Casting Defect
Casting Defect
Uploaded by
ravikataria02Copyright:
Available Formats
Casting Defect
Casting Defect
Uploaded by
ravikataria02Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Casting Defect
Casting Defect
Uploaded by
ravikataria02Copyright:
Available Formats
A
SEMINAR REPORT ON
CASTING DEFECTS
Guided by
DR.ANIL KUMAR SINGH
PROFESSOR &(H.O.D)
FOUNDRY TECHNOLOGY
NIFFT,HATIA,RANCHI
Submitted by:
RAJU KUMAR
A.D.C.(foundry tech.)
INTRODUCTION
CASTING DEFECTS:- The characteristics by
which castings quality get affected & dont fulfill
the predetermined design parameter are termed
as casting defects.
It may be classified broadly as:-
1>Major defects:-Not rectified i.e.direct
rejection.
2>Defects :-very costly if rectified
3>Minor defects:-economically repaired
WHY DEFECTIVE CASTINGS?
DUE TO
1.Casting & Pattern design
2.Pattern equipment
3.Flask equipment & rigging
4.Gating & risering
5.Moulding sand & core sand
6.Core making practice
7.Moulding practice
8.Metal composition
9.Melting practice
CASTING DEFECTS
BLOW HOLES
PIN HOLES
SCAB
RAT TAIL
HOT TEAR
SAND FUSION
BURN ON
METAL PENETRATION
SHRINKAGE DEFECT
COLD SHUT
MISRUN
SHIFT & CROSS JOINT
FINS
CRUSH
MOULD WALL MOVEMENT
SWELL
INCLUSIONS
SAND CUTS &WASHERS DROP
SHOT METAL
BLOW HOLE:-The holes found on surface or sub-
surface of casting having dia=or>2mm are called
blow holes.
Causes:-
High moisture content
in the sand moulds
Less permeability of
mould or core sand
Excess gas generating
binders & additives
used in core making.
Poor venting of mould &
core
Rusty & damp chills and
chaplets used
Hard ramming of sand
Defective gating system
Remedies:-
Moisture content should
be minimized.
Permeability can be
improved by proper
venting using coarser
sand.
Gas generating binders &
additives should be
avoided
Chills & chaplets should
be dry & clean
Ramming of sand should
not be too hard
PIN HOLES:-The holes found on surface or sub-
surface of casting having dia=or<2mm are called
blow holes.
Causes:-
High moisture content in the
mould.
Wet ladles
Wet refractory lining of
furnace
Insufficient degassing of
melt.
Metal mould reaction
Presence of Al(aluminium
present as impurity forms
Al2O3 layer over casting and
does not the trapped air to
come out).
Remedies:-
Moisture content of mould
should be minimized
Ladle and lining should be
preheated
Proper degassing melt
To avoid metal mould
reaction, zircon wash is
applied, in cse steel casting
and graphite wash in case of
cast irons.
SCAB It is rough & irregular projections on the
surface of casting.SCAB are of two
type<1>expansion scab<2>erosion scab
Causes :-
High thermal expansion of
sand
Uneven or hard ramming
High moisture content in the
mould
Low permeability
Flat surface on cope side of
the mould
Slow pouring rate
Remedies:-
Sand should be of wide
distribution
Ramming of sand should be
proper &uniform.
Pouring rate should not be
too slow
Moisture content should be
as less as possible
Enforcements can be used on
the cope side where chances
of scabbing in maximum.
RAT TAIL:-It is also an expansion defect,
similar to scab but of lower degree.
It causes lurinkles to appear on the top face
of the casting.
Causes:-
Prolonged heating of
mould surface
Excess moisture
content in the sand
Uneven ramming of
sand
Remedies:-
Moisture content
should be
minimized.
Ramming of sand
should be proper
Pouring should be
adequately fast.
HOT TEAR :-Irregular cracks occurs on the
casting, during last stages of solidification.
The cracks have very rough surface.
Causes:-
Excess mould hardness
Improper design of
casting
Insufficient collapsibility
of mould & cores
Long freezing range of
alloy, promotes hot tear
Excess shrinkage of
metal
High sulphur content
promotes hot tear
Remedies:-
Collapsibility of mould &
core should be high
Ramming should not be
too hard
If excess sulphur is
present, then
desulphurization can be
carried out
SAND FUSION
It occurs generally in ferrous castings where
pouring temperature is high. Sand particles sticks
on the surface of the casting, on all sides.
Reasons:-
High pouring
temperature
Low refractoriness
of sand
Remedies:-
Mould can be
washed by high
refractory material
Zircon sand can be
used as facing sand,
in the mould
BURN ON
It occurs in ferrous castings only where
temp. is very high. Metal mould reaction takes
place 2Fe + O2 2FeO
2FeO + SiO2 FeO. SiO2 (Fayalite)
The whole casting is covered with a layer of
fayalite.
Reasons:-
High pouring
temperature
Metal mould reaction
Remedies:-
In case of cast irons, coal
dust is added in sand mix, it
produces a reducing
atmosphere which does not
allow oxygen to react with
metal and form FeO.
Graphite mould wash can
also be done to stop metal
mould reaction
zircon wash can be applied
on the mould walls.
METAL PENETRATION
Molten metal enters the space between sand
grains and thus results in rough surface of the casting.
Reasons:-
Soft ramming
Coarse sand grains
High metallostatic
pressure
Remedies:-
Proper and uniform
ramming
Wide distribution of
sand
Washes can be
applied on the
mould wall.
SHRINKAGE DEFECT :-Irregular cavity formed in
casting due to insufficient metal
Reasons:-
Poor risering
Poor casting design
Lack of directional
solidification
Remedies:-
Proper gating and
risering
achieve directional
solidification for that
use chills,
exothermic
materials, arcing the
riser melt, etc.
COLD SHUT
When two streams of molten metal meet in
the mould cavity, but do not fuses with each
other perfectly &makes hair like crack is called
cold shut
Reasons:-
Low pouring
temperature
Slow pouring rate
Poor gating design
Less fluidity of melt
Remedies:-
sufficient pouring
temp.
higher pouring rate
Proper gating design
Increase the fluidity
of melt
MISRUN
Incompletely filled mould cavities resulting in
incomplete casting is called misrun.
Reasons:-
Very thin sections in
casting
Low pouring
temperature
Slow & intermittent
pouring
Low permeability
Poor gating design
Insufficient metal
Remedies:-
Proper gating and
risering
Proper venting
Sufficient metal should
be poured
Thin sections can be
preheated
Pouring should be fast
enough
Pouring temperature
should be correct
SHIFT & CROSS JOINT
It is a mismatch of the casting at the parting
line or a variation from specified dimensions of a
cored section due to change in position of core or
misalignment of core in assembling.
Reasons:-
Wrong assembly of mould &
core
Incorrect locating pins in the
mould
Inadequate weighing of the
cope part
Loose patterns on the plate
Pattern not properly aligned
in the cope & drag part.
Inadequate provisions for
core print or core support
Remedies:-
Core should be properly
assembled. For this purpose
core paste and other things
should be properly used.
Moulding boxes should be
properly clamped and
weighed.
Loose piece of pattern should
be properly aligned with
dowel pins
There should be adequate
core prints on pattern for the
support of core.
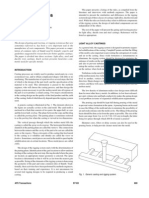
FINS
They usually occur at the parting line all
along the castings in the form of extra metal
which has to be ground off. These are called fins.
Reasons:-
Incorrect mould
assembly
Insufficient weighing
of the mould
Due to high
metallostatic
pressure
Remedies:-
Proper assembly of
coke & drag
Extra weight should
be provided over the
mould box
Length of sprue pin
should not be too
long.
CRUSH
It is the displacement of sand while closing
or mould thereby deforming mould surface. Due
to this, irregular depressions occur on the surface
of the casting.
Reasons:-
Excessive weighing
of the cope
Careless mould &
core assembly
Core print too small
to support the core
Improper ramming
Poor green strength
Remedies:-
Excess weighing
should be avoided
Mould & core should
be assembled,
carefully
Proper ramming of
sand should be done
MOULD WALL MOVEMENT
The sides of the casting bulge out, due to
mould wall movement. This occurs generally in
gray iron and S.G. Iron castings.
Reasons:-
High moisture
content in the mould
Less rigid mould
walls
Remedies:-
Moisture content
should be as low as
possible
Mould walls can be
made rigid by using
binders and
additives such as
dextrin, molasses
SWELL
Some portion of the casting may small, due
to poor ramming at that part.
This is called small defect.
Reasons:-
Poor or non uniform
ramming
Lack of rigidity of
mould walls
High metallostatic
pressure
Remedies:-
Ramming should be
uniform
Sprue pin should not
be too long
Gating should be
done properly
INCLUSIONS
When slag enters the mould cavity, it
solidifies as inclusions. If large amount of slag
enters then it forms smooth depression on the
upper surface of the casting.
Reason:-
Slag poured along
with molten metal.
Remedy:-
Metallic or ceramic
nets can be used to
filter the melt.
Skim bob gating
system can be used.
Bottom pouring
ladles can be used
for slag free, clean
metal.
SAND CUTS AND WASHES
When molten metal flows over the mould &
core surface it erodes some part of the sand and
results in cuts & washes. The place from where
sand has been eroded there extra metal solidifies
on the surface of the casting.
Reasons:-
Soft ramming
Insufficient draft on
patterns
Improper gating
system
Improper baking of
cores
Remedies:-
Ramming properly
Provide Draft
allowance
Proper Gating
system
Core baked properly
DROP
When portion of sand drops from the cope
part or from other overhanging sections in the
molten metal, then this causes drop defect
Reasons:-
Less green strength of
mould
Soft ramming
Improper casting design
Remedies:-
Green strength must be
optimum by having
optimum moisture
content & binder level
Ramming should be
done properly
Overhanging sections
can be strengthened by
using enforcements
SHOT METAL OR COLD SHOT
Due to sputtering of metal, premature
solidification of metal globules take place. This
premature solidified metal globules do not fuse
within the metal. This is called cold shot.
Reasons:-
Due to gating system which
causes turbulence.
Multiple gating
High moisture content in the
mould creates boiling action
which causes metal sputter
Those metal which are
readily oxidized are more
prone to cold shots
Slow, interrupted pouring
Remedies:-
Amount of moisture in the mould
and core sand should be controlled
so that it will not create boiling
action.
Gating system should be such that
it will prevent metal shooting into
the mould
Pouring should not be slow
You might also like
- Casting Defects & RemediesDocument40 pagesCasting Defects & RemediesMurali80% (5)
- Dental CastingDocument139 pagesDental CastingSF QuadriNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic CylindersDocument83 pagesHydraulic CylindersAndrey Gyrych100% (1)
- NADCA-High Temp DieDocument12 pagesNADCA-High Temp DiejalilemadiNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Alloy Castings Properties Processes and Applications PDFDocument321 pagesAluminum Alloy Castings Properties Processes and Applications PDFEmílio BeckerNo ratings yet
- Casting DefectsDocument38 pagesCasting DefectsAhmad Raza TararNo ratings yet
- De Fasteners CompleteDocument44 pagesDe Fasteners CompleteantblyNo ratings yet
- GCE4145 Lecture 3 - CoreDocument14 pagesGCE4145 Lecture 3 - CoreAbdullah SubbirNo ratings yet
- MT-2 Core MaterialsDocument3 pagesMT-2 Core MaterialsRavasaheb BholeNo ratings yet
- ME137L 2 Threading Operations 2Q 19 20Document91 pagesME137L 2 Threading Operations 2Q 19 20Mj GaupoNo ratings yet
- Identification and Analysis of Bearing & Accessory FailureDocument13 pagesIdentification and Analysis of Bearing & Accessory FailureAbul Ishaque Mohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Handwheels, Limit Stops and Lever Operators: Sizing & SelectionDocument8 pagesHandwheels, Limit Stops and Lever Operators: Sizing & SelectionsnamprogNo ratings yet
- Gating SystemDocument7 pagesGating SystemKiwil CtrNo ratings yet
- Din No With DrawingDocument9 pagesDin No With DrawingdurgeshwardNo ratings yet
- Seiten 9-12 Aus 249 The Influence of Filter Type and Gating SystemDocument6 pagesSeiten 9-12 Aus 249 The Influence of Filter Type and Gating Systemmecaunidos7771100% (1)
- Thread SpecificationDocument8 pagesThread Specificationsaravana perumal100% (1)
- Yield BeckermannDocument388 pagesYield BeckermannUlises Quintana Carhuancho100% (1)
- KAT-A 2014-EA RIKO-EA Edition11 04-12-2012 ENDocument7 pagesKAT-A 2014-EA RIKO-EA Edition11 04-12-2012 ENpalanaruvaNo ratings yet
- Core MANUFUCTURINGDocument35 pagesCore MANUFUCTURINGAnonymous Zx7EG1PaNo ratings yet
- BC 1700 XC Brush Cutter Exploded Parts ListDocument4 pagesBC 1700 XC Brush Cutter Exploded Parts ListΚΩΣΤΑΣ ΜΠΙΡΙΝΤΖΗΣNo ratings yet
- Brochure Bohler Benelux PDFDocument8 pagesBrochure Bohler Benelux PDFBarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinder DatasheetDocument25 pagesHydraulic Cylinder DatasheetAlican DevecioğluNo ratings yet
- Parker 2H CylindersDocument26 pagesParker 2H CylindersnitinjainmechNo ratings yet
- GN 227.2 GN 227.4: Stainless Steel-HandwheelsDocument1 pageGN 227.2 GN 227.4: Stainless Steel-HandwheelsSalpa AdenugrahaNo ratings yet
- Flow Coefficient of Butterfly Valve CV Value - VALTECCNDocument2 pagesFlow Coefficient of Butterfly Valve CV Value - VALTECCNHECTOR SUAREZ REYESNo ratings yet
- TALAT Lecture 3207: Solidification Defects in CastingsDocument29 pagesTALAT Lecture 3207: Solidification Defects in CastingsCORE Materials100% (1)
- Shaft Seal CatalogDocument66 pagesShaft Seal CatalogSadiza NasutionNo ratings yet
- NKE SuffixesDocument5 pagesNKE SuffixesNaeemSiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Custom Three Post Progressive Stamping Die Design With Feeder CoilerDocument3 pagesCustom Three Post Progressive Stamping Die Design With Feeder CoilerSIMONENo ratings yet
- Casting Process Design GuidelinesDocument8 pagesCasting Process Design GuidelinesSanjay ShahNo ratings yet
- Foundary WorkshopDocument37 pagesFoundary WorkshopAsmitaNo ratings yet
- Forgingforging ProcessDocument13 pagesForgingforging Processpatel ketanNo ratings yet
- SteelforgecatalogDocument38 pagesSteelforgecatalogStephen MaxeyNo ratings yet
- Kat A 1331 Lug Cerex300 L Wasser en 03 12Document6 pagesKat A 1331 Lug Cerex300 L Wasser en 03 12Sathishkumar DhamodaranNo ratings yet
- Bolt & Nut-1 Corrosion Table SP PDFDocument30 pagesBolt & Nut-1 Corrosion Table SP PDFSankar CdmNo ratings yet
- Core PDFDocument4 pagesCore PDFahmish kabbaxe100% (1)
- Thread GaugesDocument8 pagesThread GaugeshimanshumalNo ratings yet
- SKF Shaft SealDocument379 pagesSKF Shaft Sealsatish_trivediNo ratings yet
- Ball TimkenDocument216 pagesBall Timken5723820No ratings yet
- Excavator Bucket Tooth Failure Analysis: Kalpak. S. Dagwar, R.G. TelrandheDocument4 pagesExcavator Bucket Tooth Failure Analysis: Kalpak. S. Dagwar, R.G. TelrandheMuhammad Nur RizkiNo ratings yet
- Tie Rod 70 Bar Hydraulic Cylinders PDFDocument48 pagesTie Rod 70 Bar Hydraulic Cylinders PDFNilxon Alejandro Jaramillo DíazNo ratings yet
- SN757 2005-05 eDocument4 pagesSN757 2005-05 ehasan_676489616No ratings yet
- Content: C-Stähle Für Die WärmebehandlungDocument18 pagesContent: C-Stähle Für Die WärmebehandlungAsad EjazNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Hose SelectionDocument16 pagesHydraulic Hose Selectiondavo87No ratings yet
- Inspection and Reuse of Critical Fasteners Used in All EnginesDocument30 pagesInspection and Reuse of Critical Fasteners Used in All Enginesma.powersourceNo ratings yet
- INA Super Prescision Bearings Ac 41130 7 de enDocument242 pagesINA Super Prescision Bearings Ac 41130 7 de enDag EspedalenNo ratings yet
- Defects in CastingDocument29 pagesDefects in CastingbhimsignNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1c-Casting Defects and Remedies PDFDocument71 pagesChapter-1c-Casting Defects and Remedies PDFakrishu100% (1)
- Casting DefectsDocument30 pagesCasting DefectsMojeswara RaoNo ratings yet
- Casting DefectsDocument5 pagesCasting DefectsChinmay Das89% (9)
- Casting Defects: Numerous Opportunities To Go Wrong in A Casting OperationDocument21 pagesCasting Defects: Numerous Opportunities To Go Wrong in A Casting OperationThahir ShahNo ratings yet
- Casting DefectsDocument8 pagesCasting DefectsJavier Escalante VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2020-21 MEE1007 ETH VL2020210506859 Reference Material I 09-Apr-2021 Lec 8-MEE1007-MP-Casting Defect and InspectionDocument57 pagesWINSEM2020-21 MEE1007 ETH VL2020210506859 Reference Material I 09-Apr-2021 Lec 8-MEE1007-MP-Casting Defect and InspectionSmita AshturkarNo ratings yet
- Investment CastingDocument14 pagesInvestment CastingDeepak VelusamyNo ratings yet
- Casting 119 - EndDocument39 pagesCasting 119 - EndVarun AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Alternative Casting TechDocument93 pagesAlternative Casting TechCherif Fayez100% (1)
- Casting ProcessesDocument48 pagesCasting ProcessessumikannuNo ratings yet
- Defects in CastingDocument4 pagesDefects in CastingArjun Singh MarjaraNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument34 pagesCastingAmrutNo ratings yet
- Fusion and Pressure welding & casting effects answer assignmentDocument8 pagesFusion and Pressure welding & casting effects answer assignmentAlexi ShirleyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - October 15th 2024Document33 pagesLecture 8 - October 15th 2024kashika10084No ratings yet
- Casting DefectsDocument5 pagesCasting DefectsNayeem pashaNo ratings yet
- Astm B 367 - 09Document6 pagesAstm B 367 - 09taker6No ratings yet
- PM 1Document225 pagesPM 1danielrita570No ratings yet
- Part A (Answer All Questions) Question 1 (20 Marks) : Material To Remove 30.0 70.0 40.0Document19 pagesPart A (Answer All Questions) Question 1 (20 Marks) : Material To Remove 30.0 70.0 40.0Shah MalikNo ratings yet
- Forging Design ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesForging Design ConsiderationsChinmay Das100% (2)
- Asme Section II A-2 Sa-451Document6 pagesAsme Section II A-2 Sa-451Anonymous GhPzn1xNo ratings yet
- Foundry ProceduresDocument25 pagesFoundry Procedureskumar21081968No ratings yet
- Sand Defect PDFDocument4 pagesSand Defect PDFSachin KumbharNo ratings yet
- Radiograph InterpretationDocument12 pagesRadiograph InterpretationnithingrmeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Defects in Casting and Inspection of CastingsDocument8 pagesLecture 11 - Defects in Casting and Inspection of CastingsManan Gupta100% (1)
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT)Document2 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing (LPT)unknown unexplainedNo ratings yet
- Study of Flow and Heat Transfer in High Pressure Die Casting Cooling ChannelDocument10 pagesStudy of Flow and Heat Transfer in High Pressure Die Casting Cooling ChannelSüleymanŞentürkNo ratings yet
- Inherent Processing in Service DefectsDocument13 pagesInherent Processing in Service Defectsrandz8No ratings yet
- US Navy Foundry ManualDocument347 pagesUS Navy Foundry ManualMahdiNo ratings yet
- MP - Tamil (2 & 3 Marks)Document47 pagesMP - Tamil (2 & 3 Marks)Kal PathippagamNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Manufacturing ProcessDocument14 pagesQuestion Bank Manufacturing ProcesschandsixNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 PDFDocument42 pagesChapter10 PDFJayson SmithNo ratings yet
- Q&A Liquid Penetrant Testing Level 1 y 2 PDFDocument36 pagesQ&A Liquid Penetrant Testing Level 1 y 2 PDFGonzalo TelleríaNo ratings yet
- Gating System Design and Optimization in Sand MoldDocument19 pagesGating System Design and Optimization in Sand MoldĐinh Nguyễn Thành TrungNo ratings yet
- Unit I Casting DesignDocument25 pagesUnit I Casting DesignNandha Gopal SenthilnathanNo ratings yet
- Copper e Final PDFDocument12 pagesCopper e Final PDFLuis GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Final Revised Spec IRST-29-2016Document44 pagesFinal Revised Spec IRST-29-2016Sumit Shyamal100% (1)
- PT Level IIDocument161 pagesPT Level IIJerry100% (5)
- CastingDocument18 pagesCastingNeelu TiruvayipatiNo ratings yet
- 7 Solidification, Casting Defects.Document5 pages7 Solidification, Casting Defects.Ahmad AbdNo ratings yet
- Sama Et Al-2019-International Journal of MetalcastingDocument14 pagesSama Et Al-2019-International Journal of MetalcastingjafarNo ratings yet
- Casting DefectsDocument12 pagesCasting Defectssushil.vgiNo ratings yet