galaxie 2010 Chromatography Data System3 pages
- H27U1G8F2B Series 1 Gbit (128 M X 8 Bit) NAND FlashNo ratings yetH27U1G8F2B Series 1 Gbit (128 M X 8 Bit) NAND Flash40 pages
- Hostel Administration in Common Portal AbstractNo ratings yetHostel Administration in Common Portal Abstract6 pages
- 1_CLO1_Fundamental Components of a Computer System1_CLO1_Fundamental Components of a Computer System
- Introduction to Computers and Computer Hardware and Computer Components (1)Introduction to Computers and Computer Hardware and Computer Components (1)
- Fdre Air Force Education and Training Center: Hardware PeripheralsFdre Air Force Education and Training Center: Hardware Peripherals
- CHAPTER 1.2 Elements of Computer System and Categories of Computer PeripheralsCHAPTER 1.2 Elements of Computer System and Categories of Computer Peripherals
- Unit 1 - Types and Componenets of Computer SystemsUnit 1 - Types and Componenets of Computer Systems
- Field Configuration Guide: 2015-2016 FIRST Tech ChallengeField Configuration Guide: 2015-2016 FIRST Tech Challenge
- Creating AVD. The First Application. Android Project StructureCreating AVD. The First Application. Android Project Structure
- 10.6.11 Lab - Use Tera Term To Manage Router Configuration Files - ILM10.6.11 Lab - Use Tera Term To Manage Router Configuration Files - ILM
- Course Objectives: ICND1: Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 1Course Objectives: ICND1: Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 1
- How To Access OS5 X32 RAID Data From OS5 X64 System V0.3How To Access OS5 X32 RAID Data From OS5 X64 System V0.3
- Laboratory Exercise 9: Procedure Calls, Stack and ParametersLaboratory Exercise 9: Procedure Calls, Stack and Parameters
- Network Layer: Logical Addressing: Dr. Kunwar Pal Dept. of CSE NIT JalandharNetwork Layer: Logical Addressing: Dr. Kunwar Pal Dept. of CSE NIT Jalandhar
- LEXMARK T640, T642, T644 4061-Xx0 Parts, Service ManualLEXMARK T640, T642, T644 4061-Xx0 Parts, Service Manual
- Cad System Hardware: Design Workstations. The Workstation Is The Interface Between ComputerCad System Hardware: Design Workstations. The Workstation Is The Interface Between Computer
- Main Functions of An Operating System: 2017 Me 302 M. Usama Bin ManzoorMain Functions of An Operating System: 2017 Me 302 M. Usama Bin Manzoor
- Configuring & Troubleshooting Windows Server 2008 Active Directory Domain ServicesConfiguring & Troubleshooting Windows Server 2008 Active Directory Domain Services
- Gas Chromatography Driver Pack: Galaxie 2010 Chromatography Data SystemGas Chromatography Driver Pack: Galaxie 2010 Chromatography Data System
- H27U1G8F2B Series 1 Gbit (128 M X 8 Bit) NAND FlashH27U1G8F2B Series 1 Gbit (128 M X 8 Bit) NAND Flash