0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 viewsData Communication Short Lecture Note: Prepared by Abdul Wahid
Data Communication Short Lecture Note: Prepared by Abdul Wahid
Uploaded by
logarwall1. Data communication systems allow the exchange of data between devices via transmission mediums. They must deliver data accurately and in a timely manner.
2. The key components are messages, senders, receivers, and transmission mediums like wires or radio waves. Information can be text, numbers, images, audio or video.
3. Networks connect two or more devices via links. Connections can be point-to-point between two devices or point-to-multipoint shared between multiple devices. Networks have different topologies like mesh, star, bus or ring.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Data Communication Short Lecture Note: Prepared by Abdul Wahid
Data Communication Short Lecture Note: Prepared by Abdul Wahid
Uploaded by
logarwall0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views8 pages1. Data communication systems allow the exchange of data between devices via transmission mediums. They must deliver data accurately and in a timely manner.
2. The key components are messages, senders, receivers, and transmission mediums like wires or radio waves. Information can be text, numbers, images, audio or video.
3. Networks connect two or more devices via links. Connections can be point-to-point between two devices or point-to-multipoint shared between multiple devices. Networks have different topologies like mesh, star, bus or ring.
Original Title
Presentation 1
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
1. Data communication systems allow the exchange of data between devices via transmission mediums. They must deliver data accurately and in a timely manner.
2. The key components are messages, senders, receivers, and transmission mediums like wires or radio waves. Information can be text, numbers, images, audio or video.
3. Networks connect two or more devices via links. Connections can be point-to-point between two devices or point-to-multipoint shared between multiple devices. Networks have different topologies like mesh, star, bus or ring.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views8 pagesData Communication Short Lecture Note: Prepared by Abdul Wahid
Data Communication Short Lecture Note: Prepared by Abdul Wahid
Uploaded by
logarwall1. Data communication systems allow the exchange of data between devices via transmission mediums. They must deliver data accurately and in a timely manner.
2. The key components are messages, senders, receivers, and transmission mediums like wires or radio waves. Information can be text, numbers, images, audio or video.
3. Networks connect two or more devices via links. Connections can be point-to-point between two devices or point-to-multipoint shared between multiple devices. Networks have different topologies like mesh, star, bus or ring.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
Data
Communication
Short Lecture Note
Prepared By Abdul Wahid
Course outline
� Chapter 1Over View of Data Communication An introduction to what
kind of technologies are available
Components of data communication
Data Presentation
Types of connection
Topologies
�Chapter 2Network Models
OSI Model
Seven Layers of the OSI model
Addressing
�Chapter 3Data & Signals
Period & Frequency
Bandwidth
�Chapter 4Transmission Media
Wireless Transmission Waves
�Chapter 5Switching
manageable & unmanageable switch
�Chapter 6Wireless & wired LANs
�Chapter 7Routing
INTRODUCTION:
�Data communication and networking are changing the way we do
business and the way we live. Business decisions have to be made ever
more quickly and the decision makers require immediate access to
accurate information.
�Simply we can say Data communications are the exchange of data
between two devices via some form of transmission such as a wire cable.
The effectiveness of a data communications system depends on four
fundamental character: delivery, accuracy, timeliness and Jitter.
The fundamental Characteristic for the effectiveness of data
communication
1.Delivery:the system must deliver data to the correct destination data
must be received by the intended device or user.
2.Accuracy:the system must deliver that data accurately.
3.Timeliness:the system must deliver that data in a timely manner, data
delivered late is useless. This kind of delivery is called real-time
transmission.
4.Jitter:Jitter refers to the difference in the packets arrival time. It is the
uneven delay in the delivery of audio or video packets.
Chapter 1
Components of Data communication
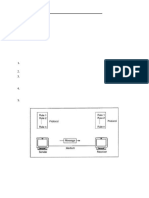
Data communalization have four components
1.Message:The message is the information (data) to be communicate.
Exp Picture, Audio & Video
2.Sender:The sender is the device that sends the data message. It can
be computer, telephone handset, video camera & so on.
3.Receiver:The receiver is the device that gets the message. It can be a
computer, telephone handset, television & so on.
4.Transmission Medium:The transmission medium is the physical path
by which a message travels from sender to receiver. some examples of
transmission media include twisted-pair wire, coaxial Cable Fiber-optic
cable and radio waves
Data Presentation
Information today comes in different forms such as text,
number,images, audio and video.
�Text:
in data communication text is represented as a bit pattern , a
sequence of bits.
�Number:
numbers are also represented by bit patterns
�Images:
Images are also represented by a bit pattern an image is composed of
a matrix of pixels (picture elements) where each pixel is a small dot.
�Audio:
Audio refers to the recording or broadcasting of sound or music.Audio
is by nature different from text, number or image. We uses
microphone to change
�Video
it refers to recording or broadcasting of a picture or movies.
Types of connection
�A network is two or more devices connected through links. A linkis a
communications pathway that transfers data from one device to another.
For visualization purposes, it is simplest to imagine any link as a line
drawn between two points. For communication to occur, two devices
must be connected in some way to the same link at the same time.
There are two possible types of connections:
Point-to-point & Point-to-Multipoint
1.Point-to-Point: provides a dedicated link between two devices. The
entire capacity of the link is reserved for transmission between these two
devices. Most point-to-point connections use and actual length of wire or
cable to connect the two ends. But also other option,such as VSAT and
Microwave links are also possible.
2.Point-to-Multipoint: Is one in which more than two specific devices
share a single link. In a multipoint environment, the capacity of the
channel is shared, either spatially or temporally.
Types of connections: P2P & (PMP)
Topologies
SUMMARY of Chapter One
�Data communication are the transfer of data from one device to another
via some form of transmission medium.
�A data communications system must transmit data to the correct
destination in an accurate and timely manner.
�The Four components that make up a data communications system are
the message, sender, receiver & medium.
�Text, number, image, audio and video are different forms of information.
�A network is set of communication devices connected by media links.
�In a point-to-point connection, two and only two devices are connected
by a dedicated link. In a multipoint connection, three or more devices
share a link.
�Topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of a network.
Devices may be arranged in a mesh, star, bus, or ring topology.
�A network can be categories as a local network or wide area network.
�A LAN is a data communication system within a building, campus, or
near by building.
�A WAN is a data communication system within a countries, or whole
world.
�An Internet is network of networks.
�The Internet is a collection of many separate network.
You might also like
- CS601 Midterm Notes 2020Document114 pagesCS601 Midterm Notes 2020SAIM ALI RASHIDNo ratings yet
- Land Patents & Allodial TitlesDocument12 pagesLand Patents & Allodial TitlesAnonymous100% (8)
- 10 Steps To Reducing Mainframe MLC CostsDocument12 pages10 Steps To Reducing Mainframe MLC CostsNagaraj Pudukotai100% (1)
- 1.1 Definition of Data CommunicationDocument14 pages1.1 Definition of Data Communicationbeneberu mulugetaNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 - EditedDocument29 pagesModule - 1 - EditedPrathiksha GowdaNo ratings yet
- Shadia S. Baloch Senior Lecturer, FEST Isra University, HyderabadDocument42 pagesShadia S. Baloch Senior Lecturer, FEST Isra University, Hyderabadshadia saad balochNo ratings yet
- NETWORKING - Lesson 01 Intro to Data CommunicationDocument48 pagesNETWORKING - Lesson 01 Intro to Data Communicationnami22039No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1mohanbabuv14No ratings yet
- CS-II Unit IVDocument22 pagesCS-II Unit IV22eg107b07No ratings yet
- Cs1302 Computer Networks Full NotesDocument135 pagesCs1302 Computer Networks Full NotesRengabilla100% (6)
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1Pon MuruganNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS 18EC71 (Prof. Nadeem Pasha)Document21 pagesMODULE 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS 18EC71 (Prof. Nadeem Pasha)Nadeem Pasha100% (1)
- EC8551 Communication Networks - Unit 1 NotesDocument48 pagesEC8551 Communication Networks - Unit 1 NotesRajanNo ratings yet
- 265 - DCCN Lecture NotesDocument132 pages265 - DCCN Lecture NotesRahul Kumar100% (1)
- Computer Network AssignmentDocument17 pagesComputer Network AssignmentMohd Sadik KhanNo ratings yet
- DCN - Week-1 - 2Document52 pagesDCN - Week-1 - 2Saad Ashfaq XaadNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Data Communications: Delivery, Accuracy, Timeliness, and JitterDocument14 pages1.1 Data Communications: Delivery, Accuracy, Timeliness, and JitterPratik KakaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Networking: IncludesDocument19 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Networking: IncludesDawod YimerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Noteskiccha suriNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1Document48 pagesLecture Notes 1alhassanalhajiibrahim036No ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument8 pagesAttachmentJamesNo ratings yet
- CN UNIT1 - Network FundamentalsDocument59 pagesCN UNIT1 - Network FundamentalsDamodhar BalireddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (Chapter 1)Document71 pagesUnit 1 (Chapter 1)pbayanagNo ratings yet
- DCN Notes - Unit 1 To 5 PDFDocument105 pagesDCN Notes - Unit 1 To 5 PDFM.tamil arasiNo ratings yet
- CNDocument47 pagesCNnanir1250No ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument133 pagesComputer NetworksAnusha MeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument277 pagesComputer NetworkshraikarNo ratings yet
- Cs3591 CN Unit 1 Notes EduenggDocument67 pagesCs3591 CN Unit 1 Notes Eduenggraheshj21No ratings yet
- Data Communication NetworkingDocument32 pagesData Communication NetworkingogheneovoaefeNo ratings yet
- DCP 1 FinalDocument22 pagesDCP 1 FinalmitaleeextraNo ratings yet
- DCC Unit 1Document16 pagesDCC Unit 1shobhitshendre986No ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Communication and Networks Data CommunicationDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Data Communication and Networks Data CommunicationNAVEENNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument136 pagesComputer NetworksEr Navdeep Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- CSC413 - Computer Networks and Communication - BOSUDocument50 pagesCSC413 - Computer Networks and Communication - BOSUaualbidawyNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Data CommunicationDocument20 pages1.1 Introduction To Data Communicationsanthini.tNo ratings yet
- CT 4Document10 pagesCT 4mj porrasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document39 pagesLecture 1yamimuto83No ratings yet
- Computer Network Unit 1Document30 pagesComputer Network Unit 1chaya777shreeNo ratings yet
- CN Notes-1Document45 pagesCN Notes-1pthrinesh42No ratings yet
- CN Chapter 2 - 2023Document64 pagesCN Chapter 2 - 2023mervismascarenhas12No ratings yet
- Computer Networks NotesDocument204 pagesComputer Networks Notessatishchinni1245No ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes 1Document40 pagesComputer Network Notes 1agam tanejaNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science: Lecture Notes ONDocument72 pagesDepartment of Computer Science: Lecture Notes ONIshetu husenNo ratings yet
- CS3591 CN Unit 1 Notes-1Document66 pagesCS3591 CN Unit 1 Notes-1nulinjeribaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL SHEET-1 (Solution) : Kcs-603: Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesTUTORIAL SHEET-1 (Solution) : Kcs-603: Computer NetworksANAMIKA SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemDocument10 pagesComputer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemShepherd AndoliniNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes PramodDocument135 pagesConcept Notes Pramodabinayam90No ratings yet
- Lecture NoteDocument72 pagesLecture NoteAbraham GadissaNo ratings yet
- CN 1 CS Unit 1Document79 pagesCN 1 CS Unit 1Chetan KmrNo ratings yet
- Notes - Data - CommunicatioinDocument126 pagesNotes - Data - CommunicatioinNepse KingNo ratings yet
- Cs3591 CN Unit 1 Notes Eduengg - RemovedDocument66 pagesCs3591 CN Unit 1 Notes Eduengg - RemovedSpam AccNo ratings yet
- CN notesDocument196 pagesCN notesramyadeviNo ratings yet
- ch1_v1Document44 pagesch1_v1yashg8883No ratings yet
- Chap1 DataCommunication For CompDocument43 pagesChap1 DataCommunication For CompGomlalaw tubeNo ratings yet
- BCAI 302 Computer Networks UNIT 1Document25 pagesBCAI 302 Computer Networks UNIT 1raghav gourNo ratings yet
- Introduction to data communicationDocument14 pagesIntroduction to data communicationDaley TingaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument198 pagesUntitledShubhamNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemDocument5 pagesComputer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemShepherd AndoliniNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Network+ (N10-009) Study Guide: Comprehensive Exam Preparation and Key Concepts for Network ProfessionalsFrom EverandCompTIA Network+ (N10-009) Study Guide: Comprehensive Exam Preparation and Key Concepts for Network ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Duas (Supplications) For Seeking Forgiveness & RepentanceDocument11 pagesDuas (Supplications) For Seeking Forgiveness & RepentanceislamicduaasNo ratings yet
- ChristianityDocument11 pagesChristianitylogarwallNo ratings yet
- Kabul UniversityDocument2 pagesKabul UniversitylogarwallNo ratings yet
- Obaidullah Ahmadi Phone#+93 (0) 20-2500236Document3 pagesObaidullah Ahmadi Phone#+93 (0) 20-2500236logarwallNo ratings yet
- WHO Doc On Pediatric IllnessesDocument399 pagesWHO Doc On Pediatric IllnessesUlanda SinghNo ratings yet
- Cartoons Caricature Him 02Document32 pagesCartoons Caricature Him 02logarwallNo ratings yet
- Unsaturated Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice-2 (A1 4pages)Document6 pagesUnsaturated Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice-2 (A1 4pages)logarwallNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Causes. Reading CompDocument4 pagesFrench Revolution Causes. Reading CompamayalibelulaNo ratings yet
- Professional Summary: Louisiana State University-Baton Rouge, LADocument1 pageProfessional Summary: Louisiana State University-Baton Rouge, LAapi-298880844No ratings yet
- Quick Lube FranchiseDocument5 pagesQuick Lube FranchisemorgytrashNo ratings yet
- PRSMLIV400-1 - Data Sheet SMART LITE-V 400 Submersible Pump 50HzDocument2 pagesPRSMLIV400-1 - Data Sheet SMART LITE-V 400 Submersible Pump 50HzKarl FrankNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument13 pagesBusiness PlanMhakeeh ParkerNo ratings yet
- Professional EthicsDocument5 pagesProfessional EthicsAshish DhangarNo ratings yet
- Digital ProcessingDocument19 pagesDigital ProcessingShimaa ashrafNo ratings yet
- 6 Legality of Object and Consideration (Sec 23Document18 pages6 Legality of Object and Consideration (Sec 23Chitraksh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Openstack HPDocument15 pagesOpenstack HPMathavan SundharamoorthyNo ratings yet
- RPS Support CatalogueDocument49 pagesRPS Support Catalogueravivarmadatla2011No ratings yet
- General Principles of Audit NOTESDocument44 pagesGeneral Principles of Audit NOTESHanna Sobreviñas AmanteNo ratings yet
- Manuela PDFDocument98 pagesManuela PDFMunguongeyo IvanNo ratings yet
- T - K4108 Toshiba Mosfet PDFDocument6 pagesT - K4108 Toshiba Mosfet PDFBrowsardNo ratings yet
- Datapath Logic CellsDocument19 pagesDatapath Logic CellsGautami SumanNo ratings yet
- SALES HW For AUG 31 or Later 9122019Document111 pagesSALES HW For AUG 31 or Later 9122019Romnick JesalvaNo ratings yet
- Assets Current AssetsDocument2 pagesAssets Current AssetsRIAN MAE DOROMPILINo ratings yet
- PPTDocument14 pagesPPTDr.Amitkumar RaiNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University Electronic Library Thesis and Dissertation PDFDocument4 pagesAddis Ababa University Electronic Library Thesis and Dissertation PDFAddison Coleman100% (2)
- LmsDocument10 pagesLmsRohit VermaNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Title Manual Book 451Document368 pagesMotor Vehicle Title Manual Book 451Tere PerezNo ratings yet
- Petrel 2020-4 Release NotesDocument19 pagesPetrel 2020-4 Release NotesAiwarikiaarNo ratings yet
- Rated Insulation VoltageDocument7 pagesRated Insulation Voltagechamara kumarasingheNo ratings yet
- American Express Issued CardsDocument1 pageAmerican Express Issued CardsFarisNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker - Quick - Command - Reference 1Document6 pagesPacemaker - Quick - Command - Reference 1aliaj005436No ratings yet
- GateCycle Software For Combined-Cycle Design and Thermal PerformanceDocument4 pagesGateCycle Software For Combined-Cycle Design and Thermal PerformanceMike Erbes100% (1)
- FDA241, FDA221: Sinteso™ Cerberus™ PRODocument12 pagesFDA241, FDA221: Sinteso™ Cerberus™ PRODaniel LowNo ratings yet
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) SolutionDocument3 pagesDense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) Solutiongreece100% (1)
- Permit Application Operate Swimming PoolDocument1 pagePermit Application Operate Swimming PoolPatricio Orozco0% (1)